📘 콜백 함수
📖 콜백 지옥과 비동기 제어
📃 콜백 지옥
-
콜백 함수를 익명 함수로 전달하는 과정이 반복 -> 들여쓰기로 인해 가독성이 지옥(hell)같은 경우
-
이벤트 처리 및 서버 통신 같은 비동기 작업을 할 때 주로 발생
📃 동기와 비동기의 개념
-
동기 - sync (scynronous)
-
현재 실행 중인 코드가 종료돼야 다음 코드 실행
-
cpu 계산으로 즉시 처리 가능한 코드
-
cpu 계산이 오래 걸리는 코드
-
-
비동기 - async
-
실행 중인 코드의 완료 여부와 무관하게 즉시 다음 코드로 넘어가는 방식
-
별도의 요청, 실행 대기, 보류 등과 관련된 코드
-
복잡도가 올라갈 수록 비동기 비중 상승
-
📃 비동기 작업의 동기적 표현
-
promise - 비동기 처리에 대해 처리가 끝나면 알려달라는 약속.
-
new 연산자로 호출한 promise의 인자로 넘거가는 콜백 함수는 즉시 실행.
-
resolve or reject 함수를 호출하는 구문이 있을때 둘 중 하나가 실행되기 전까지
다음(then),오류(catch) 구문으로 넘어가지 않음. -
비동기 작업이 완료될 때 resolve or reject 호출
var addCoffee = function (name) { return function (prevName) { return new Promise(function (resolve) { setTimeout(function () { var newName = prevName ? (prevName + ', ' + name) : name; console.log(newName); resolve(newName); }, 500); }); }; }; addCoffee('에스프레소')() .then(addCoffee('아메리카노')) .then(addCoffee('카페모카')) .then(addCoffee('카페라떼')); -
-
generator - 실행하면 iterator 객체를 반환 ( * 가 붙은 함수)
-
itrator 객체는 next 메소드로 순환. generator 함수 내부에서 가장 먼저 등장하는
yield에서 멈추고 다시 next 메소드를 호출하면 그 다음 yield까지 실행 후 멈춤. -
비동기 작업이 완료되는 시점마다 next 메소드 호출 -> 절차적으로 진행
var addCoffee = function (prevName, name) { setTimeout(function () { coffeeMaker.next(prevName ? prevName + ', ' + name : name); }, 500); }; var coffeeGenerator = function* () { var espresso = yield addCoffee('', '에스프레소'); console.log(espresso); var americano = yield addCoffee(espresso, '아메리카노'); console.log(americano); var mocha = yield addCoffee(americano, '카페모카'); console.log(mocha); var latte = yield addCoffee(mocha, '카페라떼'); console.log(latte); }; var coffeeMaker = coffeeGenerator(); coffeeMaker.next(); -
-
promise + async / await
- 실질적인 비동기 작업이 필요한 위치 마다 await을 붙인다. promise ~ then과 동일한 효과
var addCoffee = function (name) { return new Promise(function (resolve) { setTimeout(function(){ resolve(name); }, 500); }); }; var coffeeMaker = async function () { var coffeeList = ''; var _addCoffee = async function (name) { coffeeList += (coffeeList ? ', ' : '') + await addCoffee(name); }; await _addCoffee('에스프레소'); console.log(coffeeList); await _addCoffee('아메리카노'); console.log(coffeeList); await _addCoffee('카페모카'); console.log(coffeeList); await _addCoffee('카페라떼'); console.log(coffeeList); }; coffeeMaker();
📘 DOM과 클래스 그리고 클로저
📖 DOM
📃 DOM 기본 개념
-
DOM(Document Object Model) - document(html)을 javascript가 알아 볼 수 있게
object 형태로 modeling 한 것 -
DOM Tree
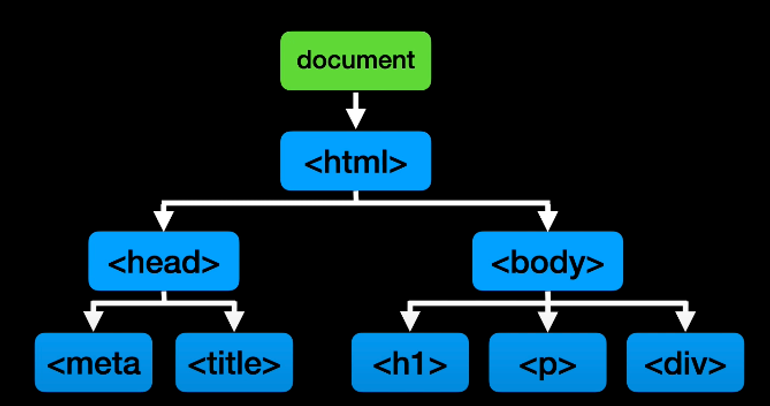
-
DOM Tree와 CSSOM Tree를 묶어 Rander Tree 구성 -> 레이아웃 계산 -> 페인팅
-
Rander Tree - 실제로 렌더링되는 최종 문서 모델
-
DOM은 브라우저에 내장되어있으므로 javascript로 접근 및 제어 가능
-
DOM의 Node - 웹 페이지 구성 요소를 하나의 블록으로 취급하는 것. 계층 구조로 연결
- Node는 속성(값)과 메소드(동작)로 구성
//getElementById = 메소드 / innerHTML = 속성 document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "Hello World!"; - Node는 부모 노드와 자식 노드 관계로 이루어져 있음.
- Node는 속성(값)과 메소드(동작)로 구성
📖 클래스(class)
📃 클래스와 인스턴스의 일반적 개념
-
클래스 - 특정 객체를 생성하기 위한 변수와 메소드를 정의한 틀.
class Example { //생성자 constructor (x, y) { this.x = x; this.x = y; } //메소드 정의 method () { console.log(`${this.x}, example`); } } // new 클래스명(매개 변수)로 객체 생성 const test1 = new Example(a, b); const test2 = new Example(c, d); // 메소드 호출 test1.method(); // "a, example" -
인스턴스 - class로 인해 만들어진 객체.
📃 Getter와 Setter
-
클래스는 getter와 setter를 사용해서 속성에 접근.
-
getter - 속성 값을 반환
-
setter - 속성 값을 설정
class Example { //생성자 constructor (x, y) { this._x = x; this._x = y; } //메소드 정의 method () { console.log(`${this._x}, example`); } //getter get x () { return this._x; } get y () { return this._y; } //setter set x (value) { //검증 //검증 끝 this._x = value; } set y (value) { //검증 //검증 끝 this._y - value; } } // new 클래스명(매개 변수)로 객체 생성 const test1 = new Example(a, b); const test2 = new Example(c, d); // 메소드 호출 test1.method(); // "a, example" -
📃 상속
-
다른 클래스의 기능을 물려받는 것.
-
상속받는 클래스를 subclass or derived class
-
상속하는 클래스를 superclass or base class
// 상속 class Aniaml { constructor (name, species) { this._name = name; this._species = species; } get name () { return this._name; } get species () { return this._species; } set name (value) { //검증 //if... //return //검증끝 this._name = value; } set species (value) { //검증 //if... //return //검증끝 this._species = value; } speak () { console.log(`${this._name} says!`); } } //상속 받는 클래스 extends 사용 class Dog extends Aniaml { // overriding 상속 받은 속성, 메소드 재정의 constructor (name) { super(name, "dog"); } speak () { console.log(`${this._name} barks!`); } } const puppy = new Dog("치즈", "dog"); puppy.speak(); console.log(puppy.species); -
📃 정적 메소드
-
static 키워드를 사용해서 class 레벨의 메소드를 정의. 인스턴스 생성x / class 직접 호출
-
인스턴스를 만들 필요가 없을 때 사용
class Calculator {
static add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
static subtract(a, b) {
return a - b;
}
}
console.log(Calculator.add(3, 5)); // 8
console.log(Calculator.subtract(3, 5)); // -2📖 클로저
📃 클로저의 개념
-
클로저는 함수와 그 함수가 선언된 렉시컬 환경과의 조합.
-
클로저
- 외부 함수보다 중첩 함수가 더 오래 유지되는 경우, 중첩 함수는 이미 종료된 외부 함수의 변수를 여전히 참조한다. 이때 중첩 함수가 클로저.
// 클로저 const x = 1; function outerFunc() { const x = 10; //중첩 함수 inner const inner = function () { console.log(x); } return inner; } const innerFunc = outerFunc(); // outerFunc 종료 innerFunc(); // 10- outer 함수의 LE를 참조하고 있는 곳이 있기 때문에
가비지 컬렉터가 outer 함수의 LE를 수거하지 않는다.
-
렉시컬 스코프
// 렉시컬 스코프
// js엔진은 함수를 어디서 '호출'했는지가 아니라
// 어디서 '정의' 했는지에 따라 스코프를 결정한다.
// 외부 렉시컬 환경에 대한 참조값 -> outer
// 함수 정의가 평가되는 시점
const x = 1;
function outerFunc() {
const x = 10;
//innerFunc 정의 -> 렉시컬 스코프
function innerFunc() {
console.log(x); // 10
}
innerFunc();
}
outerFunc(); // 10
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
const x = 1;
function outerFunc(){
const x = 10;
//호출된 시점의 outer는 관련 없음
innerFunc();
}
//정의된 시점의 outer -> x = 1
function innerFunc(){
console.log(x); // 1
}
outerFunc();📃 클로저의 활용
- 상태를 안전하게 변경하고 유지하기 위해 사용 (의도치 않은 상태 변경x, 외부 접근x)
// 즉시 실행 함수 호출 -> 함수가 반환 -> increse에 할당
const increase = (function () {
let num = 0;
//increse1 변수에 할당된 함수는 정의된 위치의 상위 스코프
// -> 즉시 실행 함수의 LE를 참조하는 클로저 let num = 0을 참조한다.
//클로저
return function () {
return ++num;
}
})();
// 즉시 실햄 함수는 -> 즉시 소멸 (call stack에서 바로 popup(소멸))
// num 이전 상태 유지
console.log(increase()); // 1
console.log(increase()); // 2
console.log(increase()); // 3
// 외부에서 접근x (은닉된 값) -> 의도되지 않은 변경x 