DefaultSecurityFilterChain에 기본적으로 등록되는 필터로 두 번째에 위치하는 WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter에 대해 알아보자.
WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter의 목적
해당 필터가 등록되는 목적은, 서블릿단에서 비동기 작업을 수행할 때 (Callable, @Async), 서블릿 입출력 스레드와 작업 스레드가 동일한 SecurityContextHolder의 SecurityContext 영역을 참조할 수 있도록 도와준다.
즉, SecurityContextHolder의 ThreadLocal 전략에 따라 동일한 스레드에서만 SecurityContext에 접근할 수 있는데, 비동기 방식의 경우 하나의 작업을 2개의 스레드로 수행하기 때문에 이 부분을 보완하기 위해 필터가 존재한다.
WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter는 커스텀 SecurityFilterChain을 생성해도 등록된다.
Callable 사용 시 스레드
@GetMapping("/async")
@ResponseBody
public Callable<String> asyncPage() {
System.out.println("start" + SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getName());
return () -> {
Thread.sleep(4000);
System.out.println("end" + SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getName());
return "async";
};
}위와 같은 코드는 Callable<> 인터페이스로 감싼 아래 부분을 다른 스레드(작업 스레드)에서 수행하게 된다.
각기 다른 스레드에서 수행하지만, ThreadLocal로 관리되는 SecurityContextHolder의 값은 WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter 및 그 밖의 다른 클래스들을 통해 동일하게 가져올 수 있다.
서블릿 단에서 비동기 처리인데 어떻게 필터 단에서 판단할까?
해당 문제를 처리하는 WebAsyncMagagerIntegrationFilter는 필터 단에 존재하는데 어떻게 필터 단을 통과하고 컨트롤러 단에서 발생하는 스레드 이동 문제를 처리할 수 있는지 의문점이 생긴다.
이는 WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter가 실제로 수행하는 작업과 Callable의 동작 방식에 관련이 있다.
WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter가 실제로 수행하는 작업
WebAsyncMagerIntegrationFilter는 서로 다른 스레드에 동일한 SecurityContext를 부여하는 것이 아닌, 현재 스레드의 SecurityContext를 다룰 수 있는 SecurityContectCallableProcessingInterceptor를 WebAsyncManager에 등록만 진행한다.
이후 서블릿단에서 WebAsyncManager을 통해 새로운 스레드에 SecurityContext를 복제한다.
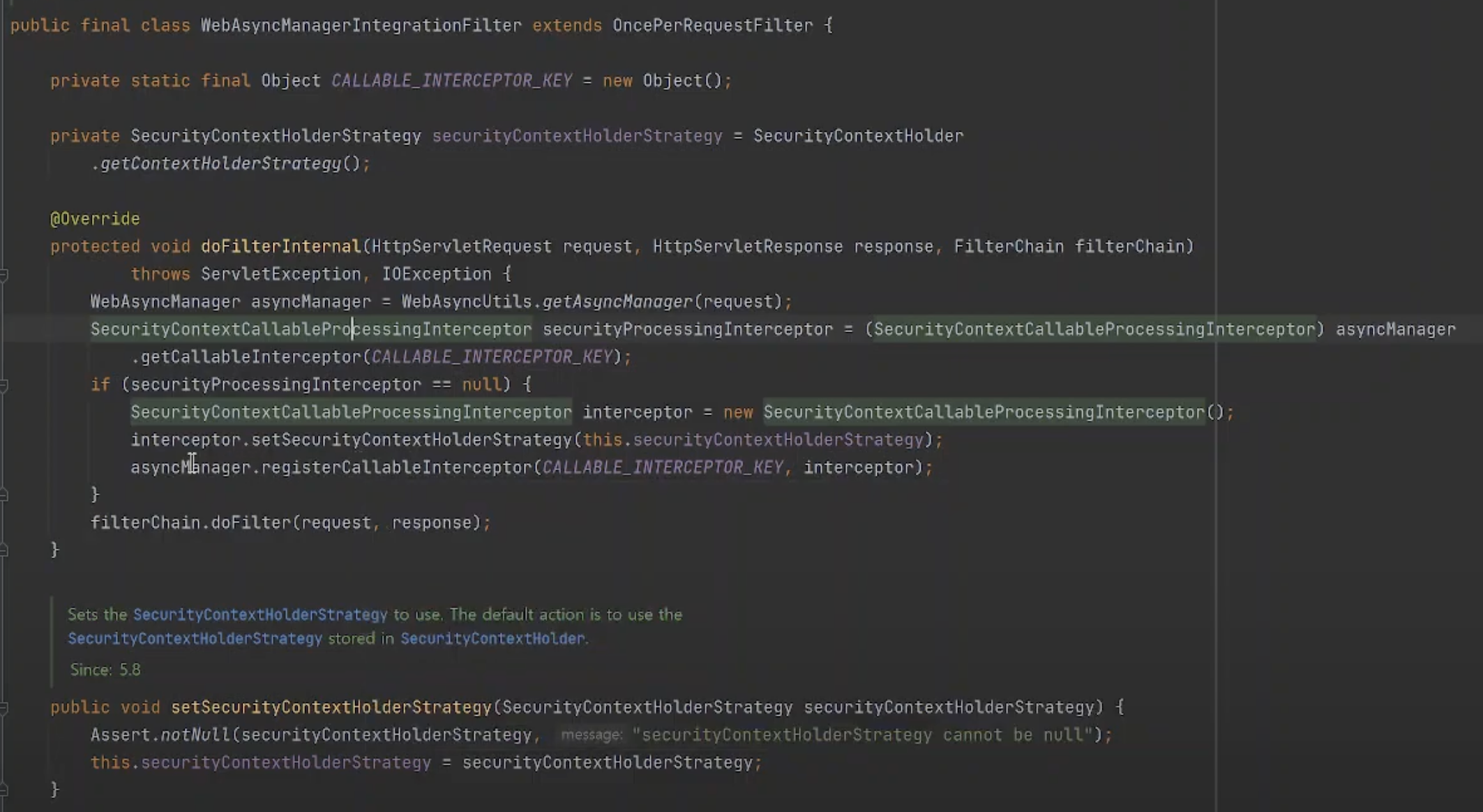
WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter.java
public final class WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
...
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
SecurityContextCallableProcessingInterceptor securityProcessingInterceptor = (SecurityContextCallableProcessingInterceptor) asyncManager
.getCallableInterceptor(CALLABLE_INTERCEPTOR_KEY);
if (securityProcessingInterceptor == null) {
SecurityContextCallableProcessingInterceptor interceptor = new SecurityContextCallableProcessingInterceptor();
interceptor.setSecurityContextHolderStrategy(this.securityContextHolderStrategy);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(CALLABLE_INTERCEPTOR_KEY, interceptor);
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
...
}스레드에 있는 값을 현재 필터에서 사용할 수 있도록 하는 SecurityContextCallableProcessingInterceptor를asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor를 통해 등록만 진행해준다. (이후 DispatcherServlet에서 사용)
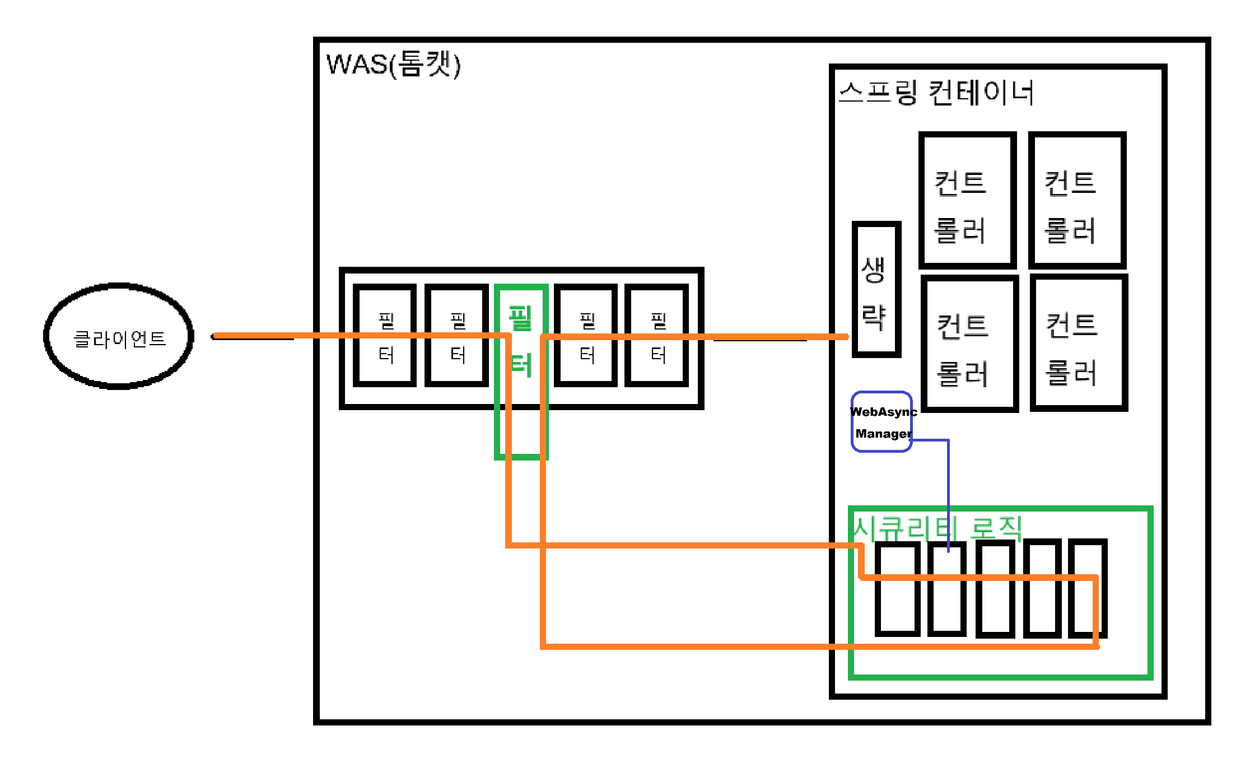
Callable 동작 방식과 DispatcherServlet
사용자의 요청은 필터단을 모두 거친 후 스프링 컨테이너에서 컨트롤러에 접근하게 된다. 이때 컨트롤러 바로 전에 DispatcherServlet이라는 서블릿이 존재하는데 (위 사진 '생략' 부분에 존재), 사용자의 요청과 알맞은 컨트롤러를 찾는 역할을 수행한다.
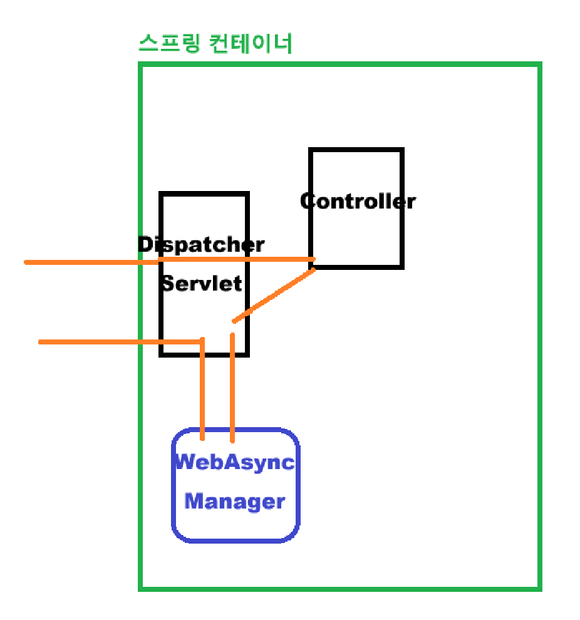
- Callable 수행 과정
- DispatcherServlet에서 알맞은 Controller를 찾아서 요청 전달
- Controller에서 요청 수행 후 Callable 부분을 DispatcherServlet으로 리턴
- DispatcherServlet은 Callable 객체를
WebAsyncManager에게 전달 WebAsyncManager가 비동기 부분을 새로운 스레드에서 수행 후 응답 (동시에 기존 스레드의 SecurityContext를 복제)
WebAsyncManager는 WebAsyncMagerIntegrationFilter에 의해 기존 스레드가 참조하던 SecurityContext를 전달 받았기 때문에 Callable을 수행할 새로운 스레드에게 기존 SecurityContext를 전달할 수 있다.
따라서 쓰레드가 바뀌더라도 SecurityContext에서 동일한 값을 획득할 수 있다.
시큐리티 설정을 진행하지 않아도
Callable사용 시 알아서 잘 적용되나,@Async를 통해 웹 동기화를 처리하는 경우에는 동작 방식이 다르므로 필터 단에서 처리가 불가능하며 다른 추가적인 작업을 진행해주어야 한다.
