문제사항
골드 4단계 문제로 유니온 파인드 문제였다.
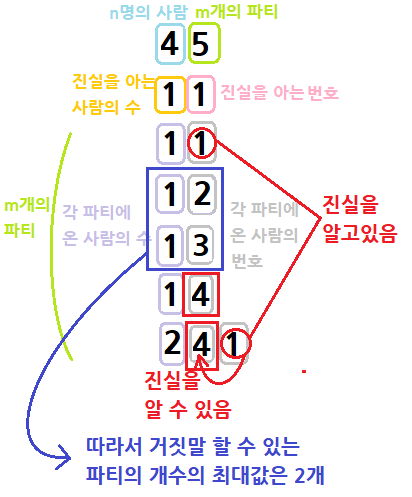
위 그림을 보면 거짓말 할 수 있는 파티의 최대 개수를 구하는 것이 이 문제의 답이다.
따라서 진실을 알고있는 번호가 있는 파티에 가서는 거짓말을 할 수 없으므로, 진실을 알고있는 번호가 있는 파티에 온 번호들은 Union 연산을 해야한다.
그 후에는 Find 연산을 하여 중복 연산을 허용하지 않는 HashSet으로 진실을 알 수 있는 번호들까지 넣어주었다.
각 파티에 참석한 번호들이 HashSet에 존재하는 요소들과 동일한지 확인하면 거짓말 할 수 있는 파티의 최대 개수를 구할 수 있다.
알고리즘 분류
- 그래프 (유니온 파인드)
코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int n, m;
static int[] parent;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
parent = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
parent[i] = i; //초기에 모든 값이 자기 자신을 가리키도록 만든다.
}
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int real = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
List<Integer> truePeople = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < real; i++) {
truePeople.add(Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken())); //이야기 진실을 말하는 번호
}
List<List<Integer>> parties = new ArrayList<>(); //m개의 파티 중 각각의 파티를 List<Integer>로 둠
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { //m개의 파티
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); //해당 파티에 오는 번호의 수
List<Integer> party = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < a; j++) {
party.add(Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken())); //해당 파티에 오는 번호
}
parties.add(party); //각 파티를 List에 추가
for (int j = 1; j < party.size(); j++) {
union(party.get(0), party.get(j)); //각 파티에서 온 번호끼리 부모로 치환
}
}
Set<Integer> trueGroup = new HashSet<>();
for (int person : truePeople) {
trueGroup.add(find(person)); //진실을 아는 번호의 부모가 있다면 찾고(진실을 아는 번호와 함께 파티에 참석한 번호), 그 값을 trueGrop에 저장
}
int answer = 0;
for (List<Integer> party : parties) {
boolean canLie = true;
for (int person : party) {
if (trueGroup.contains(find(person))) { //진실을 퍼트릴 수 있는 번호의 집합인 trueGrop의 번호가 각 파티에 참석한 번호와 동일하면
canLie = false; //거짓말을 못함
break;
}
}
if (canLie) { //위 조건문에 해당하지 않았다면 거짓말 가능 +1
answer++;
}
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
//부모를 찾는 연산
public static int find(int x) {
if (x == parent[x]) {
return x;
}
return parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
//y의 부모를 x의 부모로 치환 (x < y 경우)
static void union(int x, int y) {
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x != y) {
if (x < y) {
parent[y] = x;
} else {
parent[x] = y;
}
}
}
}

