0415
spring에서의 constructor di에 대한 정의와 constructor di를 사용하여 Bean을 등록하는 예제를 다루는 글입니다.
1. Constructor DI란?
DI란 의존성 주입을 뜻합니다.
DI의 종류에는 총 두 가지가 있는데
Setter DIConstructor DI
여기서 Constructor DI란 생성자를 통해 값을 주입하는 것을 말합니다.
public Data1 data1() {
return new Data1(30, "data1");
}위의 코드처럼 생성자로 값을 초기화한다고 생각하면 됩니다.
2. Constructor DI를 활용하여 값을 출력해보자
Constructor DI를 익히기 위해 간단한 예제를 풀어보겠습니다.
2.1. 개발 환경
- IDE: IntelliJ, maven
- Framework: Spring
- 폴더 구조:
- src > main > java > kr > hs > study > beans: 객체들의 집합
- src > main > java > kr > hs > study > config: java 설정파일
2.2. 문제 기본 세팅
pom.xml
Spring을 사용하기 위해 꼭 필요한 파일입니다.
아래의 코드를 복사붙여넣고 다시 빌드를 하면 Spring을 사용할 수 있게 됩니다.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>kr.hs.study</groupId>
<artifactId>Component2</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.22.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.slf4j/slf4j-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/ch.qos.logback/logback-classic -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.3.5</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>Chef
package kr.hs.study.beans;
public class Chef {
private String name;
private int age;
public Chef(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}Order
package kr.hs.study.beans;
public class Order {
private String menu;
private String drink;
public Order(String menu, String drink) {
this.menu = menu;
this.drink = drink;
}
public String getMenu() {
return menu;
}
public String getDrink() {
return drink;
}
}Restaurant
package kr.hs.study.beans;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Restaurant {
private Chef chef;
private Order order;
public Chef getChef() {
return chef;
}
public Order getOrder() {
return order;
}
}BeanConfigClass
실질적인 객체를 만들라는 명령을 spring에게 내리는 java 설정파일입니다.
package kr.hs.study.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "kr.hs.study.beans")
public class BeanConfigClass {
}Main
package kr.hs.study;
import kr.hs.study.config.BeanConfigClass;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanConfigClass.class);
ctx.close();
}
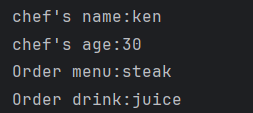
}출력되어야 하는 결과
chef's name:ken
chef's age:30
Order menu:steak
Order drink:juice2.3. Constructor DI를 사용하여 올바른 결과를 출력해보자
문제 조건
1. Chef, Order 클래스는 수정하지 않습니다.
2. Setter DI를 사용하지 않습니다.
3. Main 클래스에서는 Restaurant의 객체만 불러옵니다.
4. BeanConfigClass 설정파일에서만 객체를 생성할 수 있습니다.
BeanConfigClass
package kr.hs.study.config;
import kr.hs.study.beans.Chef;
import kr.hs.study.beans.Order;
import kr.hs.study.beans.Restaurant;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "kr.hs.study.beans")
public class BeanConfigClass {
@Bean
public Chef c1() {
return new Chef("ken", 30);
}
@Bean
public Order o1() {
return new Order("steak", "juice");
}
@Bean
public Restaurant r1() {
return new Restaurant();
}
}BeanConfigClass는 Spring에게 객체를 만들어라고 시키는 설정파일입니다.
이렇게 설정파일이라고 나타내는 것이 @Configuration입니다.
@ComponentScan은 basePackages안에 들어있는 entity들 중에서 @Component가 있는 것만 객체를 만들어라라고 지시하는 어노테이션입니다.
앞서 BeanConfigClass는 객체를 만드는 설정파일이라고 했었죠?
이 객체를 만드는 어노테이션이 바로 @Bean입니다.
setter DI를 사용하면 안 되고 Constructor DI를 사용해야 하기 때문에 return하는 객체의 생성자에 값을 집어넣어준 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
또한 이렇게 만든 객체는 각각의 메서드명으로 Main.java에서 객체를 불러와 생성할 수 있습니다.
만약 Chef라는 객체를 가져온다면 c1이라는 이름으로 가져올 수 있겠군요!
Restaurant
package kr.hs.study.beans;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Restaurant {
@Autowired
private Chef chef;
@Autowired
private Order order;
public Chef getChef() {
return chef;
}
public Order getOrder() {
return order;
}
}Chef와 Order를 멤버변수로 가지고 있는 Restaurant입니다.
앞서 제시된 코드와 뭔가 다른 점이 생긴 것을 알아차리셨을 겁니다.
그건 바로 @Autowired인데요, 이 것은 쉽게 말해 setter의 역할을 해주는 어노테이션입니다.
우리는 설정파일에서 Chef와 Order는 생성자를 사용하여 초기화를 해주었지만 Restaurant의 생성자에는 아무것도 주지 않았습니다.
그렇다면 멤버변수인 chef와 order에는 아무것도 들어가지 않았기 때문에 Restaurant에서 Chef와 Order를 사용할 수 없게 되는데, 이 때 초기화를 자동으로 해주는 @Autowired덕분에 값이 자동으로 들어가, 사용이 가능해지게 되는 것입니다.
Main
package kr.hs.study;
import kr.hs.study.beans.Restaurant;
import kr.hs.study.config.BeanConfigClass;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanConfigClass.class);
Restaurant restaurant = ctx.getBean("r1", Restaurant.class);
System.out.println("chef's name:"+restaurant.getChef().getName());
System.out.println("chef's age:"+restaurant.getChef().getAge());
System.out.println("Order menu:"+restaurant.getOrder().getMenu());
System.out.println("Order drink:"+restaurant.getOrder().getDrink());
ctx.close();
}
}Main에서는 Restaurant객체를 설정파일의 r1 메서드를 이용하여 생성한 뒤,
Restaurant안의 Chef와 Order의 getter를 통해 아래와 같은 출력 결과를 만들어낼 수 있게 됩니다!