병합 정렬
- 리스트를 절반으로 나눠 비슷한 크기의 두 부분 리스트로 나눈다.
- 각 부분 리스트를 재귀적으로 합병 정렬을 사용해 정렬한다.
- 두 부분 리스트를 다시 하나의 정렬된 리스트로 합병한다.
시간 복잡도
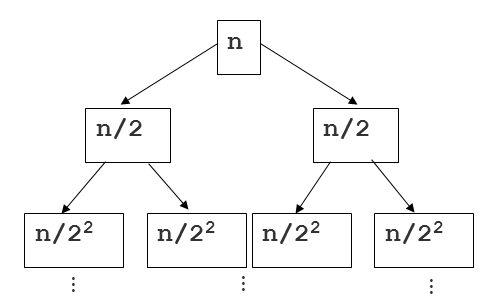
- depth를 i라 하고, 맨 위 단계를 0이라고 하자.
- 다음 그림에서 n/22 는 2단계 깊이라고 하자.
- 각 단계에 있는 하나의 노드 안의 리스트 길이는 n/22 가 된다.
- 각 단계에는 2i 개의 노드가 있다.
- 따라서, 각 단계는 항상 2i∗2in=O(n)
- 단계는 항상 log2n 개 만큼 만들어지고, 시간 복잡도는 O(log2n)이다.
- 따라서, 단계별 시간 복잡도 O(n)∗O(logn)=O(nlogn)이 된다.
병합 정렬 구현
def mergeList(left, right):
merged = list()
left_index, right_index = 0, 0
while len(left) > left_index and len(right) > right_index:
if left[left_index] > right[right_index]:
merged.append(right[right_index])
right_index += 1
else:
merged.append(left[left_index])
left_index += 1
while len(left) > left_index:
merged.append(left[left_index])
left_index += 1
while len(right) > right_index:
merged.append(right[right_index])
right_index += 1
return merged
def splitList(data_list):
if len(data_list) <=1:
return data_list
split_point = len(data_list) // 2
left = splitList(data_list[:split_point])
right = splitList(data_list[split_point:])
return mergeList(left, right)


.png)