- springBoot에서의 예외처리를 보기 전에
- 먼저 자바에 대한 예외처리를 공부하고 오자!
- https://velog.io/@yys/5.-%EC%9E%90%EB%B0%94-%EC%98%88%EC%99%B8-%EC%9D%B4%ED%95%B4
1. SpringBoot 동작과정
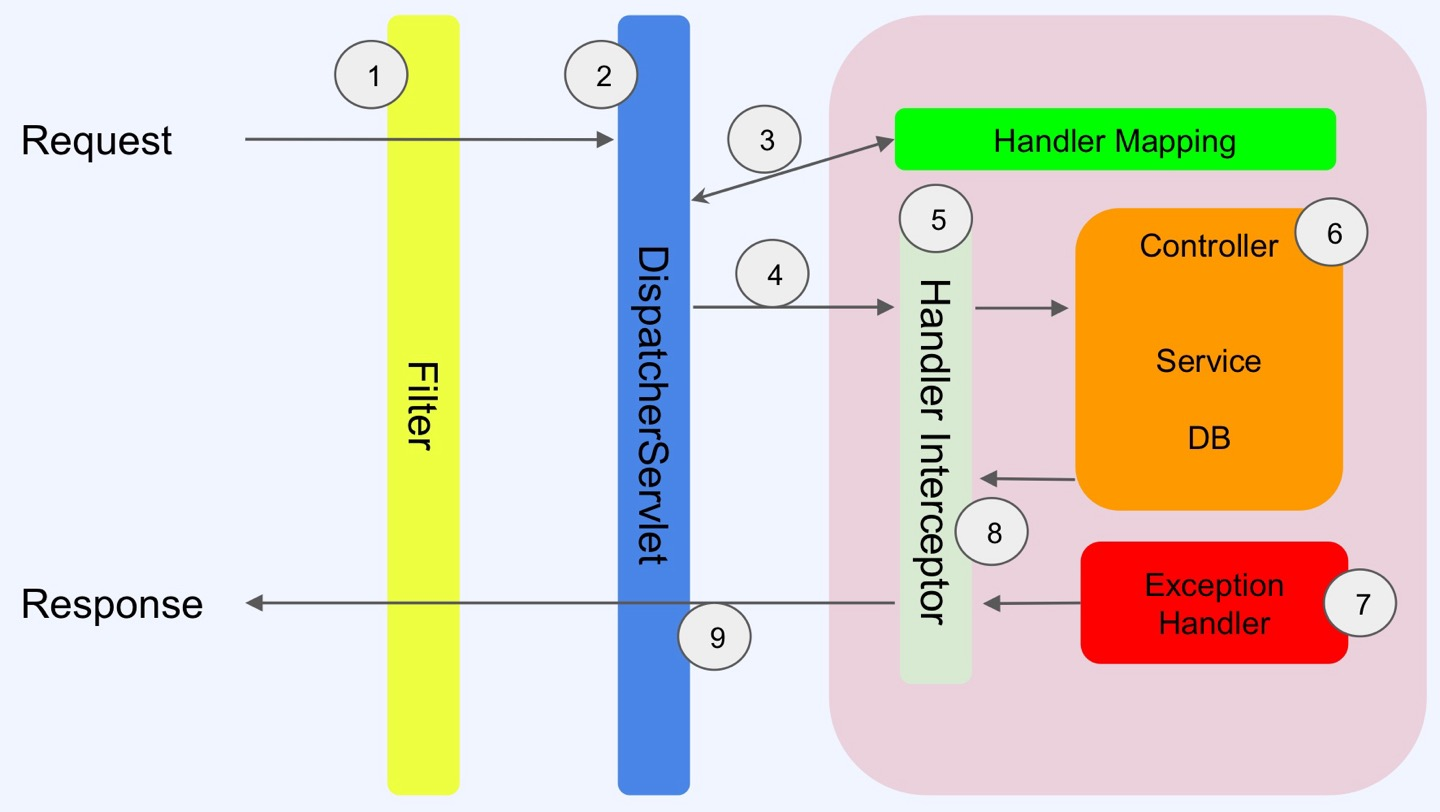
- 먼저
Request(요청)이 들어오면Filter을 거치고DispatcherServlet에서 도달한다 - 이 때,
Handler Mapping과 함께 어떤 주소를 가진 컨트롤러에 매핑할지 결정을 한다 - 결정이 끝났으면
Intercepteor을 거쳐Controller,Service,DB측에 도착한다 - 이때 만약 예외가 발생하지 않는다면
Interceptor,DispatcherServlet,Filter순을 거쳐 Response(응답)이 된다
🤔그런데 만약 컨트롤러,서비스 즉 비즈니스 로직을 처리하는 구간에서 예외가 발생한다면???
- 예외를
Exception Handler에게 던진다- Exception Handler는 그 예외를 잡아서(catch), 예외에 대한 응답을 만들어 응답을 내려준다
- 그 후에는 동일하게 작동한다
🤔 why Exception Handler?
- 그런데 예외를 굳이 Exception Handler에서 잡는 이유가 뭘까?
- 🤔try/catch문으로 그냥 잡으면 되는거 아니야?
-
그러기엔 우리가 예상치 못한 예외가 발생할 수 있다! -> 예상치 못한 예외를 Exception Handler로 잡는다
-
SRP원칙을 지키기 위해서!
- 비즈니스 로직을 처리하는 부분에서, 예외를 처리하는 로직까지 넣으면 단일 책임 원칙을 위반하게 된다
- 우리는 ✅ SRP를 지켜, 오로지 비즈니스 로직에서만 집중해서 코드를 작성할 수 있다
일단 예외를 한번 내보자 ㅎㅎ
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping(path = "/api")
public class RestApiController {
@GetMapping(path = "")
public void hello(){
List<String> list = List.of("hello");
String element = list.get(1);
log.info("element : {}",element);
}
}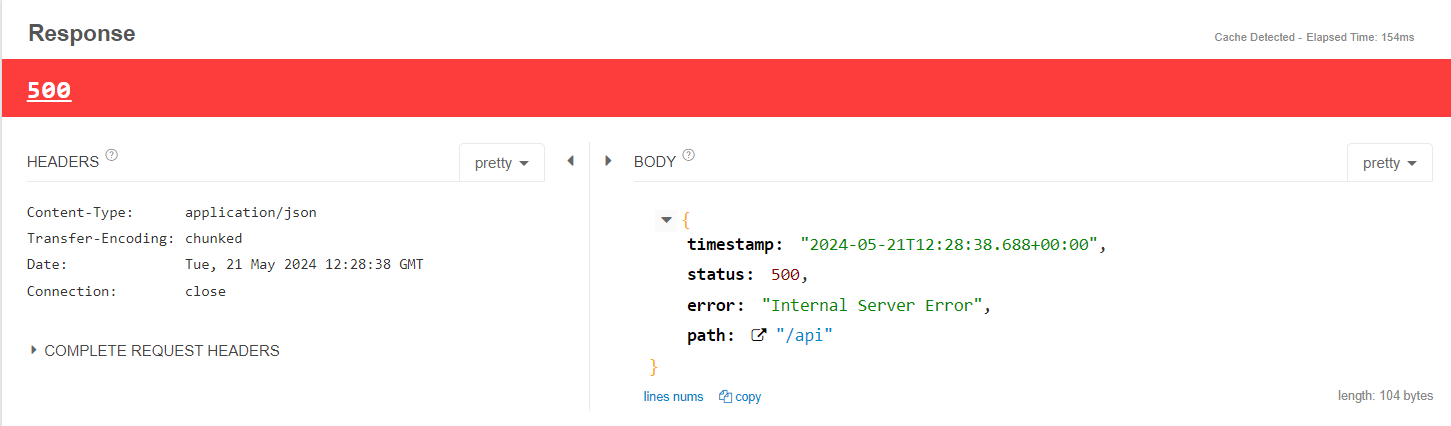
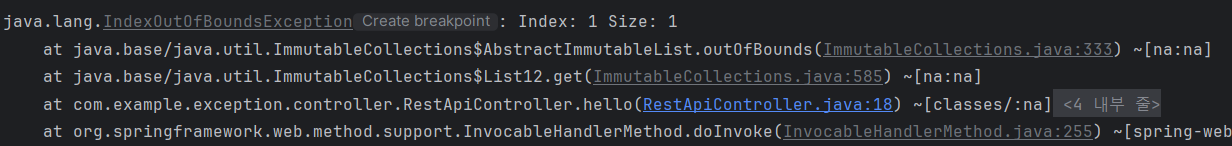
- IndexOutOfBoundException이 발생하였고, 서버 예외이므로 500 예외가 발생하였다!
- 여기서 SpringBoot가 제공하는 기본 json응답을 볼 수가 있다
- 앞서 말했듯이, 우리는 try/catch로 묶어서 예외처리를 할 수 있다
- 그런데 하나하나 예외처리하기도 어렵고 찾기도 어렵다
- 또한 비즈니스 로직이 예외 처리로직으로 오염될 수 있다
🤔우리는 global하게 이런 예외처리를 할 필요가 있다!
- Exception Handler을 이용해 처리해 보자!
2. global한 예외처리
@RestControllerAdvice
- 클래스 레벨에 붙이는 어노테이션
- 이 어노테이션이 붙은 클래스는 ✅Rest Api가 사용하는 곳에 예외가 일어나는 것을 감지 하게 된다
@ExceptionHandler
- 메서드 레벨에 붙이는 어노테이션
- 이 어노테이션이 붙은 어노테이션은, 매개변수 value를 통해 예외를 받을 예외.class를 지정해주고
- ✅해당 예외가 발생시 어노테이션이 있는 메서드를 실행해준다
- 즉 우리는
ExceptionHandler가 붙은 메서드에 해당 예외처리를 해주면 된다!
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
public class RestApiExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = {Exception.class})
public ResponseEntity exception(
Exception e
){
log.error("RestApiExceptionHandler",e);
return ResponseEntity.status(200).build();
}
@ExceptionHandler(value = {IndexOutOfBoundsException.class})
public ResponseEntity outOfBound(
IndexOutOfBoundsException e
){
log.error("IndexOutOfBoundsException",e);
return ResponseEntity.status(200).build();
}
}- 다음 코드를 봐보자
- 우리는 Exception을 예외처리하는 RestApiExceptionHandler와, IndexOutOfBoundsException의 예외를 처리하는 outOfBound를 만들었다
- 이 코드는 예외이므로, 예외가 발생해도 200응답을 하는, body 내용은 빈 코드이다
- 이제 우리의 원래 코드를 실행시켜보자...
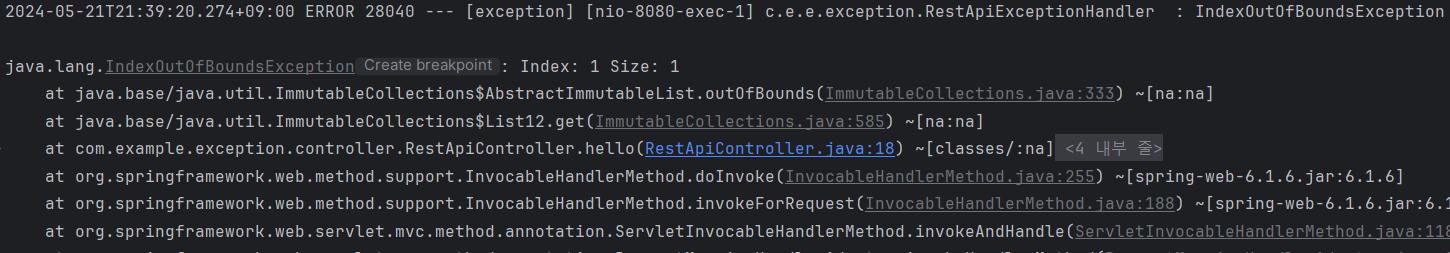
- 🤔 RestApiExceptionHandler 의 IndexOutOfBoundsException에 error 로그가 찍혔다!
- 즉,
IndexOutOfBoundsException을 잡기 위해 해당 예외가 지정된 @ExceptionHandler가 있는outOfBound메서드가 실행된 것을 알 수 있다 - 또한 예외를 잡은 곳이
RestApiController라는 사실 또한 알 수 있다
- 그리고 응답도...
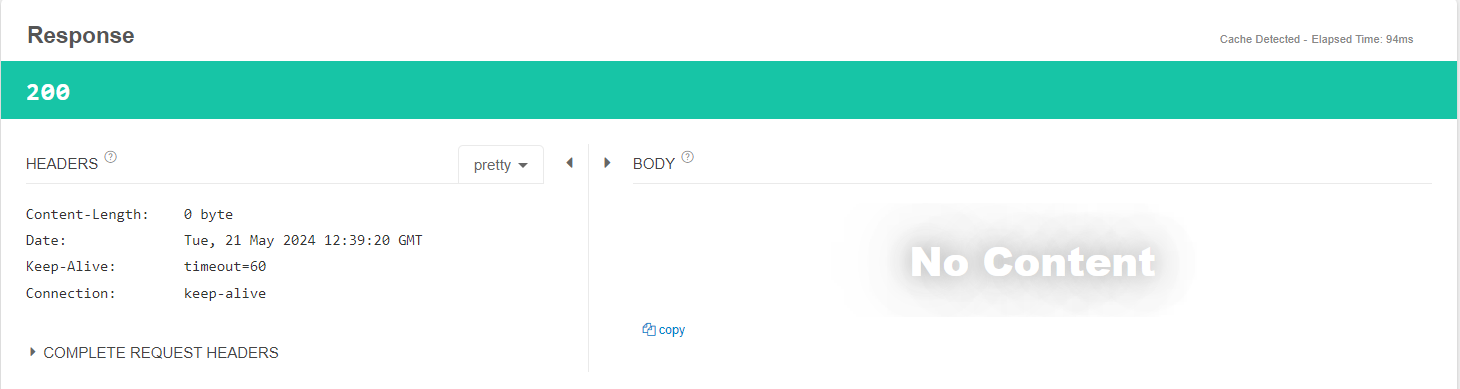
- 우리가 지정한 200상태코드를 가지고, 빈 body를 가진 응답이 일어난 것도 볼 수 있다!
a. 특정 패키지,클래스 예외처리
특정 패키지 예외처리
- 우리는 지금까지 모든 범위의 예외를
@RestControllerAdvice를 통해 처리하였다 - @RestControllerAdvice를 잘 보면
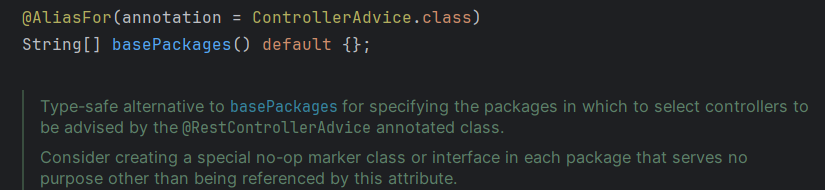
- 다음 그림과 같이, 패키지를 입력받을 수 있다!
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice(basePackages = "com.example.exception.controller")
// 이 클래스는 Rest Api가 사용하는 곳에 예외가 일어나는 것을 감지 하게 된다
public class RestApiExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = {Exception.class})
public ResponseEntity exception(
Exception e
){
log.error("RestApiExceptionHandler",e);
return ResponseEntity.status(200).build();
}
}- 다음 패키지를 지정해주고 실행을 해보자!
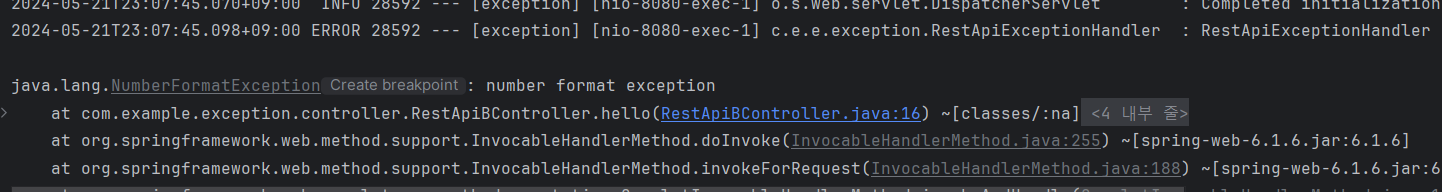
- 원하는 RestApiController에서 예외를 잘 받을 것을 알 수 있다
특정 클래스 예외처리
- 또
@RestControllerAdvice에는 클래스를 입력 받을 수도 있다 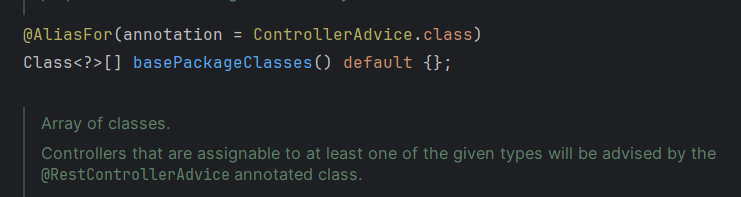
@RestControllerAdvice(basePackageClasses = {RestApiBController.class})
public class RestApiExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = {Exception.class})
public ResponseEntity exception(
Exception e
){
log.error("RestApiExceptionHandler",e);
return ResponseEntity.status(200).build();
}- 이렇게 해주면 해당 컨트롤러 어드바이스는, 특정 컨트롤러의 예외만 잡아주겠다는 의미이다
- 여기도 배열로 받아서, 여러 컨트롤러를 한번에 설정할 수도 있다
- 각 서버에는 , 정해진 Api 규격이 있다
- 어떤 내용으로 요청하여야 하고, 정해진 모양의 응답이 있다
- 즉, 예외 발생해도 항상 정해진 모양의 응답이 일어나야 한다
- 서버와 연결하는 클라이언트 입장에서, 🤔 성공과 예외의 응답의 형태가 다르다면 어떻게 응답을 파싱해야 될지 불편함이 생기고, 이는 특정 서버가 제공하는 Api의 공통성이 깨지게 된다
그렇기에 우리는 웹 서버를 만들 때
- exception handler 즉 advice handle을 통해
- 항상 우리 서버가 👌동일한 응답을 내려줄 수 있게 예외 처리를 해줘야 한다
- 이제 클라이언트는 요청이 성공이든, 예외가 발생하든 똑같은 형태의 Api의 응답을 받는다
- 클라이언트는 200일때 http body를 파싱해서 내용을 받으면 되고
- 예외 http status면 굳이 파싱을 할 필요가 없어지는 것이다!
b. 예상치 못한 오류들...
- 우리가
ExceptionHandler를 이용하는 이유이기도 하다 - 서버에서는 우리가 생각하지 못하는 예외가 발생하고, 우리는 그런 부분도 대처해야 한다
- 전혀 예측하지 못한 예외는, 서버에러라고 생각하고 500에러를 주자
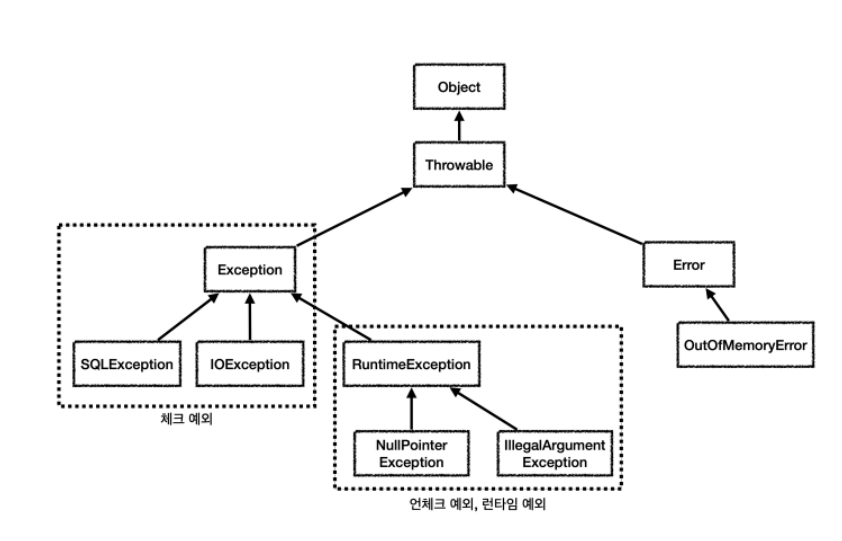
- 결국 체크 예외의 가장 상위 예외는 Exception이다
- Exception을 처리하는 예외 핸들러를 만들어주자!
GlobalExceptionHandler
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
@Order(value = Integer.MAX_VALUE) // 작을 수록 우선 실행된다, 최대값을 두어 가장 마지막에 최후의 보류의 예외 처리하는 곳!
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<Api> exception(
Exception e
){
log.error("exception",e);
Api<Object> response = Api.builder()
.resultCode(String.valueOf(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value()))
.resultMessage(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.getReasonPhrase())
.build();
return ResponseEntity
.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body(response);
}
}- GlobalExceptionHandeler라고, 예외처리의 최후의 보류인 ExceptionHandler을 만들어 주었다
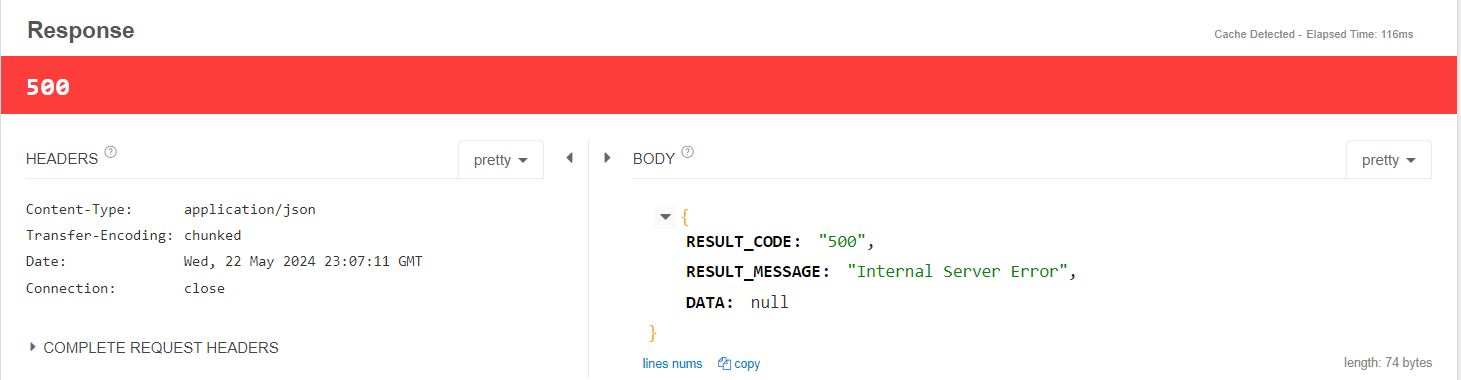
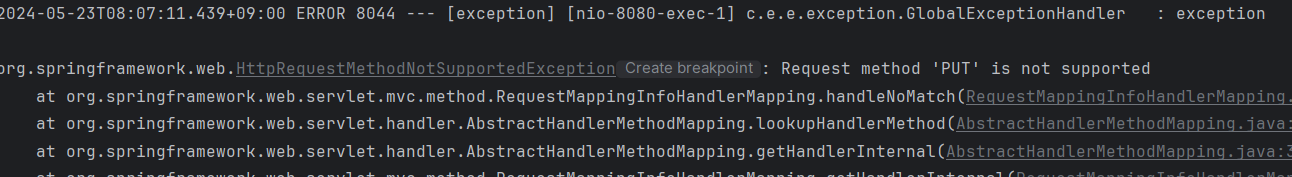
- 아무 예외나 주었고, 이는 GlobalExceptionHandeler에서, 우리가 원하는 Api형식으로 잘 처리되는 것을 볼 수 있다
- 즉, 우리는 이제 성공이든, 예외든 모두 공통된 형식으로 http 응답을 할 수 있고
- 모든 오류에 대해, 처리할 수 있게 된 것이다!
- 그런데 우리가 2개의 ExceptionHandler을 만들었다
- 🤔어떤 순서로, 뭐가 먼저 실행되는 것일까?
- 핸들러 두개시 순서를 정해준다 ->
@Order로 정함
Order
- Order는 가장작은 값이, 우선순위로 들어가 있고
- 작은 순서대로 먼저 예외처리를 하게 된다
- 그렇기에, 우리는 GlobalExceptionHandeler에서
@Order(value = Integer.MAX_VALUE)- 정수중 가장 큰 값을 주어서, 순서를 마지막으로 배치하였다
- 결국 우리가 원했던, ✅ 예외처리의 최후의 보류를
@Order의 매개변수를 통해서, 잘 적용할 수 있게 되었다!