Week 3-1. Centrality
Primary Centrality Mearsure
- Geometric
• Degree
• Closeness
• Lin
• Harmonic - Path-based
• Betweenness
• Katz - Spectral 스펙트럼의
• Dominant
• Seeley
• PageRank
• HITS
• SALSA
2. Centrality Measure in Detail
Degree Centrality
The node with most connections
Betweenness Centrality
measure Brokerage in centrality
The node you have to go through
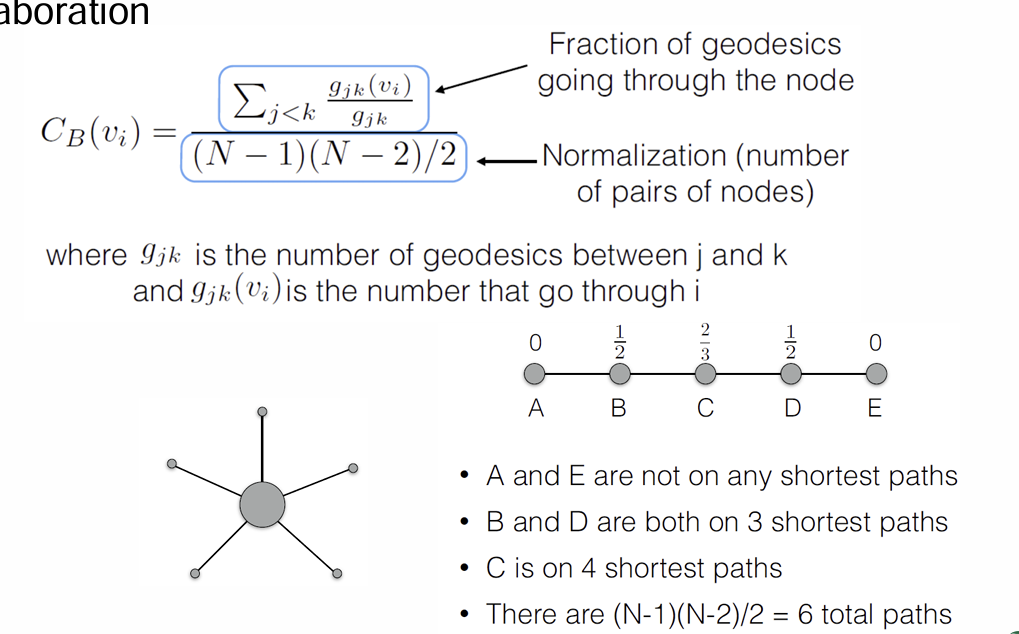
- Non-normalized version
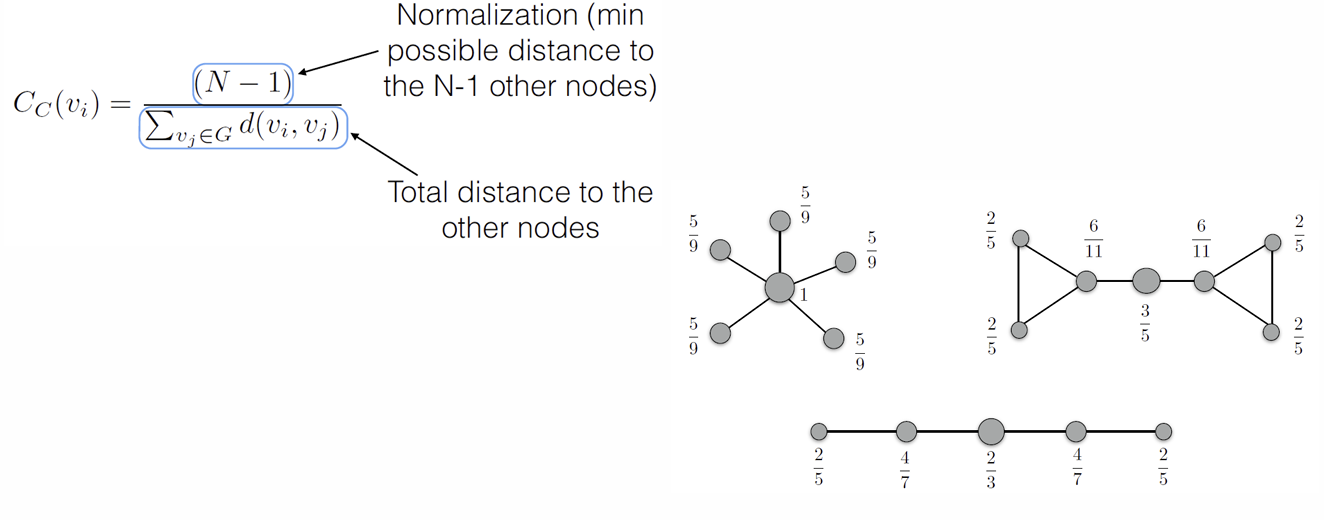
Closeness Centrality
no direct friend but middle
The node in the middle of the action
shortest distance to the other nodes
Harmonic Centrality
Replace the average distance with the harmonic mean of all distances
for nodes not connected
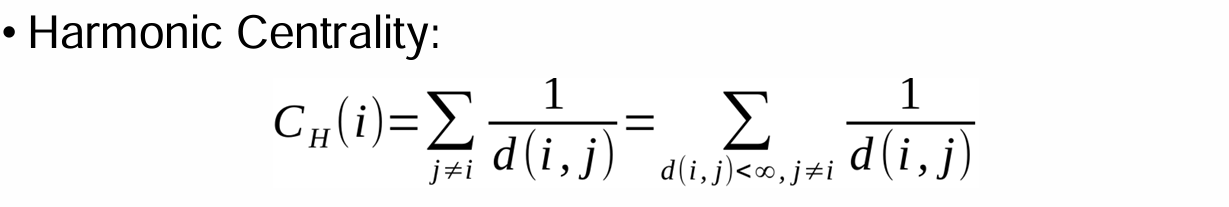
normalized form
Eigenvector Centrality
The node that connects to the important nodes
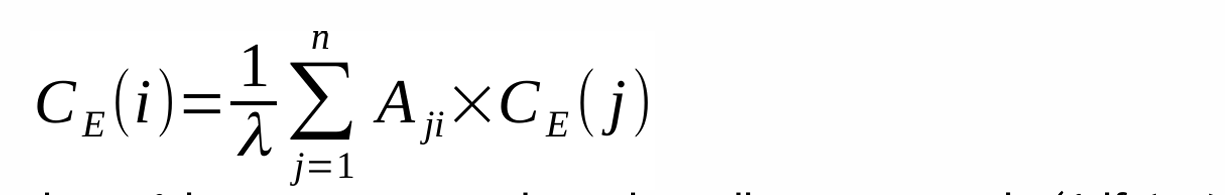
-
Bonacich eigenvector centrality
-
Variants of Eigenvector Centrality
PageRank:
Katz Centrality:
3. Centrality in Other Types of Networks
Centrality in Directed Networks
prestige: 명성
Degree: In and out centrality
Beetweenness: consider only directed paths, ordered pairs
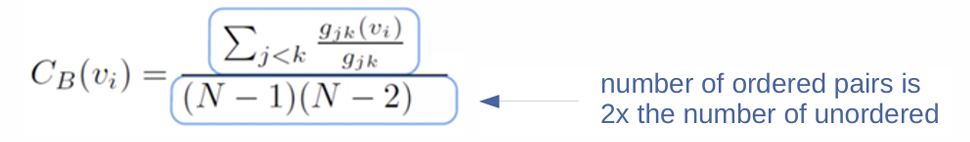
Closeness(proximity): Consider only directed paths
Eigenvector: same
Centrality in Weighted Networks
Degree: Sum weights (non-weighted equals weight=1 for all edges)
Betweenness and Closeness: Consider weighted distance
Eigenvector: Consider weighted adjacency matrix
4. More Topics
Network Centralization
Week 3-2. Motifs, Graphlets
1. Subgraphs and Motifs
Subnetworks: A Property of Graph
building blocks of networks, characterize and discriminate networks
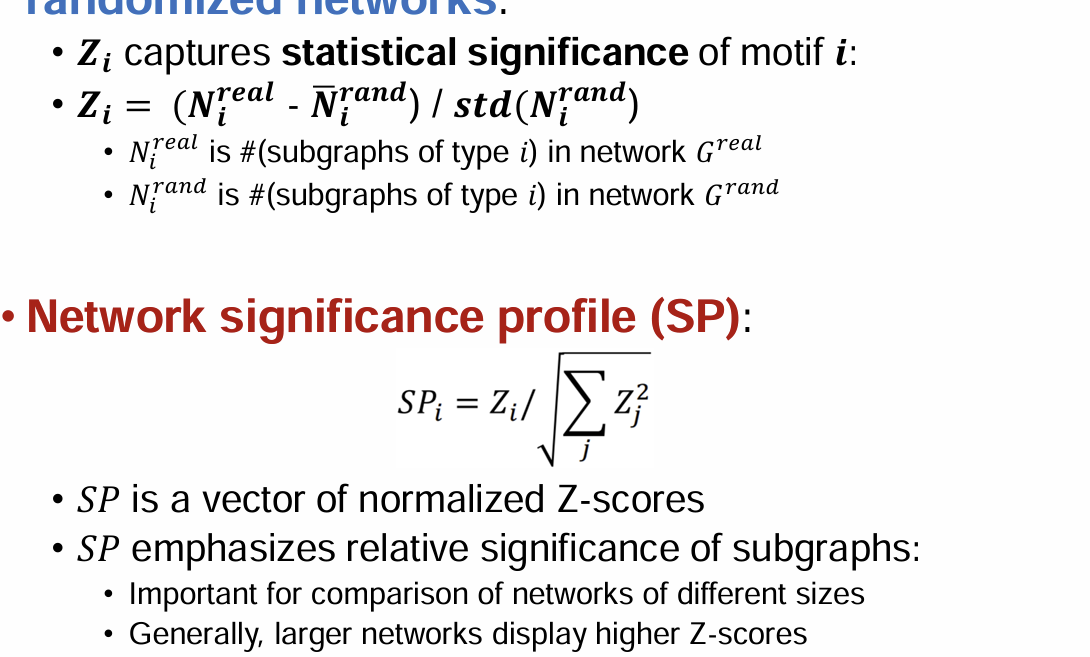
network significance profile: a feature vector for all subgraph types
Network Motifs
recurring, significant patterns of interconnections,
understand structure, predic operation and reaction in a given situation
- Motifs: Partial Subgraphs
Pattern: Small partial subgraph
- Motifs: Recurrence
Recurring: Found many times, i.e., with high frequency
재발하다

- Motifs: Significance
Significant: More frequent than expected, i.e., in randomly generated networks
Configuratoin Model
구성 모델
- Alternative for Spokes: Switching
edges 쌍 random으로 선택, endpoints 교환
result: a randomly rewired graph
Experiments: Detecting Motif
p19 week 3-2
2. Graphlets: Node Feature Vectors
Graphlets: connected non-isomorphic subgraphs
• Induced subgraphs of any frequency
Graphlet Degree Vector (GDV)
: counts # graphlets that a node touches at a particular orbit
with the frequency of the node in each orbit position
node's local network topology 위상 기하학
- Automorphism orbit symmetries of a subgraph

3. Finding Motifs and Graphlets
1) Enumerating all size-k connected subgraphs
2) Counting #(occurrences of each subgraph type) via graph isomorphisms test
Exact Subgraph EnUmeration (ESU)
: 최근에 만듬
: extend the motif할 후보 노드 set
node v로 시작해서, add node u to ,
if u's nodeid > v's and u only neighbored to new node w not already in $V{subgraph}$
recursive function

ESU-Tree Example
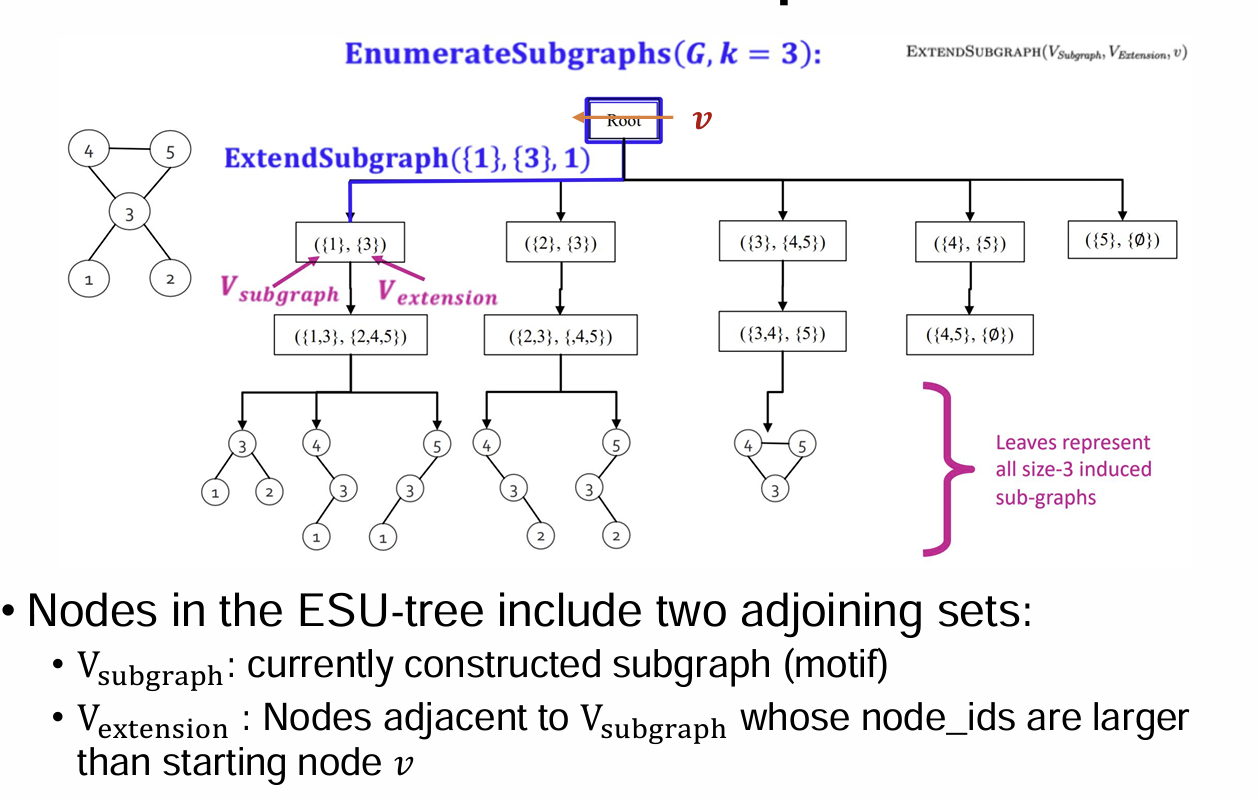
Use ESU-Tree to Count Subgraph
classify leaves into non-isomorphic size-k classes:
topologically equivalent(isomorphic) 확인
Graph Isomorphism
f: V(G) -> V(H), nodes u,v of G are adjacent in G if f(u), f(v) are adjacent in H
bijection: 전단사
Compute in igraph
