문제
적록색약은 빨간색과 초록색의 차이를 거의 느끼지 못한다. 따라서, 적록색약인 사람이 보는 그림은 아닌 사람이 보는 그림과는 좀 다를 수 있다.
크기가 N×N인 그리드의 각 칸에 R(빨강), G(초록), B(파랑) 중 하나를 색칠한 그림이 있다. 그림은 몇 개의 구역으로 나뉘어져 있는데, 구역은 같은 색으로 이루어져 있다. 또, 같은 색상이 상하좌우로 인접해 있는 경우에 두 글자는 같은 구역에 속한다. (색상의 차이를 거의 느끼지 못하는 경우도 같은 색상이라 한다)
예를 들어, 그림이 아래와 같은 경우에
RRRBB
GGBBB
BBBRR
BBRRR
RRRRR적록색약이 아닌 사람이 봤을 때 구역의 수는 총 4개이다. (빨강 2, 파랑 1, 초록 1) 하지만, 적록색약인 사람은 구역을 3개 볼 수 있다. (빨강-초록 2, 파랑 1)
그림이 입력으로 주어졌을 때, 적록색약인 사람이 봤을 때와 아닌 사람이 봤을 때 구역의 수를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력
첫째 줄에 N이 주어진다. (1 ≤ N ≤ 100)
둘째 줄부터 N개 줄에는 그림이 주어진다.
출력
적록색약이 아닌 사람이 봤을 때의 구역의 개수와 적록색약인 사람이 봤을 때의 구역의 수를 공백으로 구분해 출력한다.
예제 입력 1
5
RRRBB
GGBBB
BBBRR
BBRRR
RRRRR예제 출력 1
4 3생각
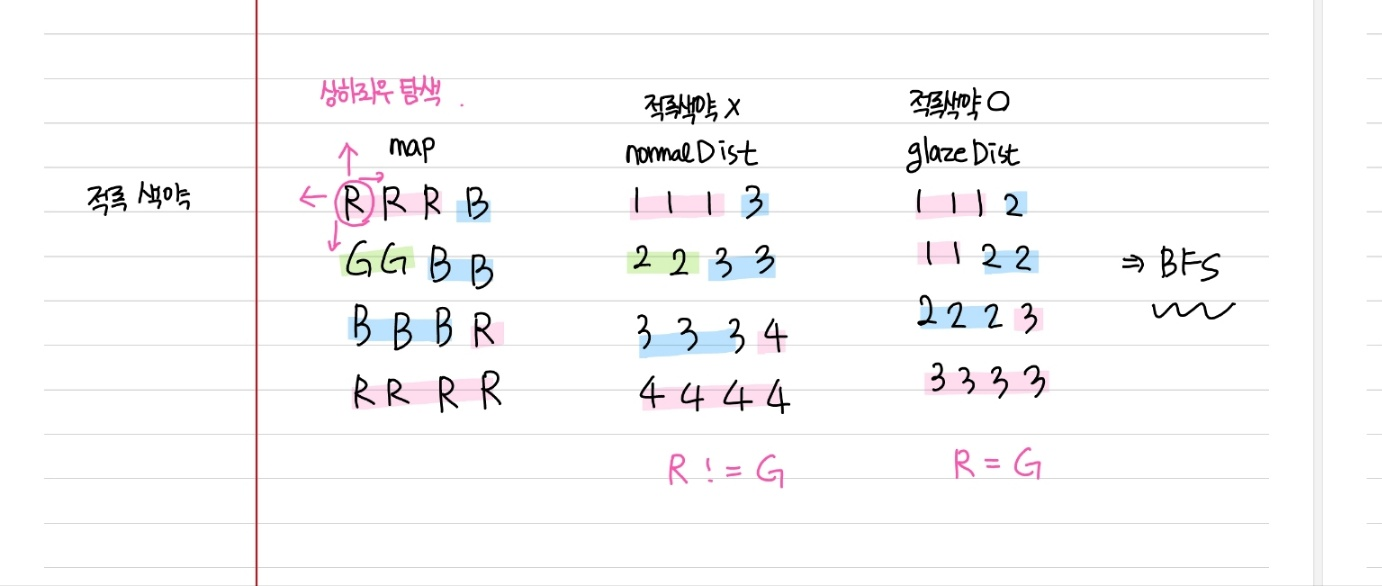
- 백준 1012번 유기농 배추 문제 생각이 났다. R과 G를 같게 보는 case와 다르게 보는 case 2가지가 있다는 점을 제외하면 거의 완벽히 동일한 문제이다
- BFS로 문제를 풀어보았다. 적록색약인 경우(R=G)와 적록색약이 아닌 경우(R!=G)를 구분하기 위해 flag
isGlaze값을 사용하였다. - 적록색약인 경우와 아닌 경우 각각
normalDist,glazeDist2차원 배열을 선언해서 구역의 개수를 BFS로 탐색하며 저장하였다:
코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class RedGreenGlaze {
static int N;
static char[][] map;
static int[][] normalDist;
static int[][] glazeDist;
static int normalCnt = 0;
static int glazeCnt = 0;
static final int[][] DIR = { { 1, 0 }, { 0, 1 }, { -1, 0 }, { 0, -1 } };
static class Point {
int x;
int y;
Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
private void BFS(int[][] dist, int x, int y, boolean isGlaze, int cnt) {
Queue<Point> Q = new LinkedList<>();
Q.offer(new Point(x, y));
dist[x][y] = cnt;
while (!Q.isEmpty()) {
Point cur = Q.poll();
for (int[] d : DIR) {
int dx = cur.x + d[0];
int dy = cur.y + d[1];
if (dx >= 0 && dx < N && dy >= 0 && dy < N && dist[dx][dy] == 0) {
boolean shouldAdd = !isGlaze
? map[dx][dy] == map[cur.x][cur.y]
: !isDifferent(dx, dy, cur.x, cur.y);
if (shouldAdd) {
dist[dx][dy] = cnt;
Q.offer(new Point(dx, dy));
}
}
}
}
}
private boolean isDifferent(int x, int y, int dx, int dy) {
return map[x][y] == 'B' && map[dx][dy] != 'B'
|| map[x][y] != 'B' && map[dx][dy] == 'B';
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RedGreenGlaze T = new RedGreenGlaze();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new char[N][N];
normalDist = new int[N][N];
glazeDist = new int[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
char[] line = br.readLine().toCharArray();
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
map[i][j] = line[j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (normalDist[i][j] == 0) {
normalCnt++;
T.BFS(normalDist, i, j, false, normalCnt);
}
if (glazeDist[i][j] == 0) {
glazeCnt++;
T.BFS(glazeDist, i, j, true, glazeCnt);
}
}
}
System.out.println(normalCnt + " " + glazeCnt);
}
}추가
- 처음
normalDist와glazeDist배열을 선언한 이유는 여기에 구역 번호를 붙여 구역 번호의 최댓값을 가져오기 위함이었다 - 하지만, 구역 번호의 최댓값을 구하기 위해 또 2차원 배열을 탐색하면 시간 복잡도가 늘어나기에
normalCnt와glazeCnt2개의 카운터를 사용해서 구역의 수를 구하였다 - 이에
normalDist와glazeDist를 선언하는 대신normalVisited와glazeVisited변수를 선언하여 방문 여부만 기록하여 개선할 수 있겠다는 생각이 들었다!
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class RedGreenGlaze {
static int N;
static char[][] map;
static boolean[][] normalVisited;
static boolean[][] glazeVisited;
static final int[][] DIR = { { 1, 0 }, { 0, 1 }, { -1, 0 }, { 0, -1 } };
static class Point {
int x;
int y;
Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
private void BFS(boolean[][] visited, int x, int y, boolean isGlaze) {
Queue<Point> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new Point(x, y));
visited[x][y] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Point cur = queue.poll();
for (int[] d : DIR) {
int dx = cur.x + d[0];
int dy = cur.y + d[1];
if (dx >= 0 && dx < N && dy >= 0 && dy < N && !visited[dx][dy]) {
boolean isSame = !isGlaze
? map[dx][dy] == map[cur.x][cur.y]
: !isDifferent(dx, dy, cur.x, cur.y);
if (isSame) {
visited[dx][dy] = true;
queue.offer(new Point(dx, dy));
}
}
}
}
}
private boolean isDifferent(int x, int y, int curX, int curY) {
return (map[x][y] == 'B' && map[curX][curY] != 'B')
|| (map[x][y] != 'B' && map[curX][curY] == 'B');
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RedGreenGlaze T = new RedGreenGlaze();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new char[N][N];
normalVisited = new boolean[N][N];
glazeVisited = new boolean[N][N];
int normalCnt = 0;
int glazeCnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
char[] line = br.readLine().toCharArray();
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
map[i][j] = line[j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (!normalVisited[i][j]) {
normalCnt++;
T.BFS(normalVisited, i, j, false);
}
if (!glazeVisited[i][j]) {
glazeCnt++;
T.BFS(glazeVisited, i, j, true);
}
}
}
System.out.println(normalCnt + " " + glazeCnt);
}
}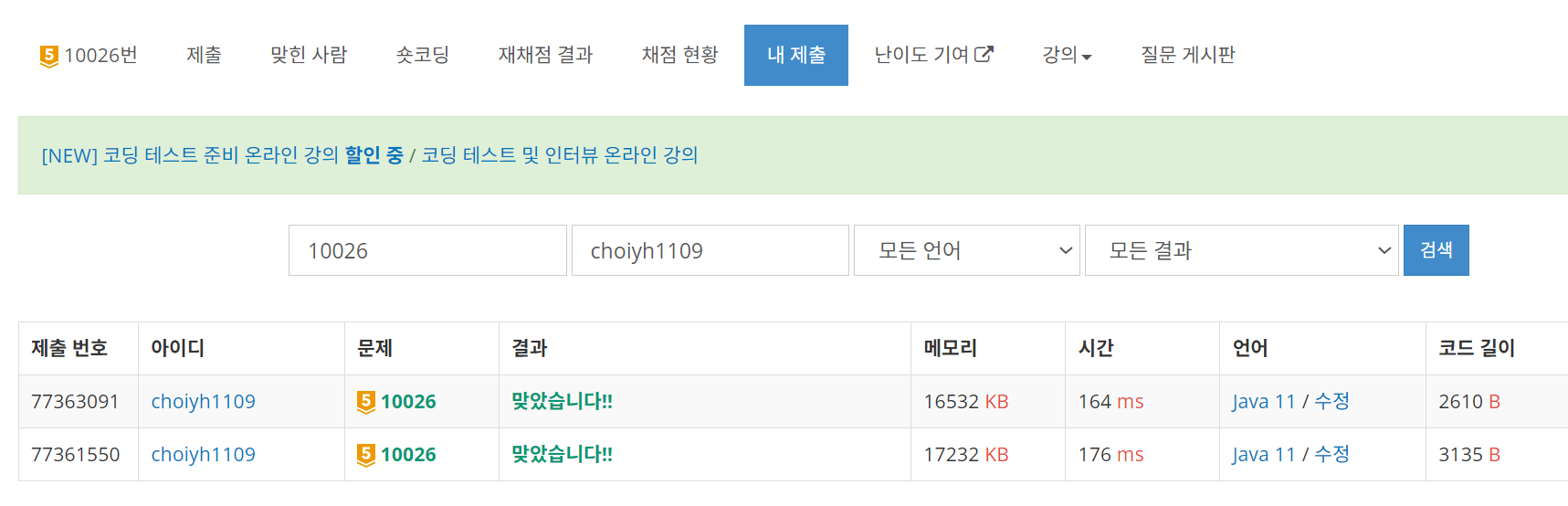
- 1행이 개선 후(visited 사용), 2행이 개선 전이다(dist 사용) 메모리와 실행 속도 측면에서 약간의 개선이 되었음을 확인 할 수 있었다. : )

잘봤습니다!