문제 설명

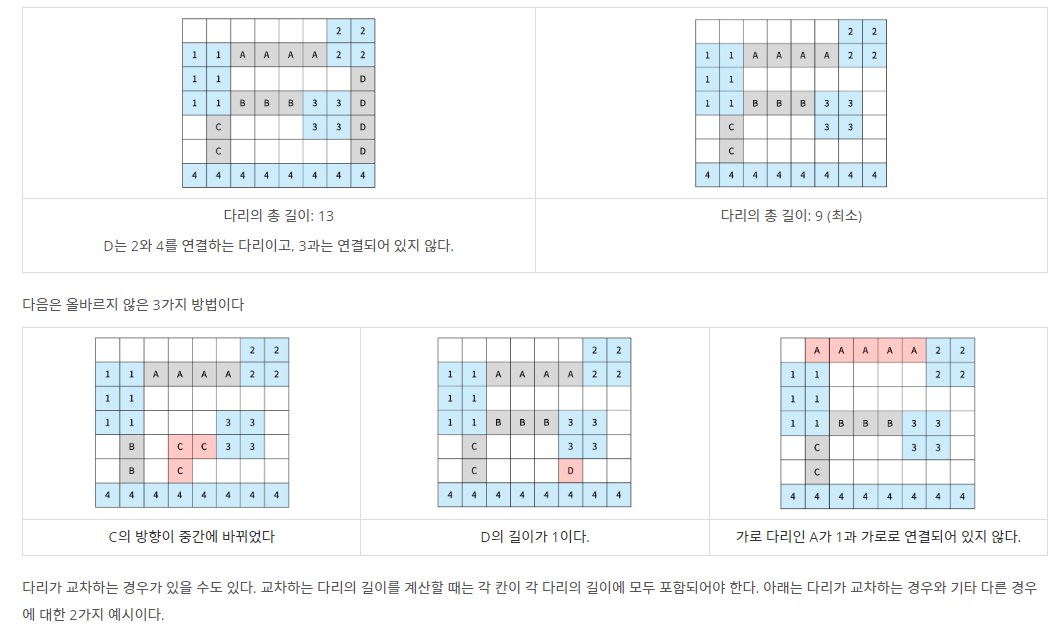

전략
-
가장 먼저 각각의 구역을 BFS로 탐색하면서 대륙별로 마킹해준다
-
각 대륙으로 부터 다른 대륙까지의 최단 거리를 구한다
-
만약 거리가 안 닿이거나 2보다 짧은 경우 INF로 초기화 한다.
-
위 과정을 거치면 각 대륙간의 거리 인접리스트가 나오게 된다
-
인접리스트를 바탕으로 크루스칼 알고리즘을 적용하면 최소 신장 트리가 나오게 되고 그 그래프가 가장 짧은 다리의 길이이다
정답 코드
package algorithms;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int start;
int end;
int cost;
public Node(int start, int end, int cost) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return this.cost - o.cost;
}
}
public class MakeBridge2 {
static int N;
static int M;
static int[][] map;
static boolean[][] visited;
static int[] dx = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
static int[] dy = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
static int[][] adjacent;
static int INF = 100000000;
static int[] parent;
static ArrayList<Node> nodeList;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
map = new int[N][M];
// bfs 돌릴 방문배열
visited = new boolean[N][M];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
int cnt = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (!visited[i][j] && map[i][j] != 0) {
bfs(i, j, cnt);
cnt++;
}
}
}
// 인접 리스트 초기화
adjacent = new int[cnt][cnt];
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cnt; j++) {
if (i == j)
adjacent[i][j] = 0;
else
adjacent[i][j] = INF;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
if (map[i][j] != 0) {
dfs(i, j, 0, map[i][j], d);
}
}
}
}
// 각자 부모노드 초기화
parent = new int[cnt];
for (int i = 1; i < cnt; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
nodeList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i < cnt; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
Node nd = new Node(i, j, adjacent[i][j]);
nodeList.add(nd);
}
}
Collections.sort(nodeList);
//크루스칼 알고리즘
int totalWeight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.size(); i++) {
if (find(nodeList.get(i).start) != find(nodeList.get(i).end)) {
totalWeight += nodeList.get(i).cost;
union(nodeList.get(i).start, nodeList.get(i).end);
}
}
if(totalWeight>=INF)System.out.println(-1);
else System.out.println(totalWeight);
}
// 섬의 영역을 나눈다
public static void bfs(int x, int y, int cnt) {
visited[x][y] = true;
map[x][y] = cnt;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= M || visited[nx][ny] || map[nx][ny] == 0)continue;
bfs(nx, ny, cnt);
}
}
// 섬 사이 거리를 구해준다
public static void dfs(int x, int y, int depth, int from, int dir) {
if (map[x][y] != 0 && map[x][y] != from) {
if (depth - 1 >= 2) {
adjacent[from][map[x][y]] = Math.min(adjacent[from][map[x][y]], depth - 1);
adjacent[map[x][y]][from] = Math.min(adjacent[map[x][y]][from], depth - 1);
}
return;
}
int nx = x + dx[dir];
int ny = y + dy[dir];
// 범위를 벗어나거나 방문 한 곳을 다시 방문하거나, 자기 자신을 만나는 경우
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= M || map[nx][ny] == from)
return;
dfs(nx, ny, depth + 1, from, dir);
return;
}
// a,b의 대소관계에 따라서 부모노드를 바꿔준다
public static void union(int a, int b) {
// 최상위 부모 찾기
int x = find(a);
int y = find(b);
if (x < y) {
parent[y] = x;
} else {
parent[x] = y;
}
}
// a의 부모노드를 찾는 연산
public static int find(int a) {
if (parent[a] == a)
return a;
return parent[a] = find(parent[a]);
}
}
