Spring Framework
Spring Framework?
-
엔터프라이즈 급 애플리케이션을 만들기 위한 모든 기능을 종합적으로 제공하는 경량화 된 솔루션
-
JEE(Java Enterprise Edition)가 제공하는 다수의 기능을 지원하고 있기 때문에, JEE를 대체하는 Framework로 자리잡고 있다
-
SpringFramework는 JEE가 제공하는 다양한 기능을 제공하는 것 뿐만 아니라, DI(Dependency Injection)나 AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)와 같은 기능도 지원한다
-
SpringFramework는 자바로 Enterprise Application을 만들 때 포괄적으로 사용하는 Programming 및 Configuration Model을 제공해주는 Framework로 Application 수준의 인프라 스트럭쳐를 제공
-
개발자가 복잡하고 실수하기 쉬운 Low Level에 신경 쓰지 않고 Business Logic 개발에 전념할 수 있도록 해준다
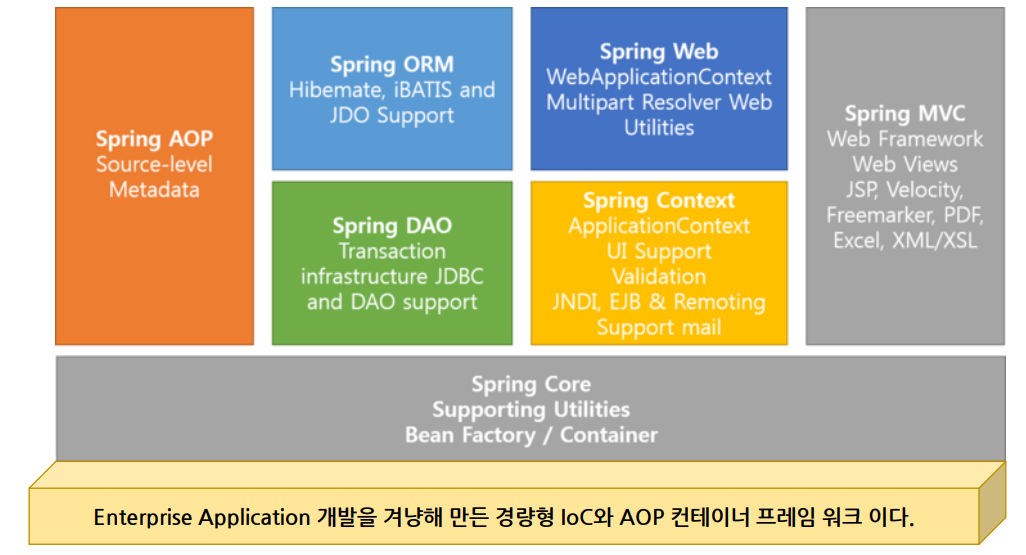
Spring Framework의 구조
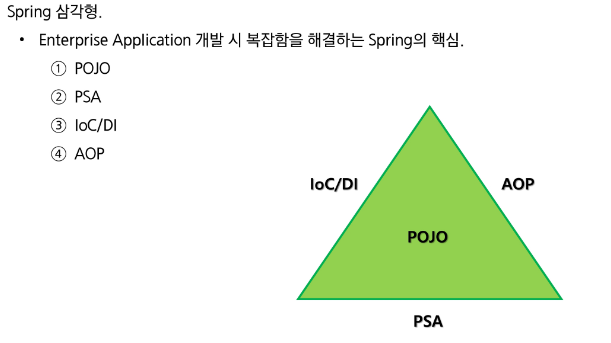




Spring Framework의 특징
- 경량 컨테이너
- 스프링은 자바 객체를 담고 있는 컨테이너 이다
- 스프링 컨테이너는 이들 자바 객체의 생성과 소멸과 같은 라이프 사이클을 관리
- 언제든지 스프링 컨테이너로부터 필요한 객체를 가져와 사용할 수 있다
- 스프링은 자바 객체를 담고 있는 컨테이너 이다
- DI(Dependency Injection - 의존성 지원) 패턴 지원
- 스프링은 설정 파일이나, 어노테이션을 통해서 객체 간의 의존 관계를 설정할 수 있다
- 따라서, 객체는 의존하고 있는 객체를 직접 생성하거나 검색할 필요가 없다.
- 스프링은 설정 파일이나, 어노테이션을 통해서 객체 간의 의존 관계를 설정할 수 있다
- AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming - 관점 지향 프로그래밍) 지원
- AOP는 문제를 바라보는 관점을 기준으로 프로그래밍하는 기법이다
- 이는 문제를 해결하기 위한 핵심 관심 사항과 전체에 적용되는 공통관심 사항을 기준으로 프로그래밍 함으로써 공통 모듈을 여러 코드에 쉽게 적용할 수 있도록 한다
- 스프링은 자체적으로 프록시 기반의 AOP를 지원하므로 트랜잭션이나, 로깅, 보안과 같이 여러 모듈에서 공통으로 필요로 하지만 실제 모듈의 핵심이 아닌 기능들을 분리하여 각 모듈에 적용이 가능하다
- AOP는 문제를 바라보는 관점을 기준으로 프로그래밍하는 기법이다
- POJO(Plain Old Java Object) 지원
- 특정 인터페이스를 구현하거나 또는 클래스를 상속하지 않는 일반 자바 객체 지원
- 스프링 컨테이너에 저장되는 자바객체는 특정한 인터페이스를 구현하거나, 클래스 상속 없이도 사용이 가능하다
- 일반적인 자바 객체를 칭하기 위한 별칭 개념이다
- 특정 인터페이스를 구현하거나 또는 클래스를 상속하지 않는 일반 자바 객체 지원
- IoC(Inverson of Control - 제어의 반전)
- IoC는 스프링이 갖고 있는 핵심적인 기능이다
- 자바의 객체 생성 및 의존관계에 있어 모든 제어권은 개발자에게 있었다
- Servlet과 EJB가 나타나면서 기존의 제어권이 Servlet Container 및 EJB Container에게 넘어가게 됐다
- 단, 모든 객체의 제어권이 넘어간 것은 아니고 Servlet, EJB에 대한 제어권을 제외한 나머지 객체 제어권은 개발자들이 담당
- 스프링에서도 객체에 대한 생성과 생명주기를 관리할 수 있는 기능을 제공하고 있는데 이런 이유로 Spring Container 또는 IoC Container 라고 한다
- IoC는 스프링이 갖고 있는 핵심적인 기능이다
- 스프링은 트랜잭션 처리를 위한 일관된 방법을 제공
- JDBC, JTA 또는 컨테이너가 제공하는 트랜잭션을 사용하든, 설정파일을 통해 트랜잭션 관련 정보를 입력하기 때문에 트랜잭션 구현에 상관없이 동일한 코드를 여러 환경에서 사용이 가능하다.
- 스프링은 영속성과 관련된 다양한 API를 지원
- 스프링은 JDBC를 비록하여 iBatis, myBatis, Hibernate, JPA등 DB처리를 위해 널리 사용되는 라이브러리와 연동을 지원하고 있다
- 스프링은 다양한 API에 대한 연동을 지원
- 스프링은 JMS, 메일, 스케쥴링 등 엔터프라이즈 어플리케이션 개발에 필요한 다양한 API를 설정 파일과 어노테이션을 통해서 손쉽게 사용할 수 있도록 지원하고 있다.
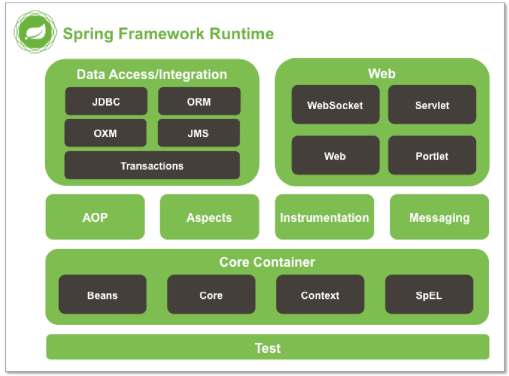
Spring Framework Module

IoC & Container
IoC (Inversion of Control, 제어의 역행)
-
IoC/DI
-
객체지향 언어에서 Object간의 연결 관계를 런타임에 결정
-
객체 간의 관계가 느슨하게 연결됨(loose coupling)
-
IoC의 구현 방법 중 하나가 DI (Dependency Injection)
IoC 유형

Dependency Lookup
-
컨테이너가 lookup context를 통해서 필요한 Resource나 Object를 얻는 방식
-
JNDI 이외의 방법을 사용한다면 JNDI 관련 코드를 오브젝트 내에서 일일이 변경해줘야 함
-
Lookup 한 Object를 필요한 타입으로 Casting 해줘야 함
-
Naming Exception을 처리하기 위한 로직이 필요
Dependency Injection
-
Object에 lookup 코드를 사용하지 않고 컨테이너가 직접 의존 구조를 Object에 설정할 수 있도록 지정해주는 방식
-
Object가 컨테이너의 존재 여부를 알 필요가 없음
-
Lookup 관련된 코드들이 Object 내에서 사라짐
-
Setter Injection과 Constructor Inject
Container
-
Container란?
- 객체의 생성,사용, 소멸에 해당하는 라이프사이클을 담당
- 라이프사이클을 기본으로 애플리케이션 사용에 필요한 주요 기능을 제공
-
Container 기능
- 라이프사이클 관리
- Dependency 객체 제공
- Thread 관리
- 기타 애플리케이션 실행에 필요한 환경
- Container 필요성
- 비즈니스 로직 외에 부가적인 기능들에 대해서는 독립적으로 관리되도록 하기 위함
- 서비스 look up 이나 Configuration에 대한 일관성을 갖기 위함
- 서비스 객체를 사용하기 위해 각각 Factory 또는 Singleton 패턴을 직접 구현하지 않아도 됨
IoC Container
-
오브젝트의 생성과 관계설정, 사용, 제거 등의 작업을 애플리케이션 코드 대신 독립된 컨테이너가 담당
-
컨테이너가 코드 대신 오브젝트에 대한 제어권을 갖고 있어 IoC라고 부름
-
이런 이유로, 스프링 컨테이너를 IoC 컨테이너라고 부르기도 함
-
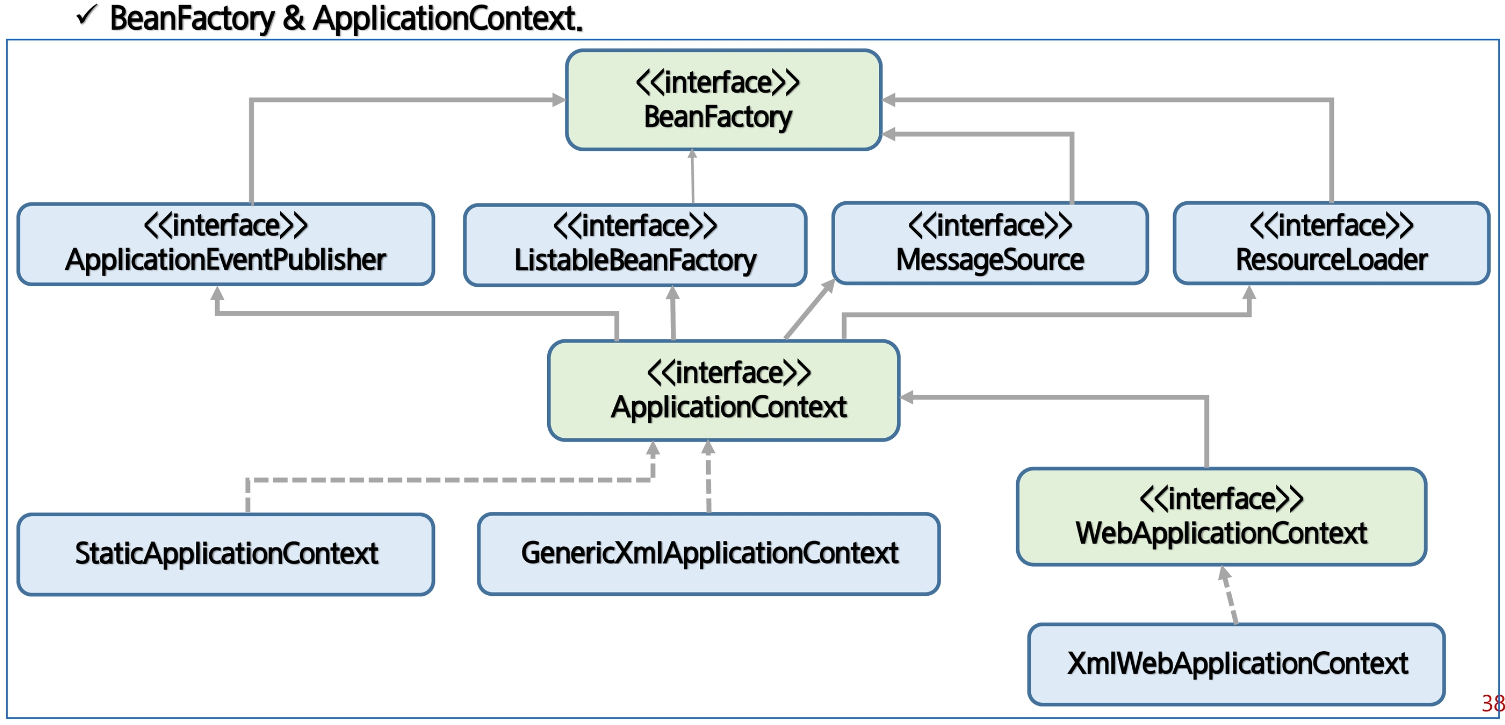
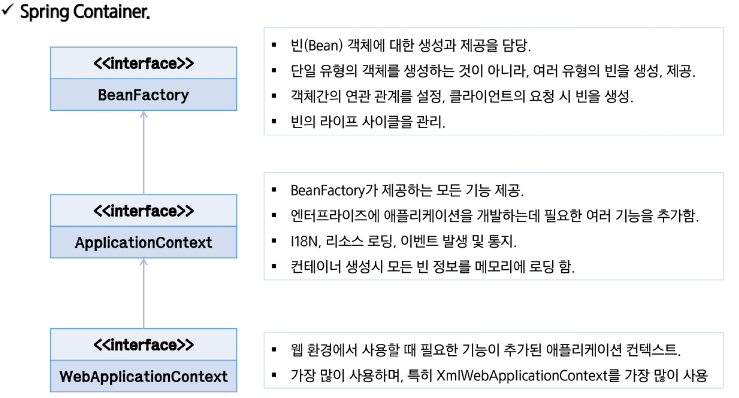
스프링에서 IoC를 담당하는 컨테이너에는 BeanFactory, ApplicationConext가 있음
Spring DI Container
-
Spring DI Container가 관리하는 객체를 Bean이라 하고, 이 빈들의 생명주기를 관리하는 의미로 BeanFactory라 한다
-
Bean Factory에 여러 가지 컨테이너 기능을 추가하여 ApplicationContext라 한다.

IoC 개념
- 객체 제어 방식
- 기존: 필요한 위치에서 개발자에게 필요한 객체 생성 로직 구현
- IoC: 객체 생성을 Container에게 위임하여 처리
- IoC 사용에 따른 장점
- 객체 간의 결합도를 떨어뜨릴 수 있음(loose coupling)
- 객체간 결합도가 높으면?
- 해당 클래스가 유지보수 될 때 그 클래스와 결합된 다른 클래스도 같이 유지보수 되어야 할 가능성이 높음
Spring DI 용어 정리
- 빈(Bean)
- 스프링이 IoC 방식으로 관리되는 오브젝트를 말한다
- 스프링이 직접 그 생성과 제어를 담당하는 오브젝트만을 Bean이라고 부른다
- 스프링이 IoC 방식으로 관리되는 오브젝트를 말한다
- 빈 팩토리(BeanFactory)
- 스프링이 IoC를 담당하는 핵심 컨테이너
- Bean을 등록, 생성, 조회, 반환하는 기능을 담당
- 일반적으로 BeanFactory를 바로 사용하지 않고 이를 확장한 ApplicationContext를 이용한다.
- 스프링이 IoC를 담당하는 핵심 컨테이너
- 애플리케이션 컨텍스트(ApplicationContext)
- BeanFactory를 확장한 IoC 컨테이너이다
- Bean을 등록하고 관리하는 기본적인 기능은 BeanFactory와 동일하다
- 스프링이 제공하는 각종 부가 서비스를 추가로 제공한다
- BeanFactory라고 부를 때는 주로 빈의 생성과 제어의 관점에서 이야기 하는 것이고, 애플리케이션 컨텍스트라고 할 때는 스프링이 제공하는 애플리케이션 지원 기능을 모두 포함해서 이야기하는 것 이라고 보면 된다.
- BeanFactory를 확장한 IoC 컨테이너이다
- 설정정보/설정 메타정보
- 스프링 설정정보란 ApplicationContext 또는 BeanFactory가 IoC를 적용하기 위해 사용하는 메타정보를 말한다. 이는 구성정보 내지는 형상정보라는 의미이다
- 설정정보는 IoC 컨테이너에 의해 관리되는 Bean 객체를 생성하고 구성할 때 사용됨
- 스프링 설정정보란 ApplicationContext 또는 BeanFactory가 IoC를 적용하기 위해 사용하는 메타정보를 말한다. 이는 구성정보 내지는 형상정보라는 의미이다
- 스프링 프레임워크
- 스프링 프레임워크는 IoC 컨테이너, ApplicationContext를 포함해서 스프링이 제공하는 모든 기능을 통틀어 말할 때 주로 사용한다.
의존성주입 (Dependency Injection)
-
객체 간의 결합을 느슨하게 하는 스프링의 핵심 기술이다
-
객체 사이의 의존관계를 자기자신이 아닌 외부에 의해서 설정된다는 개념이다
-
제어의 역행(IoC)이라는 의미로 사용한다
-
DI 컨테이너는 어떤 클래스가 필요로 하는 인스턴스를 자동으로 생성, 취득하여 연결해주는 역할을 한다
-
느슨한 결합의 주요강점
- 객체는 인터페이스에 의한 의존관계만을 알고 있으며, 이 의존관계는 구현 클래스에 대한 차이를 모르는 채 서로 다른 구현으로 대체가 가능하다.
객체간 결합도에 따른 프로그램 설계
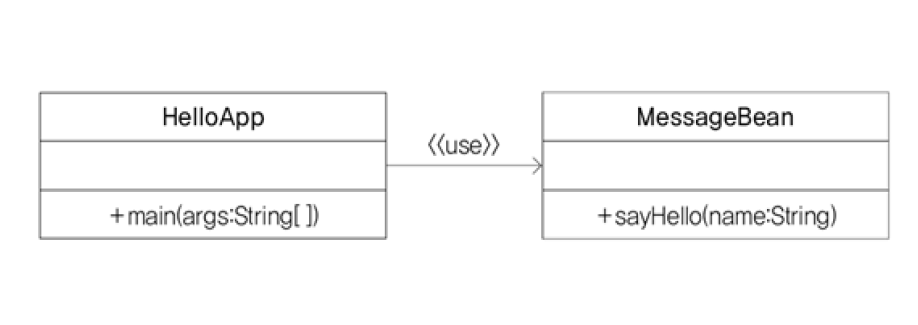
객체간 결합도가 강한 프로그램
-
HelloApp 에서 MessageBean을 직접 객체 생성하여 사용하고 있다
-
MessageBean 클래스를 다른 클래스로 변경할 경우 HelloApp의 소스를 같이 수정해주어야 한다
 |  |
|---|
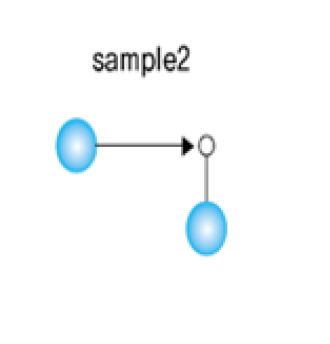
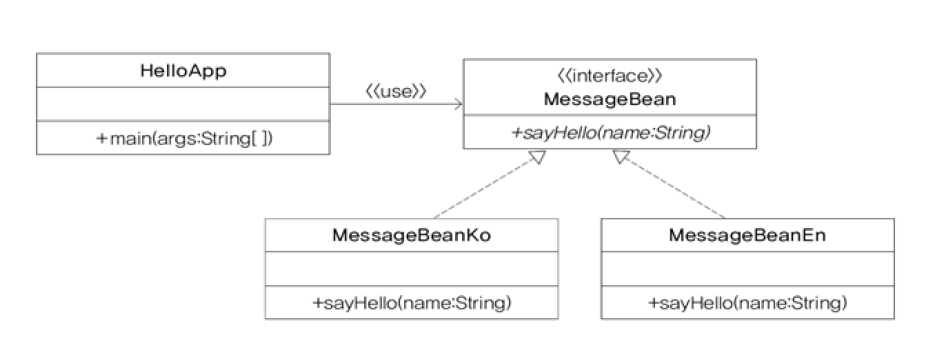
인터페이스를 사용하여 객체간 결합도를 낮춘 프로그램
-
HelloApp은 MessageBean 이라는 인터페이스를 통해서 객체를 사용한다
-
일반적으로 팩토리 메서드를 활용하여 사용할 객체 (MessageBeanKr or MessageBeanEn)를 생성한다. MessageBean이라는 MessageBeanKr가 생성되든 MessageBeanEn가 생성되든 HelloApp은 수정될 사항이 없다
 |  |
|---|
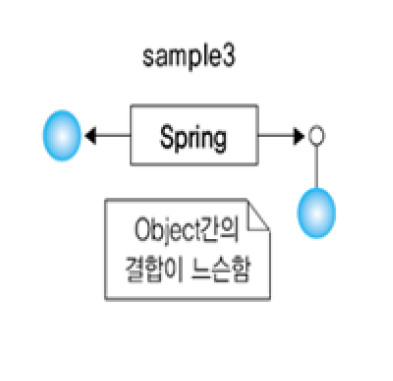
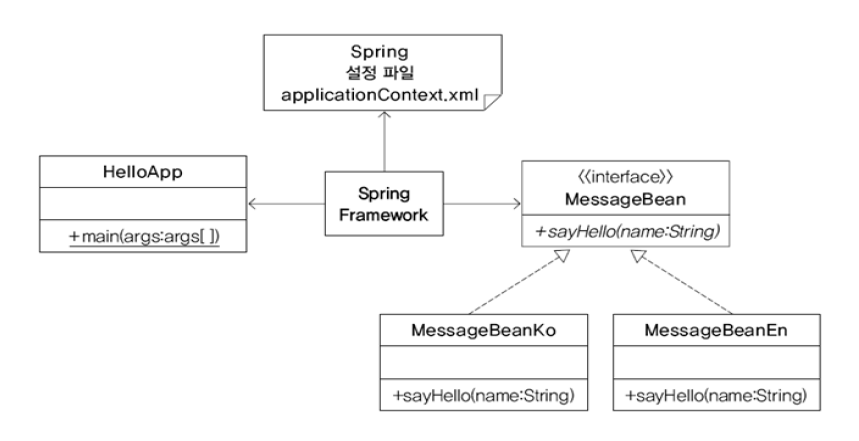
스프링을 사용한 객체간 결합도를 낮춘 프로그램
-
프로그램에서 필요한 객체를 스프링 컨테이너가 미리 생성하여 이 객체를 필요로 하는 프로그램에 생성자 또는 Setter 메서드를 통해서 주입한다
-
어떠한 객체를 생성하여 전달할 지는 디스크립터 파일(XML로 작성)을 사용한다
 |  |
|---|
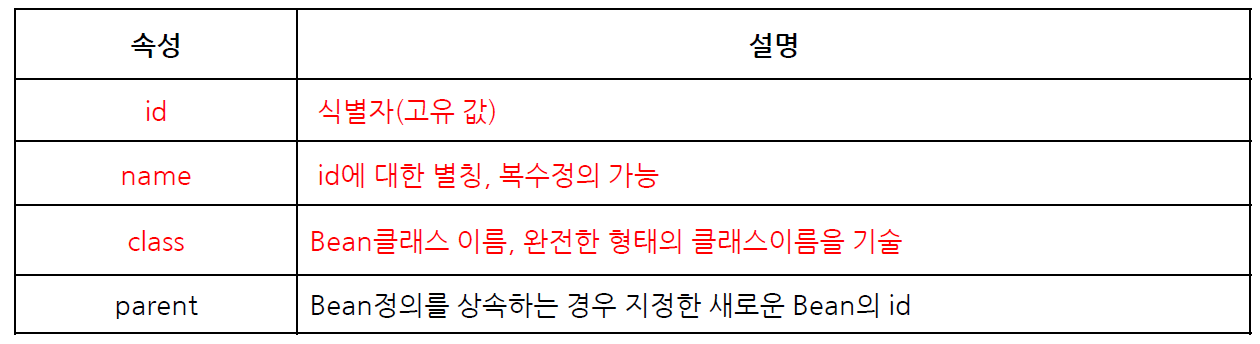
스프링 설정파일
bean 요소의 설정

의존 관계를 관리하기 위한 방법
-
Constructiuon Injection: 생성자를 통해서 의존관계를 연결시키는 것을 말함
-
Setter Injection: 클래스 사이의 의존관계를 연결시키기 위해서 setter 메소드를 이용하는 방법을 말함
ApplicationContext.xml

DI 실습
Sample1 : 객체간 결합도가 강한 프로그램
HelloSpring.java
//결합도가 높은 프로그램 연결되어있는 파일을 다 바꿔줘야한다
public class HelloSpring {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MessageBean bean=new MessageBean();
//bean.sayHello(" 스프링!!");
bean.sayHello(" Spring!!");
}
}MessageBean.java
public class MessageBean {
public void sayHello(String name) {
//System.out.println("헬로우 " + name);
System.out.println("Hello " + name);
}
}Sample2 : 인터페이스를 사용하여 객체간 결합도를 낮춘 프로그램
HelloSpring.java
//의존 관계를 약하게 설정하는 프로그램(결합도를 낮춤)
main만 바꿔주면 된다 의존도가 낮아짐
public class HelloSpring {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// MessageBean bean=new MessageBeanKr();
// bean.sayHello(" 스프링!!");
MessageBean bean=new MessageBeanEn();
bean.sayHello(" Spring!!");
}
}MessageBean.java
public interface MessageBean {
public void sayHello(String name);
}
MessageBeanEn.java
public class MessageBeanEn implements MessageBean{
@Override
public void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("Hello," + name);
}
}
MessageBeanKr.java
public class MessageBeanKr implements MessageBean{
@Override
public void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("헬로우," + name);
}
}Sample3 : 스프링을 사용한 객체간 결합도를 낮춘 프로그램
HelloSpring.java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
//Spring Framework 이용
public class HelloSpring {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("sample3/bean.xml");
MessageBean bean = (MessageBean)factory.getBean("messageBean2");
bean.sayHello(" Spring");
MessageBean bean2 = (MessageBean)factory.getBean("messageBean1");
bean2.sayHello(" 스프링");
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)factory).close();
}
}MessageBean.java
public interface MessageBean {
public void sayHello(String name);
}
MessageBeanEn.java
public class MessageBeanEn implements MessageBean{
@Override
public void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("Hello," + name);
}
}
MessageBeanKr.java
public class MessageBeanKr implements MessageBean{
@Override
public void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("헬로우," + name);
}
}bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id = "messageBean1" class = "sample3.MessageBeanKr"/>
<bean id = "messageBean2" class = "sample3.MessageBeanEn"/>
</beans>Sample4 : Spring Framework의 주입과 대입 출력
HelloSpring.java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class HelloSpring {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ApplicationContext factory=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("sample4/bean1.xml");
ApplicationContext factory=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("sample4/bean2.xml");
System.out.println("** container 초기화 작업 **");
MessageBean bean=(MessageBean)factory.getBean("messageBean");
bean.sayHello(); // 주입(DI)
bean.sayHello("banana", 1500); // 대입
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)factory).close();
}
}MessageBean.java (Interface)
public interface MessageBean {
public void sayHello();
public void sayHello(String a, int b);
}
MessageBeanImpl.java
public class MessageBeanImpl implements MessageBean {
private String fruit;
private int cost;
public MessageBeanImpl(String fruit) {
this.fruit = fruit;
System.out.println(fruit+" MessageBeanImpl 생성자");
}
public void setCost(int cost) {
this.cost = cost;
System.out.println("setCost 호출");
}
@Override
public void sayHello() { // XML를 통한 주입 (Melon 출력)
System.out.println(fruit+"\t"+cost);
}
@Override
public void sayHello(String a, int b) { // 메서드에 의한 대입 (Banana 출력)
System.out.println(a+"\t"+b);
}
}
bean1.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id = "messageBean" class = "sample4.MessageBeanImpl">
<constructor-arg>
<value>melon</value>
</constructor-arg>
<property name="cost">
<value>1000</value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
<!-- 위 코드와 동일
MessageBeanImpl messageBean = new MessageBeanImpl("melon");
messageBean.setCist(1000);
-->bean2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="messageBean" class="sample4.MessageBeanImpl" c:fruit="orange" p:cost="2500" />
</beans>Sample5 : 실습 예제 (Is-A)관계
EmpMain.java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class EmpMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext factory=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("sample6/bean2.xml");
Developer bean=(Developer)factory.getBean("developer");
System.out.println(bean.toString());
Engineer bean2=(Engineer)factory.getBean("engineer");
System.out.println(bean2.toString());
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)factory).close();
}
}Emp.java
public class Emp {
private String name;
private int salary;
public Emp() {
}
public Emp(String name, int salary) {
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "이름 : " + name + " 급여 :" + salary+"원 ";
}
}
Developer.java
public class Developer extends Emp{
private String dept;
public Developer(){}
public Developer(String name, int salary) {
super(name,salary);
}
public void setDept(String dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString()+" 부서 : " + dept;
}
}
Engineer.java
public class Engineer extends Emp{
private String dept;
public Engineer(){}
public Engineer(String name, int salary) {
super(name,salary);
}
public void setDept(String dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString()+ " 부서 : " + dept;
}
}
beans1.java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id = "developer" class = "sample6.Developer">
<constructor-arg value= "강호동" />
<constructor-arg value= "1500000"/>
<property name="dept">
<value>개발1팀(개발부)</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id = "engineer" class = "sample6.Engineer">
<constructor-arg value= "이순신" />
<constructor-arg value= "2500000"/>
<property name="dept">
<value>기술1팀(기술부)</value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>beans2.java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id = "developer" class = "sample6.Developer" c:name="강호동" c:salary="1500000"
p:dept="개발1팀(개발부)" />
<bean id = "engineer" class = "sample6.Engineer" c:name="이순신" c:salary="2500000"
p:dept="기술1팀(기술부)" />
</beans>Sample6 실습 예제 (Has-A)관계
EmpMain.java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class EmpMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext factory=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("sample7/bean1.xml");
Developer bean=(Developer)factory.getBean("developer");
System.out.println(bean.toString());
Engineer bean2=(Engineer)factory.getBean("engineer");
System.out.println(bean2.toString());
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)factory).close();
}
}Emp.java
public class Emp {
private String name;
private int salary;
public Emp() {
}
public Emp(String name, int salary) {
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "이름 : " + name + " 급여 :" + salary+"원 ";
}
}
Developer.java
public class Developer{
private String dept;
private Emp emp;
public Developer(){}
public Developer(Emp emp, String dept) {
this.emp = emp;
this.dept = dept;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return emp.toString()+" 부서 : " + dept;
}
}
Engineer.java
public class Engineer{
private String dept;
private Emp emp = null;
public Engineer(){}
public Engineer(Emp emp, String dept) {
this.emp = emp;
this.dept = dept;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return emp.toString()+ " 부서 : " + dept;
}
}
beans1.java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="developer" class="sample7.Developer">
<constructor-arg value="Demp" />
<constructor-arg value="개발1팀(개발부)" />
</bean>
<bean id="Demp" class="sample7.Emp">
<constructor-arg value="강호동" />
<constructor-arg value="1500000" />
</bean>
<bean id="engineer" class="sample7.Engineer">
<constructor-arg value="Eemp" />
<constructor-arg value="기술1팀(기술부)" />
</bean>
<bean id="Eemp" class="sample7.Emp">
<constructor-arg value="이순신" />
<constructor-arg value="2500000" />
</bean>
</beans>beans2.java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id = "developer" class = "sample7.Developer" c:emp-ref="Demp"
c:dept="개발1팀(개발부)" />
<bean id = "engineer" class = "sample7.Engineer" c:emp-ref="Eemp"
c:dept="기술1팀(기술부)" />
<bean id="Demp" class="sample7.Emp" c:name="강호동" c:salary="1500000"/>
<bean id="Eemp" class="sample7.Emp" c:name="이순신" c:salary="2500000"/>
</beans>DI - Annotation
스프링 Bean 의존 관계 설정 - annotation
- Annotation: 멤버변수에 직접 정의하는 경우 Setter method를 만들지 않아도 됨
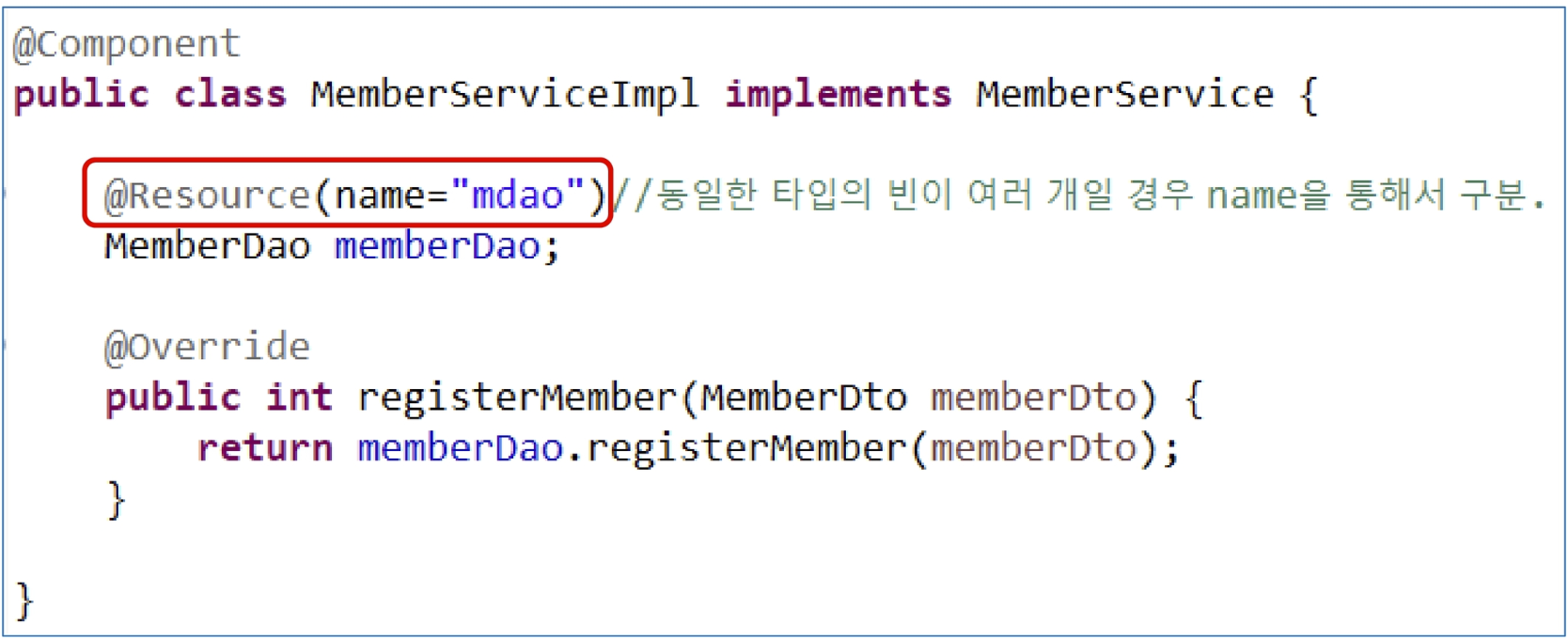
멤버변수에 @Resource
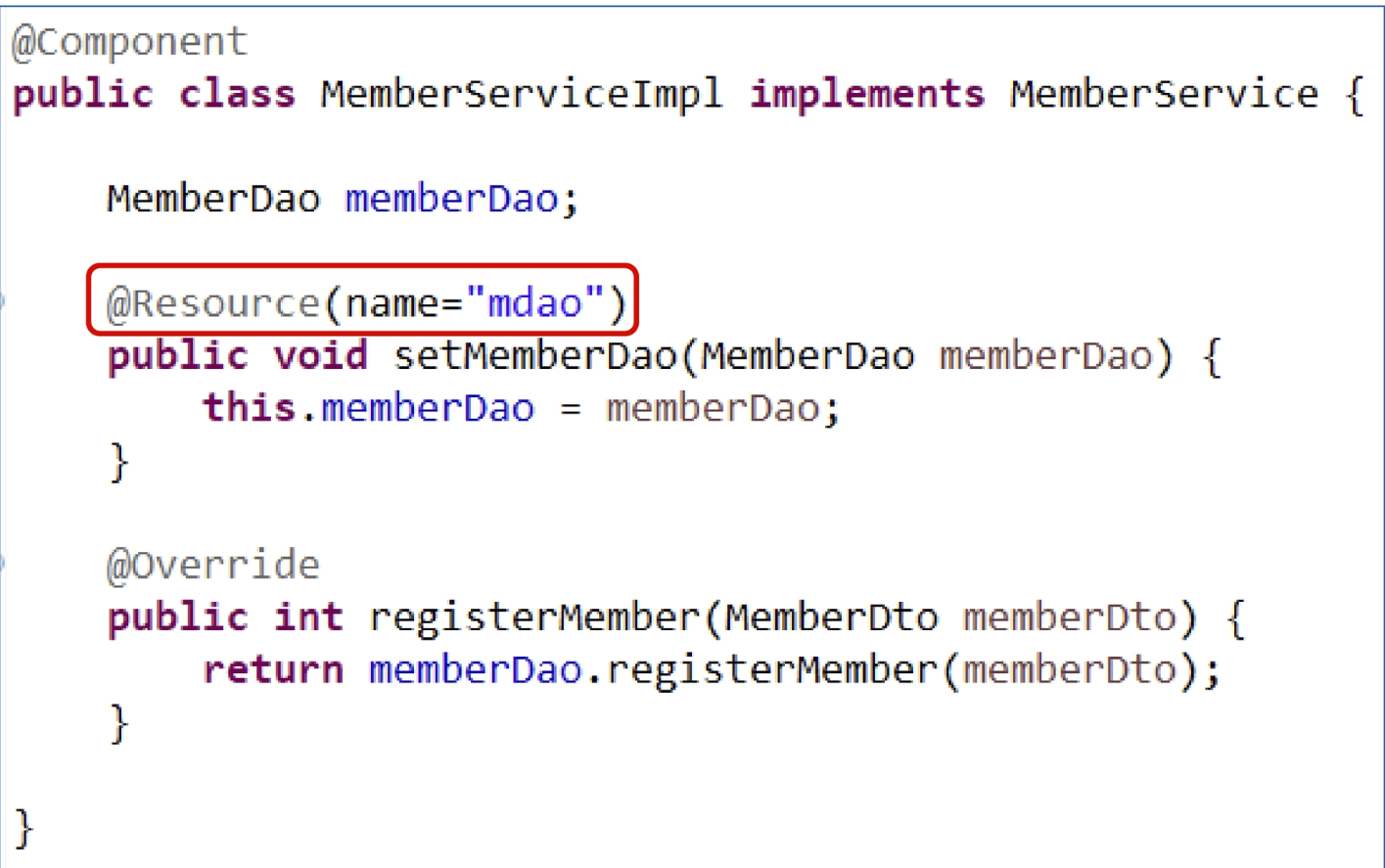
setter method에 @Resource
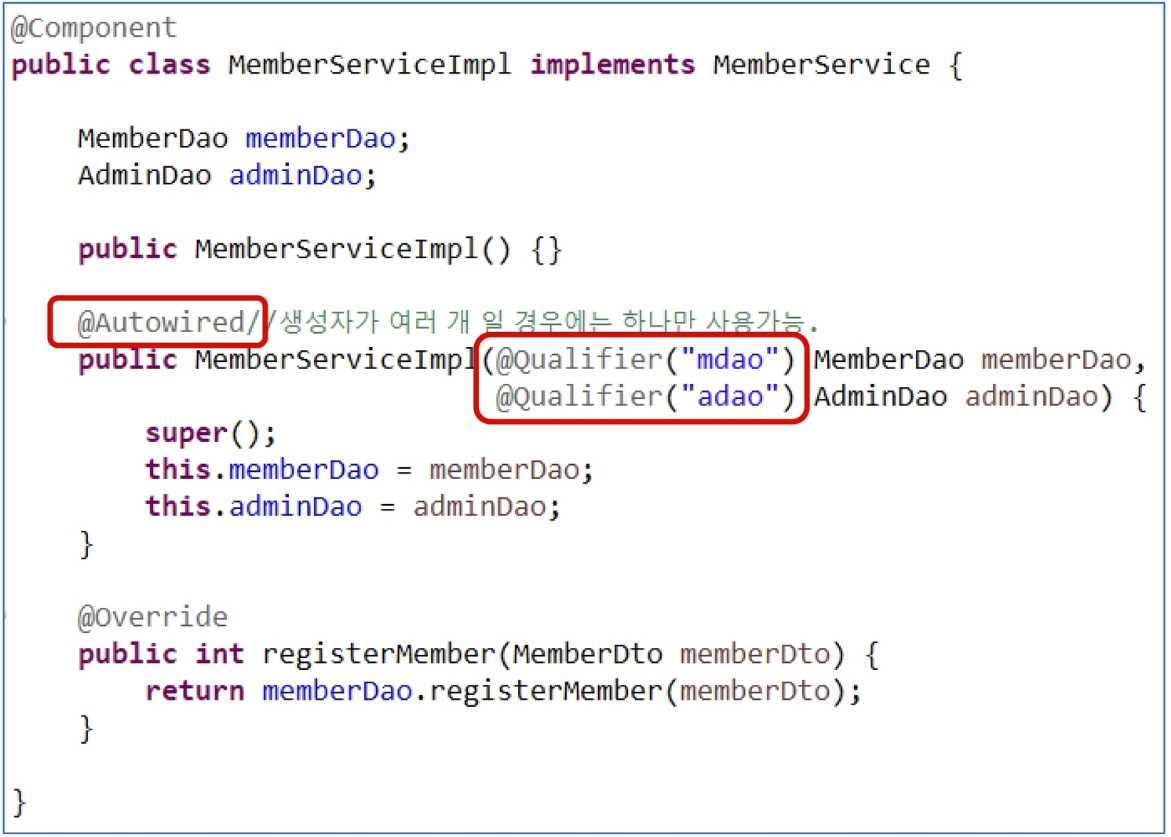
생성자에 @Autowired
- 동일한 타입의 bean이 여러 개일 경우에는 @Qualifier("name")으로 식별한다
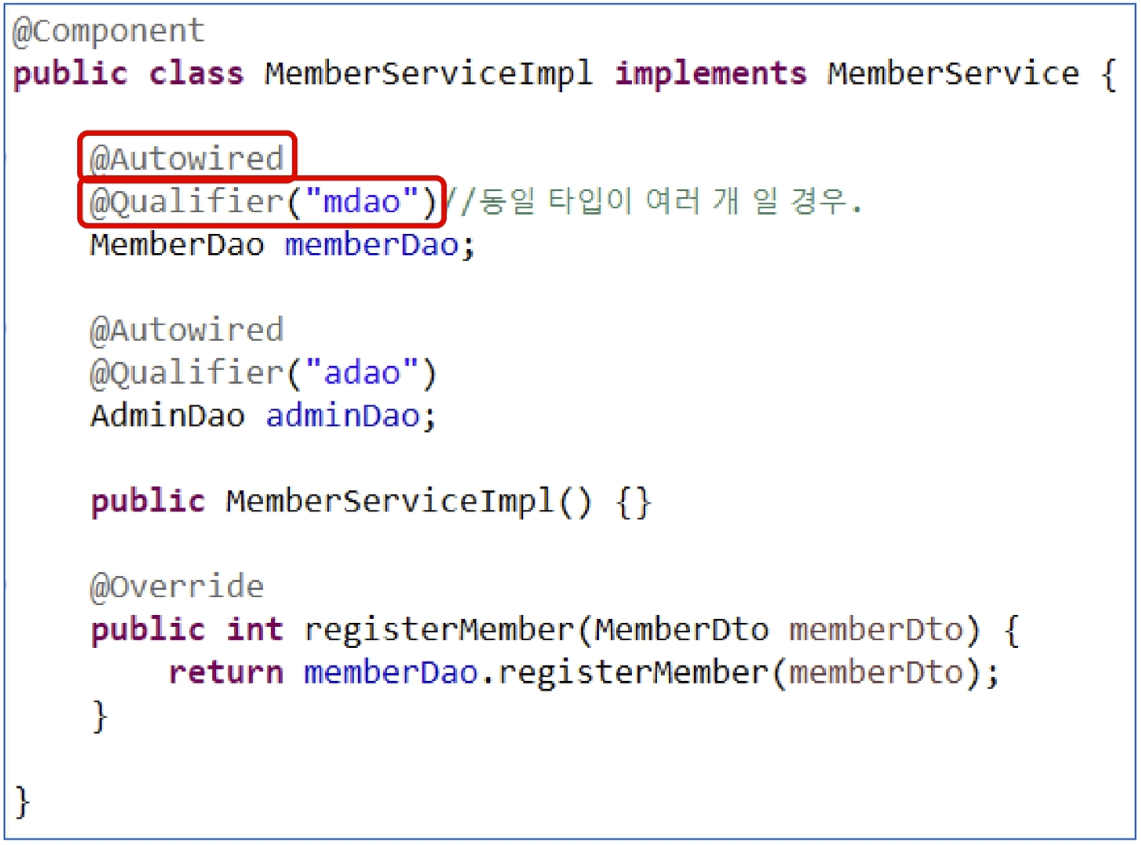
필드에 @Autowired
- 동일한 타입의 bean이 여러 개일 경우에는 @Qualifier("name")으로 식별한다
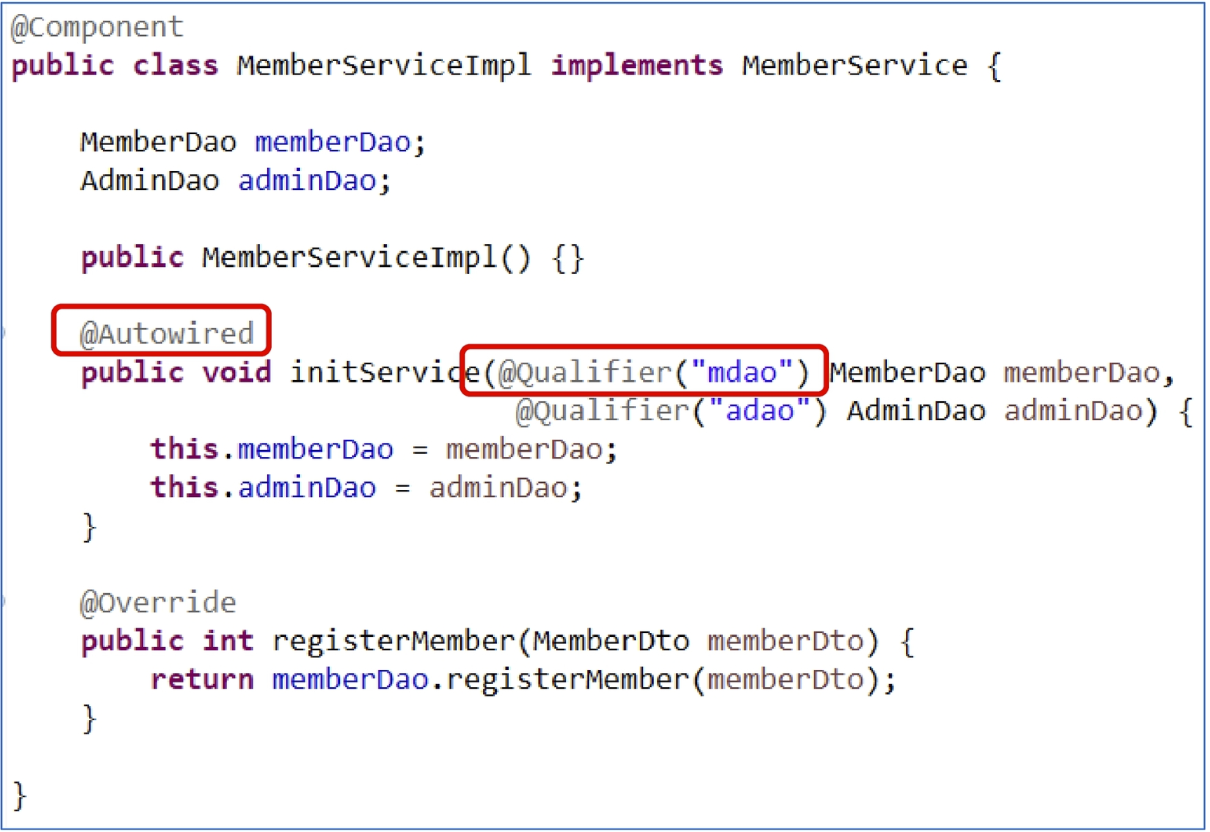
일반 메서드에 @Autowired
- 동일한 타입의 bean이 여러 개일 경우에는 @Qualifier("name")으로 식별한다
스프링 annotation 실습
1. Component, Autowired , Qualifier 이용
FoodTest,java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class FoodTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext factory=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("anno02/bean.xml");
// MyFoodMgr ob=(MyFoodMgr)factory.getBean("myFood");
//@Component로 자동생성된 클래스 명 or 정해준 이름으로 적어줘야한다
MyFoodMgr ob=factory.getBean("myFood", MyFoodMgr.class);
System.out.println(ob);
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)factory).close();
}
}
///MyFoodMgr [좋아하는 음식=Food [foodName=스파게티, foodPrice=7500], 싫어하는 음식=Food [foodName=보신탕, foodPrice=12000]]
Food.java
public class Food {
private String foodName;
private int foodPrice;
public void setFoodName(String foodName) {
this.foodName = foodName;
}
public void setFoodPrice(int foodPrice) {
this.foodPrice = foodPrice;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Food [foodName=" + foodName + ", foodPrice=" + foodPrice + "]";
}
}
FoodMgr.java
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component(value = "myFood")
public class MyFoodMgr {
@Autowired
//unfavoriteFood 객체가 favoritefood 객체로
@Qualifier(value="unfavoriteFood") //-> Auto wire로 바꾼 객체를 다른 객체로 바꿀 수 있다
//@Resource(name = "unfavoriteFood")
private Food favoriteFood;
@Autowired
private Food unfavoriteFood;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyFoodMgr [좋아하는 음식=" + favoriteFood + ", 싫어하는음식=" + unfavoriteFood + "]";
}
}
출력: 좋아하는 음식 "추어탕" "12000" 싫어하는음식 "추어탕" "12000"
// 기본값: myFoodMgr로 객체 생성 (첫번째 문자만 소문자로 변환되어 객체를 만듦)
//-> (value= "myFood")로 주면 myFood로 생성됨
@Component(value= "myFood")
public class MyFoodMgr {
@Autowired
//<bean id="myFood" class="anno02.MyFoodMgr" p:favoriteFood-ref="favoriteFood">
private Food favoriteFood;
@Autowired
//<bean id="myFood" class="anno02.MyFoodMgr" p:unfavoriteFood-ref="unfavoriteFood">
private Food unfavoriteFood; // @Autowired는 setter를 생략할수 있다
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyFoodMgr [좋아하는 음식=" + favoriteFood + ", 싫어하는음식=" + unfavoriteFood + "]";
}
}
출력: 좋아하는 음식 "냉면" "6000" 싫어하는음식 "추어탕" "12000"
bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<!-- anno02라는 패키지를 스캔하면서 @Component를 만나면 객체를 생성해준다 -->
<context:component-scan base-package = "anno02"/>
<!-- <bean id="myFood" class="anno02.MyFoodMgr"
p:favoriteFood-ref="favoriteFood" p:unfavoriteFood-ref="unfavoriteFood"/> -->
<bean id="favoriteFood" class="anno02.Food" p:foodName="냉면" p:foodPrice="6000"/>
<bean id="unfavoriteFood" class="anno02.Food" p:foodName="추어탕" p:foodPrice="12000"/>
</beans>
<!--
<context:component-scan base-package="anno02"/>
: 특정 패키지 안의 클래스들을 스캔하고 빈 인스턴스를 생성한다.
@Component/@Controller/@Service/@Repository를 사용하려면 이 태그를 넣어줘야 한다.
객체를 지정해주지 않아도 알아서 생성해준다.
base-package는 어느 범위에있는 객체를 생성해 줄것인지를 선언한다
선언된 패키지 내에 있는 객체들을 다 생성해준다.
또한 패키지내의 클래스 위에 @Component/@Controller/@Service/@Repository어노테이션을 써주어야야 한다.
@Component
|
|______________|________________|
| | |
@Controller @Service @Repository
(presentation) (Service) (Persistence/DAO)
<context:annotation-config/>
: 어플리케이션 컨텍스트안에 이미 등록된 빈들의 어노테이션을 활성화를 위해 사용한다.
@Required, @Autowired, @Configuration, @Resource 등
<context:component-scan> 를 선언했다면 <context:annotation-config>를 선언할필요가 없다
-->2. Annotation & 객체 reference로 넘겨주기
EmpTest.java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class EmpTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext factory =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("anno03/bean.xml");
Engineer ob=factory.getBean(Engineer.class);
System.out.println(ob.toString());
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)factory).close();
}
}
//홍길동은 25세이고 입사점수는 75.4입니다
//개발부에 근무합니다
Emp.java
public class Emp {
private String name;
private int age;
private double score;
public Emp() {
super();
}
public Emp(String name, int age, double score) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name+"은 " +age+"세 이고 입사점수는 " + score +"점 입니다";
}
}
Engineer.java
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Engineer {
@Autowired // Autowired는 type을 따라 간다 (class의)
//얘를 명시해주지 않으면 emp1인지 emp2인지 알 수 없음
//같은 타입일 때 id이름을 명시하지 않으면 ambiguous Error 발생
@Qualifier(value = "emp1")
//or @Resource(name = "emp1")
private Emp emp;
@Autowired
//얘가 없어도 상관x String은 xml에서 하나만 정의 되어있음
@Qualifier(value = "dev_dept")
private String Dept;
// Autowired로 연결 돼서 setter가 필요가 없다
// public void setDept(String dept) {
// this.Dept = dept;
// }
//
// public void setEmp(Emp emp) {
// this.emp = emp;
// }
@Override
public String toString() {
return emp.toString() ;
}
}Bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<!-- <bean id = "engineer" class = "anno03.Engineer" p:dept="개발부" p:emp-ref="emp"/> -->
<context:component-scan base-package="anno03"></context:component-scan>
<bean id = "dev_dept" class = "java.lang.String" c:value="개발부"/>
<bean id = "emp1" class= "anno03.Emp" p:name="홍길동" p:age="25" p:score="75.4"/>
<bean id = "emp2" class= "anno03.Emp" p:name="이순신" p:age="27" p:score="80.5"/>
</beans>
<!--
Engineer engineer = new Engineer();
engineer.setDept("개발부");
-->
<!-- @Autowired :스프링 전용
1)의존관계를 자동으로 설정해주는 어노테이션:
Autowired 어노테이션이 붙은 인스턴스 변수는 해당 변수 타입과 일치하는 컨텍스트 내의
빈을 찾아 인스턴스 변수에 주입해 준다
2)타입을 이용하여 의존객체를 자동으로 설정한다(byType to byName)
3)생성자, 필드(변수), 메서드 세곳에 적용가능하다
의존성 주입을 위해선 생성자나 setter가 필요한데 이 어노테이션을 사용할 경우 없어도 가능하다.
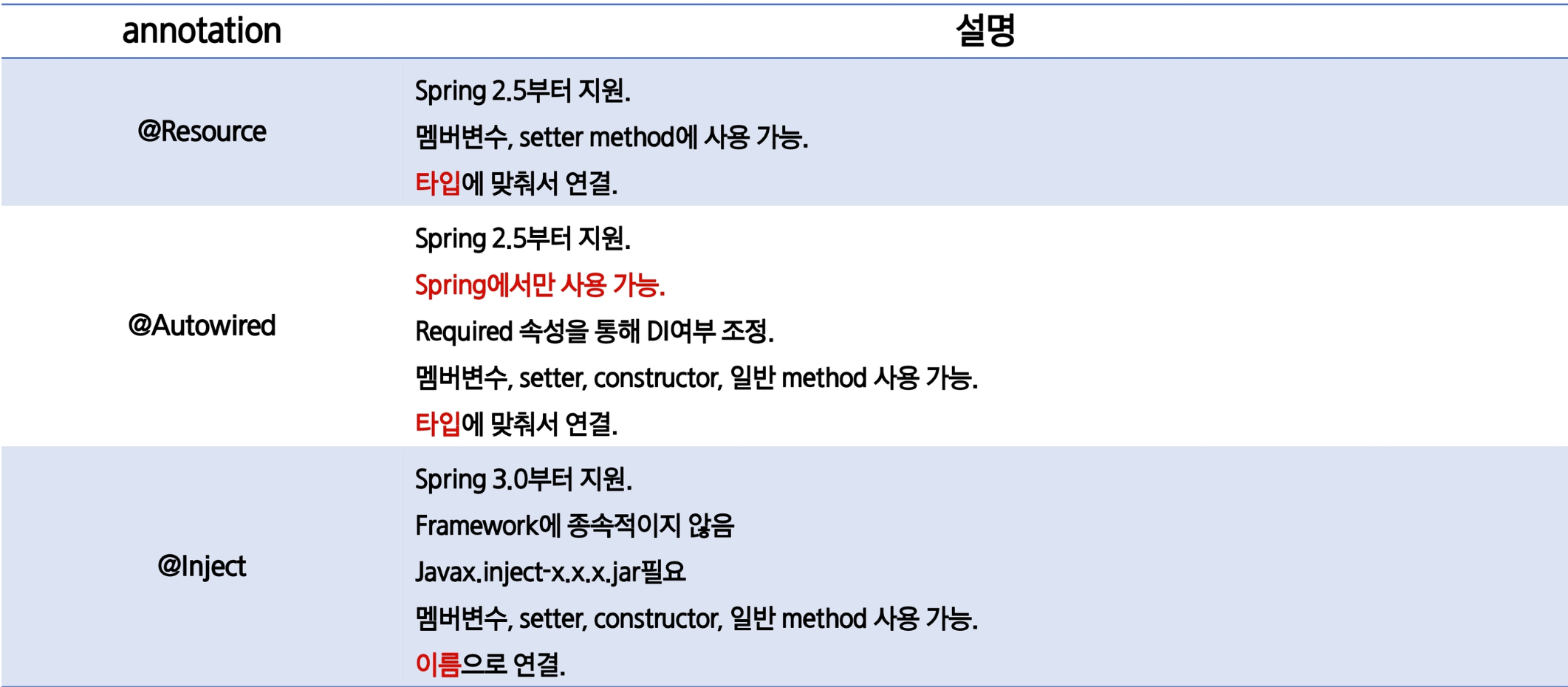
@Resource : 자바에서 지원 ,이름으로 연결(byName to byType)
@Qualifier : 빈 객체중 특정빈을 사용하도록 선언
ex)@Autowired는 메서드 앞에서 사용가능하다,
다만 인젝션 가능한 형이 2개 이상이면 오류가 발생한다
이때 @Qualifier를 사용한다
@Inject : 자바에서 지원 ,타입에 맞춰서 연결한다 -->기타 설정
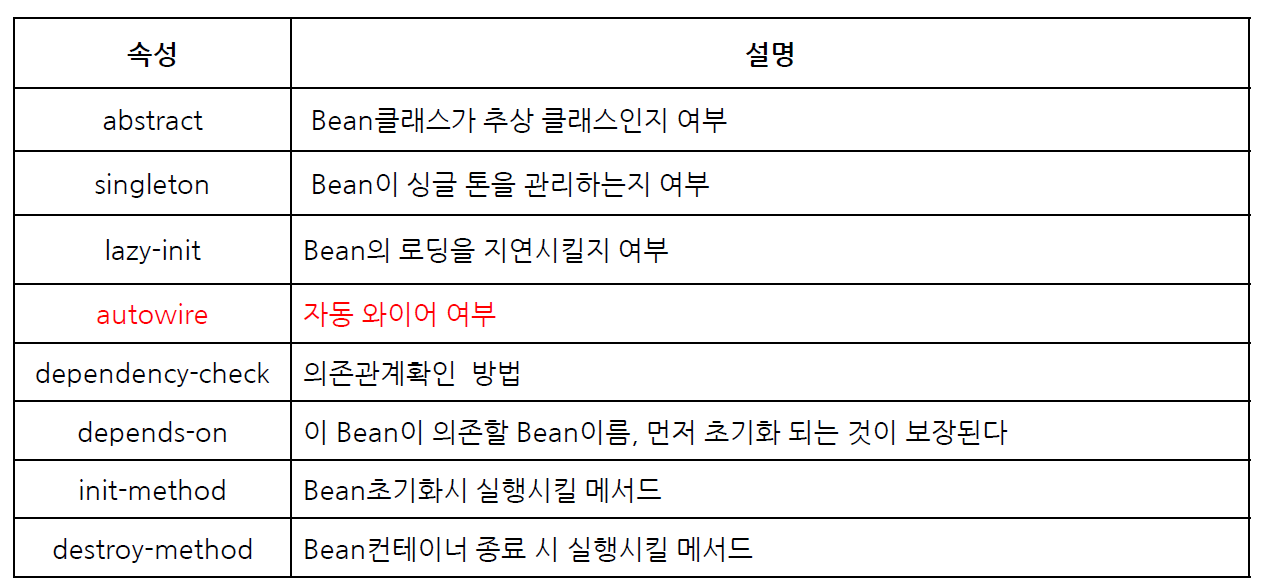
- 빈 객체의 생성 단위
- BeanFactory를 통해 Bean을 요청 시 객체생성 범위를 설정
- <bean> 의 scope 속성을 이용해 설정
- scope의 값

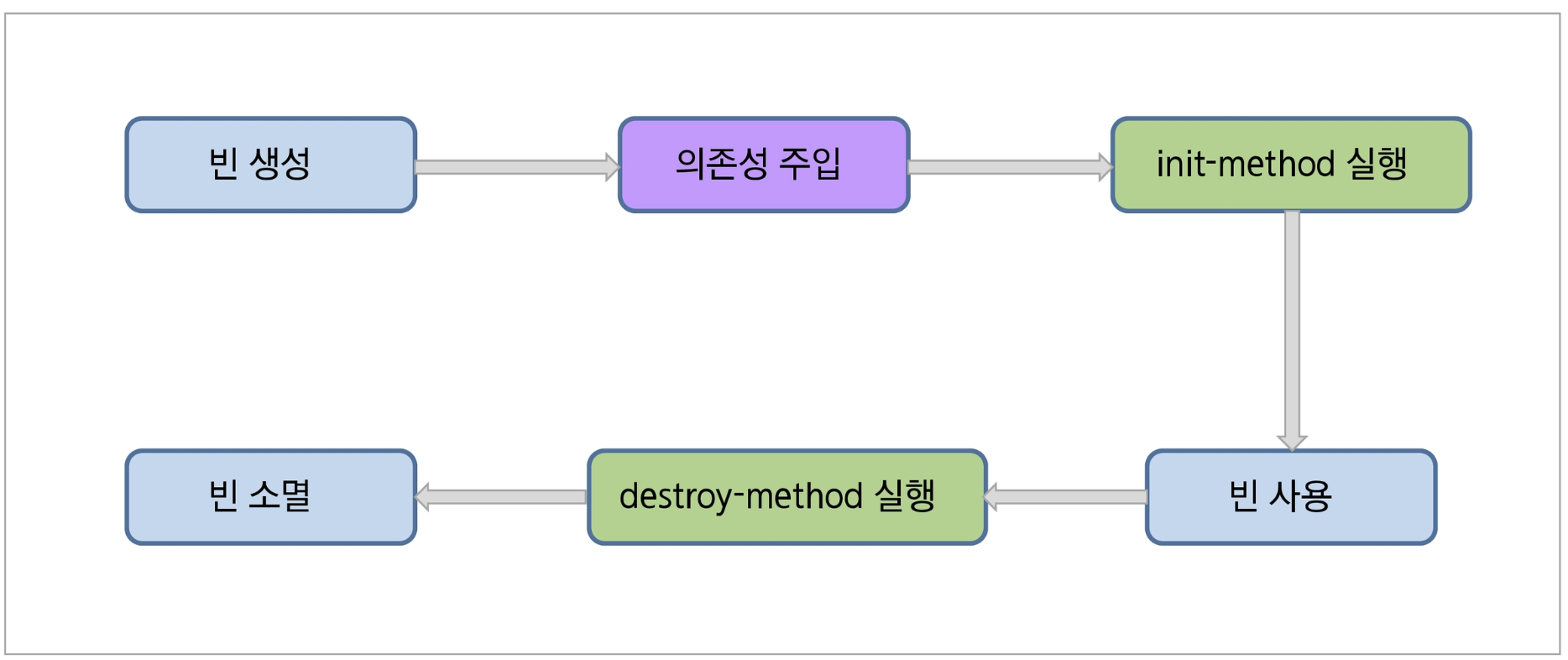
스프링 빈의 생명주기(Life Cycle)