Lecture Week 9-1. Deep Learning (CNNs)
background
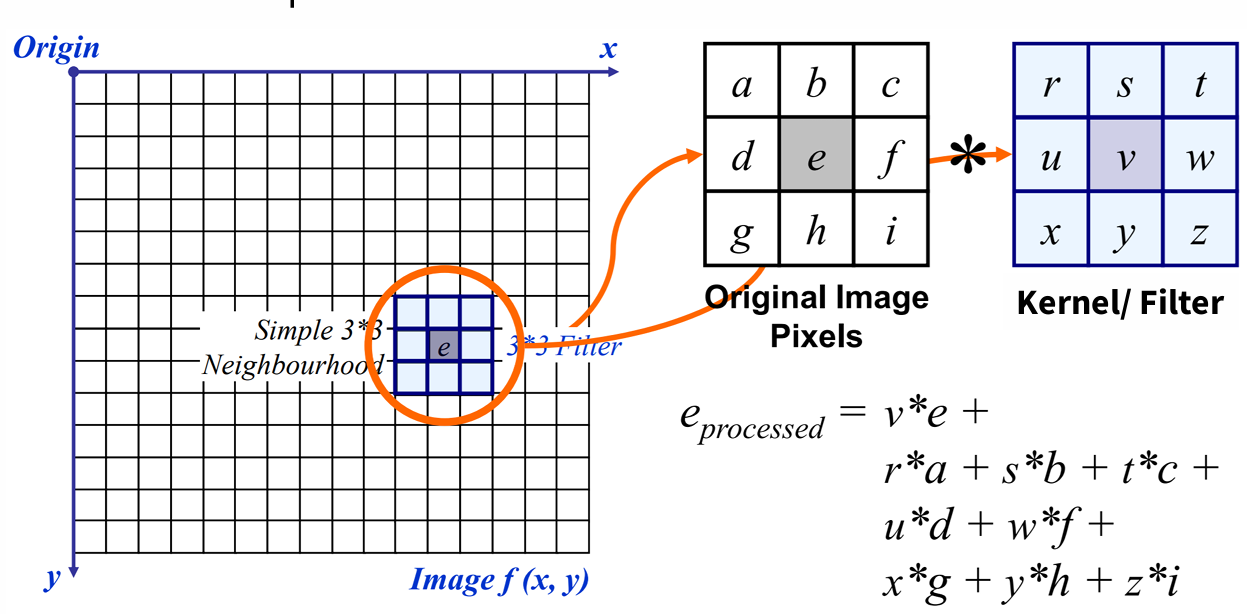
1. Discrete (digital) convolution
내부 계산
: used to smooth or sharpen an image, comprises "sum-of-products" and "shift" operation
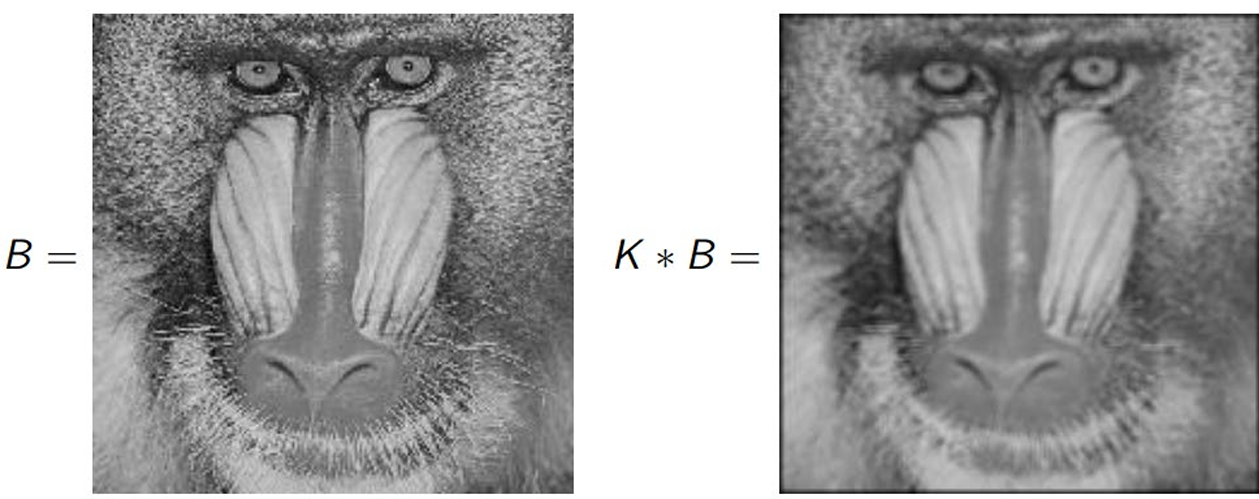
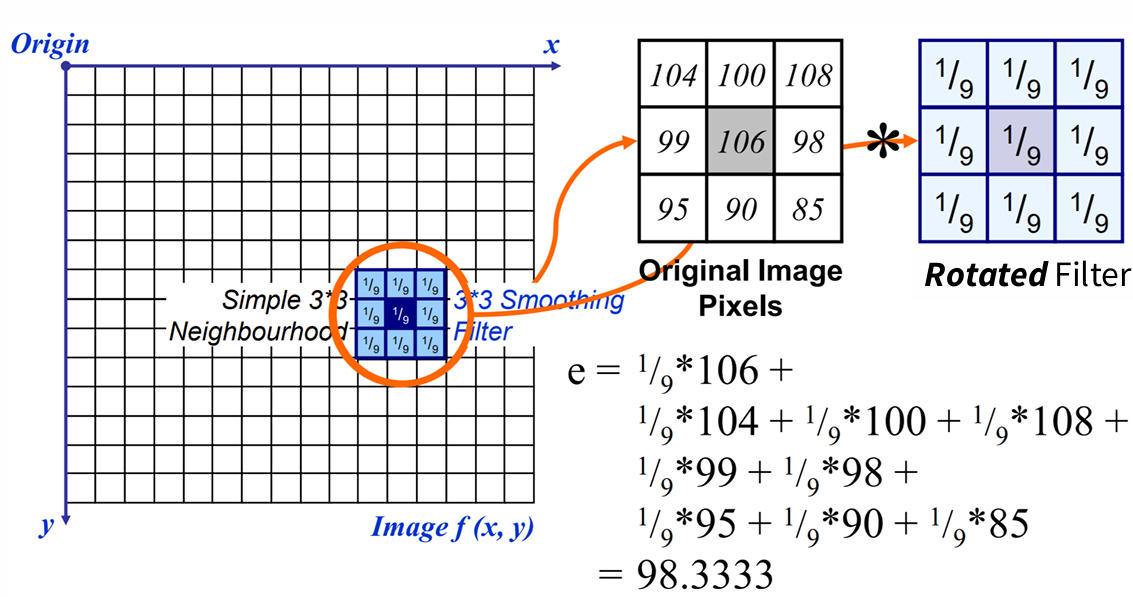
Smoothing operation
- mean filter
:average all of the pixels in the neighborhood, mean of its neighbors
removing noise, highlighting gross detail(철저한)

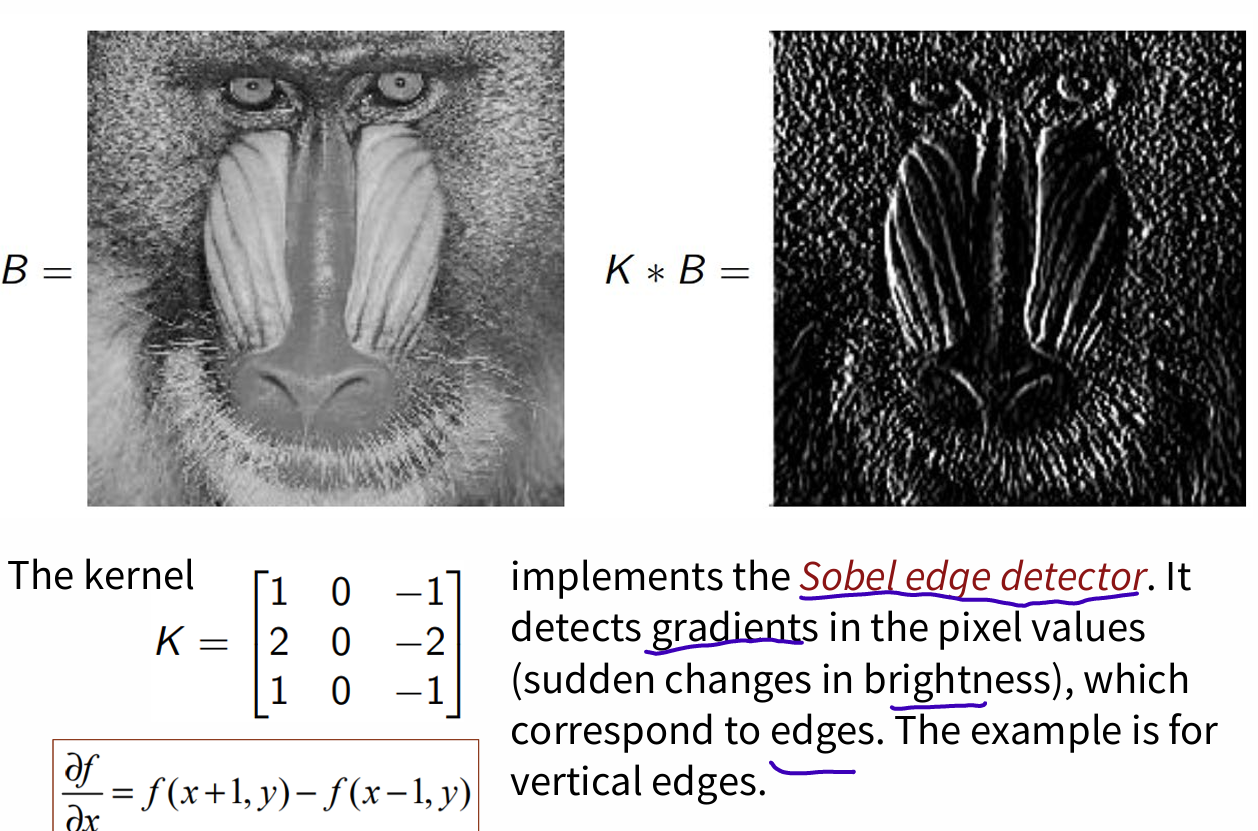
- Sobel edge detector
detect gradients, sudden changes in brightness, edges
실습 사이트: http://setosa.io/ev/image-kernels/
Convolution: pick 3x3 matrix k of weights, slide this over an image, compute inner product(similarity) of k and the corresponding field of the image, and replace the pixel in the center of the field with the output of the inner product operation
convolution extract low-level "features" from an image
varing the weights of k; parameters
used for edge detection, blurring, sharpening, etc.
2. Convolutional Neural Nets: Stride, Pooling, Padding
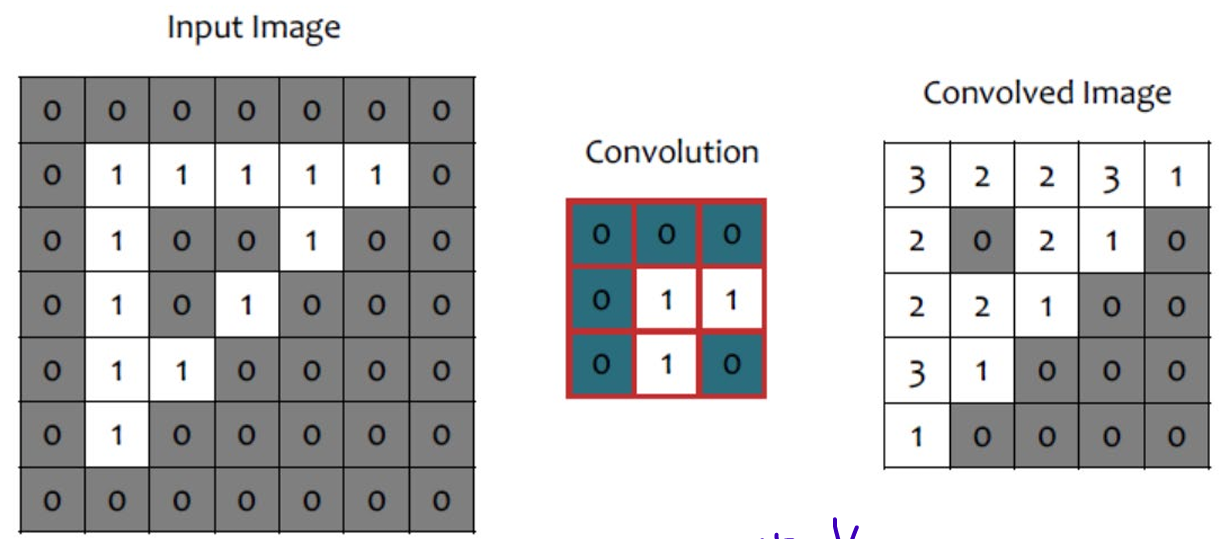
1. Stride
: skip some of the slide. Downsampling with Stride
A stride of 3 means skipping every 2 slides, downsizing roughly by factor 3.
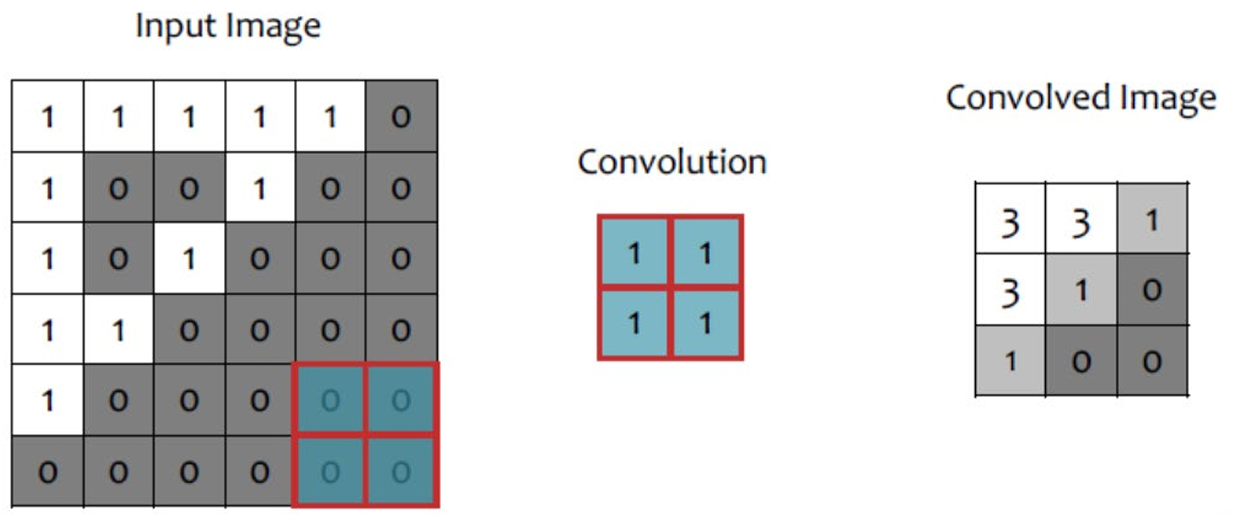
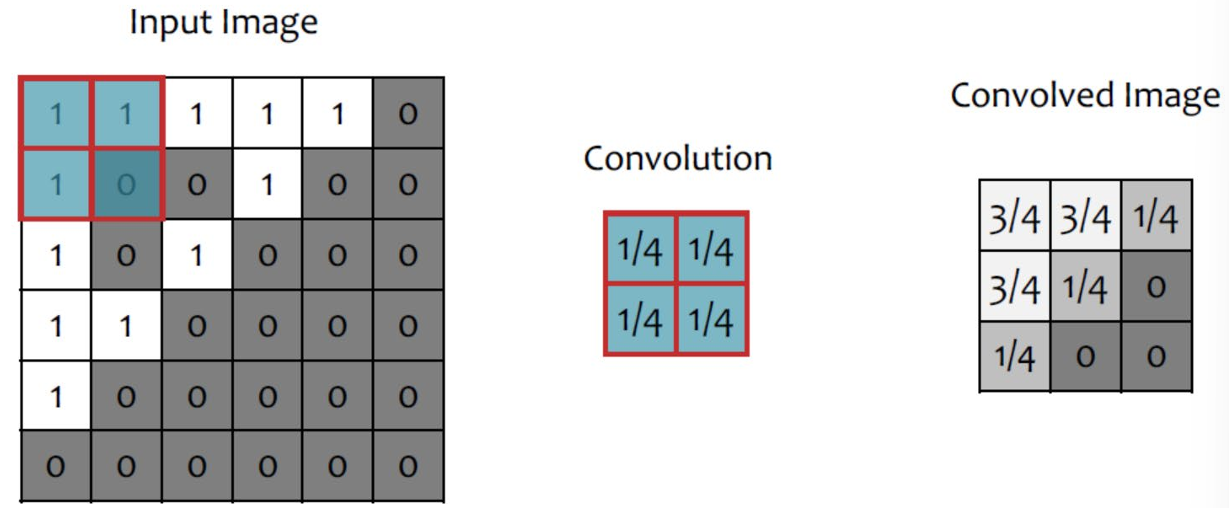
2. Pooling
- Average-Pooling
- Max-Pooling
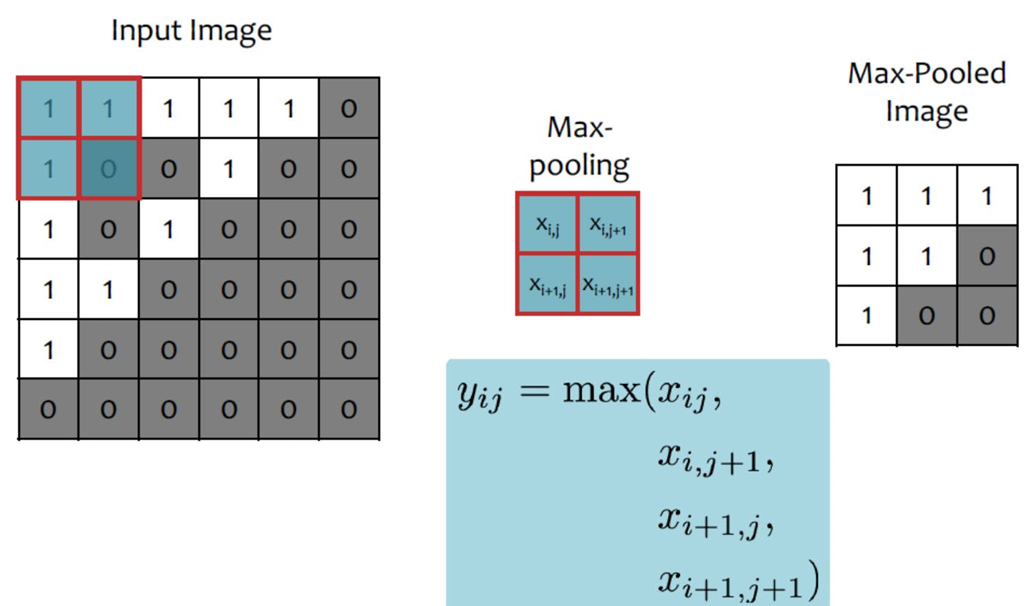
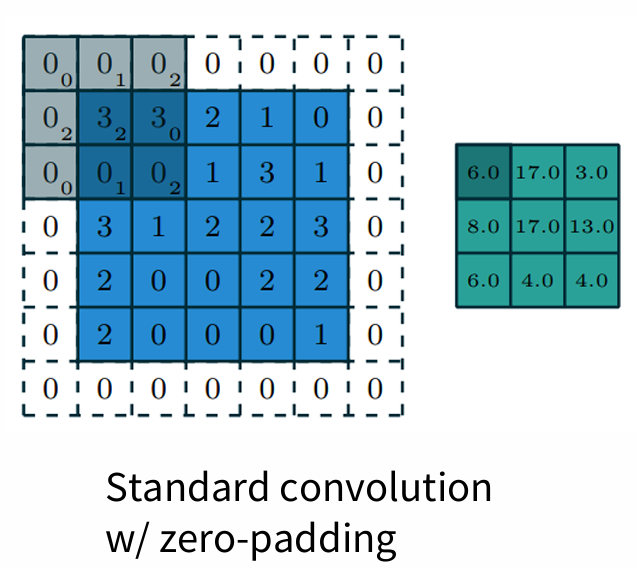
3. Padding
: put the edges with extra, fake pixels
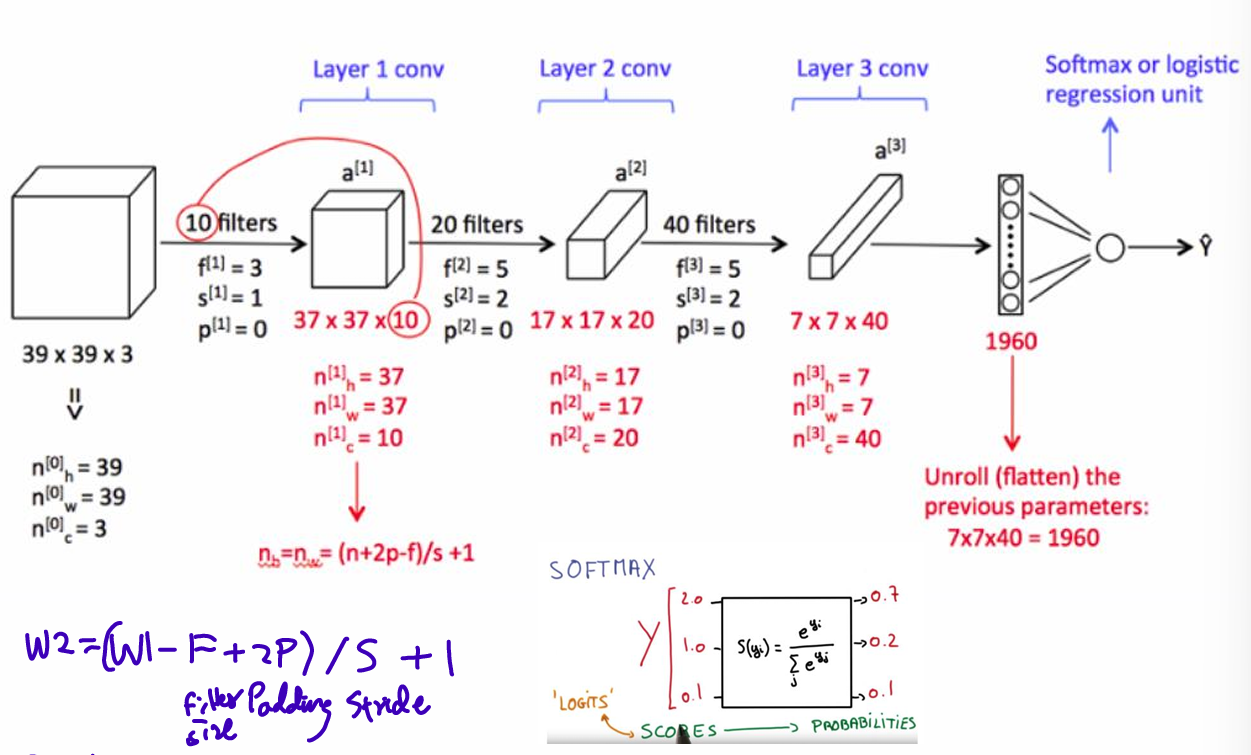
3. CNN: 3d Kernel, multiple filters
RGB color 3-dimensional
input W1 x H1 x D1
hyperparameters;
number of filters K, filters' spatial extent F, the stride S, the amount of zero padding P
produce W2 x H2 x D2
W2 = (W1 - F + 2P) / S + 1
H2= (H1 - F + 2P) / S + 1
D2 = K
total parameters(weights + biases): F D1 K + K
Why convolutions?
-
Parameter sharing: parameter saving, a feature detector is also useful in another part of the image
-
Sparsity of connections: each output value depends only on a small number of inputs
-
Structure preservation
-
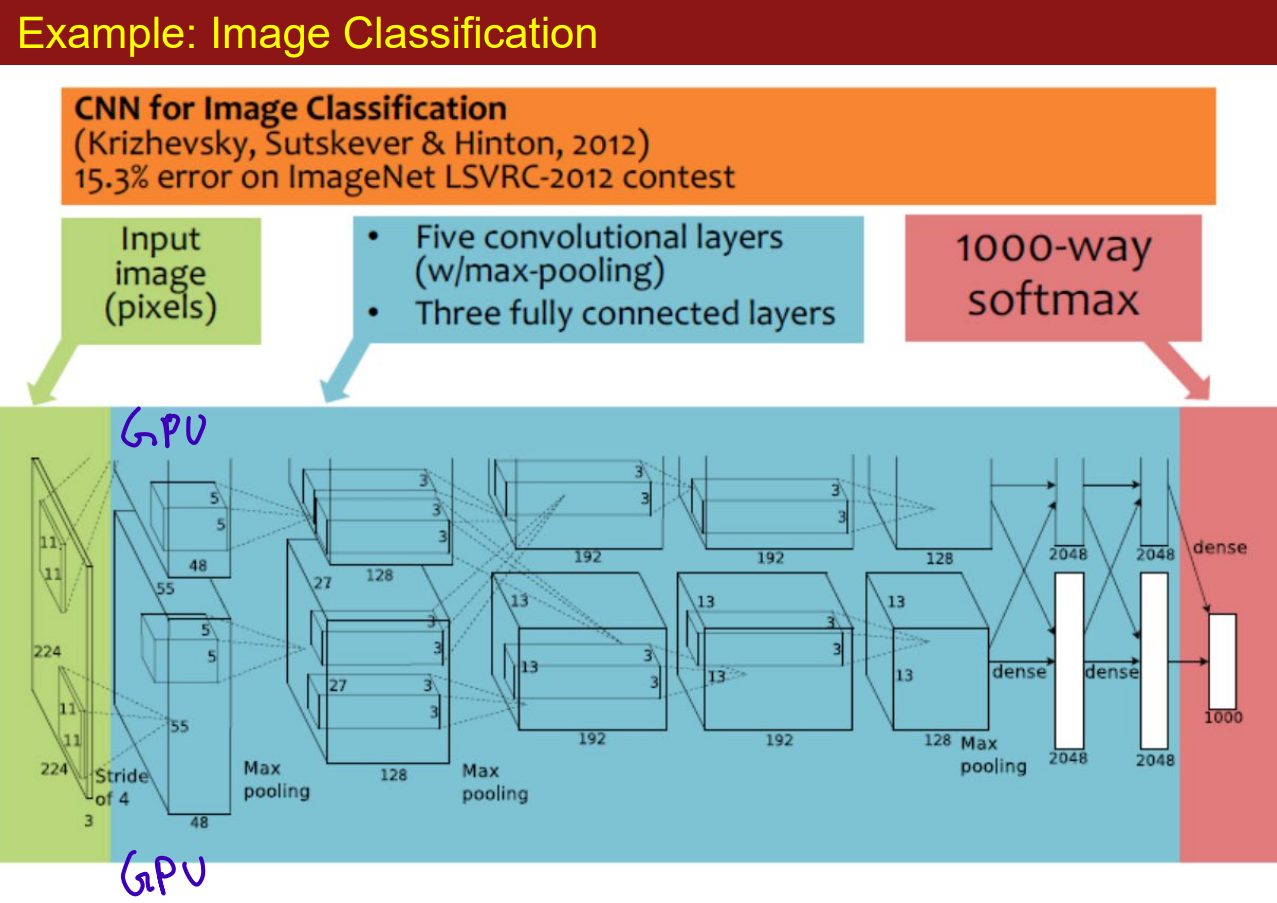
example
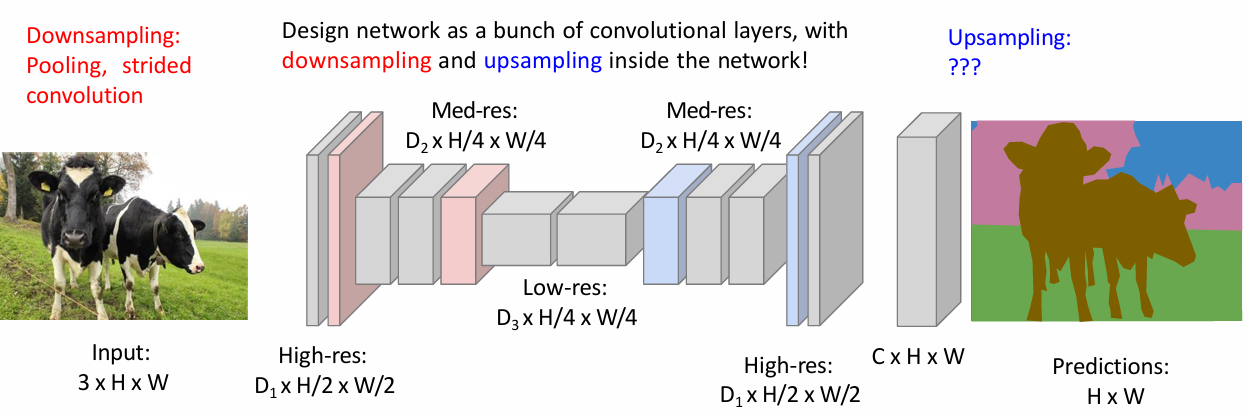
4. CNN: Upsampling
Semantic Segmentation Idea
: fully convolutional
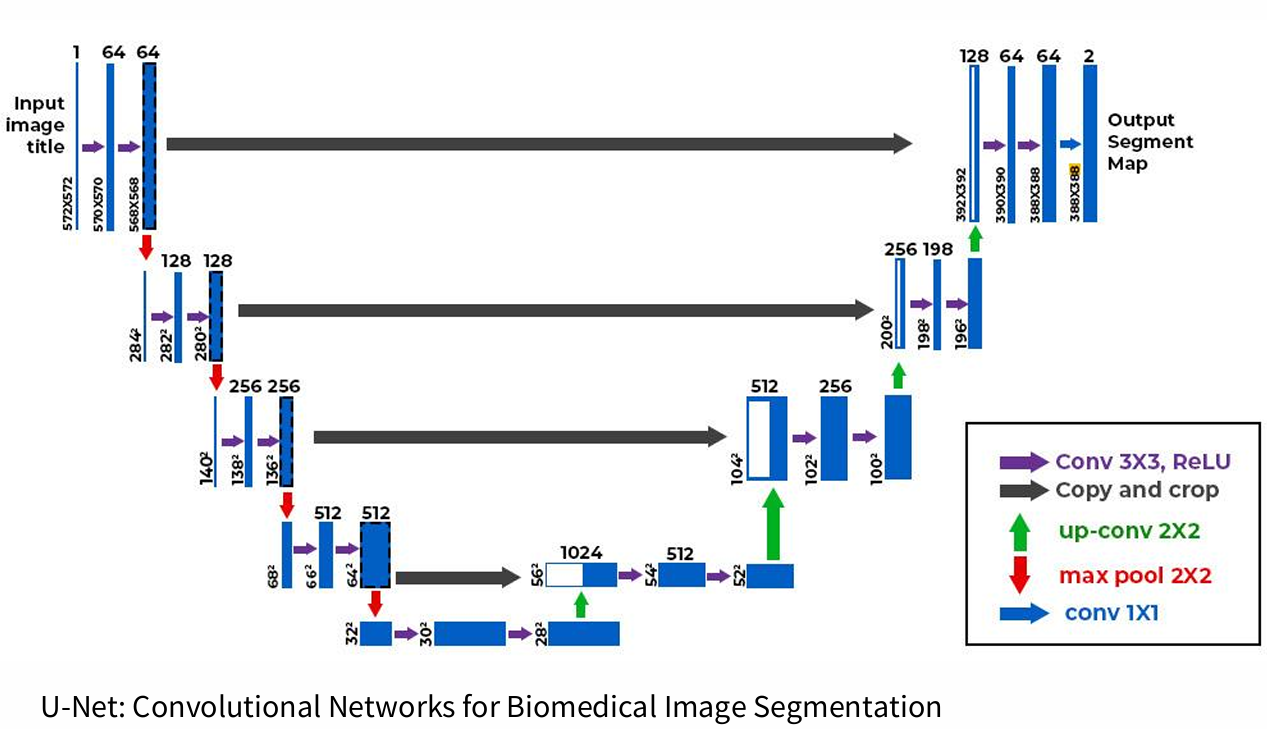
Unet: convolutional networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation
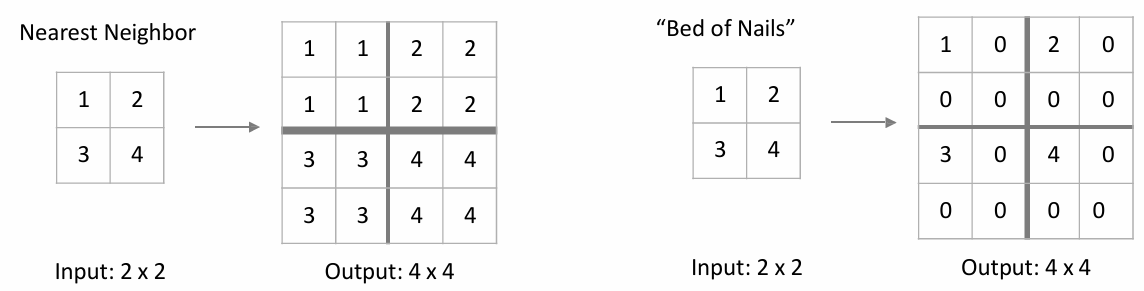
In-Network upsampling: Unpooling
Nearest Neighbor/ Bed of Nails
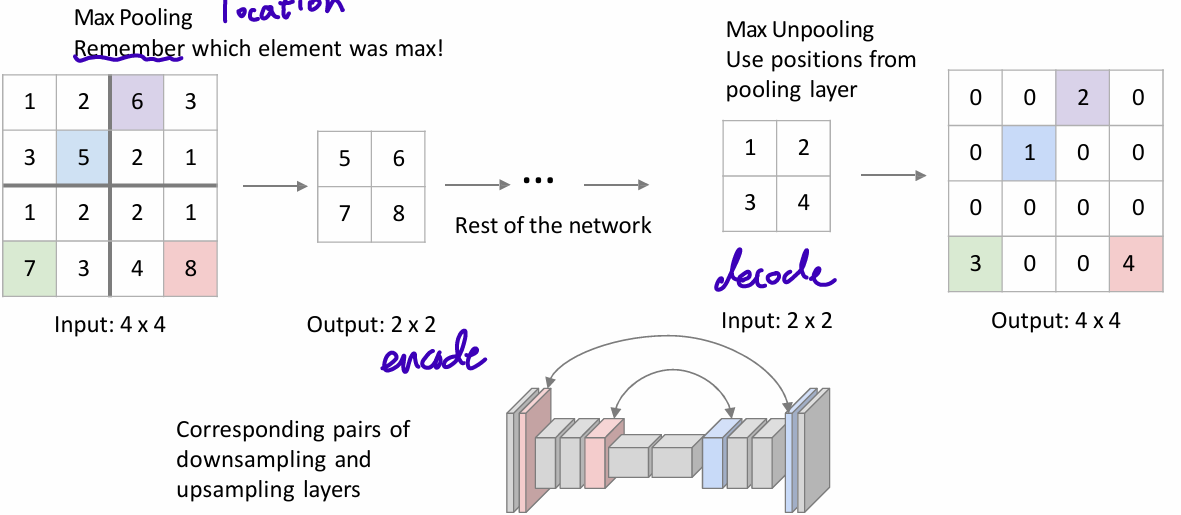
Max Unpooling
no learning process; not optimal, not using data
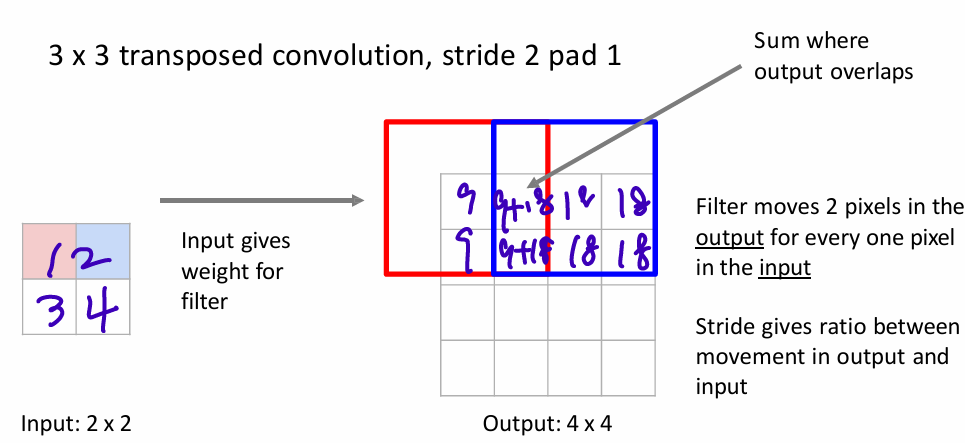
Learnable Upsampling: Transposed Convolution
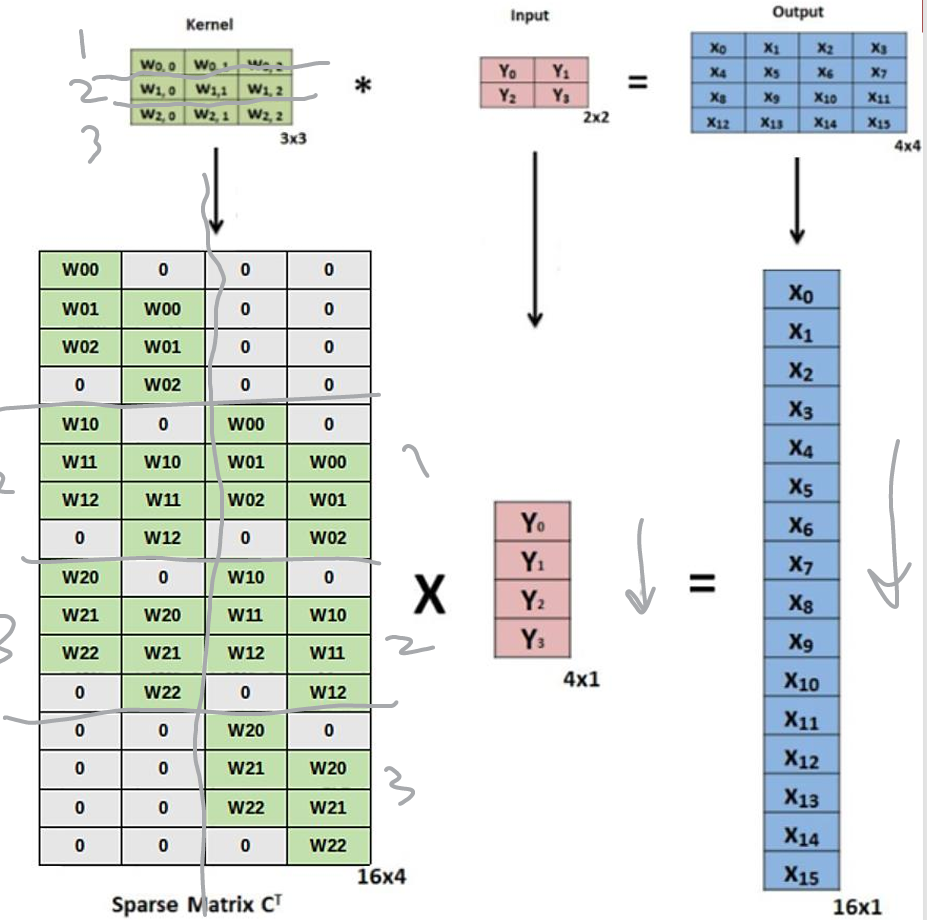
5. Convolution as Matrix Multiplication
- 1D Example
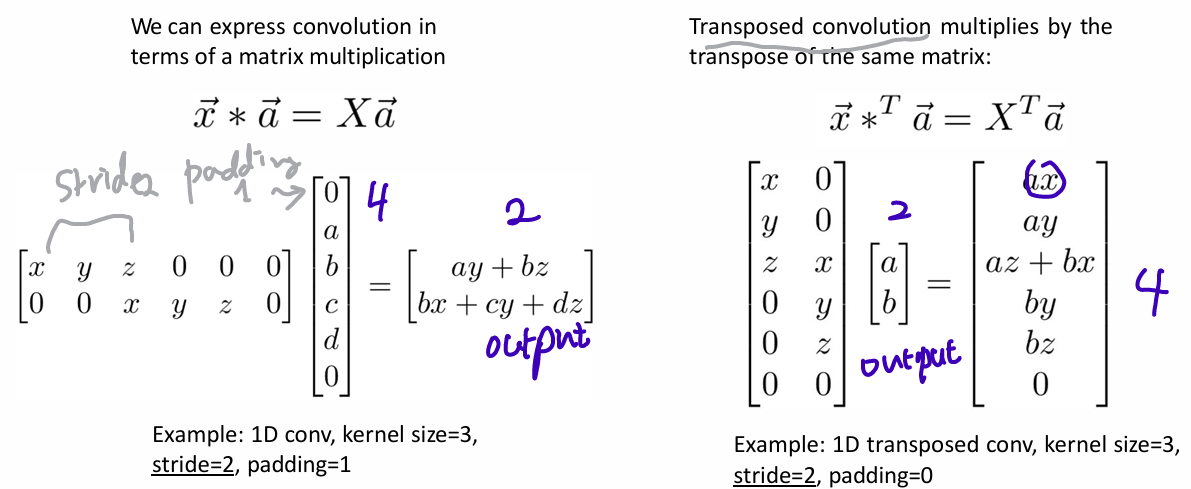
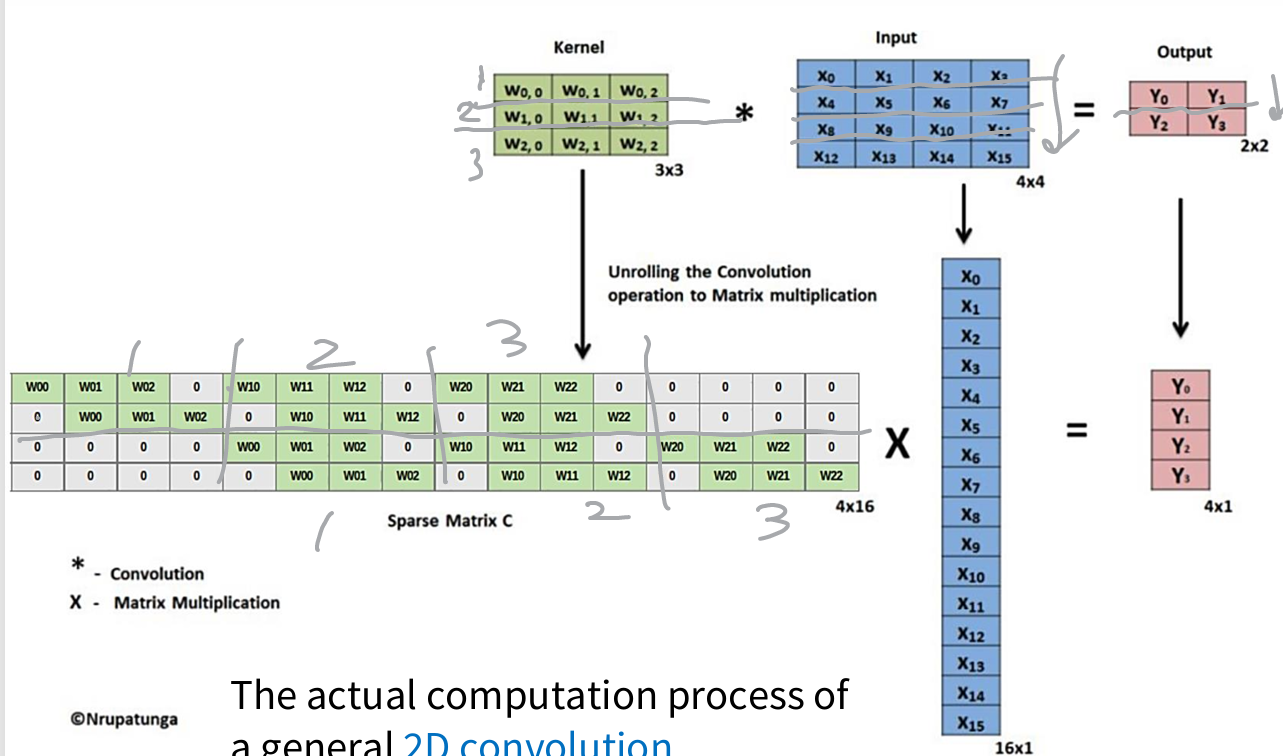
- 2D Example
The actual computation process of a general 2D convolution
;stride 1, padding 0, kernel 3x3
The actual computation process of a 2D Transpose Convolution