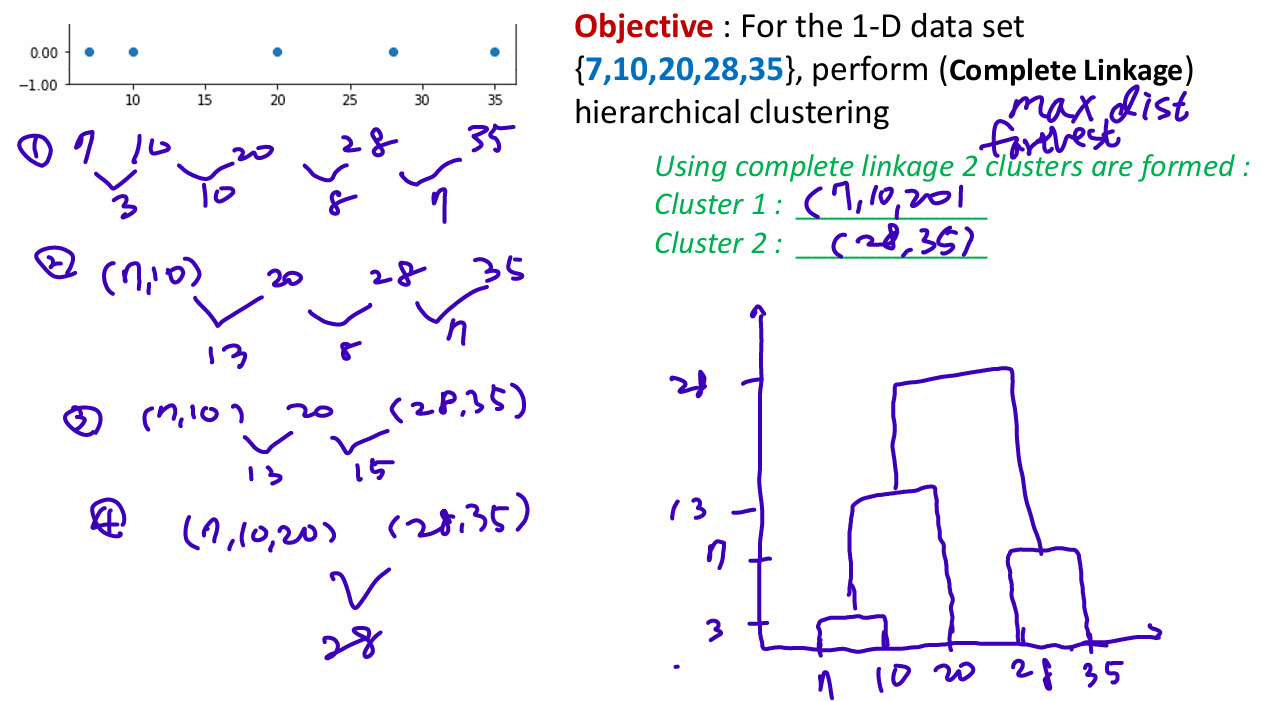
Week13-1. Unsupervised Learning: K-Means Clustering
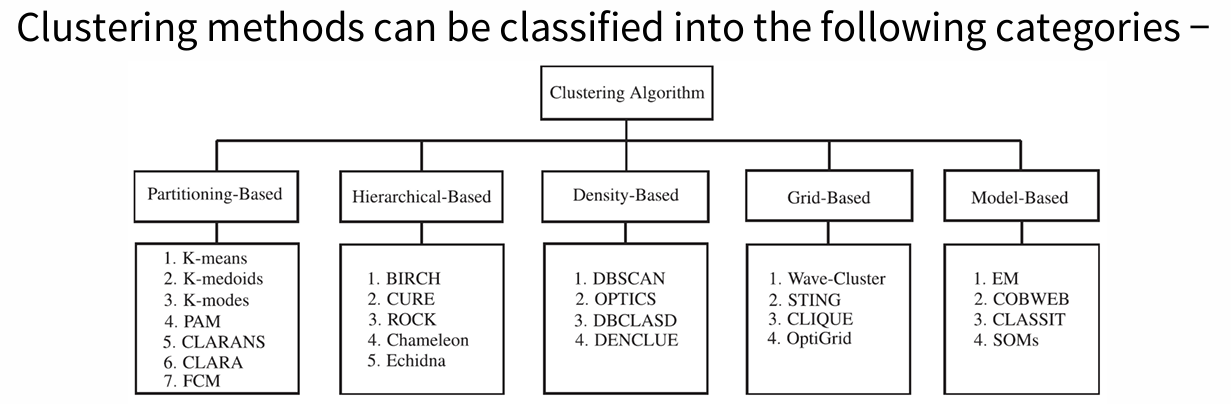
Clustering Methods
•Hard clustering (Crisp clustering)
Create non-overlapping clusters
Each object is assigned to only one cluster
• Soft clustering (Fuzzy clustering)
It is also possible to create overlapping clusters
An individual can be a probabilistic assignment to multiple clusters
• Partitioning Method
Divide the entire data area at the same time by specific criteria
Each individual yields a result belonging to one of a predefined number (K) of clusters
+)For a given number of partitions (say k), the partitioning method will create an initial partitioning.
Then it uses the iterative relocation technique to improve the partitioning by moving objects from one group to other
• Hierarchical Method
A method of gradually tying objects together from the closest group
Generates not only clustering results but also procedural dendrograms in which similar entities are combined
Partitioning Method
K-Means Clustering
Each cluster has one centroid, each object assigned to the nearest centroid, the number of clusters K is determined in advance
K-Means Clustering Execution Procedure
• Step 1: Set K initial centroids (results can differ due to it)
• Step 2: Repeat the following procedure
1. Build clusters by assigning all objects to the nearest cluster centroid
2. Reset the cluster center using assigned entities
3. Termination condition: The algorithm ends when the positions of all cluster centroids do not change and the cluster assignment results of all objects do not change.
K initial controids 고르고 가장 가까운 centroid가도록 cluster만듦, center 다시 찾음, centeroid 안 바뀌거나, cluster 요소 안 바뀔 때 멈춤
Questions
- The risk of random initial center point setting
;not necessarily find optimal configuration
place first center on top, place second center on datapoint far away from first center
Do many runs of k-means, each from different random start configuration
Week13-2. Unsupervised Learning: Hierachical Clustering
This method creates a hierarchical decomposition of the given set of data
objects.
• Agglomerative Approach (bottom-up)
• Divisive Approach (top-down)
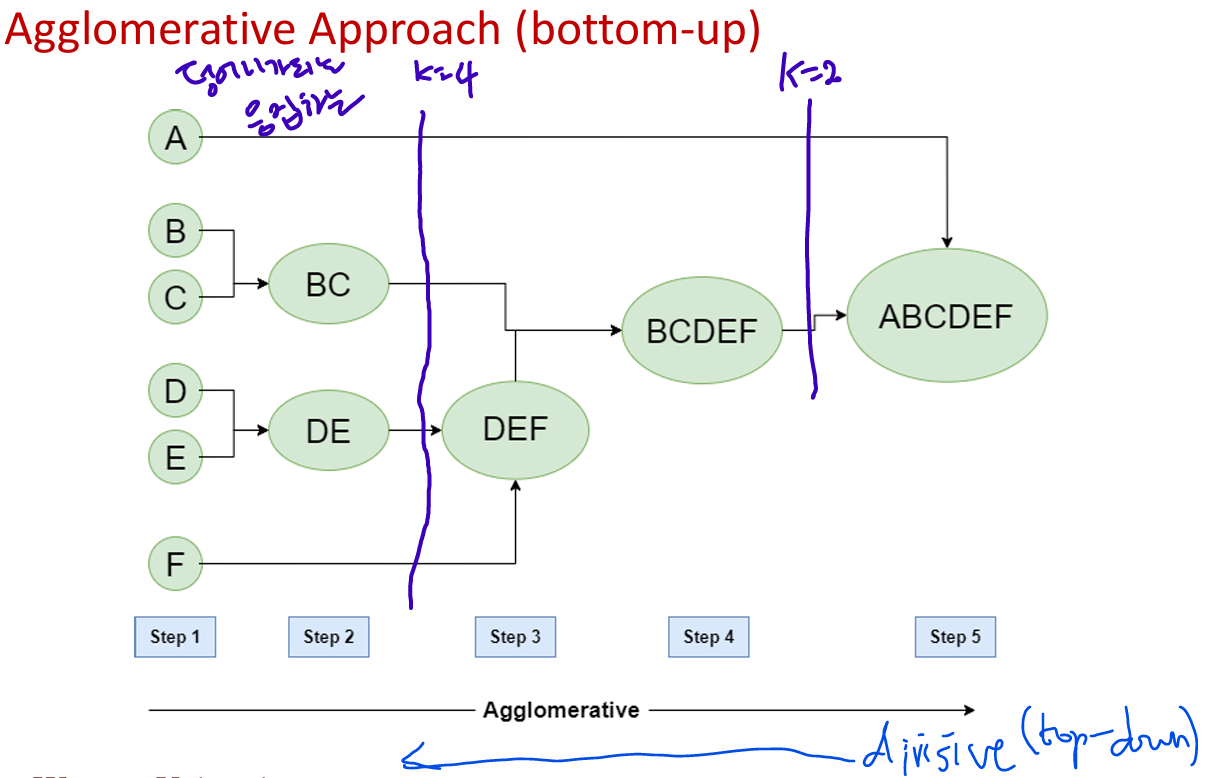
Agglomerative: Hierarchical Clustering
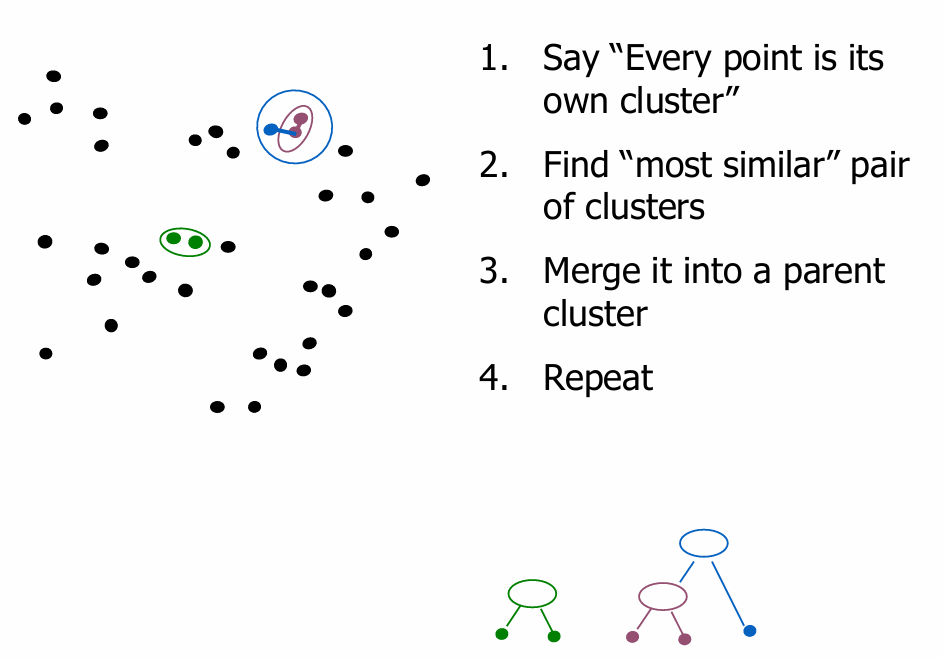
similarity: Min distance between points in clusters, Max distances between points in clusters, Average distance between points in clusters
Distances between Clustering
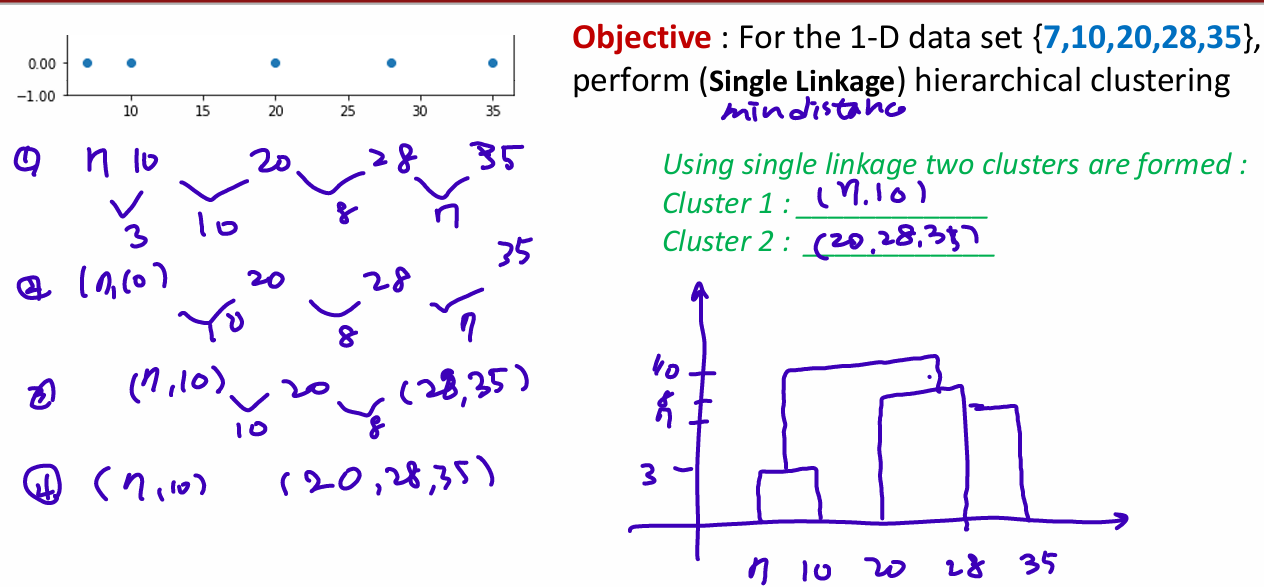
- Closest pair(single-link clustering):
가장 가까운 부분끼리
- Farther pair(complete-link clustering):
가장 먼 부분끼리 거리
-
Average of all pairs
-
Comments: requires a hierarchy, creation of a taxonomy (분류학)
if you want k groups, just cut the (k-1) longest links
no real statistical foundation to this
Week 14. Unsupervised Learning: Clustering Performance Evaluation
Cluster Validation
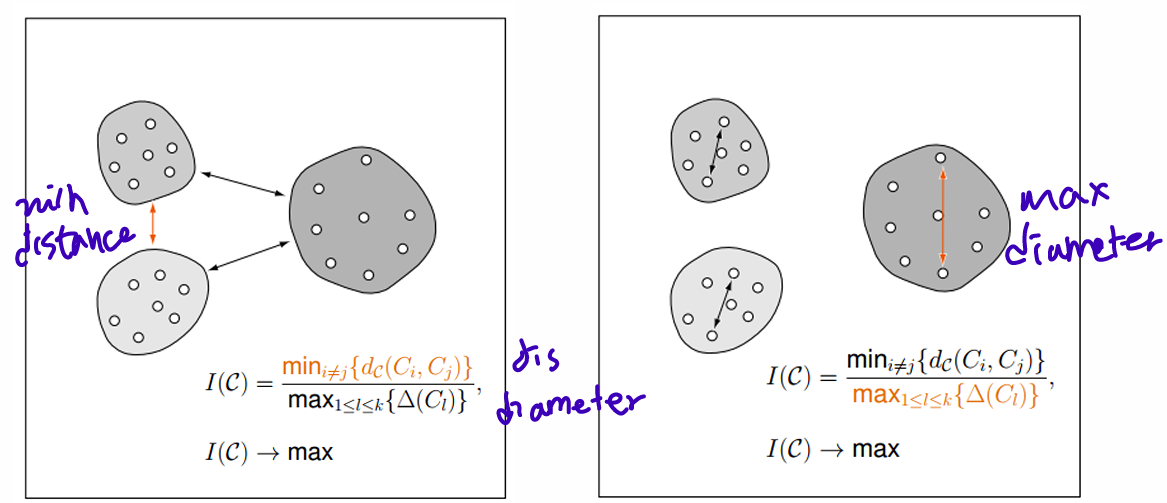
Clustering Validation measures 1: Dunn Index
(min distance within a cluster) / (max cluster diameters)
higher Dunn index value, better clustering
거리 길고 cluster 지름 작아야 better clustering
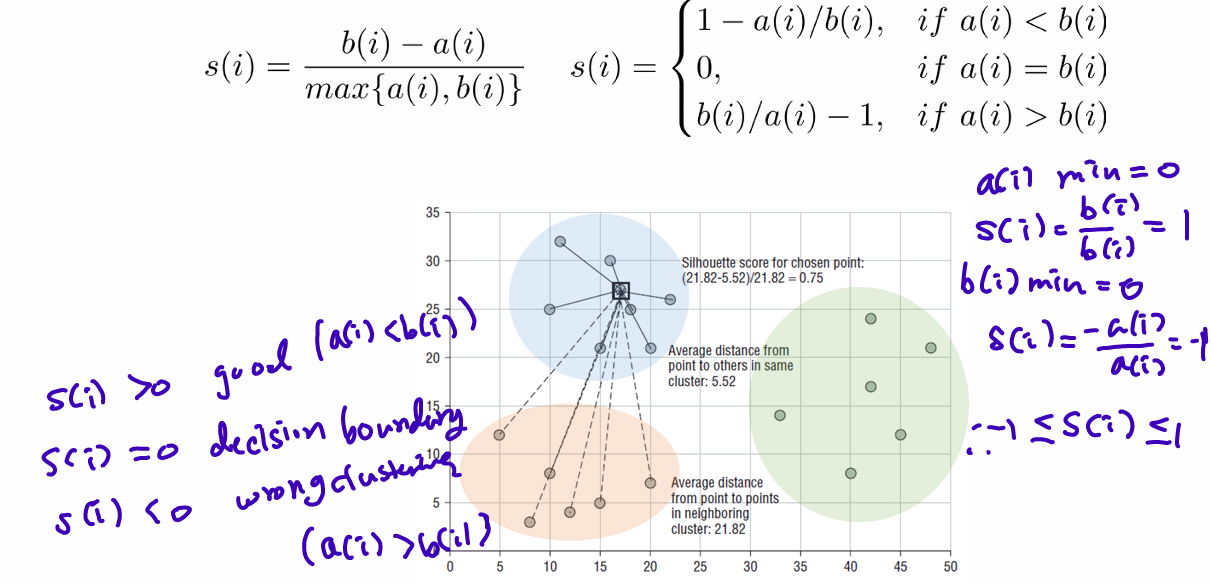
Clustering Validation measures 2: Silhouette
a(i): average distance from i to all in same cluster
b(i): smallest of average distances between i and other clusters
s(i) > 0 good (ai > bi)
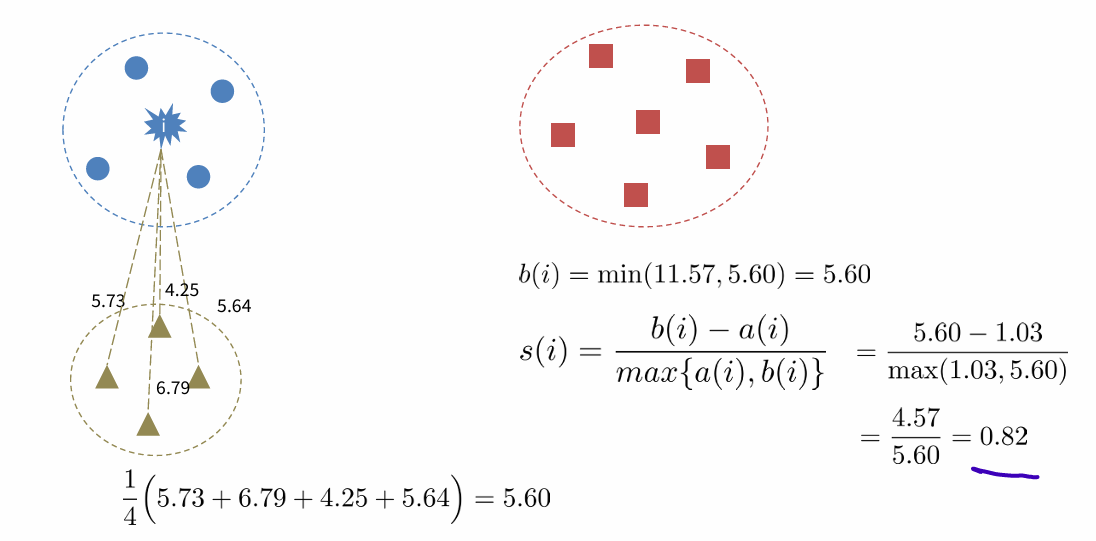
- The Silhouette measure for the entire dataset = average of the Silhouette measures fro individual samples
