
(강의 요약본입니다.)
Sockets for Server
Server란?
클라이언트의 대화상대. 클라이언트가 Socket을 생성하려면 연결할 인터넷 상의 호스트가 있어야 한다.
-> 서버
Java Socket class로는 서버를 작성할 수 없어 ServerSocket class를 사용한다.
객체의 생명주기
1. ServerSocket() 생성자를 이용하여 특정 포트에 ServerSocket 객체를 생성한다.
2. ServerSocket 객체의 accept() 메소드를 호출하여 클라이언트의 연결 요청을 기다림
accept() 메소드는 서버가 설정된 포트로 클라이언트가 연결을 시도할 때까지 블록된다.
클라이언트의 요청이 들어오면 Socket 객체가 리턴된다
3. 클라이언트와 통신하기 위해 Socket 객체의 getInputStream()과 getOutputStream() 이용하여 IO 스트림 객체를 생성한다.
4. 연결이 끝날 때까지 클라이언트와 서버가 응용 프로토콜에 따라 상호 작용한다. 상호작용은 보통 Thread로 처리된다.
5. 서버나 클라이언트 또는 양쪽 모두 연결을 종료
6. Step 2로 돌아가 다음 연결 요청을 기다림
public Socket accept() throws IOException
클라이언트의 연결 요청을 받아들이기 위한 메소드
클라이언트의 연결 요청이 들어 올 때까지 블록된다.
클라이언트의 연결 요청이 들어오면 Socket 객체를 리턴한다.
<참고>
ServerSocket으로부터 발생하는 예외는 서버를 종료시켜야 하지만, Socket이 발생시킨 예외는 활성화된 Socket만 종료시켜도 괜찮다.
Socket 객체의 close() method
로컬 호스트와 원격 호스트의 연결이 해지된다.
서비스를 끝내면 Socket 객체를 닫아야 한다. (보통 finally 구문에서 연결을 종료한다.)
예제) DayTime Server
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Date;
public class DaytimeServer {
public final static int PORT = 13;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(PORT)) {
while (true) {
try (Socket connection = server.accept()) {
Writer out = new OutputStreamWriter(connection.getOutputStream());
Date now = new Date();
out.write(now.toString() +"\r\n");
out.flush();
connection.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {}
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
}
}
} 
예제 2) 친구 서버와 클라이언트
서버 코드 :
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class FriendServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket socket = null;
InputStreamReader isr = null;
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
StringBuilder message = null;
try (ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(7009);) {
System.out.println("-- 서버가 접속을 기다린다 -- ");
socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("-- 클라이언트와 접속 성공 -- ");
// Message from Client to Server
isr = new InputStreamReader(
socket.getInputStream(), "MS949");
message = new StringBuilder();
for (int c = isr.read(); c != -1; c = isr.read()) {
message.append((char) c);
}
socket.shutdownInput();
System.out.println("클라이언트 친구로부터 받은 메세지 : " + message);
// Message from Server to Client
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(
socket.getOutputStream() );
osw.write("나 9시에 갈 예정이야" + "\r\n");
System.out.println("클라이언트 친구에게 메시지를 보내다");
osw.flush();
socket.shutdownOutput();
osw.close();
isr.close();
socket.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}클라이언트 코드 :
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class FriendClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStreamReader isr = null;
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
StringBuilder reply = null;
try (Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 7009)) {
socket.setSoTimeout(2000);
// Message from Client to Server
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(
socket.getOutputStream() );
osw.write("내일 학교에 몇 시에 올래" + "\r\n");
System.out.println("서버 친구에게 메시지를 보내다");
osw.flush();
socket.shutdownOutput();
// Message from Server to Client
isr = new InputStreamReader(
socket.getInputStream(), "MS949");
reply = new StringBuilder();
for (int c = isr.read(); c != -1; c = isr.read()) {
reply.append((char) c);
}
System.out.println("서버 친구로부터 받은 메세지 : " + reply);
osw.close();
isr.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}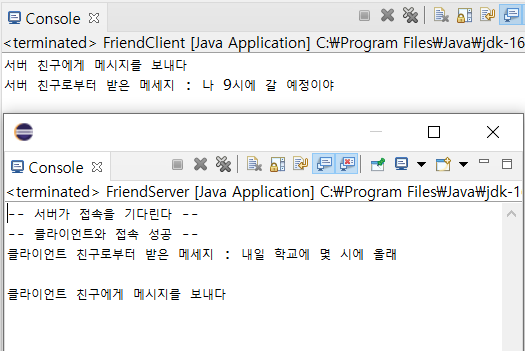
서버를 키고, 클라이언트가 질문한다. 내일 학교에 몇 시에 올래?
서버는 답한다. 나 9시에 갈 예정이야
Multithreaded Server
Server는 하나의 요청만을 처리하고 있을 수 없다!
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Date;
public class MultithreadedDaytimeServer {
public final static int PORT = 13;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(PORT)) {
while (true) {
try {
Socket connection = server.accept();
Thread task = new DaytimeThread(connection);
task.start();
} catch (IOException ex) {}
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.err.println("Couldn't start server");
}
}
private static class DaytimeThread extends Thread {
private Socket connection;
DaytimeThread(Socket connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
public void run() {
try {
Writer out = new OutputStreamWriter(connection.getOutputStream());
Date now = new Date();
out.write(now.toString() +"\r\n");
out.flush();
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
} finally {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// ignore;
}
}
}
}
}Socket 값을 return 해준다.
# + Threadpool을 이용한 서버
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class PooledDaytimeServer {
public final static int PORT = 13;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(50);
try (ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(PORT)) {
while (true) {
try {
Socket connection = server.accept();
Callable<Void> task = new DaytimeTask(connection);
pool.submit(task);
} catch (IOException ex) {}
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.err.println("Couldn't start server");
}
}
private static class DaytimeTask implements Callable<Void> {
private Socket connection;
DaytimeTask(Socket connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
public void call() {
try {
Writer out = new OutputStreamWriter(connection.getOutputStream());
Date now = new Date();
out.write(now.toString() +"\r\n");
out.flush();
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
} finally {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// ignore;
}
}
return null;
}
}
}Echo Server
말 그대로 클라이언트가 보낸 메시지 그대로 응답한다.
클라이언트 코드 :
// . 문장을 입력하면 종료
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class EchoClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String hostname = "localhost";
if (args.length > 0) {
hostname = args[0];
}
PrintWriter networkOut = null;
BufferedReader networkIn = null;
try {
Socket theSocket = new Socket(hostname, 7);
networkIn = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(theSocket.getInputStream()));
BufferedReader userIn = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
networkOut = new PrintWriter(theSocket.getOutputStream());
System.out.println("Connected to echo server");
while (true) {
String theLine = userIn.readLine();
if (theLine.equals(".")) break;
networkOut.println(theLine);
networkOut.flush();
System.out.println(networkIn.readLine());
}
} // end try
catch (IOException ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
}
finally {
try {
if (networkIn != null) networkIn.close();
if (networkOut != null) networkOut.close();
}
catch (IOException ex) {}
}
} // end main
} // end EchoClientnetworkIn : 서버로부터 자료를 받을 스트림
networkOut : 서버로부터 자료를 보낼 스트림
userIn: 사용자로부터 서버로 보낼 메시지를 받는 스트림
try 블록과 finally 블록은 별도의 블록이다. 양 블록에서 변수를 공유하려면 블록 밖으로 빼서 선언해야 한다. 이 프로그램의 다음 부분이 부분이 여기에 해당된다.
BufferedReader networkIn=null;
PrintWriter networkOut=null;
에코 서버는 클라이언트로부터 받은 데이터를 그대로 다시 클라이언트로 보낸다. 따라서 보통의 경우 정상적인 처리를 기대하기 어려운 PrintWriter나 readLine() 등도 무난히 사용할 수 있다.
networkIn의 현재의 Default Encoding은 운영체제 기본 인코딩 방법이다.
Echo Server
클라이언트가 어떤 메시지를 보내 오기 전에는 서버는 어떤 메시지도 클라이언트에게 보내지 않는다.
클라이언트와 서버 사이에서 주고 받는 메시지에는 개행문자(줄바꿈 문자)가 포함되어야 한다.
소켓은 InputStream/OutputStream을 반환하지만 InputStream은 InputStreamReader, BufferedReader로, OutputStream은 PrintWriter로 변환하여 사용하여야 한다.
송신측에서는 PrintWriter의 println()으로 보내고
수신측은 BufferedReader의 readLine()으로 읽는다.
개행
메시지를 받는 서버나 에코된 메시지를 받는 클라이언트는 readLine()으로 읽어 들이기 때문에 라인의 끝이 인식되어야 한다. 보내는 쪽에서 메시지의 끝에 개행문자를 포함시키려면 println(msg) 또는 write(msg + “\r\n"); 방식으로 출력해야 한다.
readLine() 메소드는 개행문자를 제거하고 데이터를 읽어 들이므로 그 데이터를 되보내더라도 개행문자를 다시 추가 해야 한다.
네트워크 프로그램에서 멀티 바이트 데이터를 출력한 다음에는 flush()를 호출해주어야 한다.
연결된 리모트 클라이언트가 누구인지 서버 운영자에게 알리기 위해서는 다음의 코드가 필요하다.
InetAddress inetaddr = sock.getInetAddress();
System.out.println("클라이언트: " + inetaddr.getHostAddress());
클라이언트가 접속을 종료하면 BufferedReader의 readLine()이 null을 반환한다.
클라이언트가 비정상적으로 종료하면 서버의 클라이언트 상대 코드도 종료해야 한다.
클라이언트에서 “.” 으로 종료 시키는 부분을 “exit” 문구로 변경하면 클라이언트는 종료가 가능하지만 서버는 종료 되지 않는다
예제) 한 클라이언트에게만 서비스하고 실행을 끝내버리는 에코 서버
// . 문장을 입력하면 종료
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class EchoClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String hostname = "localhost";
if (args.length > 0) {
hostname = args[0];
}
PrintWriter networkOut = null;
BufferedReader networkIn = null;
try {
Socket theSocket = new Socket(hostname, 7);
networkIn = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(theSocket.getInputStream()));
BufferedReader userIn = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
networkOut = new PrintWriter(theSocket.getOutputStream());
System.out.println("Connected to echo server");
while (true) {
String theLine = userIn.readLine();
if (theLine.equals(".")) break;
networkOut.println(theLine);
networkOut.flush();
System.out.println(networkIn.readLine());
}
} // end try
catch (IOException ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
}
finally {
try {
if (networkIn != null) networkIn.close();
if (networkOut != null) networkOut.close();
}
catch (IOException ex) {}
}
} // end main
} // end EchoClient
순서적으로 여러 클라이언트를 상대하는 서버
단, 한 클라이언트에 대한 서비스가 종료되어야 다른 클라이언트에게 서비스할 수 있다
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class EchoServer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(7);
while (true) {
System.out.println("에코 서버가 접속을 기다립니다.");
Socket sock = server.accept();
System.out.println(sock.getInetAddress() + "- port" + sock.getPort() + " 이 접속하였습니다.");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(sock.getInputStream()));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(sock.getOutputStream()));
String line = null;
line = br.readLine();
while (line != null) {
System.out.println("클라이언트로 부터 전송 받은 문자열 : " + line);
pw.println(line);
pw.flush();
line = br.readLine();
}
System.out.println("입출력 완료, 클라이언트와의 스트림 및 소켓 닫기");
pw.close();
br.close();
try {
if(sock != null)
sock.close();
}
catch(IOException e) {
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
} // main
}multi thread로 바꾸려면??
NIO(New Input Output)를 사용하는 에코 서버
일반 IO와 조금씩 차이가 있다.
import java.nio.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class EchoServer9_5 {
public static int DEFAULT_PORT = 7;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port;
try {
port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
port = DEFAULT_PORT;
}
System.out.println("Listening for connections on port " + port);
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel;
Selector selector;
try {
serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ServerSocket ss = serverChannel.socket();
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(port);
ss.bind(address);
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
selector = Selector.open();
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
return;
}
while (true) {
try {
selector.select();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
break;
}
Set<SelectionKey> readyKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = readyKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
try {
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel client = server.accept();
System.out.println("Accepted connection from " + client);
client.configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey clientKey = client.register(
selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE | SelectionKey.OP_READ);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
clientKey.attach(buffer);
}
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer output = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
client.read(output);
}
if (key.isWritable()) {
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer output = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
output.flip();
client.write(output);
output.compact();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
key.cancel();
try {
key.channel().close();
} catch (IOException cex) {}
}
}
}
}
}public void close() throws IOException
저번 소켓의 사용이 끝나면 ServerSocket 객체의 close() 메소드를 호출하여 서버 소켓을 닫아야 한다.
점유하고 있던 port를 반환하여 다른 서버가 바인드 할 수 있게 함
서버 소켓의 accept()를 통해 열린 모든 Socket도 삭제한다
서버 소켓을 반드시 닫아야 하는가?
프로그램이 끝나면 자동으로 닫힌다
관련 메소드
public boolean isClosed()
public boolean isBound()
isBound()는 ServerSocket이 닫혀 있더라도 이전에 바인드된 적이 있으면 true를 리턴
서버 소켓이 연결된 적이 있는가를 정확히 체크하려면 다음과 같은 식으로 처리해야 한다.
public static boolean isOpen()(ServerSocket ss){
return ss.isBound() && ! ss.isClosed();
}