- Spring Boot에서 다음과 같은 설정을 통해 api를 호출 시 수행되는 쿼리에 대해 출력되도록 설정하였다.
application.properties
spring.jpa.show-sql= true- 아래와 같이 실행된 쿼리가 출력됨을 확인할 수 있었다.
- 하지만 여러 개의 api를 호출하면 이러한 쿼리들이 어떠한 controller의 handler에서 호출되는지, 어떤 repository의 메서드가 실행되는지 식별하기 힘들었다.
- 이에 쿼리문과 별개로 어떠한 메서드가 실행되는지에 대한 로그처리의 필요성을 느끼게 되었다.
- 이를 구현하는 가장 간단한 방법은 로그처리하고싶은 메서드에
@Slf4j애노테이션을 이용한log.info()를 사용하는 것이다. - 하지만 몇십개가 될 지 모르는 메서드에 하나하나 중복된 로그처리를 하기에는 코드의 가독성, 유지보수 측면에서 좋지 못하다고 생각한다.
- 이에 핵심 로직과 별도로 반복적인 기능을 추가는 방법인
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)을 사용하여AOP의 개념과 구현 방법을 학습하려고 한다.
요구사항
- 모든
@RestController을 붙인 클래스의 메서드가 호출될 때마다
{methodName} in {className} ({api-url]) was called by {IPaddress}로 로그처리하기 - 모든
@Repository을 붙인 인터페이스의 메서드가 호출될 때마다
{methodName} in {interfaceName} was executed로 로그처리하기
구현
build.gradle
// AOP
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop'ControllerLoggingAspect
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class ControllerLoggingAspect {
@Before("@within(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController)")
public void beforeControllerMethods(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Method method = getMethod(joinPoint);
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName();
String clientIp = getclientIp();
String mappingInfo = getClassMappingInfo(joinPoint.getTarget().getClass()) + getMappingInfo(method);
log.info("[{}] in {} ({}) was called from {}", method.getName(), className, mappingInfo, clientIp);
}
private Method getMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
return signature.getMethod();
}
private String getClassMappingInfo(Class<?> targetClass) {
String url;
if (targetClass.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)) {
url = Arrays.toString(targetClass.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class).value());
return url.substring(1, url.length() - 1);
}
return "";
}
private String getMappingInfo(Method method) {
String mappingValue = "";
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(GetMapping.class)) {
mappingValue = Arrays.toString(method.getAnnotation(GetMapping.class).value());
} else if (method.isAnnotationPresent(PostMapping.class)) {
mappingValue = Arrays.toString(method.getAnnotation(PostMapping.class).value());
} else if (method.isAnnotationPresent(PutMapping.class)) {
mappingValue = Arrays.toString(method.getAnnotation(PutMapping.class).value());
} else if (method.isAnnotationPresent(DeleteMapping.class)) {
mappingValue = Arrays.toString(method.getAnnotation(DeleteMapping.class).value());
} else if (method.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)) {
mappingValue = Arrays.toString(method.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class).value());
}
return mappingValue.substring(1, mappingValue.length() - 1);
}
private String getclientIp() {
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
if (attributes == null) {
return "Unkown IP";
}
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
String ip = request.getHeader("X-Forwarded-For");
if (ip == null || ip.isEmpty() || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) ip = request.getRemoteAddr();
if (ip.equals("0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1")) return "localhost";
return ip;
}
}-
@Aspect: 해당 클래스를AOP기능을 사용할 수 있도록 설정 -
@Component: 해당 클래스를 빈 컴포넌트로 설정 -
@Before(~): ~에 해당하는 메소드가 실행되기 전에 호출되도록 설정
@After(~): 은 메소드가 실행된 후 호출되도록 설정 -
@within(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController):@RestControler애노테이션이 붙은 클래스의 메소드들을 대상으로 하겠다는 뜻이다.
즉,@Before("@within(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController)")은@RestController애노테이션이 붙은 클래스의 메소드가 실행되기 전에 호출되는 메서드로 정의하겠다 라는 뜻이다. -
JoinPoint: 실행 중인 메서드와 실행 정보를 제공
이를 이용하여 어떤 메서드가 호출되었는지, 어떤 클래스에 속하는지, 어떤 인수와 함께 호출되었는지에 관한 정보를 얻을 수 있다. -
호출한 url을
mappingInfo에 담았다.
클래스 레벨의@RequestMapping("/api/v1/member")과 메서드 레벨의@(Get|Post|Patch|Put|Delete)Mapping("/create")이 더해져 url이 만들어진다.
이에 클래스 레벨과 메서드 레벨의 경로값을 각각 구해mappingInfo를 로깅처리하였다.
-
IP는
RequestContextHolder에서 가져올 수 있다. 이때 프록시 혹은 로드밸런서를 거치면X-Forwarded-For라는 HTTP헤더에 IP가 담기므로 이를 고려하여 IP를 가져올 수 있다. (0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 는 localhost의 IPv6)
RepositoryLoggingAspect
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class RepositoryLoggingAspect {
@Before("@within(org.springframework.stereotype.Repository)")
public void beforeRepositoryMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Method method = getMethod(joinPoint);
Class<?>[] interfaces = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getInterfaces();
String interfaceName = interfaces.length > 0 ? interfaces[0].getSimpleName() : "unknown Interface";
log.info("[{}] in {} executed", method.getName(), interfaceName);
}
private Method getMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
return signature.getMethod();
}
}-
위의
ControllerLoggingAspect와 비슷하다. -
@within(org.springframework.stereotype.Repository)를 사용하여@Repository애노테이션을 붙인 인터페이스의 메서드를 대상임을 설정한다. -
여기서 주의할 점은 인터페이스가 아닌 구현 클래스의 이름으로 로그를 찍게 되면 안된다.
Spring Data JPA에서 Repository의 구현체는 런타임시점에 프록시 객체로 생성되므로 AOP에서 클래스이름을 가져오게 되면 다음과 같이 프록시 이름이 찍히게 된다.

-
getTarget().getClass().getInterfaces()를 통해 프록시가 구현하는 인터페이스를 가져와야 한다.

-
특정 구현체가 구현한 인터페이스가 여러 개 일 수 있다. 하지만 해당 JpaRepository구현체는 JpaRepository 하나만 구현하기 때문에
interfaces[0].getSimpleName()를 통해 인터페이스의 이름을 가져올 수 있다.
실행
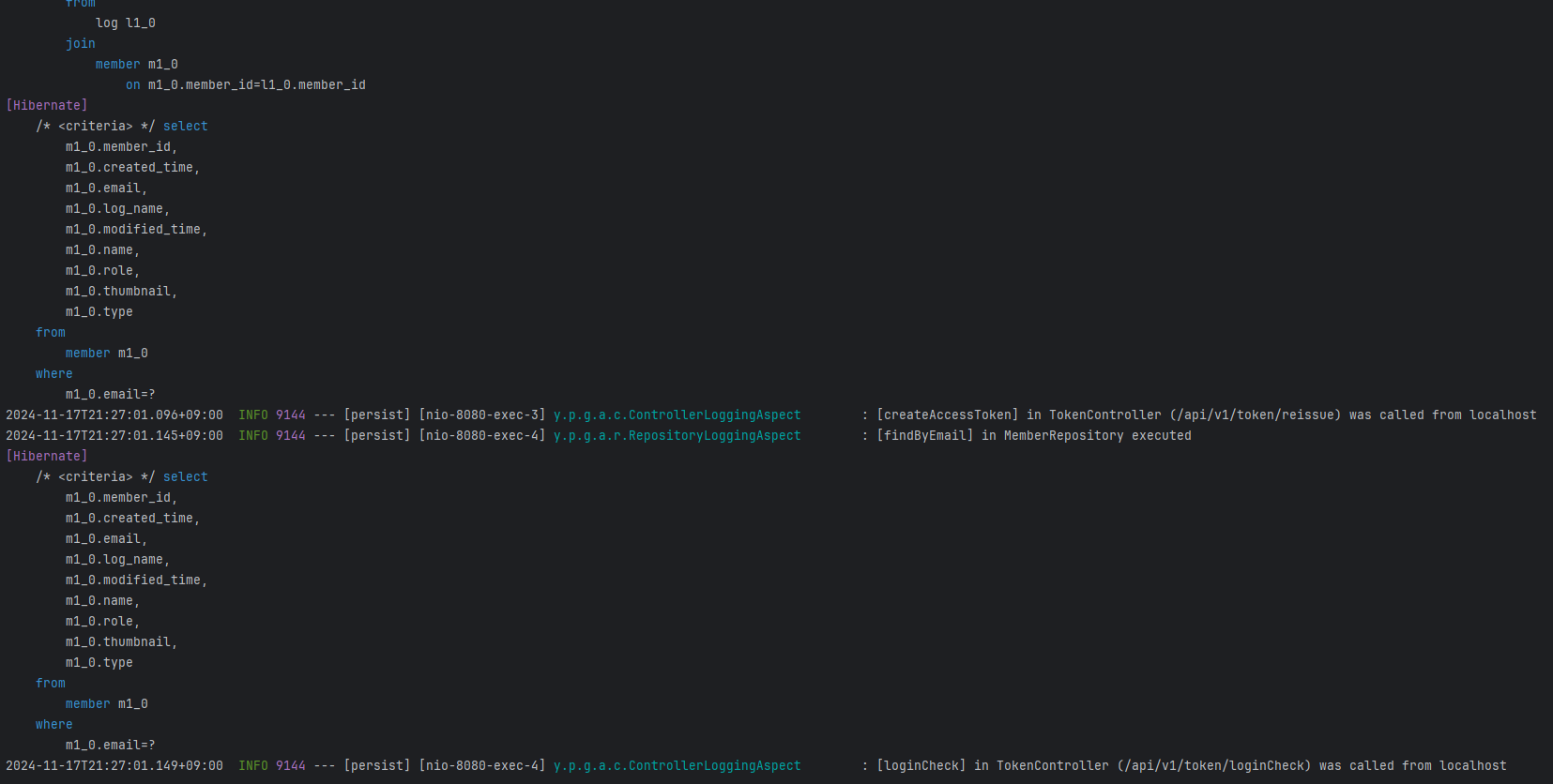
- 다음과 같이
ControllerLoggingAspect와RepositoryLoggingAspect에서 설정한 메서드들이 호출될 때 로그가 찍히는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. - Controller에서 메서드의 이름과 해당 클래스의 이름, url 경로, 추가로 호출한 객체인 IP까지의 정보를 로그에 남겨 한줄로 간결하게 표현하였다.
- Repository 레이어에서는 메서드이름과 해당 클래스가 구현한 인터페이스의 이름을 로그로 남기도록 하였다.
- 이렇게 하여 어떤 경로의 어떤 api가 호출되었는지, 누가 호출했는지, 해당 메서드가 어떤 repository의 메서드 쿼리를 실행했는지 쉽게 파악할 수 있다.