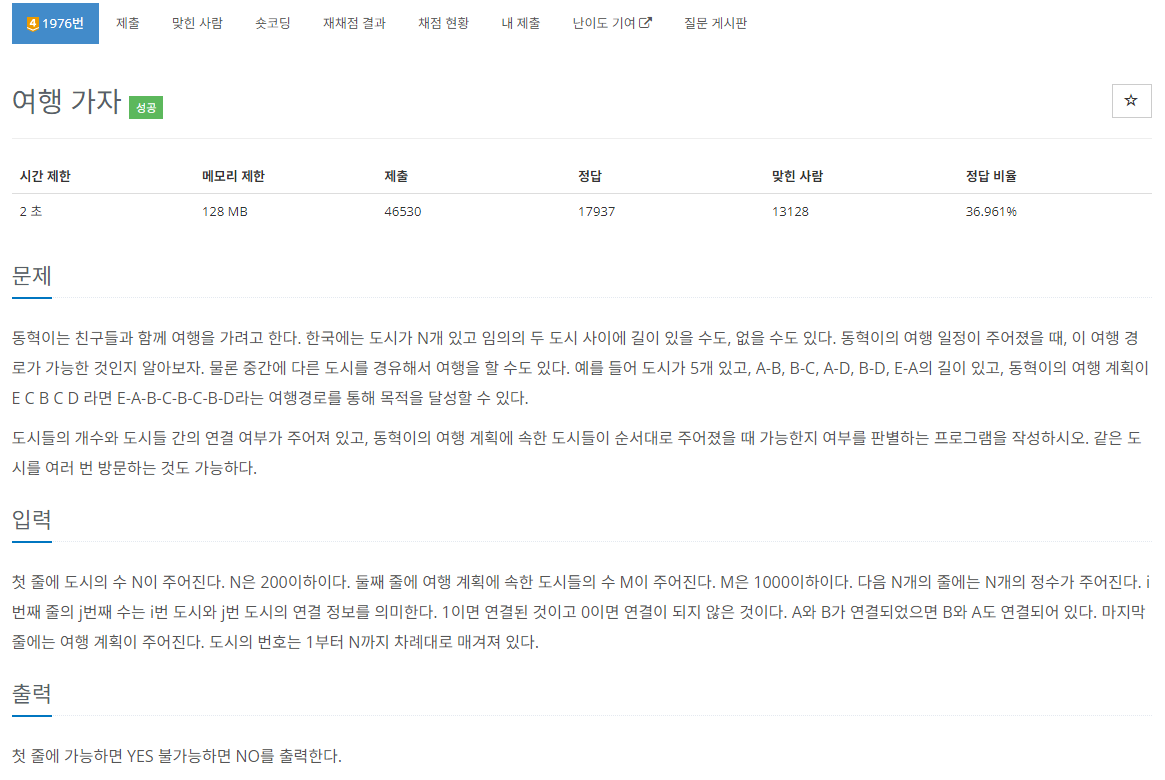
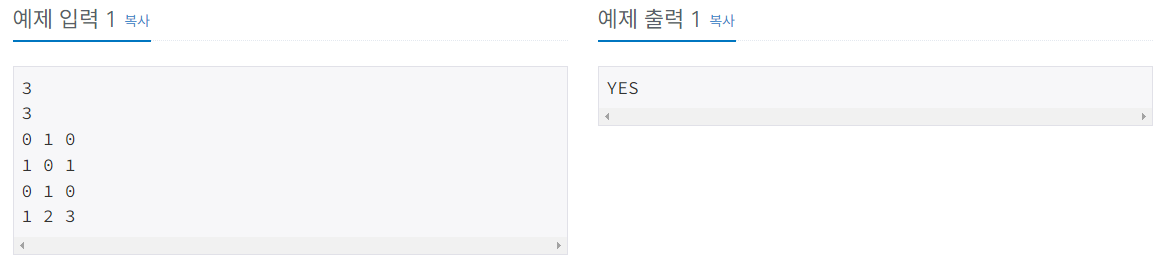
문제사항
골드 5단계 문제였다.
앞전에 풀었던 백준 1717번, 집합의 표현 문제와 비슷한 유형이며 알고리즘은 유니온 파인드가 쓰였다.
유니온 파인드 개념과 백준 1717번 문제 풀이를 보고 싶다면 앞전 게시물을 참고하길 바란다.
알고리즘 분류
- 그래프 (유니온 파인드)
코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int n, m;
static int[] parent;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
m = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
parent = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
int temp = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if (temp == 1) //1을 인자로 받으면 부모를 치환하는 과정 진행
union(i, j);
}
}
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int first = find(Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken())); //m 개의 수를 받되, 첫번째 숫자를 first 변수로 받아놓는다
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) { //first로 한 개는 미리 받아놨기 때문에 m-1번 반복
int now = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if (first != find(now)) { //첫번째로 받은 숫자 first의 값이 다음으로 받는 숫자들의 부모여야 함, 따라서 다르다면 NO 출력
System.out.println("NO");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("YES");
}
//부모를 찾는 연산
static int find(int x) {
if (x == parent[x]) { //부모로 치환 안한 경우는 자기 자신
return x;
}
return parent[x] = find(parent[x]); //부모로 치환된 경우 부모를 찾아감
}
//y의 부모를 x의 부모로 치환 (x < y 경우)
static void union(int x, int y) {
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x != y) {
if (x < y) { // 부모의 숫자가 작은쪽으로 치환 (부모로 이동할 수록, 부모의 숫자 자체가 작아짐)
parent[y] = x;
} else {
parent[x] = y;
}
}
}
}

