📌 개요
findViewById<TextView>(R.id.sample_text).apply {
text = viewModel.userName
}
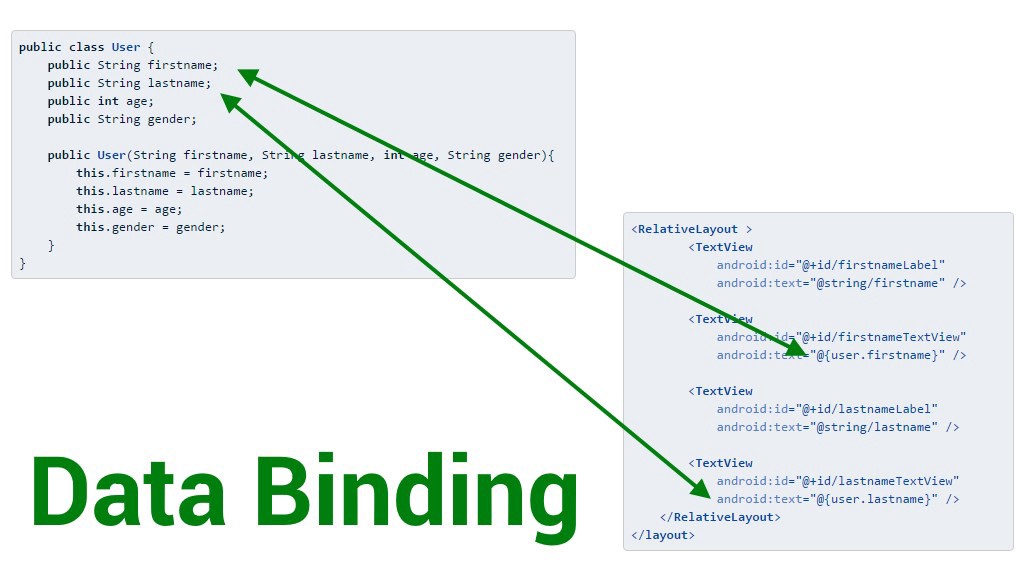
그동안 우리는 View에 데이터를 할당하기 위해서 View에 대한 참조를 얻고 속성 값을 변경하기 위해 Activity 또는 Fragment 에서 findViewById() 를 사용해왔다.
DataBinding 을 사용하면findViewById() 를 사용하지 않고 View 에 대한 참조를 얻을 수 있고,
<TextView
android:text="@{viewmodel.userName}" />
다음과 같이 레이아웃 xml 파일에 선언함으로써, ViewModel 의 값이 변경 됨에 따라 View 의 속성 값도 자동으로 업데이트 할 수 있다.
다만, 할당 식에
@{}구문을 사용해주어야 한다.
따라서, DataBinding을 사용함으로써, findViewById()를 사용하지 않고 View를 참조할 수 있고 속성 값을 설정하기 위해 작성했던 코드가 레이아웃 xml 코드로 대체될 수 있음을 알 수 있다.
📌 시작하기
android {
...
dataBinding {
enabled = true
}
}
먼저 다음과 같이, build.gradle 파일에 추가하여, 라이브러리를 프로젝트에 다운로드 받자.
실제로 적용해보자.
build.gradle(Module:프로젝트명) 에 다음과 같이 추가해주면 된다.
android {
...
defaultConfig {
...
}
buildTypes {
release {
...
}
}
compileOptions {
...
}
kotlinOptions {
...
}
dataBinding {
enabled = true
}
}위와 같이 android { } 안에 다음과 같이 dataBinding { enabled = true } 를 입력해주고 Sync Now 하자.
사용법
xml
DataBinding을 적용할 Activity 또는 Fragment의 xml 파일로 이동하자.
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<data>
<variable
name="viewmodel"
type="com.myapp.data.ViewModel" />
</data>
<ConstraintLayout... /> <!-- UI layout's root element -->
</layout>다음과 같이 사용할 수 있다.
- 루트 태그에
<layout> </layout>을 추가해준다. - 그 하위에는
<data> </data>가 올 수 있다. <data> </data>하위에는<variable>태그를 추가하여 레이아웃 파일에 할당할 데이터를 설정할 수 있다.
전체 xml 코드를 <layout> </layout>으로 둘러싸주고, 그 하위에는 <data> </data> 안에 참조하는 클래스의 패키지명을 변수명으로 사용할 수 있다.
@{viewmodel.userName}은 com.myapp.data.ViewModel에 있는 userName 이라는 프로퍼티를 참조한다고 보면 된다. ViewModel의 userName 값이 변경이 되더라도 View의 속성 값이 업데이트 된다.
Activity
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
val binding: ActivityMainBinding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_main)
binding.user = User("Test", "User")
} 레이아웃 파일의 이름이
activity_main.xml이라면 Binding 클래스의 이름은ActivityMainBinding이 된다.
위와 같이 DataBindingUtil 클래스를 사용하여 적용하는 방법도 있고, 아래와 같이
val binding: ActivityMainBinding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater())Binding 클래스의 inflate() 메서드를 사용할 수 있다.
Fragment or ListView Adapter
Fragment, ListView 또는 RecyclerView 어댑터 내에서 DataBinding을 사용하고 있다면 다음 코드와 같이 Binding 클래스 또는 DataBindingUtil 클래스의 inflate() 메서드를 사용해서 적용할 수 있다.
val listItemBinding = ListItemBinding.inflate(layoutInflater, viewGroup, false)
// or
val listItemBinding = DataBindingUtil.inflate(layoutInflater, R.layout.list_item, viewGroup, false)R.layout.list_item 이라는 레이아웃 파일의 이름을 생략할 수 있고, Binding 클래스의 이름에서 레이아웃 파일의 이름을 유추할 수 있기 때문에, 생략하는 편이 코드가 더 간결하고 좋을 수도 있다.
표현식 언어
대표적으로는 레이아웃 xml 파일에서 값을 참조하기 위해 @{}을 많이 사용한다.
하지만, 앞으로 DataBinding을 할 때, 수식을 참조해야 한다면 다음 링크를 참조하거나 구글링을 통해서 찾아보는 것이 좋을 것이다.
@{} 참조, 삼항 연산자, 문자열 연결 예시
android:text="@{String.valueOf(index + 1)}"
android:visibility="@{age > 13 ? View.GONE : View.VISIBLE}"
android:transitionName='@{"image_" + id}'index + 1값을 문자열로 가져온다.age의 값이 13보다 클 때,View.GONE, 13보다 작거나 같을 때,View.VISIBLEid의 값을 문자열 "image_" 뒤에 연결 연산한다.
Null값이거나 Null이 아닐때 처리 예시
android:text="@{user.displayName ?? user.lastName}"위 코드는 다음 예시와 동작이 같다.
android:text="@{user.displayName != null ? user.displayName : user.lastName}"Null값이 아닌 경우, user.displayName을, Null값인 경우, user.lastName을 적용한다.
📌 커스텀 속성 정의하기
BindingAdapter , BindingConversion 을 적용하여 커스텀 속성을 정의할 수 있다.
BindingAdatper
ImageView같은 경우는 어떻게 해야할까 ? 우리는 주로 Glide 라이브러리를 사용하여 이미지의 링크를 전달한다.
레이아웃 xml 코드에서는 이미지의 링크를 전달해서 설정할 수 있는 속성이 없으므로, DataBinding의 BindingAdapter 기능을 사용하여 설정할 수 있다.
ImageBindingAdapter
import android.widget.ImageView
import androidx.databinding.BindingAdapter
import com.youngsun.shoppi.app.GlideApp
@BindingAdapter("imageUrl")
fun loadImage( imageView : ImageView, imageUrl : String ) {
GlideApp.with(imageView)
.load( imageUrl )
.into( imageView)
}다음과 같이 @BindingAdapter(속성이름)을 통해 설정할 수 있고, 이 속성에 값이 전달되었을 때, 그 값으로 무엇을 할 지 다음과 같이 loadImage 라는 함수를 정의하여 사용하였다.
<ImageView
..
imageUrl="@{title.iconUrl}"
..
/>다음과 같이 BindingAdapter를 설정해주면, 레이아웃의 ImageView 속성 값이 imageUrl 이 생긴다.
이 값에 값을 전달해주면 BindingAdapter에 지정된, loadImage에 값이 전달되어 Glide 를 사용하는 구문이 실행될 것이다.
만약 원래의 가격을 표시하는 TextView와, 할인된 가격을 표시하는 TextView가 있다고 하자.
<string name="unit_discount_rate">%d%%</string>
<string name="unit_discount_currency">%s원</string>할인 퍼센티지(%)와 원화 단위를 표현하는 포매팅을 미리 values/strings 에 정의하였다.
%d 를 통해, 10진수 정수 값을 받을 수 있고, %s를 통해 문자열 값을 받을 수 있다.
unit_discount_rate의 경우, 뒤에오는 %가 포매팅과 중복되므로, %를 하나 더 입력해주어야 한다.
TextBindingAdapters
import android.widget.TextView
import androidx.databinding.BindingAdapter
import com.youngsun.shoppi.app.R
import java.text.DecimalFormat
import kotlin.math.roundToInt
@BindingAdapter("priceAmount")
fun applyPriceFormat( view : TextView, price : Int ) {
val decimalFormat = DecimalFormat("#,###")
view.text = view.context.getString(R.string.unit_discount_currency, decimalFormat.format(price))
}
@BindingAdapter("priceAmount", "discountRate")
fun applyPriceDiscountRate(view: TextView, price: Int, discountRate : Int) {
val discountPrice = (((100 - discountRate) / 100.0) * price).roundToInt()
applyPriceFormat(view, discountPrice)
}레이아웃 코드에서, priceAmount 속성 하나만 정의할 경우,
@BindingAdapter("priceAmount")
fun applyPriceFormat( view : TextView, price : Int ) {
val decimalFormat = DecimalFormat("#,###")
view.text = view.context.getString(R.string.unit_discount_currency, decimalFormat.format(price))
}위 어댑터 @BindingAdapter("priceAmount") 를 호출하여 속성을 정의한다.
priceAmount , discountRate 두 개 속성이 모두 호출될 경우,
@BindingAdapter("priceAmount", "discountRate")
fun applyPriceDiscountRate(view: TextView, price: Int, discountRate : Int) {
val discountPrice = (((100 - discountRate) / 100.0) * price).roundToInt()
applyPriceFormat(view, discountPrice)
}위 어댑터 @BindingAdapter("priceAmount", "discountRate") 는 두 개의 속성을 모두 포함하는 View에서만 호출된다.
레이아웃 코드
<TextView
할인율을 표시하는 TextView
...
android:text="@{@string/unit_discount_rate(banner.productDetail.discountRate)}"
... />
<TextView
할인된 가격을 표시하는 TextView
...
discountRate="@{banner.productDetail.discountRate}"
priceAmount="@{banner.productDetail.price}"
...
/>
<TextView
원래 가격을 표시하는 TextView
...
priceAmount="@{banner.productDetail.price}"
...
/>레이아웃 코드는 다음과 같이 작성하였다.
할인율을 표시하는 TextView에서 포매팅은 다음과 같이 하면되고,
원래 가격을 표시하는 곳에서는 첫 번째 어댑터가
할인된 가격을 표시하는 곳에서는 두 번째 어댑터가 호출이 됨을 알 수 있다.
BindingConversion
예를 들어, Color Hex 값을 문자열로 받아왔을 때, background 색상을 어떻게 지정할 수 있을까 ?
background 속성에는 Drawable 형태의 값을 넘겨주어야 한다.
ColorDrawable( Color.parseColor("color Hex 문자열") ) 이 구문을 사용하면, Color Hex 값을 문자열로 받더라도, Color 형태의 Drawable 객체로 만들어줄 수 있다.
이러한 경우 BindingConversion 을 사용하여 커스텀 속성을 정의해주면 된다.
BindingConversions
BindingConversion들을 모아두는 BindingConversions 파일이다.
import android.graphics.Color
import android.graphics.drawable.ColorDrawable
import android.graphics.drawable.Drawable
import androidx.databinding.BindingConversion
@BindingConversion
fun convertToColorDrawable(color : String) : Drawable {
return ColorDrawable( Color.parseColor(color) )
}속성 값에 ColorDrawable 값의 형태가 들어와야 할 때, String 타입의 문자열이 들어오면, 자동으로 Conversion이 진행되게끔 작성해둔 것이다.
<TextView
...
android:text="@{banner.badge.label}"
android:background="@{banner.badge.backgroundColor}"
... />다음과 같은 android:background 속성에 ColorDrawable 타입이 아닌 String 타입을 전달이 되었다.
우리가 앞에 BindingConversion 을 설정해두었으므로 String 타입은 Conversion 자동으로 일어나서 ColorDrawable 타입이 전달될 것이다.
