HW1을 위한 전체 정리
Week 1-2. Fundamentals on Graph
1. Network & Applications
Graph Example: Social Networks, Social Circle Detection, Content Propagation, Blogger Connections, Information Cascades 폭포, Multi-layered Graph
Application: Recommendation, Interest Graph, Polarization, Virality
Do: Node classification, Link prediction, Community detection, Network similarity, graph-based algorithms
2. Graph Basic & Modeling
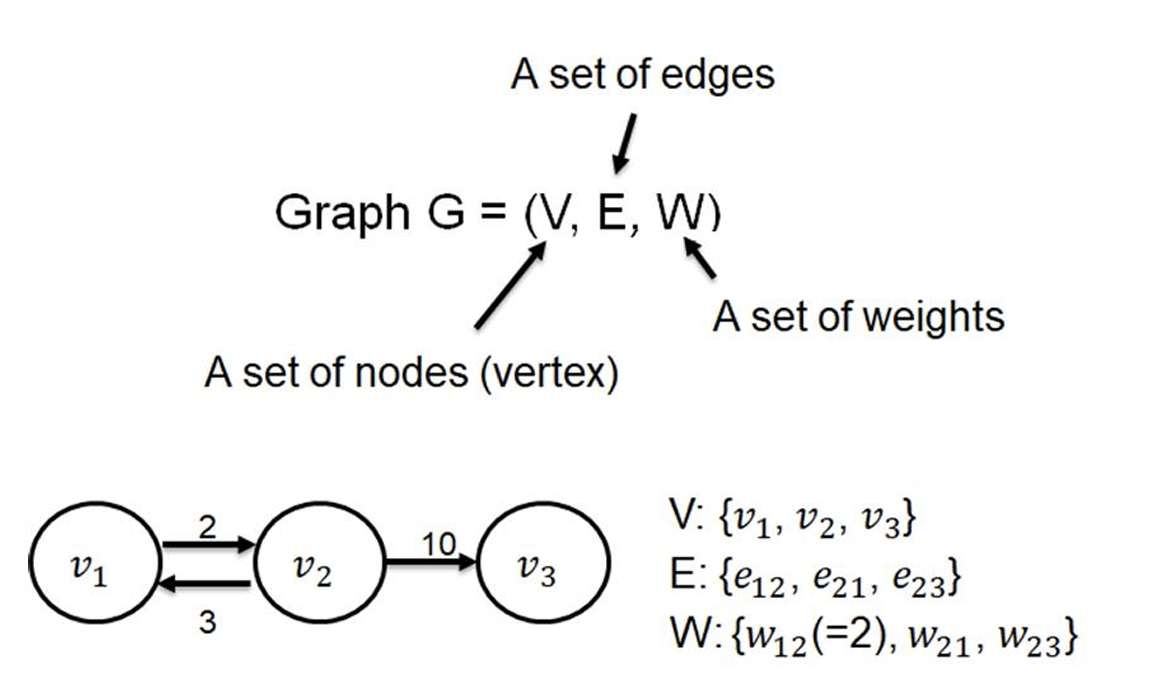
Components of a network
• Objects: nodes, vertices
• Interactions: links, edges
• System: network, graph
Graph Types
Undirected Graph: a - b
Directed Graph: a -> b
Unweighted Graph: a 1-> b
- Complete Graph: undirected graph with the number of edges E = Emax(N(N-1)/2)
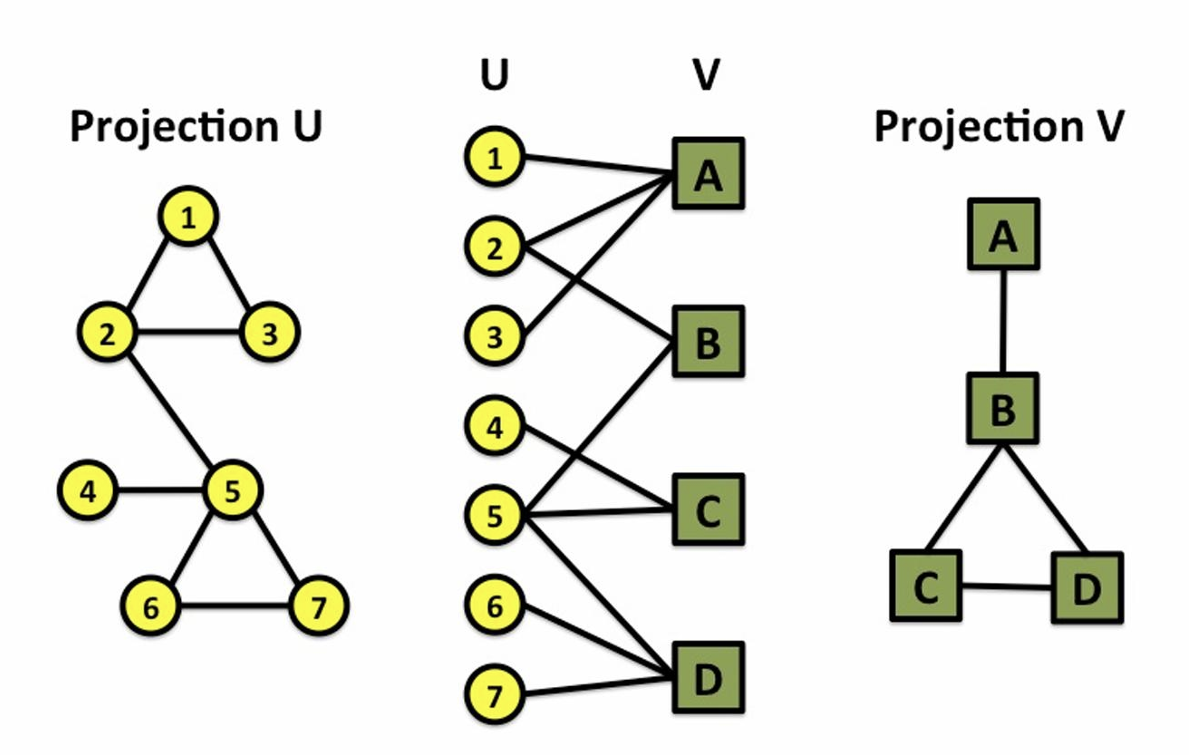
- Bipartite Graph: two disjoint sets U - V 다 서로 연결됨
- Folded/Projected Bipartite Graph: Author collaboration networks, Movie co-rating networks
- Tree: All nodes are connected, No cycles
Representing Graphs
- Adjacency Matrix
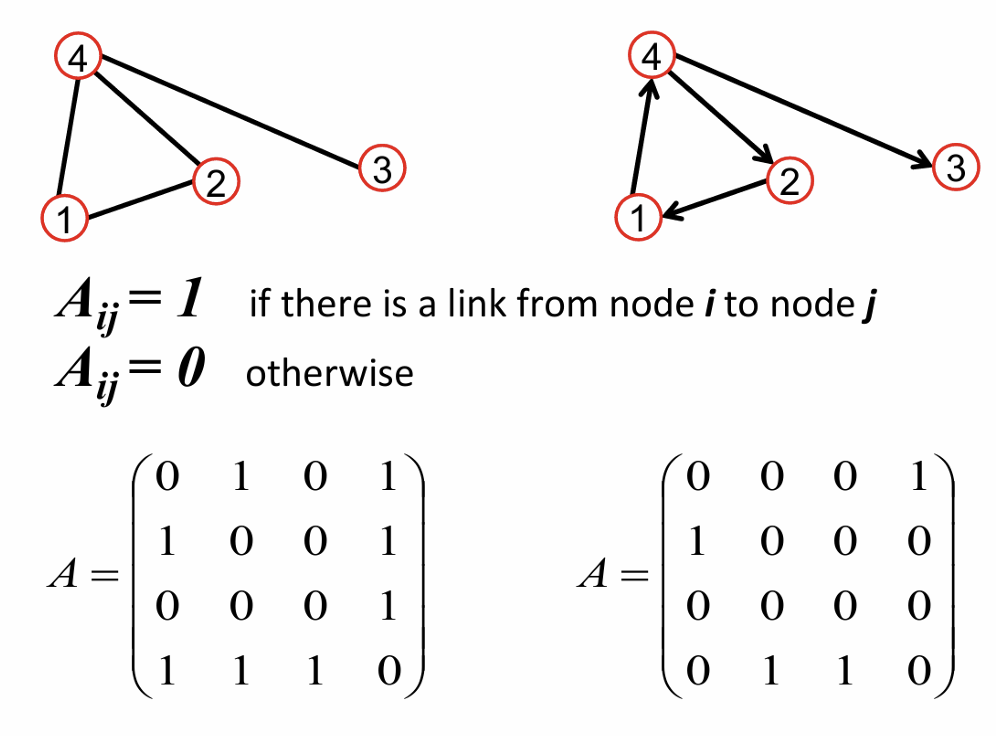
- Unweighted, Weighted, Self-edges, Multigraph
real-world networks are sparse
- Alternatives: Edge List: set of edges
- Adjacency List: all neighbors of node
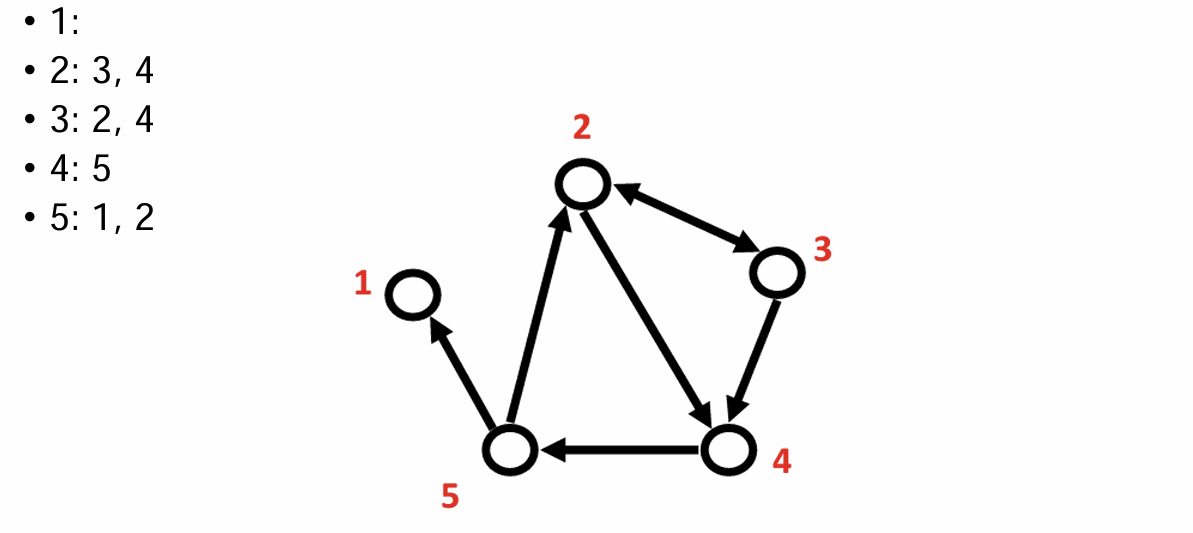
Modeling a Network with Graph
target object - node
relation, want to represent - edges
Week 2-1. Graph Properties
1. Network Properties
coarse-grained characteristics: 거친 입자 특성
Network Properties: Degree Distribution
P(k): Probability that a randomly chosen node has degree k
= # nodes with degree k
Paths in a Graph
A path is a sequence of nodes in which each node is linked
to the next one
Network Properties: Distance(Shortest Path Length)
The number of edges along the shortest path connecting the nodes
• If the two nodes are not connected, the distance is usually defined as infinite (or zero)
Network Properties: Diameter & APL
• Diameter: The maximum (shortest path) distance between any pair of nodes in a graph
• Average path length (for a connected graph or a strongly connected directed graph)
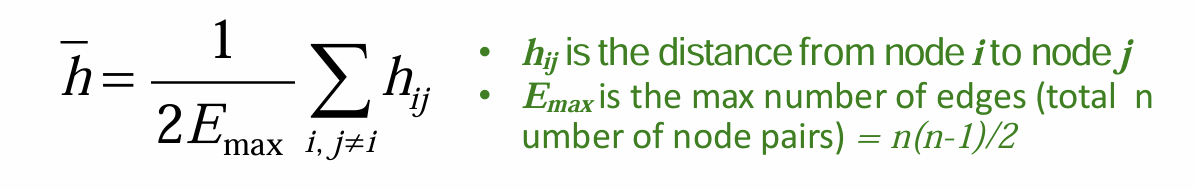
+isolated nodes are not considered
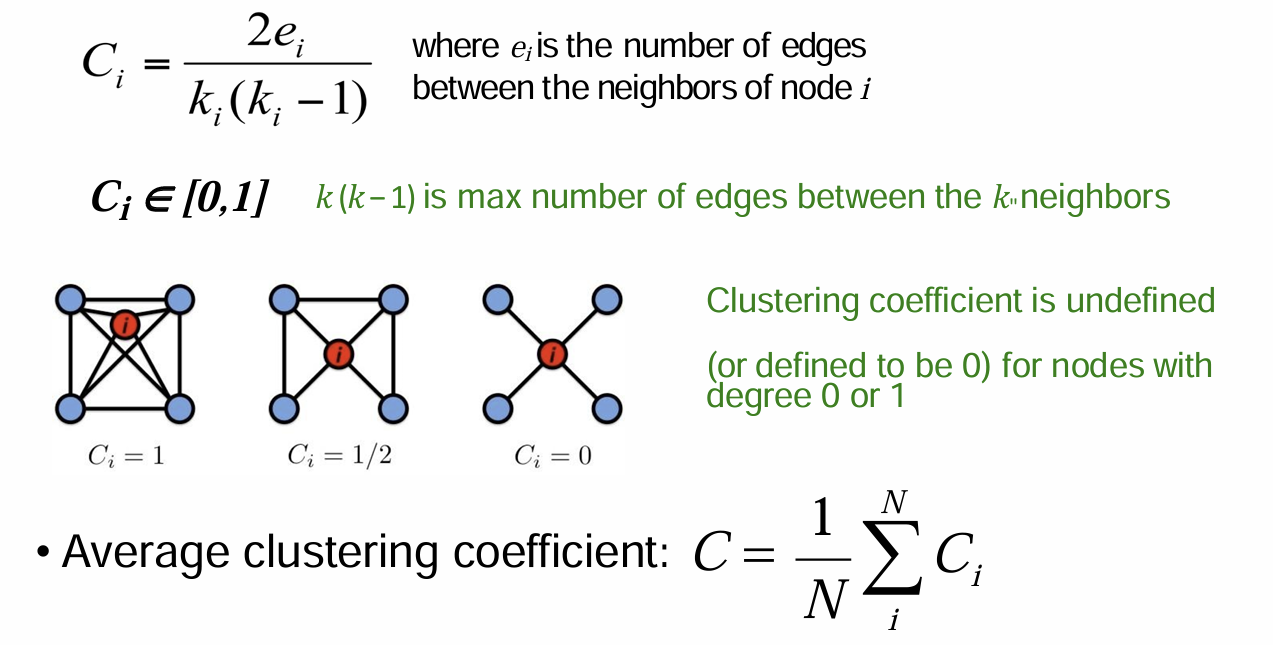
Network Properties: Clustering Coefficient
for undirected graphs
• How connected are ’s neighbors to each other? 이웃끼리 얼마나 연결돼있는지, 이웃들이 연결돼있을수록 1에 가까움, 연결 없으면 0
• Node i with degree
Network Properties: Connectivity
Size of the largest connected component
• Largest set where any two vertices can be joined by a path
Finding connected components: BFS, find unvisited node and BFS
2. Network Properties in Real-world Networks
Example: MSN Messenger
p13 week2
Week 2-2. Random Graph Generation & Small World
1. Generating Random Graph(Erdos-Renyi)
Random Graph Model
: undirected graph on n nodes where each edge (u, v)
appears i.i.d. with probability p
- Degree Distribution
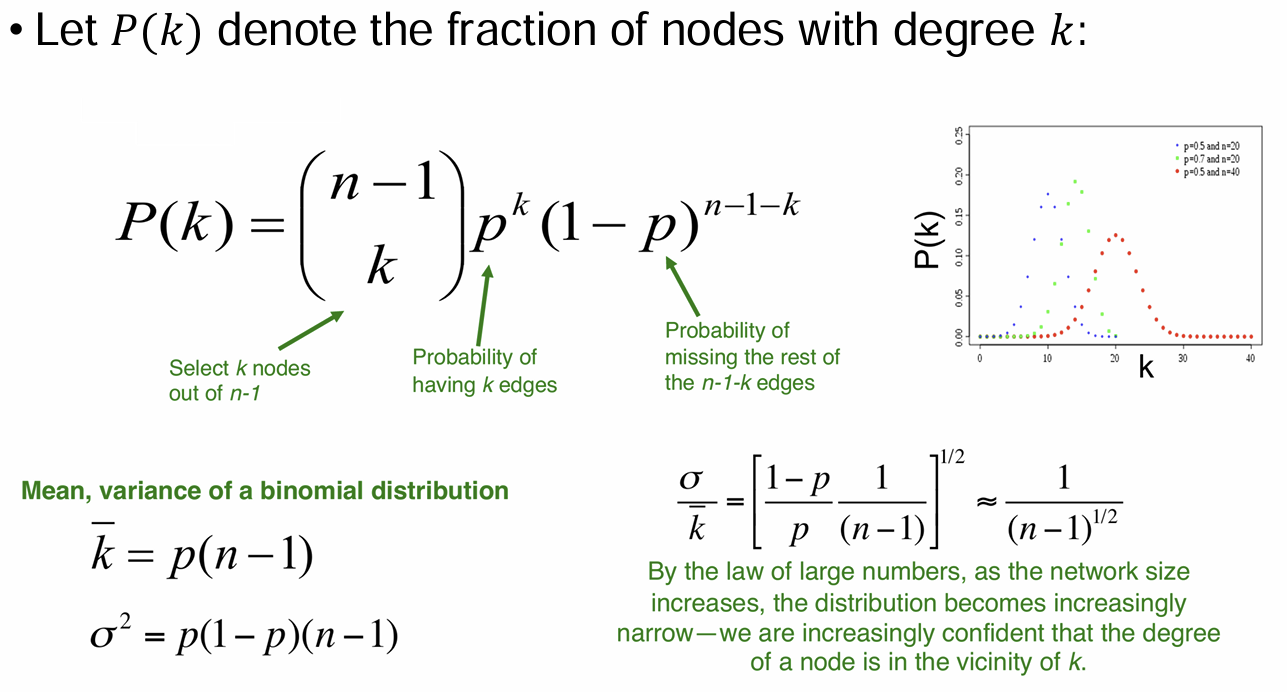
binomial: 이항식
- Clustering Coefficient of
i.i.i, prob p
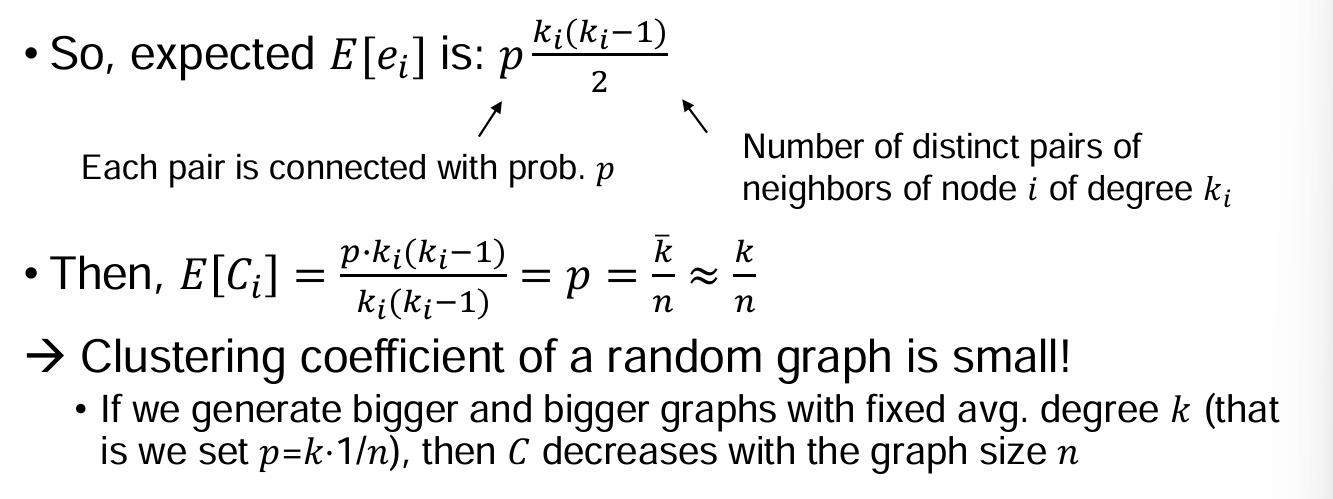
Ref) Definition of Expansion
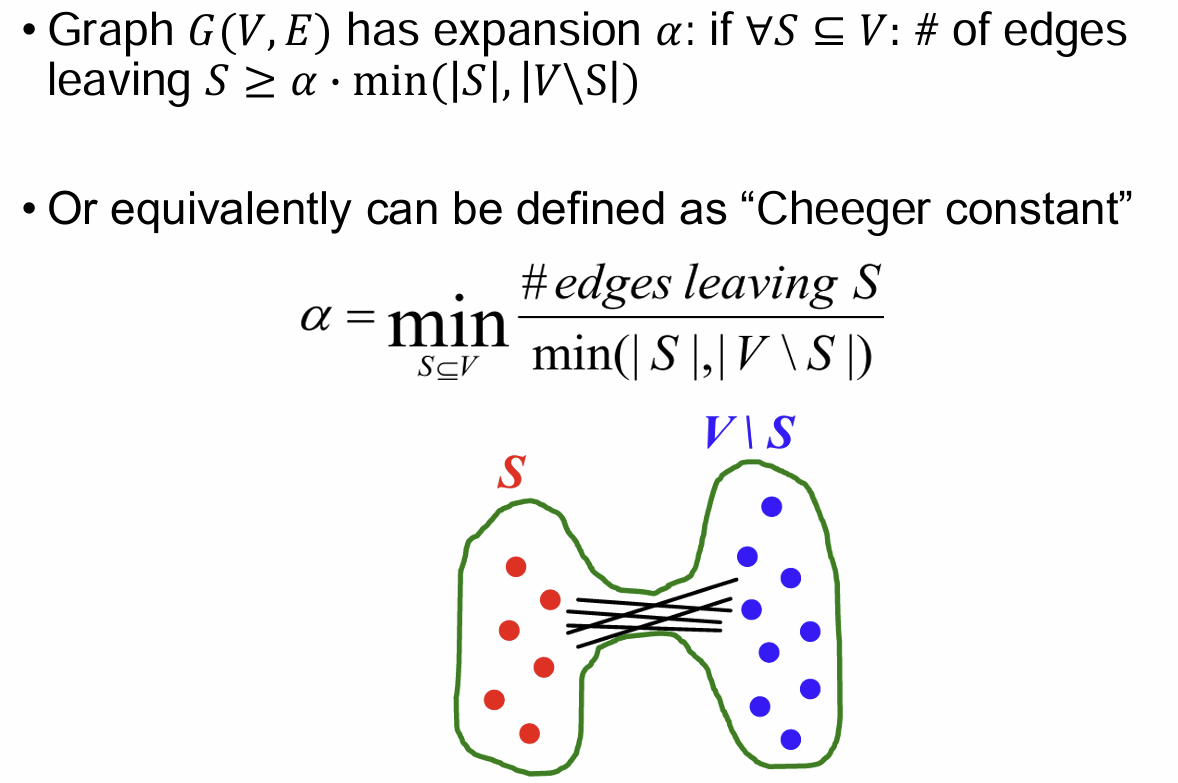
- Expansion in Random Graphs
logarthmic number of steps for BFS to visit all nodes
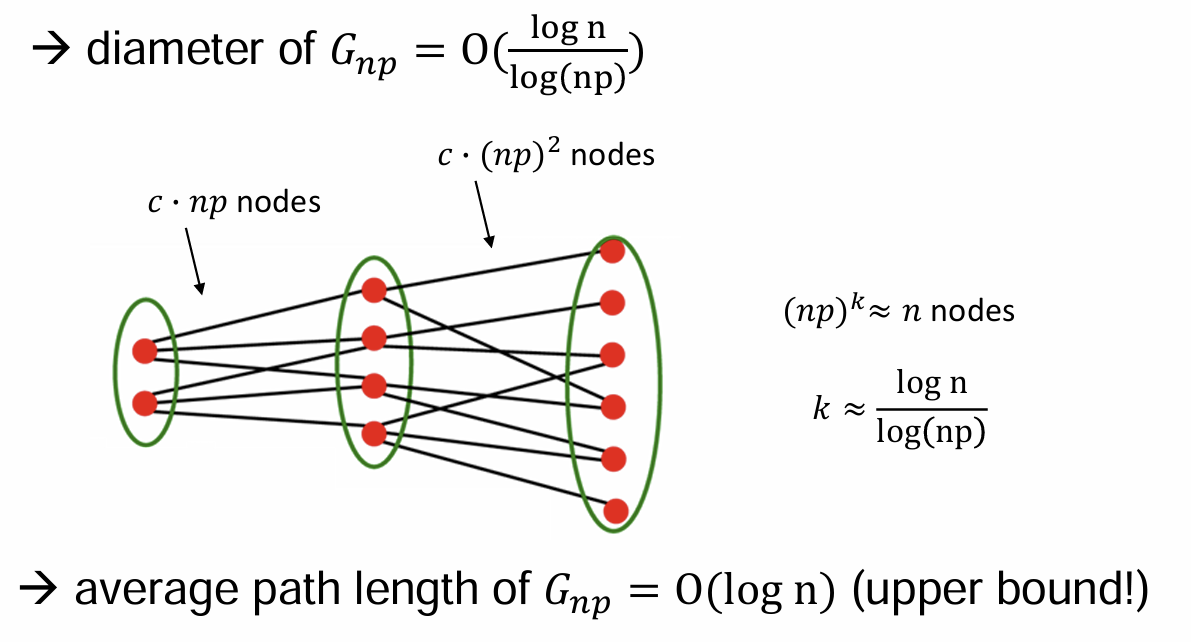
- Evolution of a Random Graph
Real-world Networks vs.
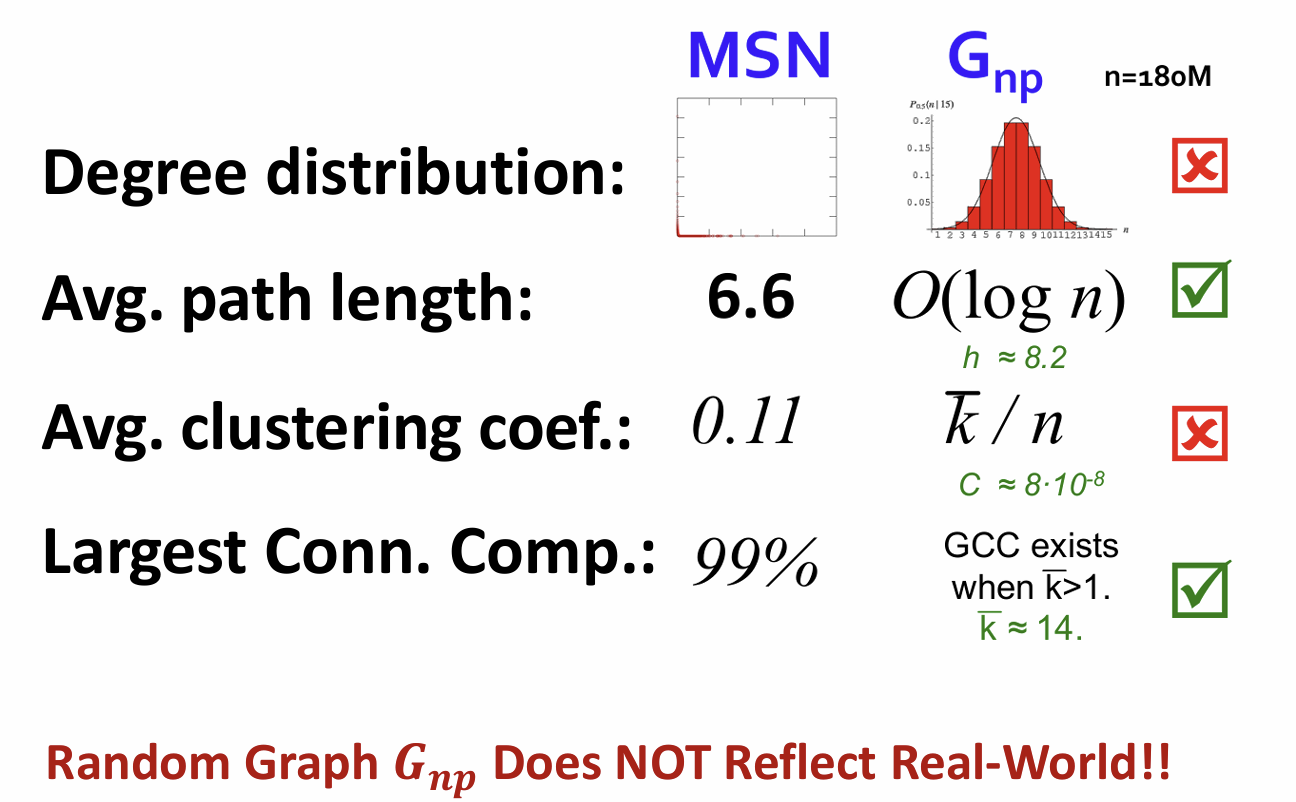
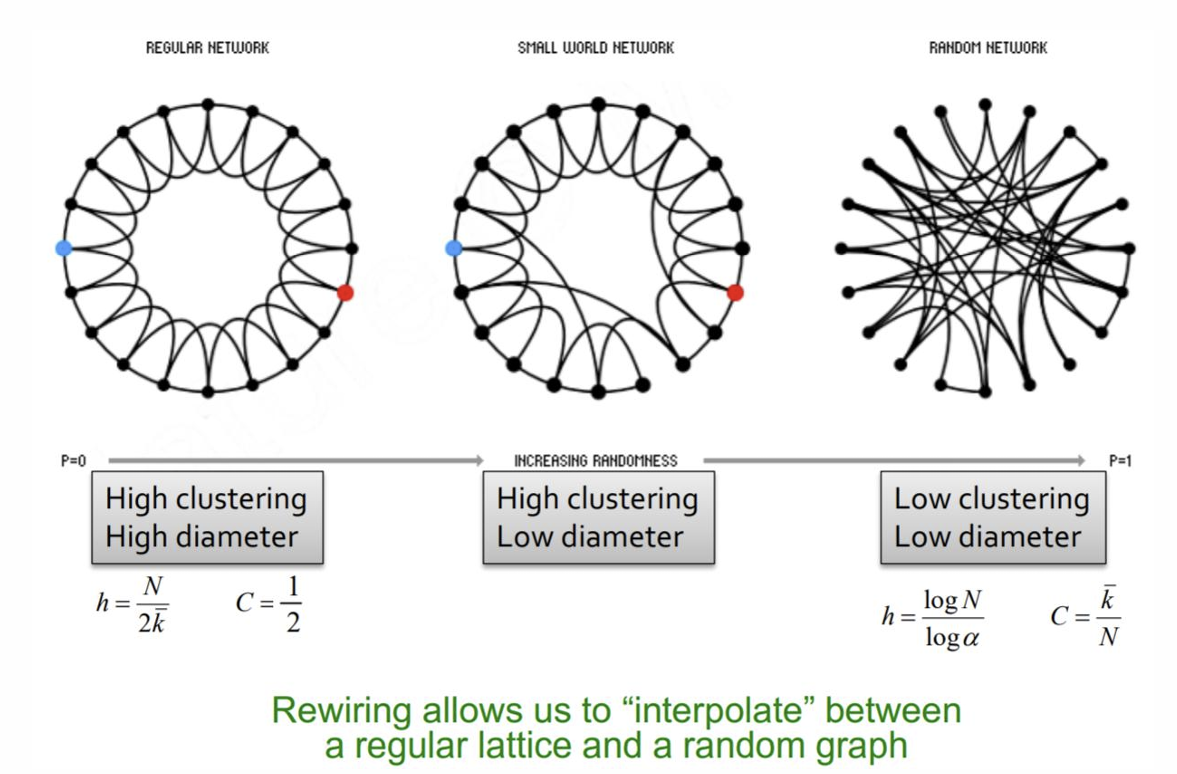
2. The Small-World Model
Solution: The Small World Model
Start with a low-dimensional regular lattice with high clustering coefficient
introduce randomness: add/remove edges to create shortcuts to join remote parts
lattice: 격자
regular high diameter - random low diameter
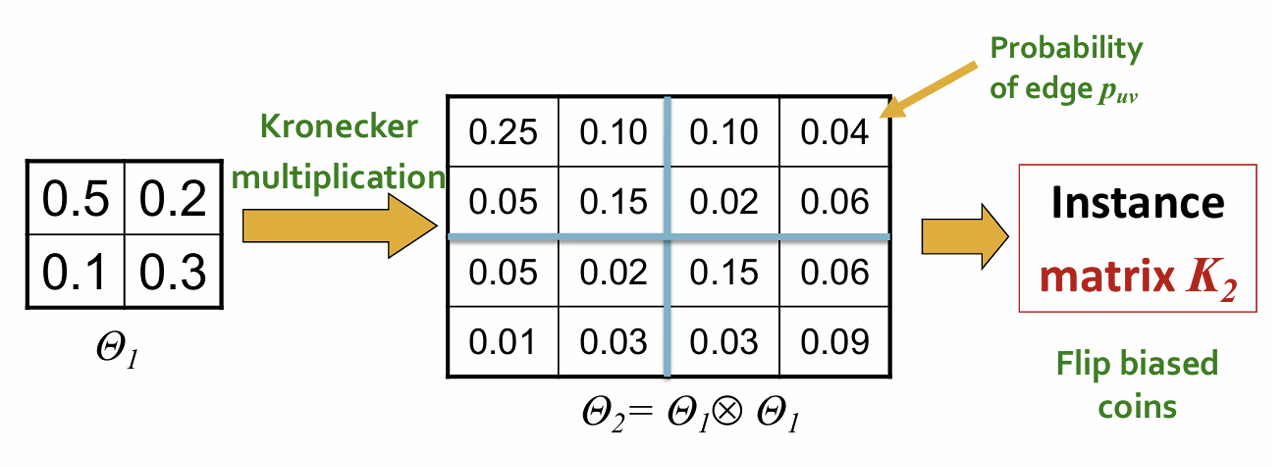
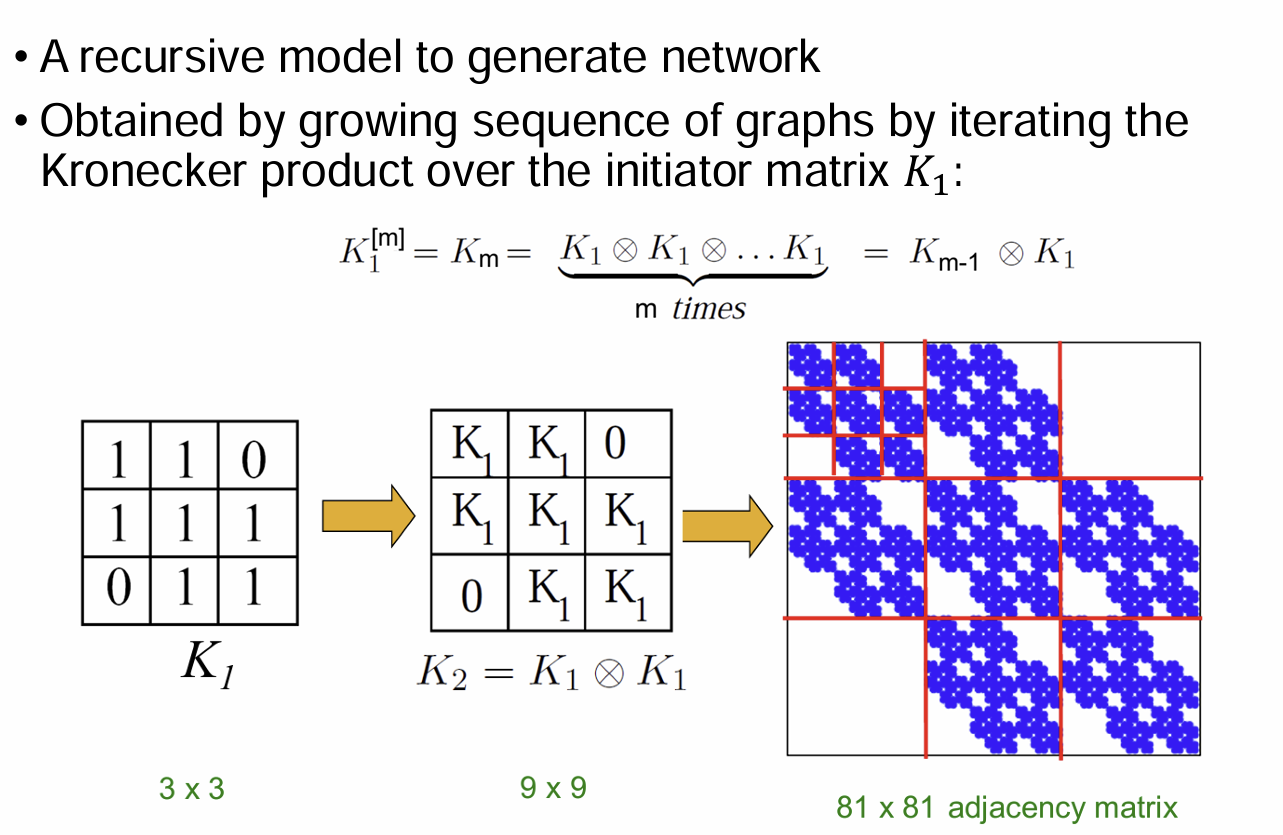
3. Kronecker Graph Model
Idea: Recursive Graph Generation
Self-similarity
Ref.) Definition of Kronecker Product
- Stochastic Kronecker Graph