The Orthodox Canonical Class Form (OCCF)
- 기본 생성자 (Default Constructor)
- 소멸자 (Destructor)
- 복사생성자 (Copy Constructor)
- 대입연산자 오버로딩 (Copy Assignment Operator)
- https://www.francescmm.com/orthodox-canonical-class-form/
Copy constructor vs Assignment operator
- 원래 복사 생성자는 메모리 할당해서 복사. 대입연산자는 메모리 할당 없이 그냥 복사 https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/copy-constructor-vs-assignment-operator-in-c/
ex00
Fixed a;
Fixed b(a); --> 복사생성자
Fixed c;
c = b; --> 대입연산자 오버로딩/* 복사생성자 */
Fixed::Fixed(const Fixed &fixed)
{
std::cout << "Copy constructor called" << std::endl;
this->fixed_point_value = fixed.fixed_point_value;
}/* 대입연산자 오버로딩 */
Fixed & Fixed::operator=(const Fixed &fixed)
{
std::cout << "Copy assignment operator called" << std::endl;
this->fixed_point_value = fixed.fixed_point_value;
return *this;
}복사생성자 & 대입연산자 오버로딩
- 복사생성자를 따로 정의하지 않는 경우 시스템에서 기본적으로 복사생성자를 정의해준다.
- 하지만 문제점은 기본으로 생성된 복사생성자는
얕은 복사만을 사용한다는 것. - 메모리를 할당한 변수를 가지고 있는 경우, 복사시에도 메모리를 새로 할당하고 복사하는
깊은 복사를 사용해야만 나중에 소멸자 호출 시 메모리가 이중해제되는 문제를 막을 수 있다. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/copy-constructor-in-cpp/ - https://modoocode.com/188
복사 생성자에서 인자로 받은 객체의 private 변수에 접근할 수 있는 이유
- private은 object 단위가 아니라 class 단위의 접근권한.
- 요약 : 접근 지정자는 object 수준이 아닌, class 수준에서 이뤄지며 그 이유는 같은 클래스의 다른 객체로 해야할 작업이 많기 때문. 간단히 생각해보면 이미 구현의 세부사항을 조작하고있는데 구현부를 숨길 이유는 전혀 없지 않은가..
출처: https://kid5.tistory.com/306 [Valentyne's Note:티스토리]
ex01
고정소수점
- 부동소수점 vs 고정소수점 https://jiminish.tistory.com/81
- 소수점이 고정 돼있다고 고정소수점, 고정 안 돼있다고 부동소수점이 아님.
- 고정소수점 표현에 따르면 비트는 부호비트, 정수부 비트, 소수부 비트로 나뉨.
- ex01에선 fractional bits를 8비트로 고정해놓고 있음.
- 때문에 int형 인자를 받으면 value << fractional_bits 로 left shift를 해줘서 저장(오른쪽에 0 8개로 채워짐).
- float형 인자의 경우 shift 연산을 쓸 수 없음. 2^fractional_bits를 곱해서 오른쪽에 0을 채워줌. 이 때 roundf사용.
<< 연산자 오버로딩
std::ostream& operator<<( std::ostream &os, const Fixed &fixed );- "하지만 우리는 클래스의 연산자 함수를 추가하는 방법으로, 멤버 함수를 사용하는 것 말고도 한 가지 더 있다는 것을 알고 있지요. 바로 ostream 클래스 객체와 Complex 객체 두 개를 인자로 받는 전역 operator<< 함수를 정의하면 됩니다." https://modoocode.com/203
입출력 연산자 오버로딩을 전역함수로만 구현할 수 있는 이유
>><<입출력 연산자 오버로딩은 멤버 함수로는 구현할 수 없고 전역 함수로만 구현할 수 있다.- 만약
<<오버로딩을 멤버 함수로 구현하려면 ostream 타입의 객체이자 왼쪽 피연산자인 std::cout이 호출하여야 한다. - 왼쪽 피연산자가 멤버 함수를 호출하는 객체가 되고 오른쪽 피연산자는 인수가 되기 때문!
- 따라서 멤버 함수로 만들기 위해선 ostream 클래스의 멤버 함수로 구현을 해야 하는데, ostream 클래스는 C++ 표준이기 때문에 직접 ostream 클래스의 멤버 함수로 A 타입의 객체를 인수로 받는 <<연산자 오버로딩을 만들어 줄 수는 없다.
- C++ 표준으로 구현된 것들은 사용자가 수정할 수 없기 떄문이다.
따라서 입출력 연산자 오버로딩은 전역함수로 구현할 수 밖에 없다. - 출처: https://ansohxxn.github.io/cpp/chapter9-3/
ex02
비교연산자 오버로딩
증감연산자 오버로딩
- https://modoocode.com/203
- 전위 증감 연산자와 후위 증감 연산자를 구분하기 위해 전위 증감 연산자는
operator++( void );operator--( void );꼴로, 후위 증감 연산자는operator++( int );operator--( int );꼴로 나누어 구분한다. 후위 증감 연산자의 매개변수는 사용할 일은 없다. 단순히 구분을 위해 추가해 준 것. - 후위 증감 연산자의 경우 증감 연산이 일어나기 전의 객체를 리턴해줘야 하기 때문에 추가로 복사생성자를 호출하게 된다. 따라서 후위 연산이 전위 연산보다 느림!
함수 선언시 const 위치에 따른 의미
bool operator>( Fixed &fixed ) const;
const Fixed &max( const Fixed &a, const Fixed &b);- 함수 뒤에 const: 해당 함수의 멤버변수를 모두 RDONLY로 쓰겠다.
- 매개변수 앞에 const: 해당 매개변수를 RDONLY로 쓰겠다.
- 함수 앞에 const: 해당 함수의 리턴 밸류를 RDONLY로 쓰겠다.
- https://pangtrue.tistory.com/16
- https://kldp.org/node/71134 (함수 앞 const에 대한 글)
글쓴이: ixevexi / 작성시간: 금, 2006/06/16 - 12:13오후
이 const값에 대해서 아주 잘 정리된 글이 여기 bbs에 있는데
어딨는지 찾질 못하겠네요거기 내용을 간추리자면
- const 리턴값은 아무런 의미가 없다
- const 리턴값이 의미가 있는 경우는 단 한가지 레퍼런스로 리턴하는 경우이다
우선 int func();이란 함수가 있을때
const가 붙어있지 않더라도
리턴값은 r-value이기 때문에 수정이 불가능합니다.
다시 풀어서 설명하면++func();
이라는 구문은 문법적으로 const int를 반환하지 않더라도
r-value를 수정하려고 했기때문에 오류가 납니다.
그러므로 const return값은 레퍼런스 리턴이 아닌 이상 전혀 쓸때가 없습니다.혹 틀린게 있다면 ^^ 고수님들이 수정해 주시겠죠??
PS 생각해보니 레퍼런스뿐이 아닌 const형 포인터를 리턴할때도 필요하긴 하겠네요 ^^
- 사실상 함수 앞의 const는 반환값이 reference가 아닌 이상 의미가 없다.
출력문 분석
#include <iostream>
int main( void ) {
Fixed a;
Fixed const b( Fixed( 5.05f ) * Fixed( 2 ) );
std::cout << a << std::endl;
std::cout << ++a << std::endl;
std::cout << a << std::endl;
std::cout << a++ << std::endl;
std::cout << a << std::endl;
std::cout << b << std::endl;
std::cout << Fixed::max( a, b ) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Default constructor called // Fixed a;
Float constructor called // Fixed( 5.05f );
Int constructor called // Fixed( 2 )
Float constructor called // Fixed const b;
Destructor called // Fixed( 5. 05f ) 의 소멸자
Destructor called // Fixed( 2 ) 의 소멸자
0 // 기본소멸자로 생성된 a. 0으로 초기화 했던 값이 나옴
0.00390625 // ++a라고 1이 아니라 fixed_point_value를 ++하는 거기 때문에
// (1 / 2^8)한 값이 float형태로 출력되는 것.
0.00390625
Copy constructor called // 후위 증감 연산자에서는 복사 생성자가 호출됨
0.00390625 // 후위 증감 연산자이기 때문에 연산이 일어나기 전의 값이 리턴
Destructor called // 복사 생성자의 소멸자
0.0078125
10.1016
10.1016
Destructor called // b의 소멸자
Destructor called // a의 소멸자ex03
const 멤버변수 초기화 : 초기화 리스트
- https://simplesolace.tistory.com/entry/const-%ED%81%B4%EB%9E%98%EC%8A%A4-%EB%A9%A4%EB%B2%84%EB%B3%80%EC%88%98-%EC%B4%88%EA%B8%B0%ED%99%94%ED%95%98%EA%B8%B0
- 변수가 const일 경우 기존에 사용했던 생성자에서 변수를 초기화 하는 방법(this->value = value)으로 초기화를 하면 오류가 발생한다.
- 이 때 쓸 수 있는 방법은
Point::Point()
: x(Fixed(0)), y(Fixed(0))
{
}- 이렇게 초기화 리스트를 사용하여 생성자 호출과 동시에 초기화를 해주면 된다.
- 기존 방법이 문제가 되는 이유는 생성자 호출 시 const값이 쓰레기 값으로 초기화가 되게 되고, 이를 나중에 정의하는 부분에서 다시 변경하려 하기 때문에 문제가 생긴다고 한다.
- 때문에 생성과 동시에 초기화가 돼야하는 레퍼런스의 경우도 초기화 리스트를 사용해서 초기화를 해야만 한다.
BSP( Binary space partitioning ) : 이진공간분할법
-
BSP에 대한 개요: https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%EC%9D%B4%EC%A7%84_%EA%B3%B5%EA%B0%84_%EB%B6%84%ED%95%A0%EB%B2%95
-
How to determine if a point is in a 2D triangle?: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2049582/how-to-determine-if-a-point-is-in-a-2d-triangle -> 대충 어떻게 사용하는진 알겠는데 완벽히 이해는 안 됨..
-
ㅇㅎ 그니까 sign 함수에서 하는 역할이 p1이 p2,p3을 잇는 선분으로 나뉘는 두 평면 중 어디에 위치하는 지를 판단하는 듯.
-
그러니 check_point를 기준으로 (check, p1, p2), (check, p2, p3), (check, p3, p1) 각각을 비교해서 check할 점이 삼각형의 세 변을 기준으로 나뉘는 이분 평면 중 어느 쪽에 위치하는지로 결정 되는 것
-
Direction of a Point from a Line Segment https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/direction-point-line-segment/
-
ㅇㅎ 한 점을 0,0으로 맞추고 외적을 구해주는 것
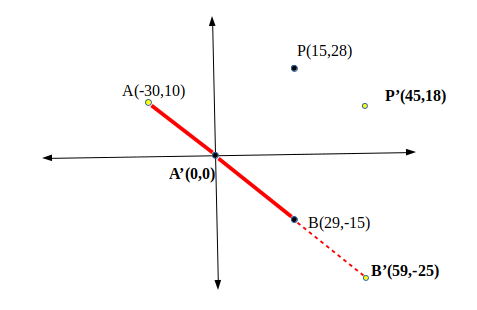
-
a, b -> b, c -> c, a 순으로 가니까 부호가 다 같아야 하는 거였음
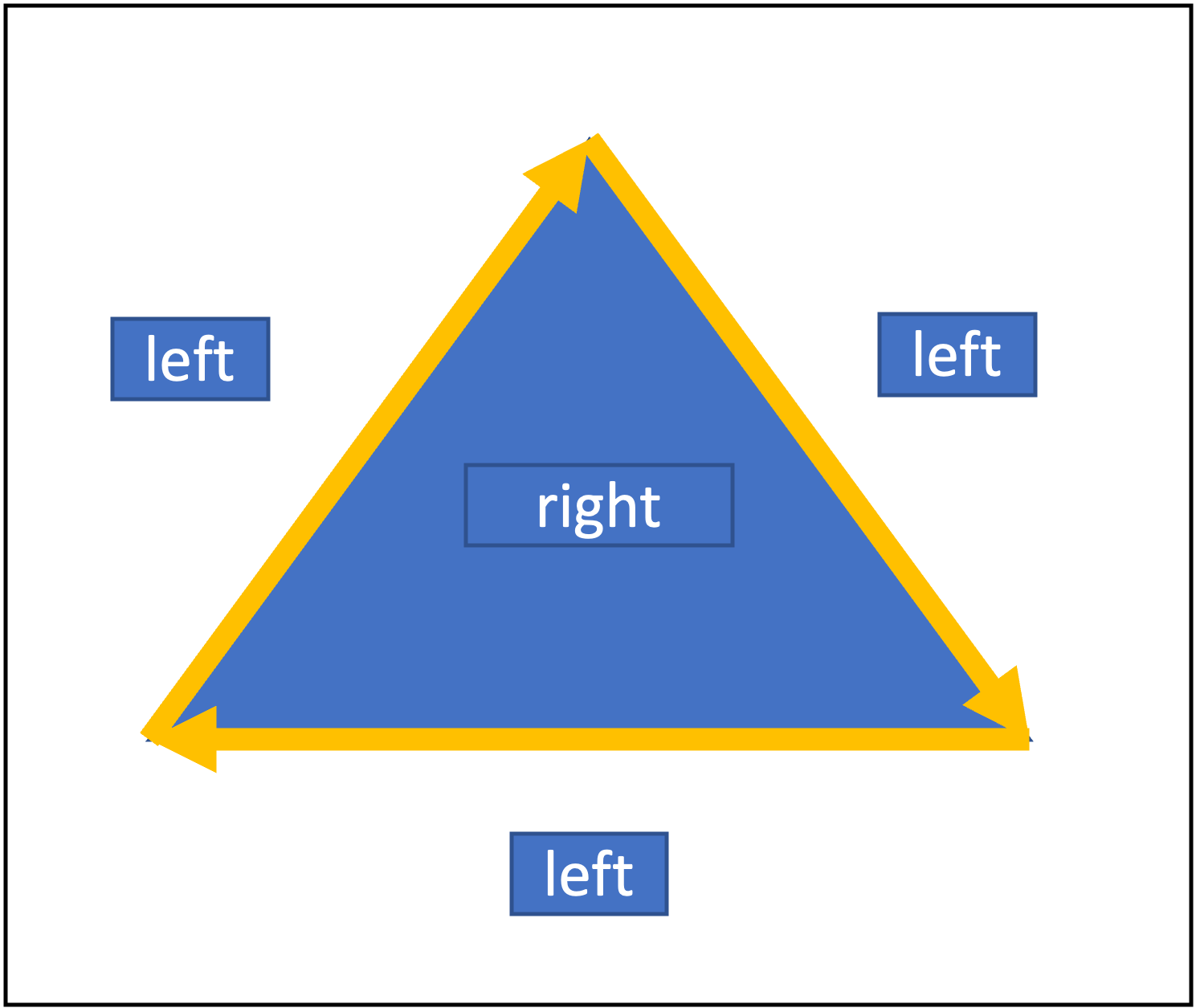
-
더 읽어보면 좋을 자료: https://iq.opengenus.org/binary-space-partitioning/
