Week 13-2. Graph Transformers
1. Intro to Transformers
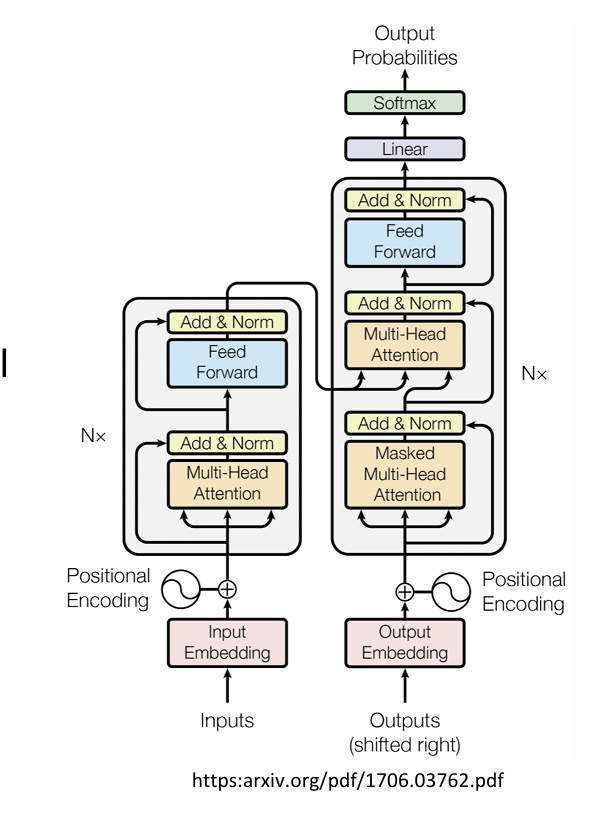
Transformer Overview
• Model: advanced version of AE
Final cost/error function is standard cross-entropy error on top of a softmax classifier
• Sequence-to-sequence prediction
Task: machine translation with parallel corpus (predict each translated word)
• Popularly adopted in LLMs, a backbone of generative AI in NLP domain

Tasks with Transformers
• Transformers map 1D sequences of vectors to 1D sequences of vectors known as tokens
Tokens describe a ”piece” of data – e.g., a word
• What output sequence?
Option 1: next token => GPT
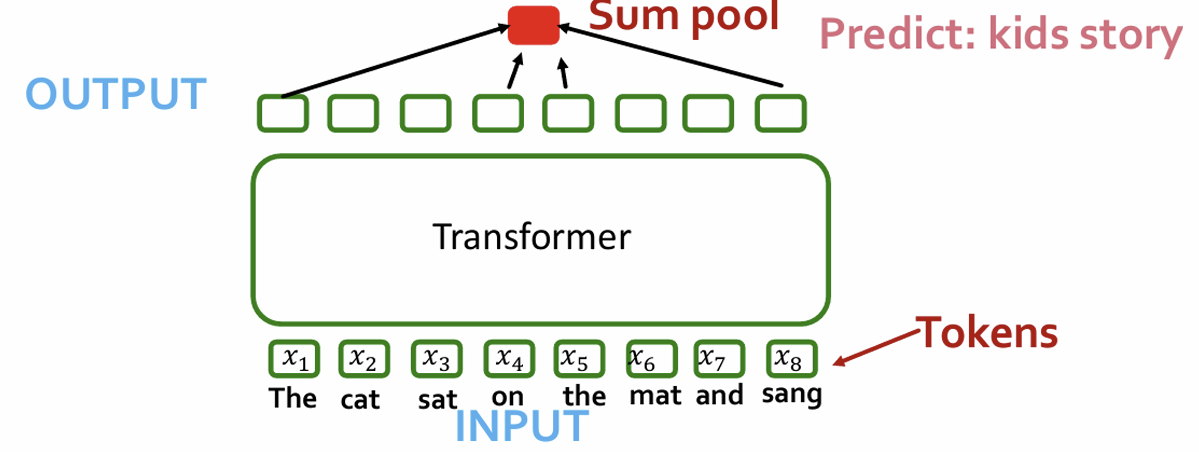
Option 2: pool (e.g., sum-pool) to get sequence level-embedding (e.g., for classification task)
sequence to one
Transformer Blueprint
How are tokens processed?
Lots of components
• Normalization
• Skip-connection
• Feed forward networks
• Multi-head self-attention
• Positional encoding
To understand how to process graphs with transformers, we must:
1. understand the key components
2. decide how to make suitable graph versions of each
Understanding Multi-Attention: Self-Attention
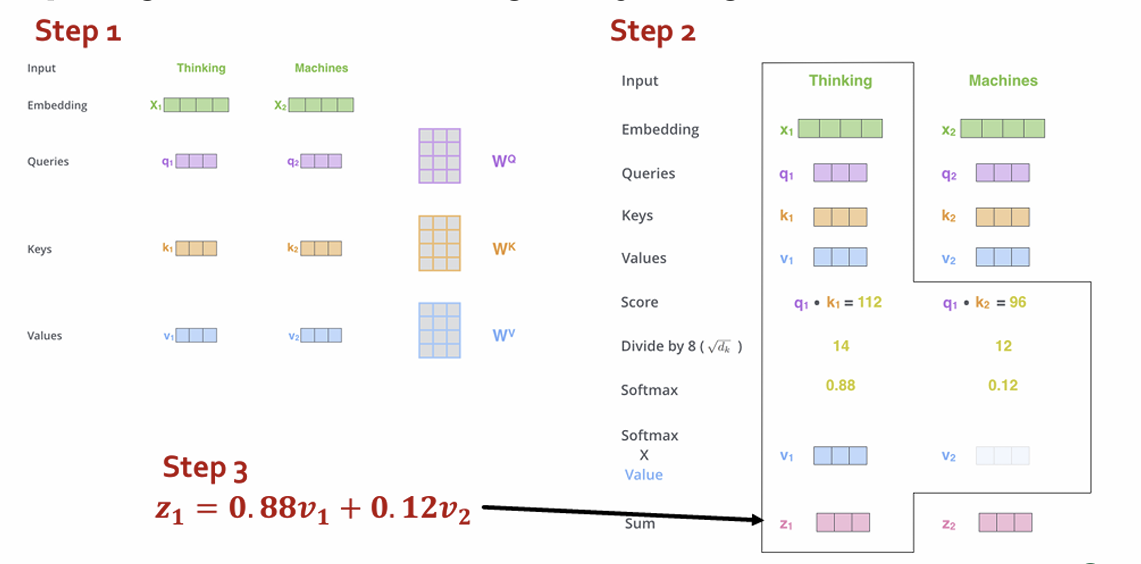
• Step 1: compute “key, value, query” for each input
• Step 2 (just for 𝑥1): compute scores between pairs, turn into probabilities (same for 𝑥2)
• Step 3: get new embedding 𝑧1 by weighted sum of 𝑣1, 𝑣2
input x1, similarity between q1, k1, softmax(0-1), a value + b value2 = weighted sum
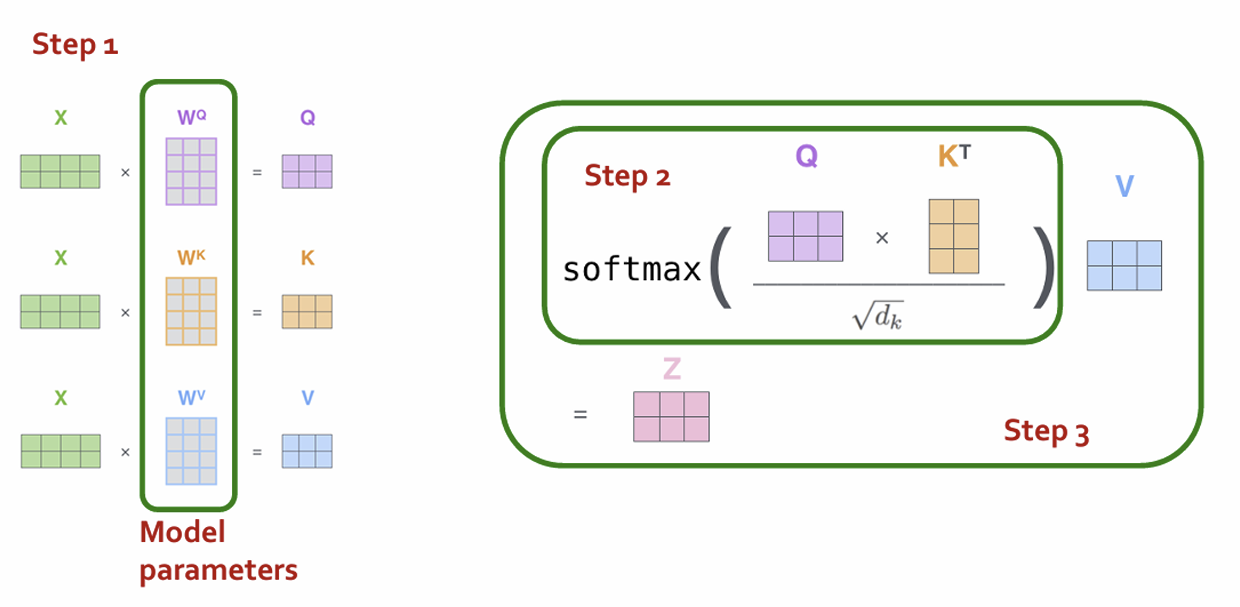
- same calculation in matrix form
Multi-head self-attention
• Do many self-attentions in parallel, and combine
• Different heads can learn different “similarities” between inputs
• Each has own set of parameters
different weight matrix

Comparing Transformers and GNN
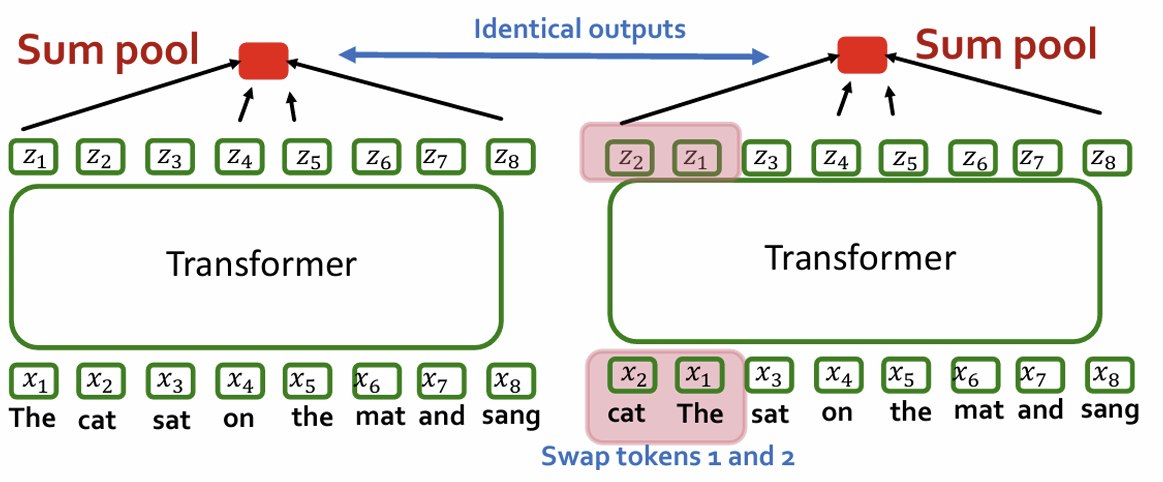
• Similarity: GNNs also take in a sequence of vectors (in no particular order) and output a sequence of embeddings
• Difference: GNNs use message passing, Transformer uses self-attention- NO, almost similar, can be inpreted as self-attention
• Are self-attention and message passing really different?
Interpreting the Self-Attention Update
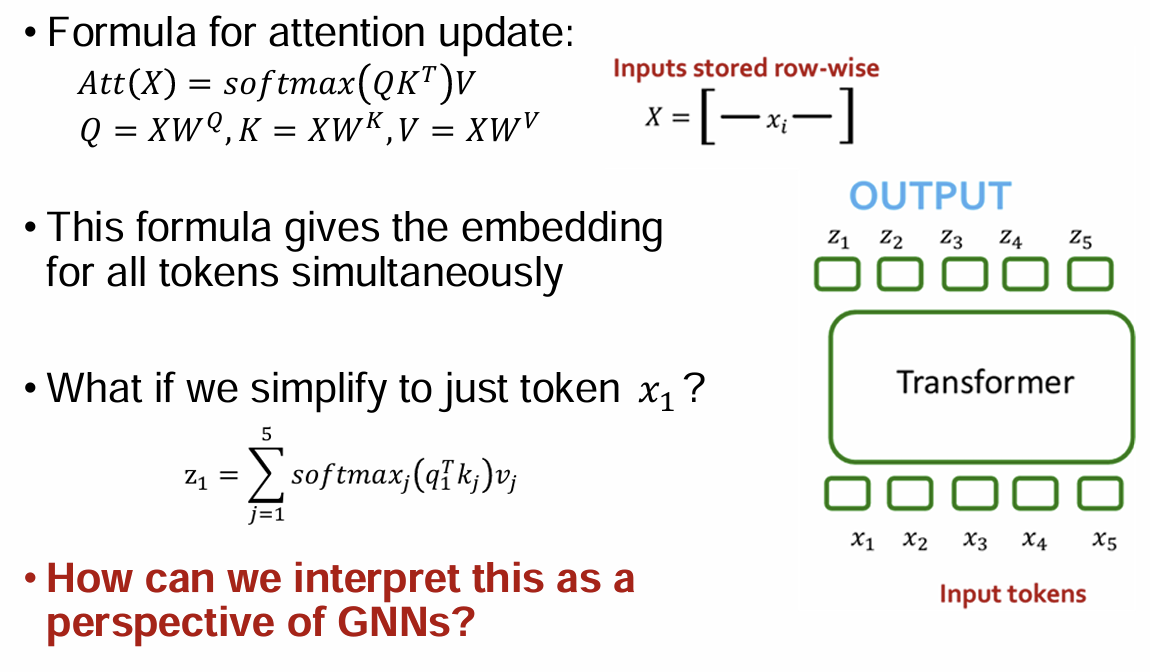
Formula for attention update:
embedding for all tokens simultaneously
simplify to just token x_1?
Self-attention as Message Passing
GNN -> MSG + AGG + Activation
message from j: (v, k)
compute query for 1: q_1 - MSG(x_1)
Aggregate all messages
- visualize
Nodes = tokens
Edges = not explicit relations, but “fully connected!” to other tokens in the same input
그래프를 fc layer로 바꿔서 구할 수 있다

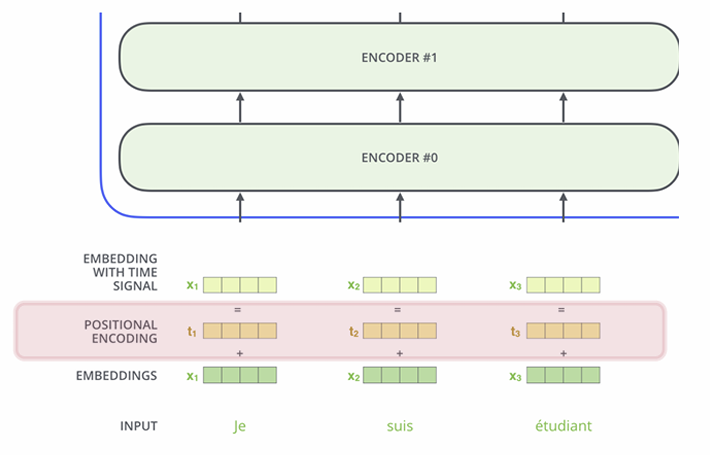
Tokenization & Positional Encoding in Transformer
Considering formula
Problem: using just embeddings of tokens- order of tokens does not matter
Positional Encoding
2. New Design Landscape for Graph Transformers
Processing Graphs with Transformers
- Components of a Transformer- graph transformer must take the following inputs
Tokenizing- Node features
positional encoding- Adjacency information
self-attnetion- Edge features
Different approaches correspond to different “matchings” between graph inputs
그래프-transformer components 매치에 따라 달라짐
테스크 제약에 맞게 mapping 잘하는 게 중요
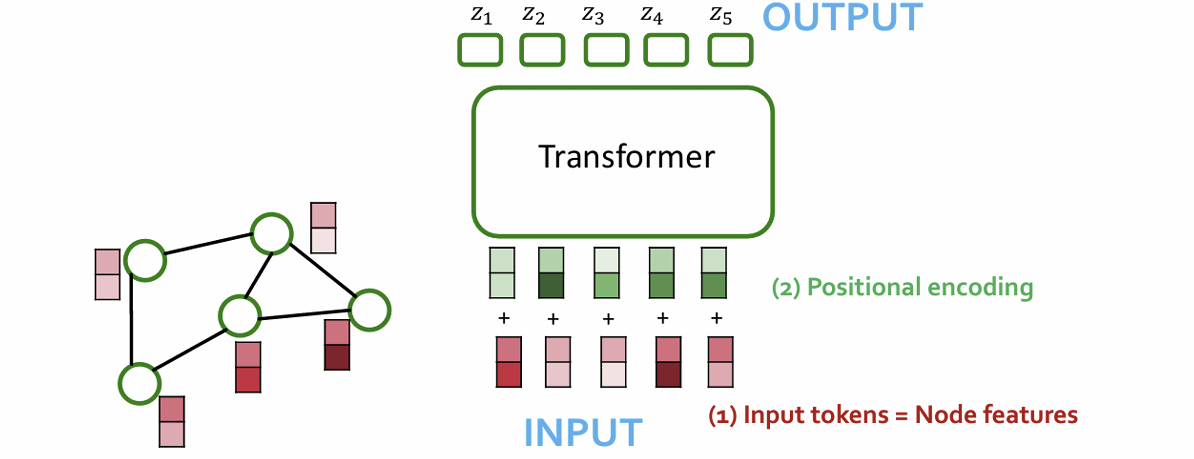
Nodes as Tokens
• Sensible Idea: node features = input tokens
• This matches the setting for the “attention is message passing on the fully connected graph” observation
노드 단위로 하면 편함, relation 정보는 아래
How to Add Back Adgacency Info?
• Idea: Encode adjacency info in the positional encoding for each node
• Positional encoding describes where a node is in the graph
positional encoding을 넣음
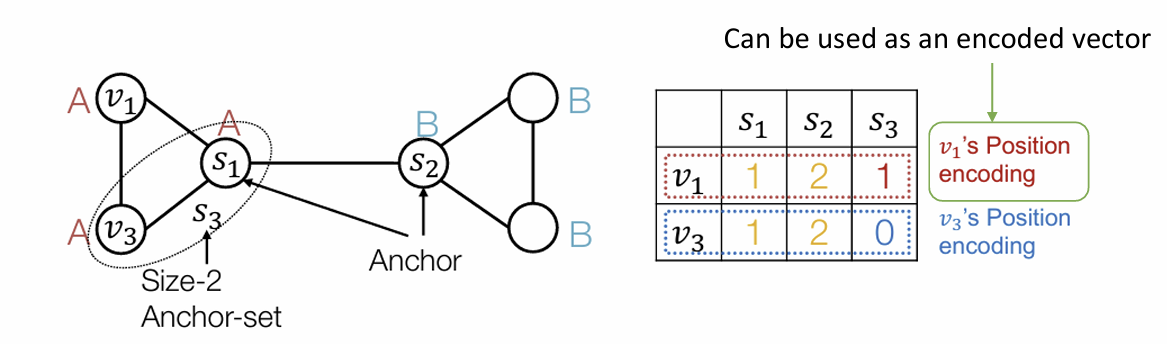
Option 1: Relative Distances
• Last lecture: positional encoding based on relative distances
• Similar methods based on random walks
• This is a good idea! It works well in many cases
• Especially strong for tasks that require counting cycles
• Issue: not suited to structure-aware tasks!
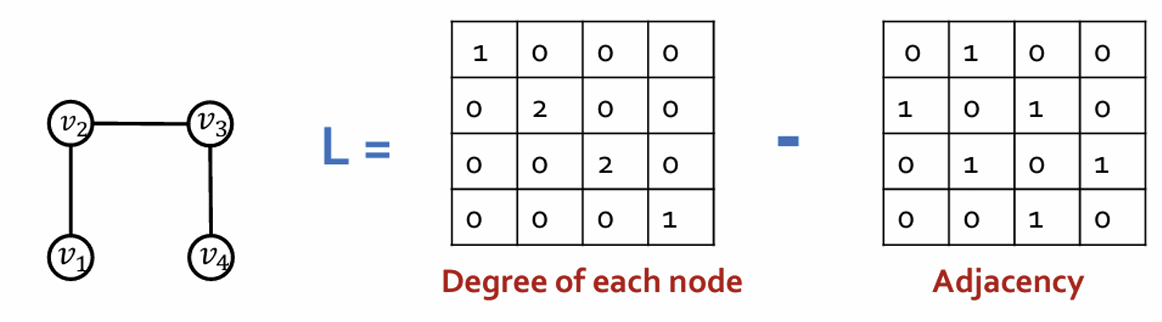
Option 2: Laplacian Eigenvector Positional Encodings
• Draw on knowledge of Graph Theory (many useful and powerful tools)
• Key object: Laplacian Matrix L = Degrees - Adjacency
Each graph has its own Laplacian matrix
Laplacian encodes the graph structure
Several Laplacian variants that add degree information differently
eigen vector 쌓아 놓음
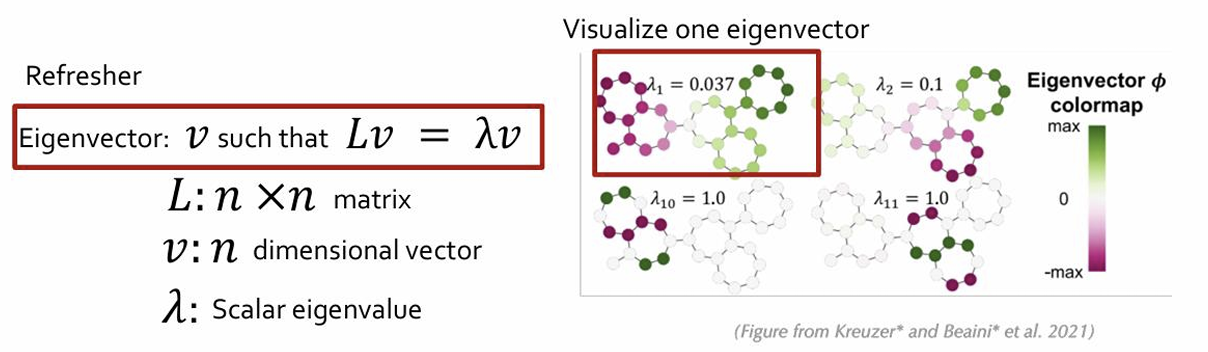
• Laplacian matrix captures graph structure!
• Its eigenvectors inherit this structure
• This is important because eigenvectors are vectors (!) and
so can be fed into a Transformer
Eigenvectors with small eigenvalue = global structure
Eigenvectors with large eigenvalue = local symmetries
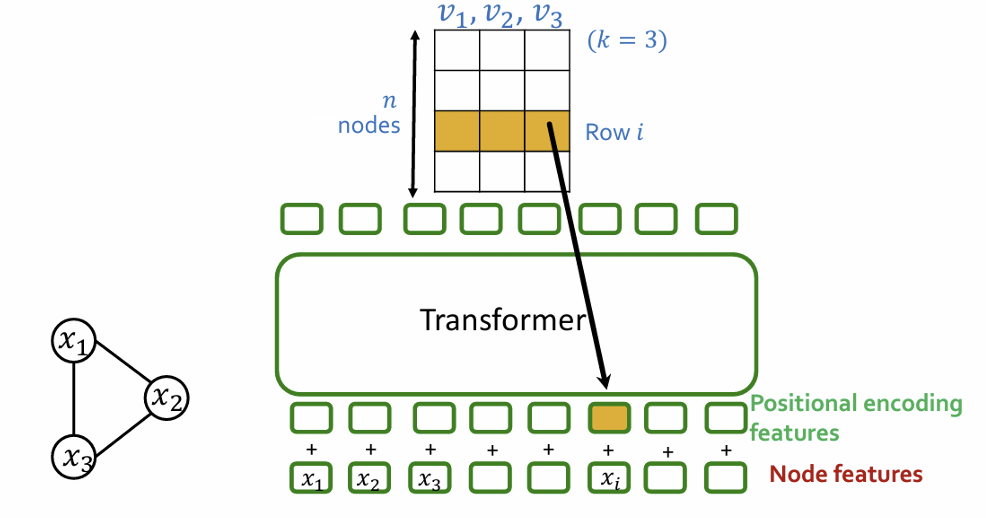
- Positional encoding steps
Compute 𝑘 eigenvectors
Stack into matrix:
𝑖-th row is positional encoding for node i
수학 설명 많이 안 할거임
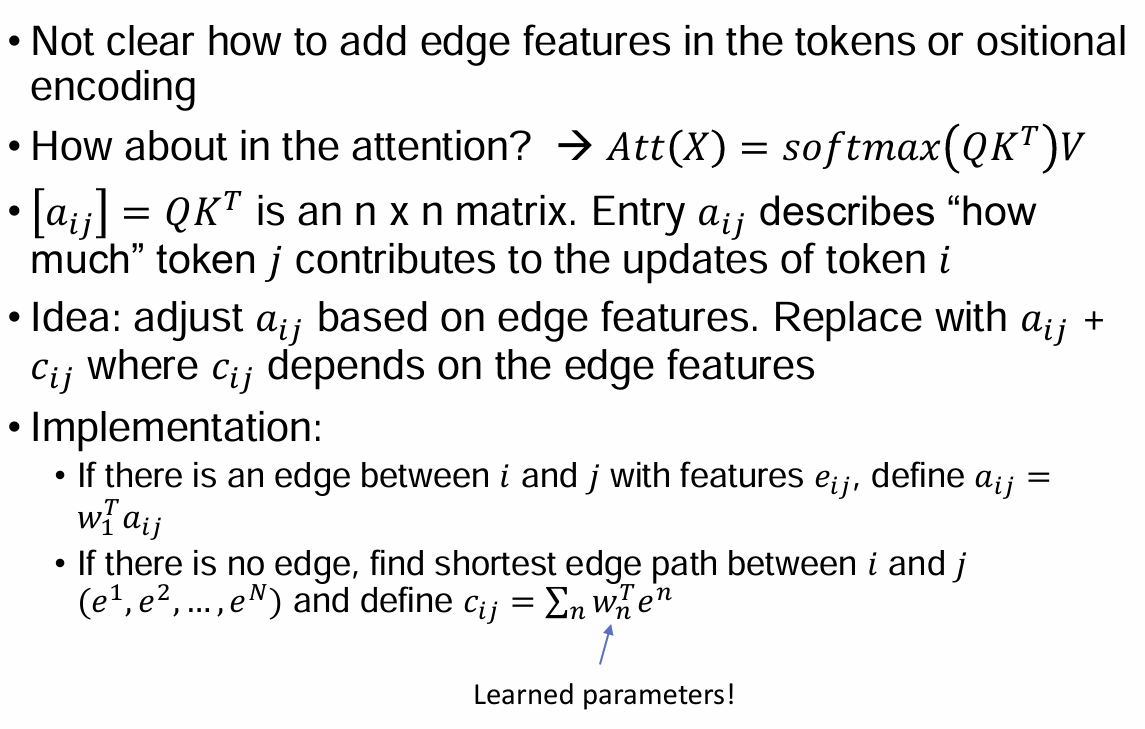
Edge Features in Self-Attention
edge가 있으면 attention을 더 써보자
Summary
• Tokenization
Usually node features
Other options, such as subgraphs, and node + edge features (not discussed today)
• Positional Encoding
Relative distances, or Laplacian eigenvectors
Gives Transformer adjacency structure of graph
• Modified Attention
Reweight attention using edge features
