📒 CSS
📕 CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
1. CSS 문법
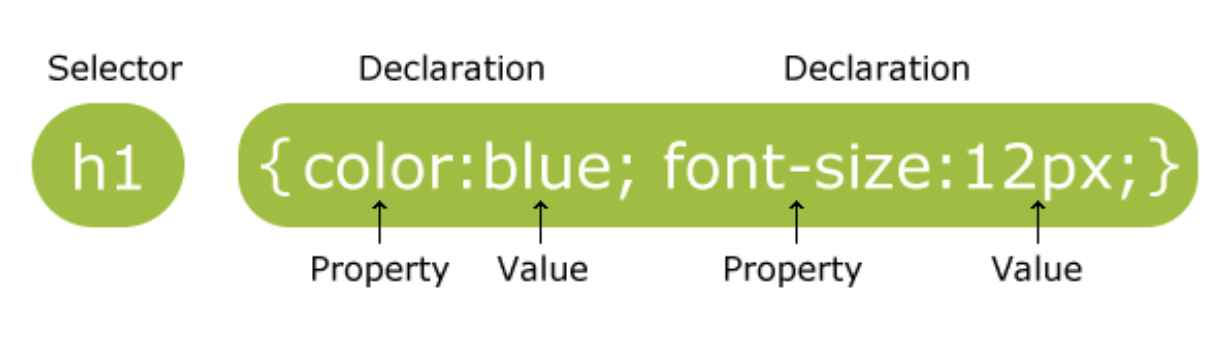
1) 문법 형식
- 선택자와 선언부로 구분
- 선택자 : CSS 스타일을 적용할 HTML 태그(요소)를 선택하는 영역
- 선언부 : 선택자에서 선택한 태그에 적용할 스타일을 작성한 영역 (속성 : 값으로 구성)
2) 주석
- /* */ 주석
- 웹 브라우저에서 소스 보기로 보면 주석 내용 노출
2. CSS 적용
1) internal 스타일
- 적용하려는 태그가 포함된 html 파일에서 사용
- HTML 파일 내부에 CSS 코드를 작성
- HTML 제공하는 style 태그의 콘텐츠로 CSS 코드 작성 (head 태그 안에 위치)
- 형식 : <style> css 코드 </style>
2) external 스타일
- html 파일과 다른 파일에서 css 적용 (*.css 외부 파일 사용)
- CSS 코드를 작성하는 별도 파일을 만들어 HTML 문서와 CSS 연결
- 별도로 작성한 CSS 파일을 HTML 문서에서 연결할 때 link 태크 이용
- 성능 면에서 가장 좋은 CSS 적용 방법
- 형식 : <link rel="stylesheet" hrefe="css 파일 경로">
3) inline 스타일
- 적용하려는 태그 내에서 직접 style="css" 형식 사용
- HTML 태그에서 사용할 수 있는 style 속성에 CSS 코드 작성
- 태그에 직접 CSS 코드 작성하는 방식 (CSS 문법의 선택자 부분 필요X)
- 형식 : <태그 style="CSS 코드"></태그>
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>CSS 실습</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/external.css">
<style>
.internal{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello</p>
<!-- inline style 적용 -->
<p style="color:blue;">inline Style</p>
<!-- internal style 적용: -->
<p class="internal">internal style</p>
<!-- external style 적용: 외부 파일로 CSS 정의 -->
<p id="external">external style</p>
</body>
</html>📋 실행 📋

3. CSS 특징
1) 특징
- 풍부한 스타일 효과
- 사용의 편리함
- cascading
- 작은 파일 크기
2) 장점
- html에 비해 훨씬 많은 표현 형식 기능을 제공
- 사이트 내의 모든 페이지에 연결된 하나의 외부 스타일시트에 모든 스타일을 정의
- 재사용 및 유지보수 향상
📕 CSS 선택자
1. 기본 선택자
1) 전체 선택자
- html 문서 안의 모든 태크 선택 (*)
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>전체 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> *{ color:red; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>전체 선택자 실습</h1> <p>모든 태그의 color 속성에 red를 적용한다.</p> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 📋 코드 📋
2) 태그 선택자
- 특정한 html 태그 선택 (태그)
- 한 번에 여러개 선택시 ,(쉼표) 사용
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>태그 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* h1 태그의 color 속성에 red를 적용한다.*/ h1{ color:red; } /* p 태그의 color 속성에 blue를 적용한다.*/ p{ color:blue; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>태그 선택자 실습</h1> <p>특정 태그의 color 속성에 CSS를 적용한다.</p> </body> </html>
3) 아이디 선택자
- 특정한 id 속성을 가지고 있는 태그 선택 (#id)
- id 중복 불가
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>아이디 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> #one { color: red; } #two { color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="one"> <h1>Hello</h1> <p>Hello2</p> <h2>Hello3</h2> </div> <div id="two"> <h1>world</h1> <p>world2</p> <h2>world3</h2> </div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

4) 클래스 선택자
- 특정한 class 속성을 가지고 있는 태그 선택 (.class)
- class 중복 가능
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>클래스 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* 클래스가 select인 태그 선택 */ .select { color: red; } /* 다음 3가지 경우가 모두 다른 의미이다. */ .select .aaa { /* class 가 select 자손인 aaa 인경우 */ color: red; } .select.aaa { /* class 가 select이면서 aaa 인경우 */ background-color: yellow } .select , .aaa { /* class 가 select 또는 aaa 인경우 */ font-size: 30px } </style> </head> <body> <ul> <li class="select aaa">홍길동</li> <li>이순신</li> <li class="select bbb">유관순</li> <li>강감찬</li> <li class="aaa">강감찬</li> <li> <ul class="select"> <li>AAA</li> <li class="aaa">BBB</li> <li>CCC</li> </ul> </li> </ul> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

5) 속성 선택자
- 특정 속성의 존재 유무와 속성값을 이용하여 선택할 때 사용
- 선택자[속성] : 특정한 속성이 있는 태그 선택
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>속성 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> [id]{ color:red; } a[id]{ background-color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 id="one">홍길동</h1> <h2>이순신</h2> <h3 id="two">유관순</h3> <h2>강감찬</h2> <h2>윤봉길</h2> <a href="#" id="link">go</a> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 선택자[속성=값][속성=값] : 특정한 속성 안의 값이 특정 값과 같은 문서 객체 선택
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>속성 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> [id="two"]{ color:red; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 id="one">홍길동</h1> <h2>이순신</h2> <h3 id="two">유관순</h3> <h2>강감찬</h2> <h2>윤봉길</h2> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 선택자[속성^=값] : 속성 안의 값이 특정 값으로 시작하는 태그 선택
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>속성 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> a[href^='https']{ color:red; } </style> </head> <body> <a href="http://naver.com">one</a><br/> <a href="https://naver.com" target="_blank">two</a><br/> <a href="https://daum.net">three</a><br/> <a href="http://daum.net" target="_blank">four</a><br/> <a href="https://korea.com">five</a><br/> <a href="http://korea.com" target="_blank">six</a><br> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 선택자[속성$=값] : 속성 안의 값이 특정 값으로 끝나는 태그 선택
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>속성 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> a[href$='net']{ color:red; } </style> </head> <body> <a href="http://naver.com">one</a><br/> <a href="https://naver.com" target="_blank">two</a><br/> <a href="https://daum.net">three</a><br/> <a href="http://daum.net" target="_blank">four</a><br/> <a href="https://korea.com">five</a><br/> <a href="http://korea.com" target="_blank">six</a><br> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 선택자[속성*=값] : 속성 안의 값이 특정 값을 포함하는 태그 선택
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>속성 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> div[class*='man']{ color:red; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="man-news">man-news</div> <div class="milk man">milk man</div> <div class="letterman2">letterman2</div> <div class="newmilk">newmilk</div> <div class="superman">superman</div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 선택자[속성][속성=값]
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>속성 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> div[id][class$='man']{ color:red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="one">man-news</div> <div class="milk man">milk man</div> <div class="letterman2">letterman2</div> <div class="newmilk">newmilk</div> <div id="two" class="superman">superman</div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 선택자[속성!=속성값]
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>속성 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* [속성명 |= "속성값"] 선택자는 언더바_ 및 공백이 없는 합성어는 선택할 수 없습니다. */ div[class |='en']{ color:red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="one">man-news</div> <div class="en" >milk man</div> <div class="kr en">letterman2</div> <div class="kr">newmilk</div> <div id="two" class="en-UK">superman</div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 선택자[속성~=속성값]
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>속성 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* "값"과 일치하는 속성값이 면 선택. 속성값은 공백으로 구분한 여러 개의 속성값 들 중 1개가 될 수 있음 */ div[class ~='en']{ color:red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="one">man-news</div> <div class="en" >milk man</div> <div class="kr en">letterman2</div> <div class="kr">newmilk</div> <div id="two" class="en-UK">superman</div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

2. 조합 선택자
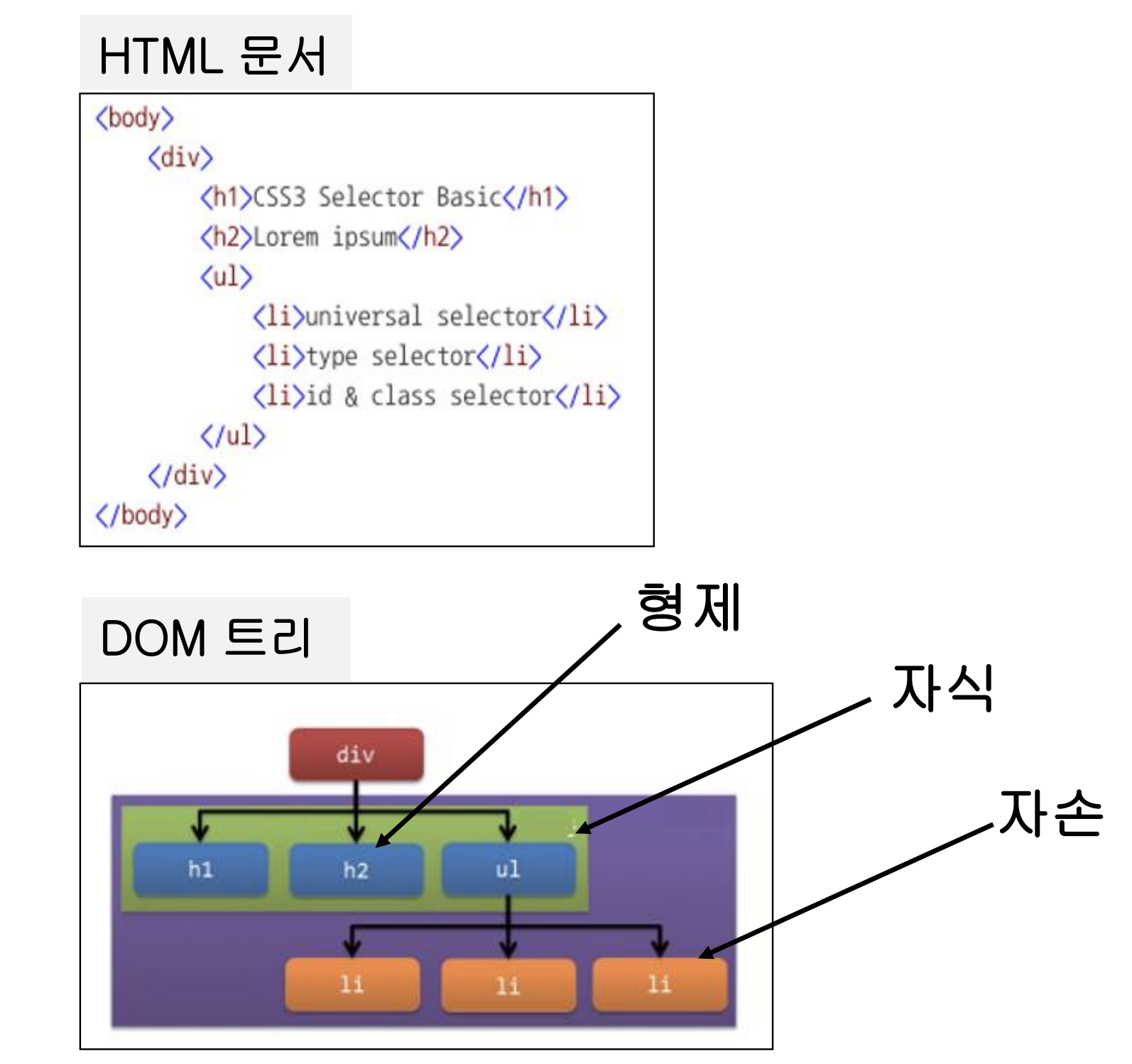
1) 자식 선택자
- 부모 선택자(특정한 태그)의 자식 요소를 선택할 때 사용 (부모선택자 > 자식선택자)
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>자식 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> #one > h1 { color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="one"> <h1>Hello</h1> <p>Hello2</p> <div> <h1>world</h1> </div> </div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 📋 코드 📋
2) 하위 선택자 (자손 선택자)
- 부모 선택자(특정한 태그)의 자손 요소를 선택할 때 사용 (부모선택자 자식선택자)
- 공백으로 구분
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>자손 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> #one h1 { color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="one"> <h1>Hello</h1> <p>Hello2</p> <div> <h1>world</h1> </div> </div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

3) 인접 형제 선택자
- 인접한 바로 뒤의 형제 요소를 선택할 때 사용 (선택자 + 형제 선택자)
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>형제 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* 인접 형제 선택자는 + 기호를 사용하며, A와 B가 같은 계층에 있을 때 A 바로 뒤에 B를 선택자로 지정합니다. */ h1 + h2 { color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>홍길동</h1> <h2>이순신</h2> <h3>유관순</h3> <h2>강감찬</h2> <h2>윤봉길</h2> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 📋 코드 📋
4) 일반 형제 선택자
- 뒤의 모든 형제 요소를 선택할 때 사용 (선택자 ~ 형제 선택자)
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>형제 선택자 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* 일반 형제 선택자는 ~ 기호를 사용하며, A와 B가 같은 계층에 있을 때 A 뒤에 있는 모든 B를 선택자로 지정합니다. */ h1 ~ h2 { color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>홍길동</h1> <h2>이순신</h2> <h3>유관순</h3> <h2>강감찬</h2> <h2>윤봉길</h2> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 📋 코드 📋
3. 의사코드 선택자 (가상 클래스/요소 선택자)
1) 링크 가상 클래스 선택자
- a 태그 사용시 상태에 따른 선택자
- a:link (한 번도 방문하지 않은 링크일 때 선택)
- a:visited (한 번이라도 방문한 적이 있는 링크일 때 선택)
2) 동적 가상 클래스 선택자
- a 태그 사용시 상태에 따른 선택자
- a:hover (요소에 마우스 올리면 해당 태그가 선택자로 지정)
- a:active (요소를 마우스로 클릭하고 있는 동안 해당 태그가 선택자로 지정)
- 📋 코드 📋
/* :link, :visited, :hover, :active, :focus */ <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>pseudo 실습</title> <style> a:link {color:red;} /* unvisited link */ a:visited {color:green;} /* visited link */ a:hover {color:yellow;} /* mouse over link */ a:active {color:blue;} /* selected link */ input:focus { background-color:lightblue } </style> </head> <body> <a href="#" target="_blank">This is a link</a><br> 이름<input type="text" name="username"><br> 나이<input type="text" name="userage"><br> 주소<input type="text" name="useraddress"><br> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

3) 입력 요소 가상 클래스 선택자
-
input:focus (입력 요소에 커서가 활성화되면 선택자로 지정)
-
input:enabled (상호작용 요소가 활성화되면 선택자로 지정함)
-
input:disabled (상호작용 요소가 비활성화되면 선택자로 지정함)
- disabled 속성이 사용되지 않은 상태면 default
-
input:checked (체크박스가 표시되어 있으면 선택자로 지정)
-
input:default (default 스타일 적용)
-
input:indeterminate (정확히 슈정할 수 없는 상태를 입력한 경우)
-
input:invalid (모든 입력 요소가 유효하지 않은 값)
-
input:valid (모든 입력 요소가 유효한 값)
-
input:in-range (정해둔 범위에 맞는 값을 입력했을 때)
-
input:out-of-range (정해둔 범위를 벗어나는 값을 입력했을 때)
-
input::placeholder (placeholder 속성이 있을 경우)
-
input:read-only (readonly 속성이 있을 경우)
-
input:read-write (readonly 속성이 없을 경우)
-
input:required (required 속성이 있을 경우)
-
input:optional (required 속성이 없을 경우)
-
📋 코드 📋
/* :enabled, :disabled */ <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> <style type="text/css"> input:disabled { background: green; } input:enabled { background: yellow; } </style> </head> <body> <input type="text" disabled="disabled" /> <input type="text" /> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋
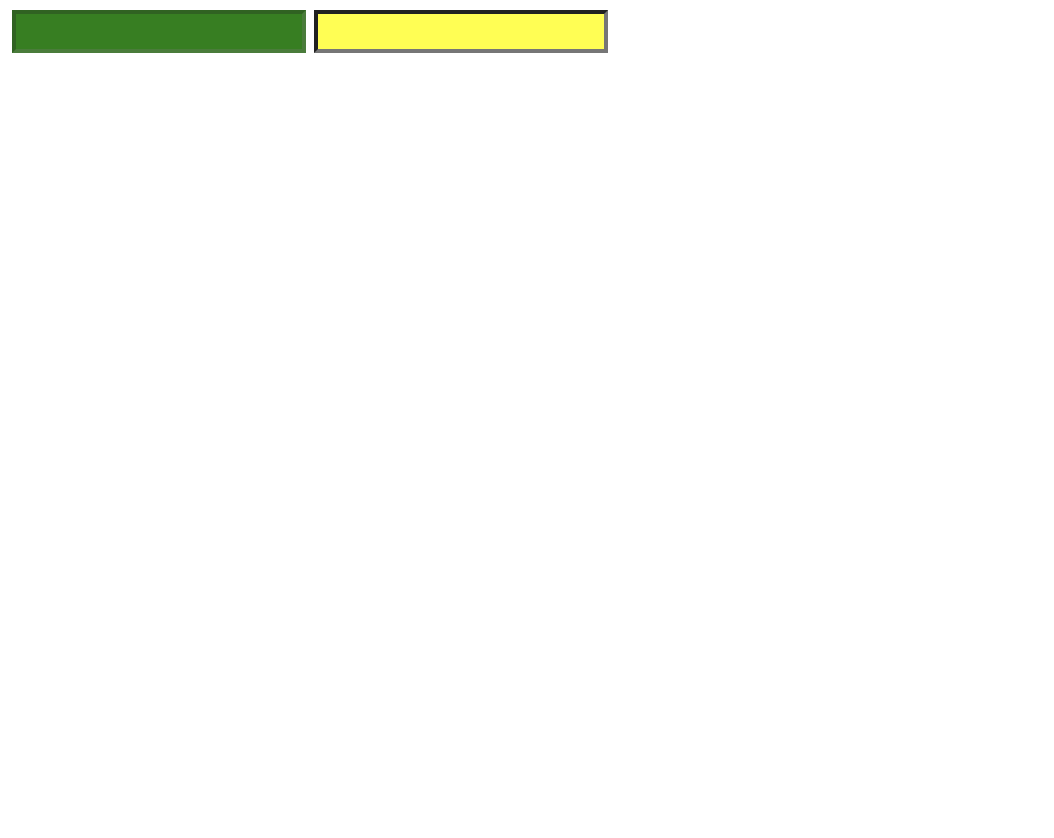

-
📋 코드 📋
/* :checked */ <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> <style type="text/css"> input:checked{ height: 50px; width: 50px; } </style> </head> <body> 사과<input type="checkbox" checked="checked" /> 배<input type="checkbox" /> 바나나<input type="checkbox" checked="checked" /> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

4) 구조적 가상 클래스 선택자
-
p:first-child (부모의 첫 번째 자식인 모든 p 요소 선택)
- p::first-letter (p 요소의 철번째 글자)
- p::first-line (p 요소의 첫번째 문장)
- p:first-of-type (부모의 첫 번째 자식 p 요소인 모든 p 요소 선택)
-
p:last-child (p 요소의 마지막 자식 요소를 선택자로 지정)
- p:last-of-type (부모의 마지막 자식 p 요소인 모든 p 요소 선택)
-
p:only-child (부모의 유일한 자식인 모든p 요소 선택)
- p-only-of-type (부모의 유일한 p 요소인 모든 p 요소를 선택)
-
p:ntn-child(n) (p 요소가 부모 요소의 자식 요소 중 n번째 순서가 맞으면 선택)
- p:ntn-last-child(n) (마지막 자식을 기준으로 부모의 n번째 자식인 모든 p 요소를 선택)
- p:ntn-last-of-type(n) (마지막 자식에서 부모의 n번째 p 요소인 모든 p 요소를 선택)
- p:ntn-of-type(n) (부모의 n번째 자녀인 모든 p 요소 선택)
-
📋 코드 📋
/* first-child */ <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>pseudo 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* p:first-child {} : p 태그의 부모기준으로 첫 번째 p태그 반환. */ p:first-child { color:red; } </style> </head> <body> <p>I am a strong man.</p> <p>I am a strong man.</p> <div> <p>div의 첫자식</p> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
/* last-child */ <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>pseudo 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* CSS3 모든 <p>태그중에서 마지막 <i> 태그를 지정한다. 즉, p태그가 부모인 모든 마지막 i태그를 선택한다. */ p > i:last-child { color:red; } </style> </head> <body> <p>I am a <i>strong</i> man. I am a <i>strong</i> man.</p> <p>I am a <i>strong</i> man. I am a <i>strong</i> man.</p> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
/* only-child */ <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>pseudo 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* CSS3 p:only-child{} : 유일한 자식으로 된 모든 p태그 선택 */ p:only-child{ color:red; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <p>1</p> </div> <div> <p>2</p> <p>3</p> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
/* ntn-child(n) */ <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> <style type="text/css"> table{ font-size:30pt; } /* CSS3 p:nth-child(n){} : n번째 자식으로 된 모든 p태그 선택 */ tr:nth-child(even) { background: #CCC } tr:nth-child(odd) { background: #999 } </style> </head> <body> <table> <tr> <td>111</td> <td>222</td> <td>333</td> <td>444</td> <td>555</td> </tr> <tr> <td>111</td> <td>222</td> <td>333</td> <td>444</td> <td>555</td> </tr> <tr> <td>111</td> <td>222</td> <td>333</td> <td>444</td> <td>555</td> </tr> <tr> <td>111</td> <td>222</td> <td>333</td> <td>444</td> <td>555</td> </tr> </table> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

5) not(선택자)
- p:not() (선택자에 해당되지 않는 항목 선택)
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>pseudo 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* CSS3 p:not(p:nth-child(n)){} : n번째 자식이 아닌 모든 p태그 선택 */ p:not(p:nth-child(even)){ color:red; } </style> </head> <body> <p>1</p> <p>2</p> <p>3</p> <p>4</p> <p>5</p> <p>6</p> <p>7</p> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 📋 코드 📋
6) :empty
-
p:empty (몸체(body)가 없는 항목 선택)
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> <style type="text/css"> p:empty{ width: 100px; height: 20px; background: #ff0000; } </style> </head> <body> <p></p> <p>홍길동</p> <p>이순신</p> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋
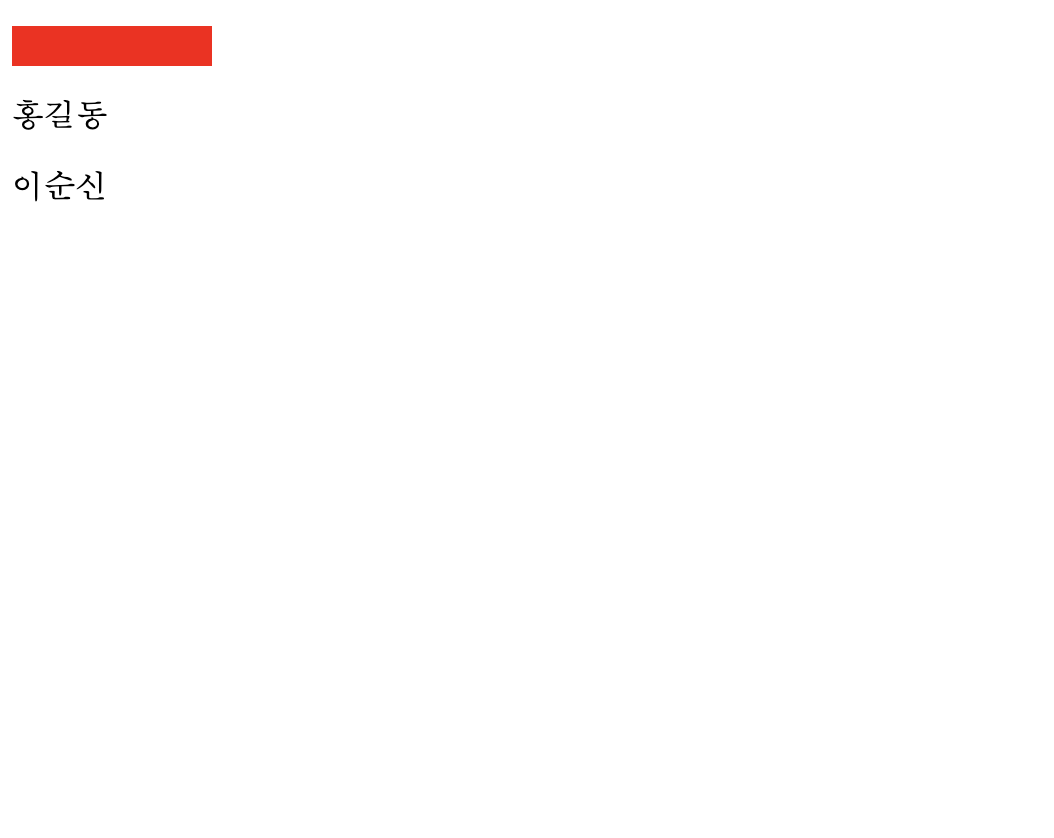

- 📋 코드 📋
7) ::after, ::before, ::placeholder
- p::after (콘텐츠 뒤의 공간 선택)
- p:: before (콘텐츠 앞의 공간 선택)
- 📋 코드 📋
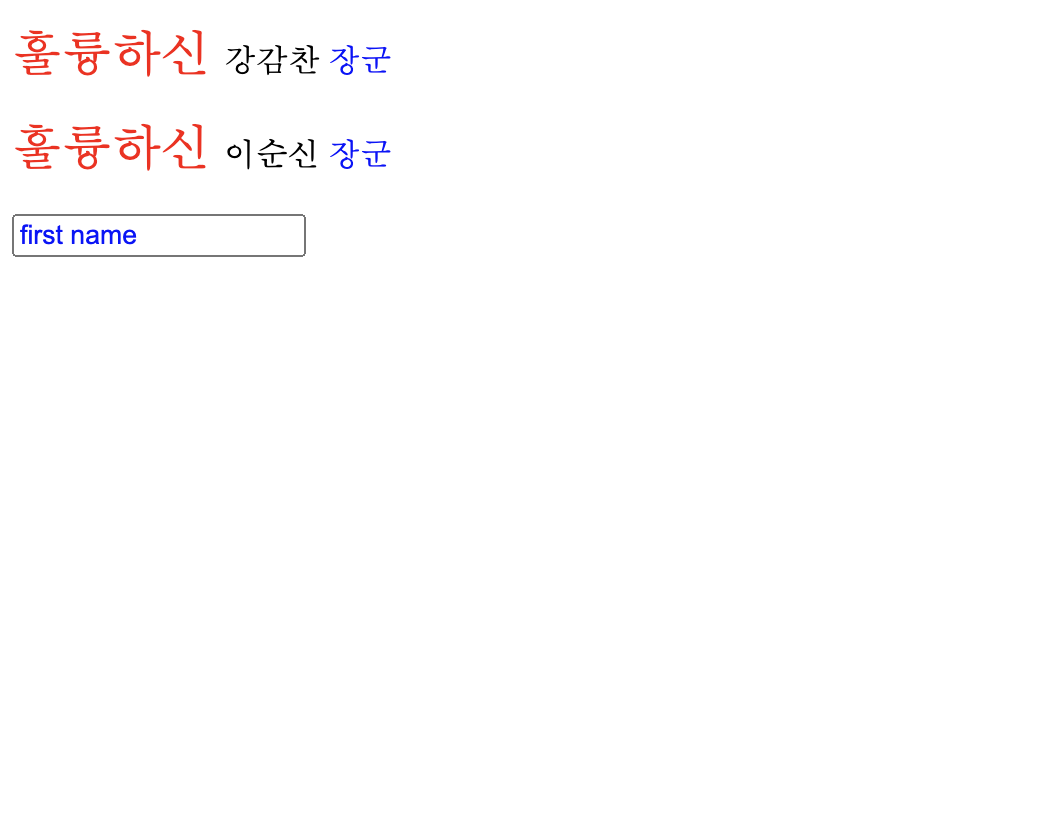
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> <style type="text/css"> p::before{ content:' 훌륭하신 '; color:red; font-size: 25px; } p::after{ content:' 장군'; color:blue; } ::placeholder{ color:blue; } </style> </head> <body> <p>강감찬</p> <p>이순신</p> <input type="text" placeholder="first name"> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋
📕 CSS 속성
1. CSS 특징
1) 크기 단위 (units)
- CSS에서 width, margin, padding, font-size 등에 사용
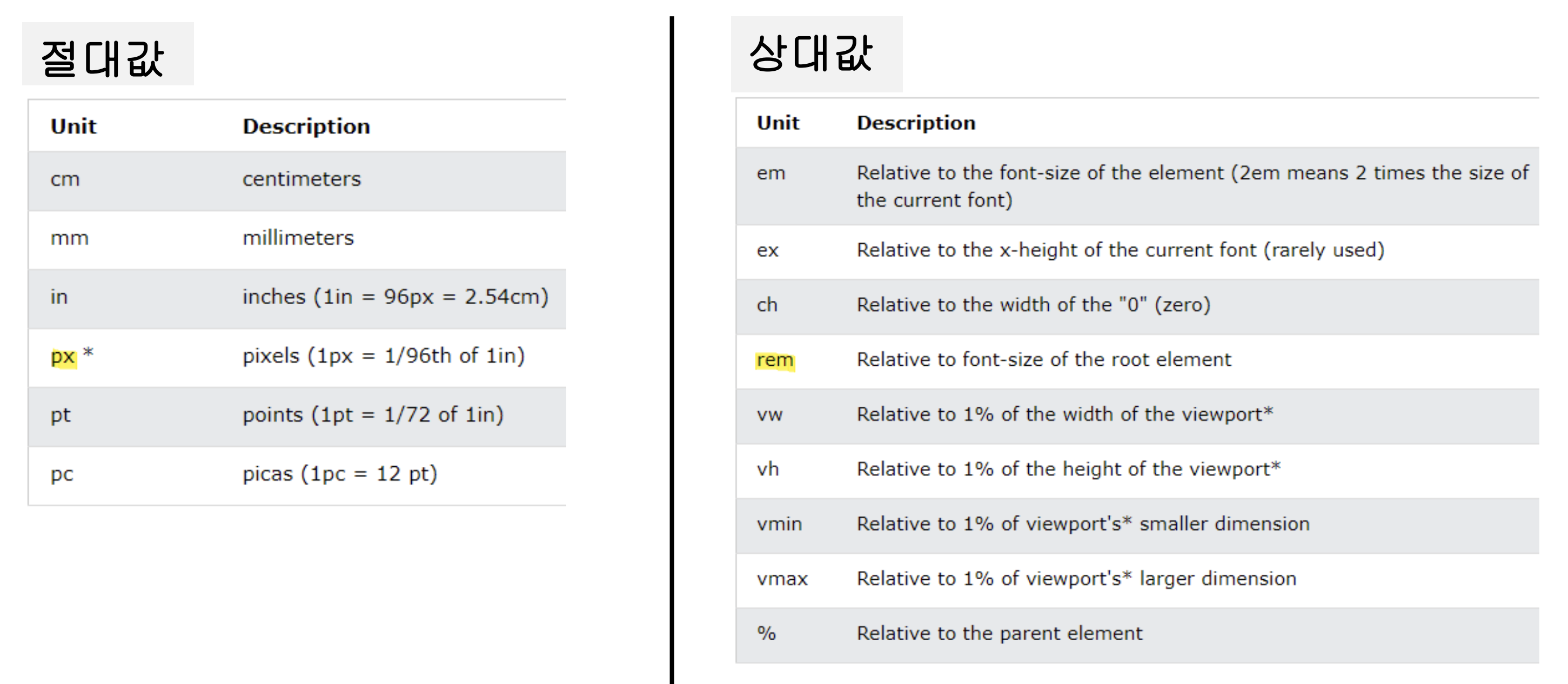
- 절대 단위 : 어떤 환경이라도 동일한 크기로 보이는 단위
- px (pixel) : 모니터 화면을 구성하는 사각형 1개의 크기
- 웹 브라우저에서 다른 단위로 값을 결정하더라도 px 단위로 환산되어 계산
- 상대 단위 : 부모 요소 또는 웹 브라우저의 창 크기에 따라 상대적으로 결정되는 단위
- % : 해당 속성의 상위 요소 속성값에 상대적인 크기
- em : 부모 요소의 텍스트 크기에 상대적인 크기
- rem : html 태그의 텍스트 크기에 상대적인 크기 (1rem = 16px)
- vw : 뷰포트의 너비 기준으로 상대적인 크기
- vh : 뷰포트의 높이 기준으로 상대적인 크기
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>CSS 크기 단위 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .basic{ font-size: 8px; } #_16px{ font-size: 16px; } #one{ font-size: 100%; } #two{ font-size: 200%; } #three1{ font-size: 1em; } #three2{ font-size: 1rem; } #four{ font-size: 2em; } #five{ font-size: 32px; } #six{ /* viewport width 1vw = 1% of viewport width */ font-size: 20vw; } </style> </head> <body class="basic"> <div>홍길동_default</div> <div id="_16px">홍길동_16px</div> <div id="one">홍길동_100%</div> <div id="two">이순신_200%</div> <div id="three1">유관순_1em</div> <div id="three2">유관순_1rem</div> <div id="four">강감찬_2em</div> <div id="five">윤봉길_32</div> <div id="six">강감찬_vw</div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>font-size 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> html{ font-size: 10px } #a li{ /* html 부모 지정하고 부모의 상대값으로 1.5배로 지정 상대값 문제점은 중첩되는 경우에 2번 적용됨 따라서 실습문제에서는 BBB가 AAA보다 글꼴크기가 더 커진다. 해결방법은 root em인 rem이다. 이것은 root인 html을 기준으로 상대값이 적용된다. */ /* em의 경우, 해당 단위가 사용되고 있는 요소의 font-size 속성값이 기준이 됩니다. rem에서 r은 root, 즉 최상위 요소의 font-size 속성값 의미합니다. */ font-size: 1.5em; } #b li{ font-size: 1.5rem; } </style> </head> <body> <p>Hello</p> <ul id="a"> <li>AAAA</li> <li>AAAA2</li> <li> <ul> <li>BBBB</li> <li>BBBB2</li> </ul> </li> </ul> <ul id="b"> <li>AAAA</li> <li>AAAA2</li> <li> <ul> <li>BBBB</li> <li>BBBB2</li> </ul> </li> </ul> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

2) 색상 표기법
- 색상 이름 영단어 표기 (red, black, blue 등)
- 색상 16진수 표기 (6비트 #RRGGBB, 3비트#RGB)
- 색상 10진수 표기 (RGBA 값)
- alpha : 투명도 (0이면 완전 투명, 10이면 완전 불투명)
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>CSS 색상 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> #one{ color:red /* 120가지 색상이 영단어로 제공됨 */ } /* #ffffff: 흰색 #000000: 검정 */ #two{ color:#00ff00; /* 16진수 표기 */ } #three{ color:rgb(0,0,255); /* 10진수 표기 red, green, blue 3가지 색상 조합*/ } /* red, green, blue 3가지 색상 조합과 alpha 값 alpha는 0~1 까지 사용 1은 완전 불투명 0은 완전 투명 */ #four{ color:rgba(0,0,255,0.3); } </style> </head> <body> <div id="one">홍길동</div> <div id="two">이순신</div> <div id="three">유관순</div> <div id="four">강감찬</div> <div id="five">윤봉길</div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

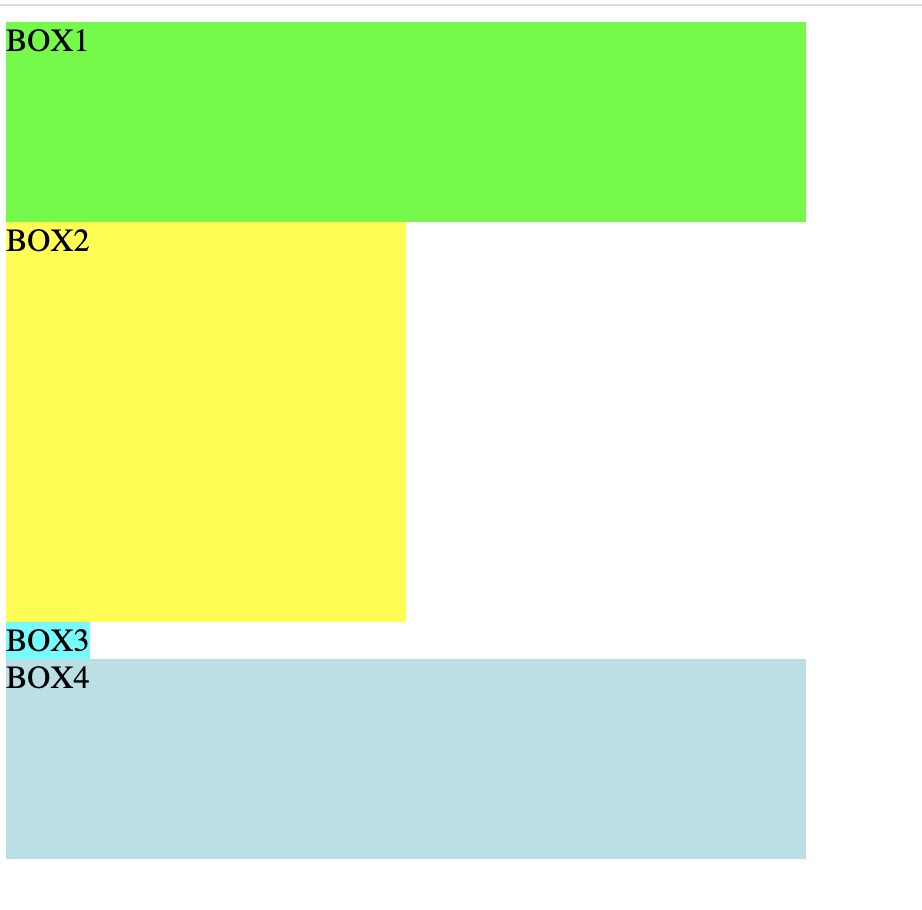
3) display 속성
- HTML 태그가 기본적으로 가지고 있는 박스 모델의 성격을 변경함
- 태그의 영역 표현 방식을 지정하는 속성
- none : 태그를 화면에서 보이지 않게 지정
- block : 태그를 block 형식으로 지정
- hn, p, div 태그 사용했을 때 요소의 너비가 콘텐츠 유무와 상관 없이 항상 가로 한 줄을 다 차지
- 태그 사용시 무조건 줄바꿈됨
- inline : 태그를 inline 형식으로 지정
- a, span, string 태그 사용했을 때 요소의 너비를 콘텐츠 크기만큼 차지
- 웹 브라우저의 수평 공간이 남아있으면, 한 줄로 배치
- padding, margin 좌우만 적용 (width, height X)
- inline-block : 태그를 inline-block 형식으로 지정
- img 태그 사용했을 때 요소의 너비가 콘텐츠 크기만큼 차지하지만, 그 외는 블록 성격
- inline처럼 배치되지만 block처럼 width와 height 적용이 가능하도록 할 때 사용
- width, height, margin, padding 속성 전부 적용
- margin은 상하좌우 모두 적용됨
// block -> inline
h1, h2{
display:inline;
}
// inline -> inline-block;
a{
display:inline-block;
}
// inline -> block
img{
display:block;
}- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>display 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* block태그인 p를 inline 태그로 표시 */ p{ display: inline; } div.two{ /* 영역유지 안됨 */ display:none; } /* inline 태그를 block 태그로 표시 */ span{ display: block; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="one"> <p>Hello</p> <p>world</p> </div> <div class="two"> <p>Hello2</p> <p>world2</p> </div> <p>Hello3<span>world3</span></p> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>display 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .box1{ background: lime; width:400px; height:100px } .box2{ /* display:inline; */ background: yellow; width:200px; height:200px } .box3{ background: aqua; /* inline 스타일 span는 width와 height 적용안됨 */ width:400px; height:100px } .box4{ /* inline-block 스타일은 inline이지만 width와 height 적용 가능 */ display: inline-block; background: powderblue; width:400px; height:100px } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box1">BOX1</div> <div class="box2">BOX2</div> <span class="box3">BOX3</span><br> <span class="box4">BOX4</span> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋
4) visibility 속성
- 요소를 보이거나 보이지 않게 지정하는 속성 (영역 유지됨)
속성
- visible : 태그를 보이게 만듦
- hidden : 태그를 보이지 않게 만듦
- collapse : table 태그를 보이지 않게 만듦
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>visibility 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> #box{ visibility: hidden; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <span>Dummy</span> <div id="box"> <span>죽는날 까지 하늘을 우러러 한점 부끄럼이 없기를, 잎새에 이는 바람에도 나는 괴로워했다.</span> </div> <span>Dummy</span> </div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>visibility 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* table이 제거시 영역도 같이 제거됨. */ td { visibility: collapse; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <span>Dummy</span> <table> <tr> <td>Test</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Test</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Test</td> </tr> </table> <span>Dummy</span> </div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

5) opacity 속성
- 요소의 투명도를 지정하는 속성
- 0 ~ 1 사이의 숫자 입력 (0 투명, 1 불투명)
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>opacity 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> #box{ opacity:0.2; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <span>Dummy</span> <div id="box"> <span>죽는날 까지 하늘을 우러러 한점 부끄럼이 없기를, 잎새에 이는 바람에도 나는 괴로워했다.</span> </div> <span>Dummy</span> </div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>RGBA</title> <style> div { width: 300px; } div.a1 { opacity: 1.0 } div.a2 { opacity: 0.8 } div.a3 { opacity: 0.6 } div.a4 { opacity: 0.4 } div.a5 { opacity: 0.2 } </style> </head> <body> <div class="a1">Hello</div> <div class="a2">Hello</div> <div class="a3">Hello</div> <div class="a4">Hello</div> <div class="a5">Hello</div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

2. 박스 모델 구성 속성
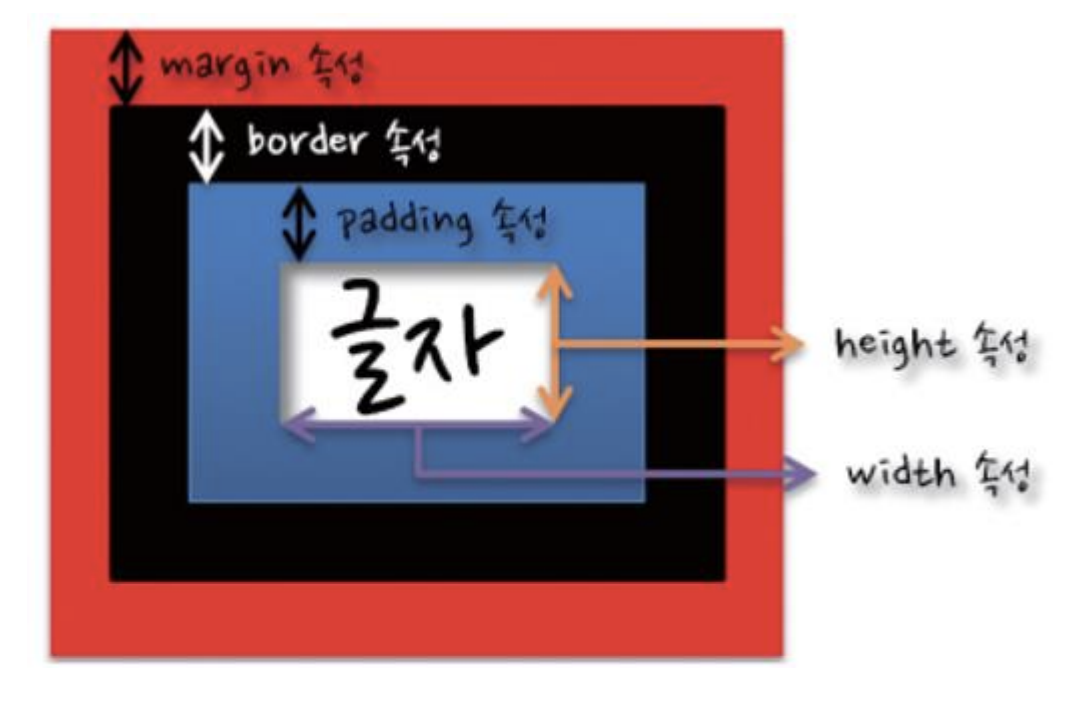
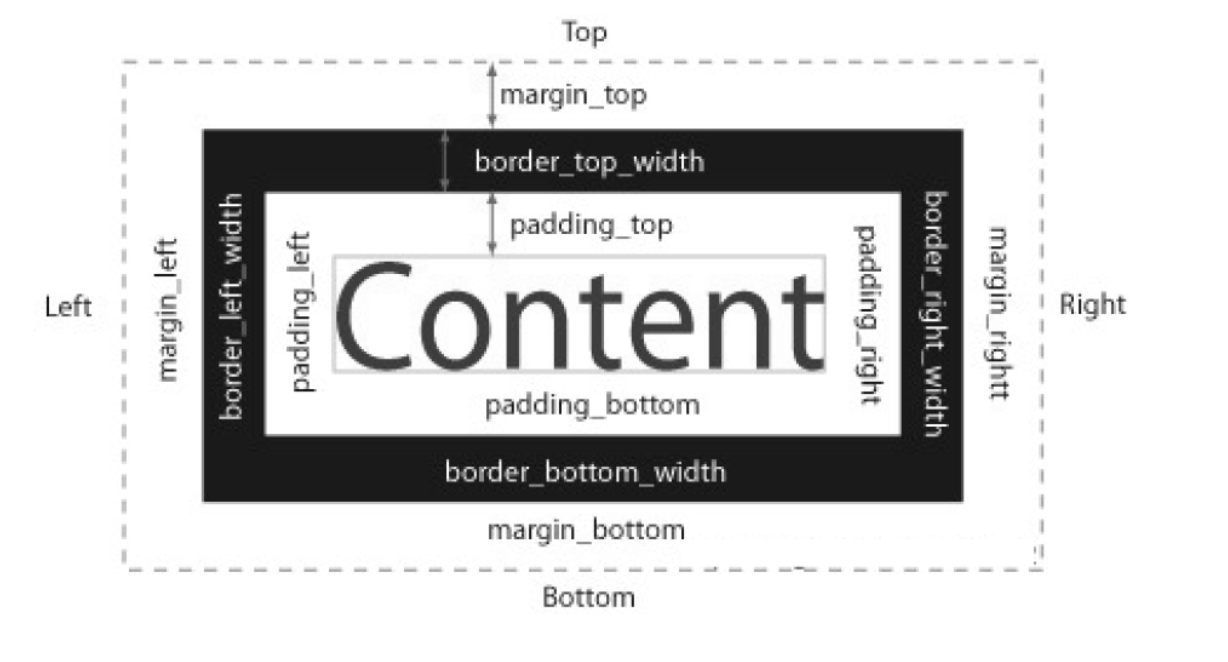
1) margin 영역
- 박스 모델에서 가장 외부에 있는 영역
- width 속성과 height 속성과 별도로 적용됨
- Box 사이의 여백을 제어하고, 그 값들의 길이 또는 %로 설정
- margin 겹침 현상
- margin 병합/상쇄
- 두 요소의 margin 영역이 중첩되면 더 큰 값을 가진 margin 영역으로 병합되어 출력
속성
- margin : auto (자동으로 중앙 정렬)
margin-top:<크기>;
margin-right:<크기>;
margin-bottom:<크기>;
margin-left:<크기>;
margin:<margin-top> <margin-right> <margin-bottom> <margin-left>;
margin:<margin-top> <margin-right> <margin-bottom>;
margin:<margin-top & margin-bottom> <margin-right & margin-left>;
margin:<margin-top & margin-right & margin-bottom & margin-left>;-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Box 모델 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* margin 은 바깥쪽 여백 */ div{ width:100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; } #one{ margin-top:10px; margin-right:10px; margin-bottom:10px; margin-left:10px; } #two{ margin:10px 10px 10px 10px; /* 상 우 하 좌 */ } #three{ margin:10px; } #four{ margin:10px 20px; /* 상하: 10px 좌우: 20 px*/ } #five{ margin:10px 20px 30px; /* 상: 10px 좌우: 20 px 하:30px */ } #six{ margin:10px 30px 0 40px; /* 상: 10px 우: 30px 하:0px 좌: 40px */ } </style> </head> <body> <div id="one">one</div> <div id="two">two</div> <div id="three">three</div> <div id="four">four</div> <div id="five">five</div> <div id="six">six</div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>margin:auto 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> div { width: 300px; margin: auto; border: 1px solid red; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>Use of the auto Value</h2> <p>You can set the margin property to auto to horizontally center the element within its container. The element will then take up the specified width, and the remaining space will be split equally between the left and right margins:</p> <div> This div will be centered because it has margin: auto; </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>margin:병합상쇄 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* 첫번째 박스에는 margin-bottom: 50px; 두번째 박스에는 margin-top: 100px; 두 박스 사이에는 50 + 100 = 150px의 margin이 적용 되어야 하지만, 마진 병합 현상으로 인해 둘 중 더 큰 속성값인 100px로 병합 되었다. */ div#a { width: 300px; height: 100px; background-color: red; margin: 50px; } div#b { width: 300px; height:100px; background-color: powderblue; margin: 100px; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>상하 블럭간의 margin는 값이 큰 margin으로 적용됨</h2> <div id="a">a</div> <div id="b">b</div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

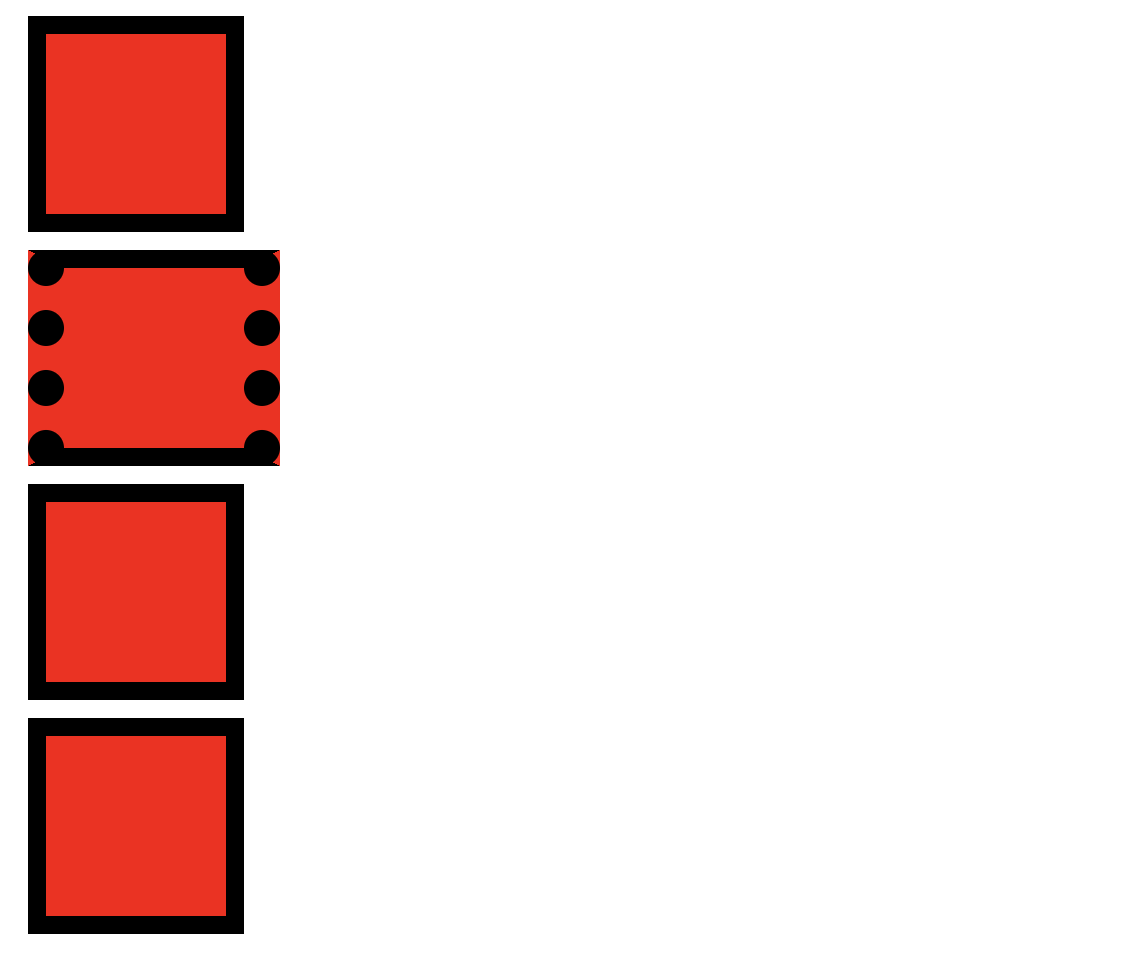
2) border 영역
-
요소의 테두리 (경계선)
-
padding과 content를 둘러싸고 있는 영역 (margin과 padding 사이)
-
속성
-
border-width : border의 너비 지정하는 속성 (테두리 굵기)
-
border-style : border의 스타일 지정하는 속성 (테두리 모양)
- none : 테두리X
- hidden : 테두리 숨김
- solid : 실선 테두리
- double : 이중 실선 테두리
- dotted : 점선 테두리
- dashed : dotted보다 긴 점선 테두리
- groove : 테두리가 파인 것 처럼 그림
- ridge : 테두리가 튀어나온 것처럼 그림
- inset : 테두리를 요소가 파인 것처럼 그림
- outset : 테두리를 요소가 튀어나온 것처럼 그림
-
border-color : border의 색상 지정하는 속성
-
border-radius : 박스 모서리 둥글게 설정하는 방법
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Box 모델 border 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> div{ width:100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; margin:10px; } #one{ border-top-width: 10px; border-right-width: 10px; border-bottom-width: 10px; border-left-width: 10px; border-top-style: solid; border-right-style: solid; border-bottom-style: solid; border-left-style: solid; border-color: black; } #two{ border-width: 10px 20px; border-style: solid dotted; border-color: black; } #three{ border-width: 10px; border-style: solid; border-color: black; } #four{ border: 10px solid black; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="one"></div> <div id="two"></div> <div id="three"></div> <div id="four"></div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>Box 모델 border-radius 실습</title> <style> .grad { width:300px; padding:10px; border:8px solid #0F0; } .grad2 { width:300px; padding:10px; border:8px solid #F00; border-radius: 20px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="grad"> <p>내 그늘 아래 그림자 길어질수록 <br> 나의 어지럼증 깊어져 <br> 세상이 몇바퀴씩 곤두박질치네요</p> </div> <br/> <div class="grad2"> <p>내 그늘 아래 그림자 길어질수록 <br> 나의 어지럼증 깊어져 <br> 세상이 몇바퀴씩 곤두박질치네요</p> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
3) padding 영역
- 요소의 내부 여백 담당
- content를 둘러싸고 있는 영역으로 투명함 (안쪽 여백)
- width 속성과 height 속성과 별도로 적용됨 (고정값, 상대값)
속성
padding-top:<크기>;
padding-right:<크기>;
padding-bottom:<크기>;
padding-left:<크기>;
padding:[padding-top] [padding-right] [padding-bottom] [padding-left];
padding:[padding-top] [padding-right] [padding-bottom];
padding:[padding-top & padding-bottom] [padding-right & padding-left];
padding:[padding-top & padding-right & padding-bottom & padding-left];- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Box 모델 padding 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* padding 은 안쪽 여백 */ div{ width:100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; margin:10px; border: 10px solid black; } #one{ padding-top:10px; padding-right:10px; padding-bottom:10px; padding-left:10px; } #two{ padding:10px 10px 10px 10px; /* 상 우 하 좌 */ } #three{ padding:10px; } #four{ padding:50px 20px; /* 상하: 50px 좌우: 20 px*/ } #five{ padding:50px 20px 30px; /* 상: 50px 좌우: 20 px 하:30px */ } </style> </head> <body> <div id="one">hello one</div> <div id="two">hello two</div> <div id="three">hello three</div> <div id="four">hello four</div> <div id="five">hello five</div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

4) content 영역
-
텍스트 및 이미지 등 실제 내용이 보여지는 곳
-
시작 태그와 종료 태그 사이에 사용된 콘텐츠가 사용된 영역
-
속성
-
width : content 영역의 너비 (border + padding + content 영역 포함)
-
height : content 영역의 높이
-
box-sizing : width, height 속성에 지정한 크기에 요소를 맞추기 위해 내부 content 영역의 너비와 높이 자동 조절
- content-box (width, height 속성 적용 범위를 content 영역으로 제한, default값)
- border-box (width, height 속성 적용 범위를 border 영역으로 제한)
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Box 모델 width-height 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> div#a{ width:100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; } div#b{ background-color: powderblue; } </style> </head> <body> width 속성과 height 속성은 실제 내용을 감싸는 영역의 크기를 지정하는 속성이다. 지정하지 않으면 실제 요소의 크기로 설정(고정값, 상대값)된다 <div id="a">a</div> <div id="b">b</div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>BOX 모델 box sizing 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> #one { width: 300px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid blue; box-sizing: content-box; } #two { width: 300px; height: 100px; padding: 50px; border: 1px solid red; box-sizing: content-box; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="one">hello</div> <div id="two">hello</div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋
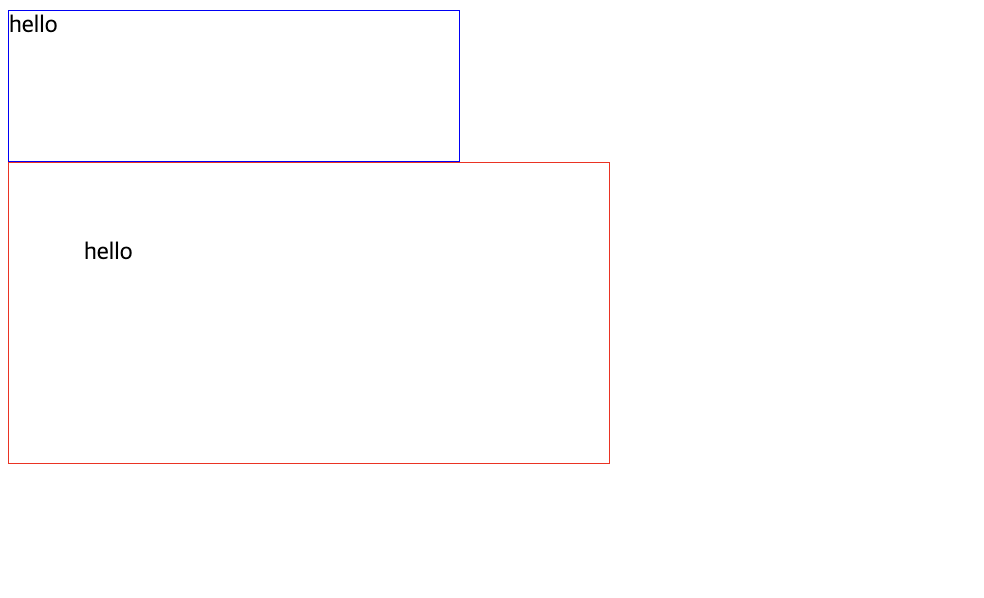

-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>BOX 모델 box sizing 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> #one { width: 300px; height: 100px; padding: 20px; border: 1px solid blue; box-sizing: border-box; } #two { width: 300px; height: 100px; padding: 50px; border: 3px solid red; box-sizing: border-box; } </style> </head> <body> 여러개의 블럭박스에 box-sizing: border-box; 지정하고 width와 height속성을 같게 주면 padding이나 border값이 달라도 결과적으로 박스크기는 같아진다. box-sizing시 border-box로 지정하면 width와 height로 설정된 값에 padding,border,margin값이 포함되어 만들어지기 때문이다. <div id="one">hello</div> <div id="two">hello</div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
3. 배경 속성
1) background-color 속성
- 배경에 색상 지정
background-color:<색상값>;2) background-image 속성
- 배경에 이미지 지정
- 속성값은 삽입할 이미지의 경로를
url()함수로 지정 - 요소의 배경 크기가 반드시 필요
- 요소 배경의 너비와 높이 지정하지 않으면 이미지가 보이지 않음
- background-color도 동일
background-image:url('이미지 경로');3) background-repeat 속성
- 배경 크기가 삽입하려는 이미지보다 크면, 이미지를 자동으로 반복해서 채움
- 이미지 반복 설정 바꾸기
속성값
- no-repeat : 이미지 반복X
- repeat-x : 이미지를 가로 방향으로 반복
- repeat-y : 이미지를 세로 방향으로 반복
- repeat : 이미지를 가로와 세로 방향으로 반복
- round : 이미지 반복하되 이미지가 요소에 딱 맞도록 크기 자동 조절
- space : 이미지가 잘리지 않도록 반복
background-repeat:<속성값>;4) background-size 속성
- 배경 이미지 크기를 지정해서 처리 가능
속성값
- auto : 이미지 크기 유지
- cover : 이미지 가로 세로 비율 유지하며 배경 꽉채움
- contain : 이미지 가로 세로 비율 유지하며 배경 요소 안에 들어가도록 크기 확대/축소
- <너비 높이> : 이미지 크기 직접 지정
background-size:auto|cover|contain|<너비 높이>;5) background-position 속성
- 삽입하려는 배경 이미지의 위치 결정
- background-size=cover와 같이 사용하면 이미지 정중앙 위치한 것처럼 보임
속성값
- left, center, right : x축(가로) 방향의 위치 지정
- top, center, botton : y축(세로) 방향의 위치 지정
- px, rem, em, % : 위치 직접 지정
background-position:<x 위치> <y 위치>;- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>background-position 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> body{ background-image:url('images/001.png'); background-repeat: no-repeat; background-attachment: scroll; background-position: bottom; background-color: powderblue; /* cover: 이미지를 늘리거나 가장자리 중 하나를 약간 잘라야 하는 경우에도 전체 컨테이너를 덮도록 배경 이미지의 크기를 조정. contain:이미지가 완전히 보이도록 배경 이미지의 크기를 조정 */ background-size: cover; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet</h1> <p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.</p> <p>Pellentesque est velit, laoreet vel rhoncus sit amet.</p> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

6) background-attachment 속성
- 요소에 삽입된 이미지를 스크롤 할 때, 이미지 작동 방식 결정
속성값
- local : 삽입된 이미지 요소와 웹 브라우저에서 모두 스크롤
- scroll : 삽입된 이미지가 요소에서는 고정되지만, 웹 브라우저에서는 스크롤
- fixed : 삽입된 이미지가 요소와 웹 브라우저에서 모두 고정
background-attachment:<속성값>;4. 텍스트 속성
1) font-family 속성
-
폰트를 지정하는 속성으로 여러 개의 값 지정 가능
- 사용자의 컴퓨터에 폰트가 없으면 폰트 적용되지X
- 여러 개의 폰트를 연속적으로 입력하고, 마지막에 글꼴 유형 사용 (유사한 형태로 폰트 지원)
-
font family 이름
- generic family : 웹 브라우저에서 기본으로 제공 ('Serif', 'Monospace')
- font family : 구체적인 font family를 의미 ('Arial', 'Times New Roman')
-
글꼴 유형
-
serif : 삐침이 있는 명조 계열의 글꼴
-
sans-serif : 삐침이 없고 굵기가 일정한 고딕 계열의 글꼴
-
monospace : 텍스트 폭과 간격이 일정한 글꼴
-
fantasy : 화려한 글꼴
-
cursive : 손으로 쓴 것 같은 필기체 계열의 글꼴
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>font-family 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* C:\Windows\Fonts */ .font-arial{ font-family: '없는 폰트' , sans-serif; } .font-roman{ font-family: '없는 폰트' , serif; } .font-ansang{ font-family: '굵은안상수체' , sans-serif; } .font-md{ font-family: 'MD솔체' , sans-serif; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 class="font-arial">Lorem ipsum</h1> <h1 class="font-roman">Lorem ipsum</h1> <h1 class="font-ansang">Lorem ipsum</h1> <h1 class="font-md">Lorem ipsum</h1> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>font 단축 표현식 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> p{ /* font-size: 2em; font-style: italic; font-weight: bold; */ /* 100 ~ 900 사이의 값지정도 가능 */ /* 단축 표현 font: font-style font-weight font-size font-family */ font: italic bold 50px Arial, Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif; } </style> </head> <body> <p>Lorem ipsum</p> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
2) font-size 속성
-
폰트 크기를 지정하는 속성
-
고정길이 또는 상대길이, 7단계의 값으로 사용 (기본 웹 브라우저 폰트 사이즈 16px)
-
고정길이 : px
-
상대길이 : %, em, rem (1em = 16px)
-
7단계 값 : xx-small, x-small, small, medium, large, x-large, xx-large
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>font-size 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .a{ font-size: xx-small; } .b{ font-size: x-small; } .c{ font-size: small; } .d{ font-size: medium; } .e{ font-size: large; } .f{ font-size: x-large; } .g{ font-size: xx-large; } </style> </head> <body> <p>Lorem ipsum</p> <p class="a">Lorem ipsum_xx-small</p> <p class="b">Lorem ipsum_x-small</p> <p class="c">Lorem ipsum_small</p> <p class="d">Lorem ipsum_medium</p> <p class="e">Lorem ipsum_large</p> <p class="f">Lorem ipsum_x-large</p> <p class="g">Lorem ipsum_xx-large</p> <p class="h">Lorem ipsum-default</p> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>font-size 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .a{ font-size: 2rem; } .b{ font-size: 32px; } .c{ font-size: 2.5em; /* 40px/16=2.5em */ } .d{ font-size: 1.875em; /* 30px/16=1.875em */ } .e{ font-size: 0.875em; /* 14px/16=0.875em */ } </style> </head> <body> <p>Lorem ipsum_default</p> <p class="a">Lorem ipsum_2em</p> <p class="b">Lorem ipsum_32px</p> <p class="c">Lorem ipsum_2.5em</p> <p class="d">Lorem ipsum_1.875em</p> <p class="e">Lorem ipsum_0.875em</p> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
3) font-weight 속성
- 텍스트의 굵기 지정
- 숫자 표기법
- font-weight:100 (최소 굵기)
- font-weight:900 (최대 굵기)
- 키워드 표기법
- font-weight:lighter
- font-weight:normal (400)
- font-weight:bold (700)
- font-weight:bolder
4) font-style 속성
- 글꼴의 스타일 지정
속성값
- normal : 기본 형태로 표시
- italic : 이탤릭체로 표시
- oblique : 기울임꼴로 표시
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>font-weight & style 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> p{ font-style: italic; font-weight: bold; /* 100 ~ 900 사이의 값 지정도 가능 */ font-size: 2em; } </style> </head> <body> <p>Lorem ipsum</p> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

5) font-face (웹 폰트)
-
웹 문서 작성시 웹 문서 안에 글꼴 정보도 함께 저장
-
사용자가 웹 문서에 접속하면 글꼴을 사용자 시스템으로 다운로드하여 사용
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>@font-face</title> <style> @font-face { font-family:cheri; src:url('fonts/cheri.ttf') format('truetype'); } .text1 { font-family:cheri, Arial Black; font-size:80px; color: #006; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="normal_text">ABCDEF</div> <div class="text1">123456</div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

- 📋 코드 📋
6) color 속성
- 글자의 색상 지정
color:<속성값>;7) text-align 속성
- 글자의 수평 정렬 지정
속성값
- left : 왼쪽 정렬
- center : 가운데 정렬
- right : 오른쪽 정렬
- justify : 양쪽 정렬 (모든 라인의 width가 늘어남)
text-align:<속성값>;8) text-decoration 속성
- 글자의 밑줄 지정 및 해제
속성값
- none : 텍스트 장식 모두 지움
- line-through : 텍스트 중간에 선 긋기
- overline : 텍스트 위에 선 긋기
- underline : 텍스트 아래에 선 긋기
text-decoration:<속성값>;9) text-transform 속성
- 글자의 대/소문자 지정 및 첫 글자 대문자 지정
속성값
- none : 없음
- capitalize : 첫 글자만 대문자 지정
- uppercase : 대문자 지정
- lowercase : 소문자 지정
text-transform:<속성값>;10) text-indent 속성
- 첫 라인 들여쓰기
text-indent:<크기>;11) letter-spacing 속성
- 글자 간격 설정 (자간 조절)
속성값
- normal : 웹 브라우저에서 정한 기본값 적용
- <크기> : 사용자 지정값 적용
letter-spacing:normal|<크기>;12) line-height 속성
- 라인 간격 설정 (텍스트 한 줄 높이 지정)
속성값
- normal : 웹 브라우저에서 정한 기본값 적용
- 숫자 : 현재 font-size 값에 입력한 숫자를 곱한 값 적용
- 퍼센트 : 현재 font-size 값에 입력한 비율 곱한 값 적용
- 크기 : 입력한 크기 적용
line-height:normal|<속성값>;13) word-spacing 속성
- 단어 간격 설정
word-spacing:normal|<크기>;- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>text color 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> p{ color:red; text-align: right; text-decoration: line-through; text-transform: uppercase; } div { border: 1px solid black; padding: 10px; width: 200px; height: 250px; text-align: justify; text-indent: 50px; } p.small { line-height: 0.8; text-align: center; } h1 { letter-spacing: 3px; word-spacing: 10px; } h2 { letter-spacing: -3px; word-spacing: -5px; } </style> </head> <body> <p>Lorem ipsum</p> <div> In my younger and more vulnerable years my father gave me some advice that I've been turning over in my mind ever since. 'Whenever you feel like criticizing anyone,' he told me, 'just remember that all the people in this world haven't had the advantages that you've had.' </div> <p class="small"> smaller line-height.<br> smaller line-height.<br> </p> <h1>This is heading 1</h1> <h2>This is heading 2</h2> </body> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

5. 위치 속성
1) position 속성 (static)
-
태그의 위치 설정을 변경할 때 사용
-
태그가 위에서 아래로 순서대로 배치 (기본 흐름따라 배치)
- 모든 html 태그는 기본으로 static position으로 위치 결정
- top, bottom, left, right 속성에 영향 받지X
-
static으로 지정하면 아무런 변화X
-
좌표 속성을 사용할 수 없으며 위치 속성을 사용하지 않을 때와 같음
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>position static 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* static: static인 요소는 HTML 문서 상에서 원래 있어야하는 위치에 배치됩니다. top, left, bottom, right 속성값은 position 속성이 static일 때는 무시됩니다. */ main { width: 300px; height: 400px; background: tomato; } div { width: 200px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid; background: yellow; text-align: center; line-height: 100px; box-sizing: border-box; } div:nth-of-type(2) { position: static; background: cyan; opacity: 0.8; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>position: static;</h2> <main> <div>첫 번째 요소 static</div> <div>두 번째 요소 static</div> <div>세 번째 요소 static</div> </main> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋
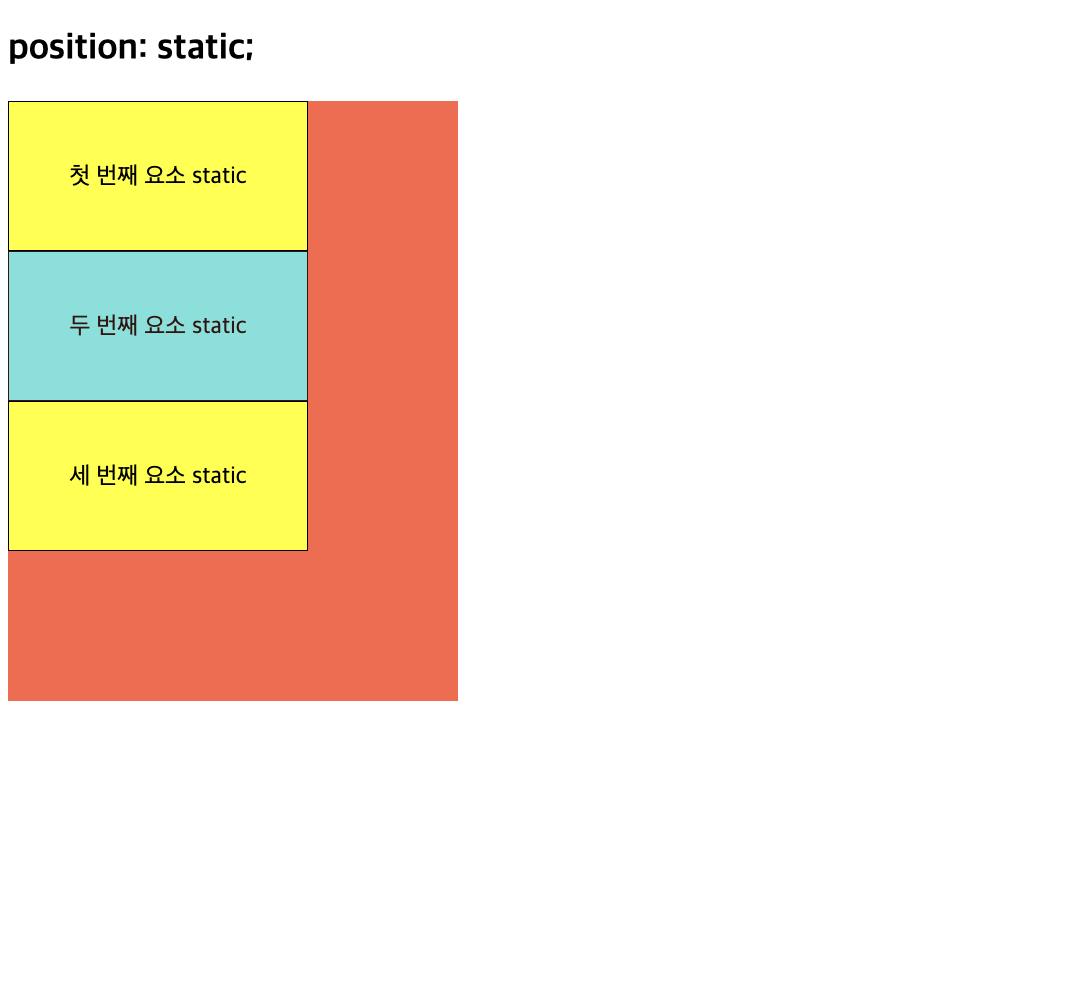
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>position static 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* static: static인 요소는 HTML 문서 상에서 원래 있어야하는 위치에 배치됩니다. top, left, bottom, right 속성값은 position 속성이 static일 때는 무시됩니다. */ main { width: 300px; height: 400px; background: tomato; } div { width: 200px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid; background: yellow; text-align: center; line-height: 100px; box-sizing: border-box; } div:nth-of-type(2) { position: static; background: cyan; opacity: 0.8; top: 100px; left: 100px; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>position: static;</h2> <main> <div>첫 번째 요소 static</div> <div>두 번째 요소 static</div> <div>세 번째 요소 static</div> </main> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋
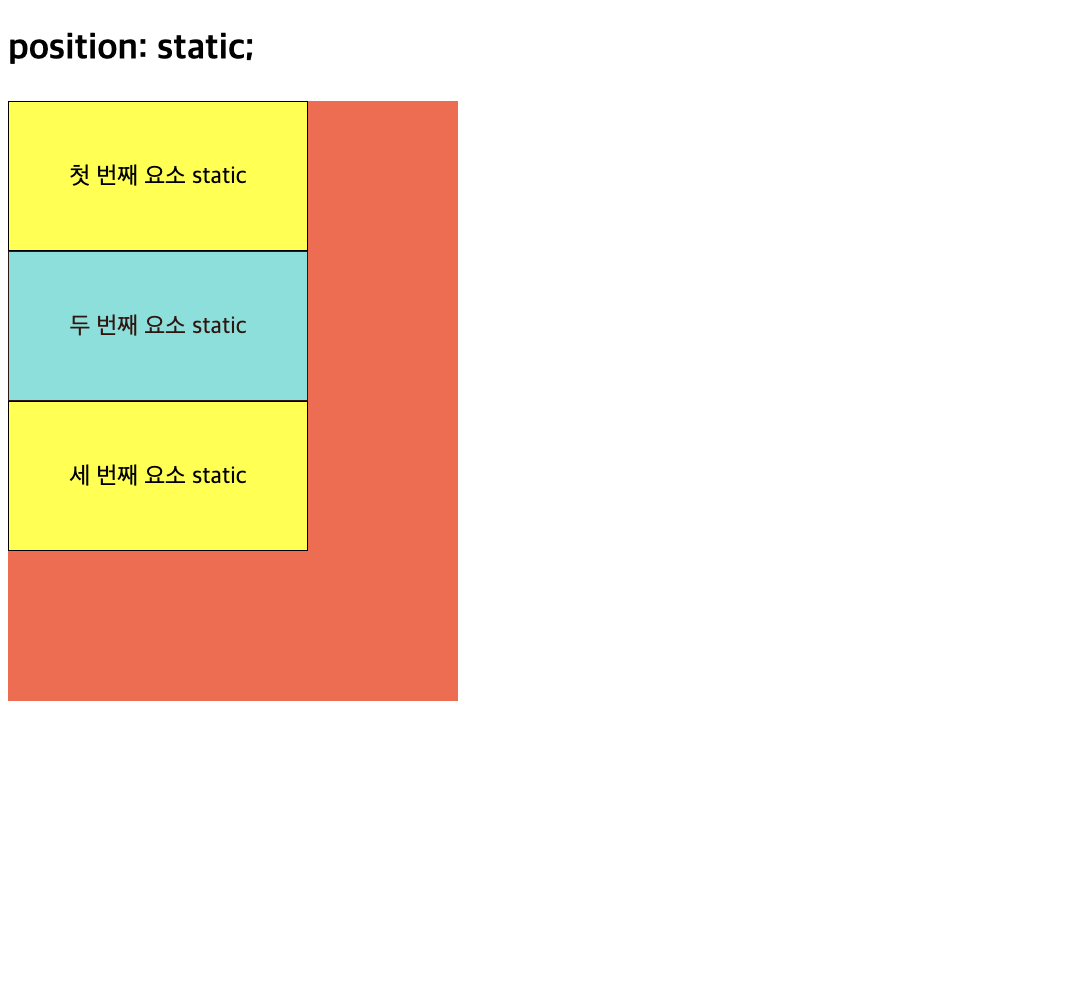
-
2) position 속성 (relative)
-
초기 위치 상태에서 상하좌우로 위치 이동 (좌표 속성 사용)
-
normal position 기준으로 상대적인 위치 결정
-
top, bottom, left, right 속성과 같이 사용
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>position relative 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* relative: relative로 설정하게 되면, 요소를 원래 위치에서 벗어나게 배치할 수 있게 됩니다. 요소를 원래 위치를 기준으로 상대적(relative)으로 배치 해준다. 요소의 위치 지정은 top, bottom, left, right 속성을 이용해서 요소가 원래 위치에 있을 때의 상하좌우로 부터 얼마나 떨어지게 할지를 지정할 수 있다. */ main { width: 300px; height: 400px; background: tomato; } div { width: 200px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid; background: yellow; text-align: center; line-height: 100px; box-sizing: border-box; } div:nth-of-type(2) { position: relative; top: 28px; left: 48px; background: cyan; opacity: 0.8; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>position: relative;</h2> <main> <div>첫 번째 요소 static</div> <div>두 번째 요소 relative</div> <div>세 번째 요소 static</div> </main> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋
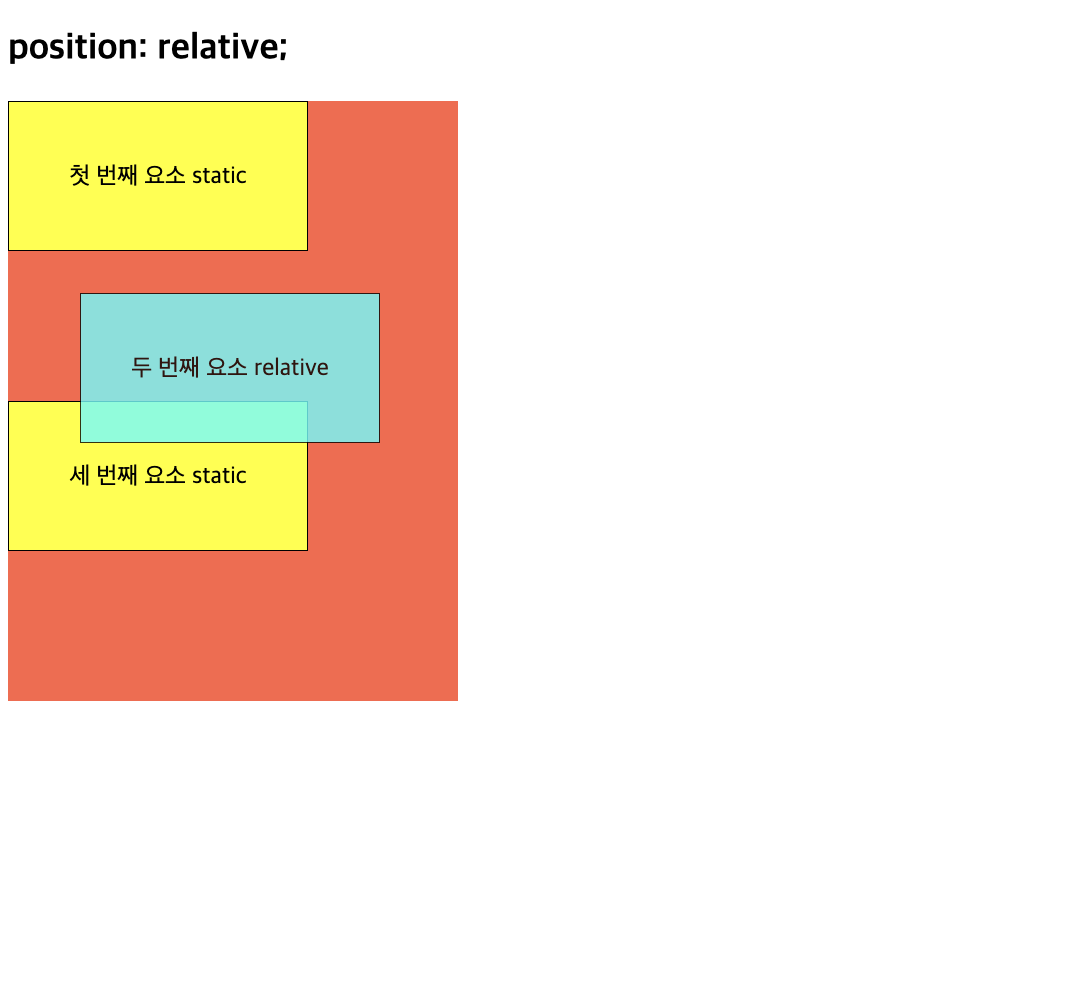
-
3) position 속성 (fixed)
-
화면을 기준으로 절대 위치 좌표 설정 (절대적인 좌표 위치)
-
viewport 기준으로 상대적인 위치 결정 (브라우저 화면 기준)
-
페이지가 scroll 되는 경우에도 항상 고정된 위치에 보여짐
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>position fixed 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* fixed: position 속성을 fixed로 지정하면 요소를 항상 고정된(fixed) 위치에 배치할 수 있습니다 fixed 속성값의 배치 기준이 자신이나 부모 요소가 아닌 뷰포트(viewport), 즉 브라우저 전체화면이다. top, left, bottom, right 속성은 각각 브라우저 상단, 좌측, 하단, 우측으로 부터 해당 요소가 얼마나 떨어져 있는지를 결정합니다. */ main { width: 300px; height: 400px; background: tomato; } div { width: 200px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid; background: yellow; text-align: center; line-height: 100px; box-sizing: border-box; } div:nth-of-type(2) { position: fixed; bottom: 8px; right: 16px; background: cyan; opacity: 0.8; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>position: fixed;</h2> <main> <div>첫 번째 요소 static</div> <div>두 번째 요소 fixed</div> <div>세 번째 요소 static</div> </main> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>position fixed 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> div.fixed { position: fixed; bottom: 0; right: 0; width: 300px; border: 3px solid #73AD21; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>position: fixed;</h2> <p>An element with position: fixed; is positioned relative to the viewport, which means it always stays in the same place even if the page is scrolled: An element with position: fixed; is positioned relative to the viewport, which means it always stays in the same place </p> <div class="fixed"> This div element has position: fixed; </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
4) position 속성 (absolute)
-
절대 위치 좌표 설정 (절대적인 좌표 위치)
- 가장 가까운 부모 요소 기준으로 하는 상대적인 위치 결정 (부모 요소 기준)
- 부모 요소가 없거나 부모요소에 position 설정값 설정하지 않으면 body 요소 기준으로 설정
- 부모 요소에 relative 설정 ➡️ 자식 요소에 absolute 설정
-
relative일 때는 기준점이 요소의 왼쪽 위 모서리지만, absolute일 때는 웹 브라우저의 왼쪽 위 모서리
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>position static 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* absolute: position 속성이 absolute일 때 해당 요소는 배치 기준을 자신이 아닌 상위 요소에서 찾습니다. DOM 트리를 따라 올라가다가 position 속성이 static이 아닌 첫 번째 상위 요소가 해당 요소의 배치 기준으로 설정된다. 만약에 해당 요소 상위에 position 속성이 static이 아닌 요소가 없다면, DOM 트리에 최상위에 있는 <body> 요소가 배치 기준이 됩니다. absolute 속성값은 relative 속성값과 함께 사용되는 경우가 많다. */ main { width: 300px; height: 400px; background: tomato; } div { width: 200px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid; background: yellow; text-align: center; line-height: 100px; box-sizing: border-box; } div:nth-of-type(2) { position: absolute; bottom: 8px; right: 16px; background: cyan; opacity: 0.8; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>position: static;</h2> <main> <div>첫 번째 요소 static</div> <div>두 번째 요소 absolute</div> <div>세 번째 요소 static</div> </main> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>position static 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> /* absolute: 어떤 요소의 display 속성을 absolute로 설정하면, 부모 요소의 display 속성을 relative로 지정해주는 것이 관례입니다. */ main { position: relative; width: 300px; height: 400px; background: tomato; } div { width: 200px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid; background: yellow; text-align: center; line-height: 100px; box-sizing: border-box; } div:nth-of-type(2) { position: absolute; bottom: 8px; right: 16px; background: cyan; opacity: 0.8; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>position: relative 와 position;</h2> <main> <div>첫 번째 요소 relative</div> <div>두 번째 요소 absolute</div> <div>세 번째 요소 static</div> </main> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋
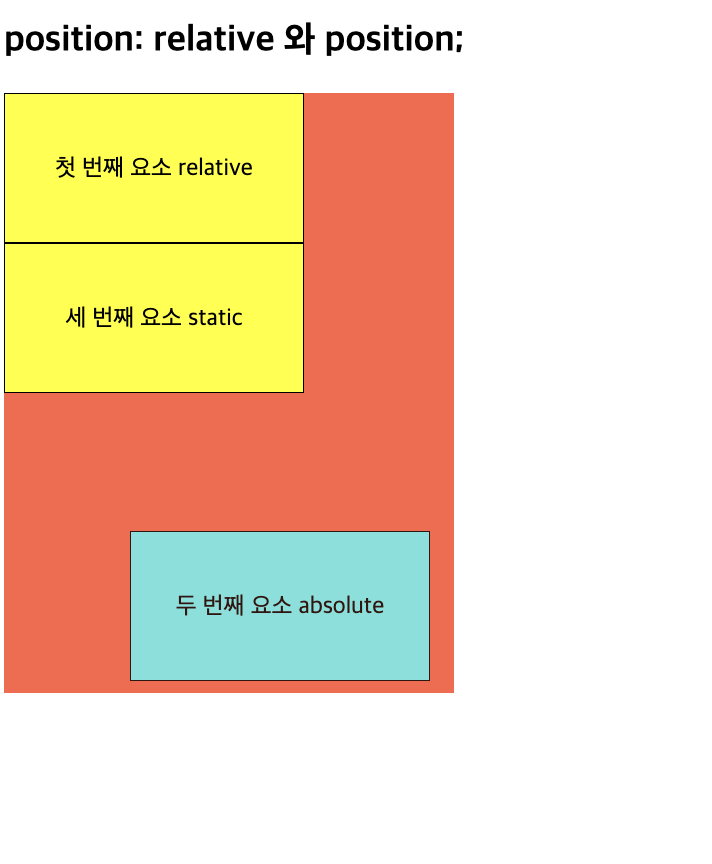
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>position absolute 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> div.container { position: relative; background-color: yellow; } div.container2 { position: relative; background-color: grey; width:300px; height:200px; } img{ position: absolute; bottom:0px; right:0px; } /* div.absolute { position: absolute; top: 80px; right: 0; width: 200px; height: 100px; border: 3px solid #73AD21; } */ </style> </head> <body> <h2>position: absolute1</h2> <div class="container"> <div class="container2"> <img src="images/001.png" width="50px" height="50px"> </div> <p> sadfasfdfsdfasfasfdasdfasdfasdfasfdasfdasfdsadfasfdfsdfasfasfdasdfasdfasdfasfdasfdasfdsadfasfdfsdfasfasfdasdfasdfasdfasfdasfdasfd </p> <img src="images/001.png" width="50px" height="50px"> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
5) z-index 속성
-
position 속성으로 배치한 요소의 z축 위치를 결정
-
position 속성이 static 값이 아닐 때는 좌표 속성에 따라 요소 배치함
-
요소가 position 될 때 겹쳐져 보임
-
요소의 stack 순서를 변경할 수 있는 속성
-
큰 값을 입력할 수록 위로 올라옴
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>z-index 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> img { position: absolute; left: 0px; top: 0px; z-index: -1; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>This is a heading</h1> <img src="images/001.png" width="100" height="140"> <p>Because the image has a z-index of -1, it will be placed behind the text.</p> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
6) float 속성
-
필요에 따라 요소를 가로 방향으로 배치하기 위해서 사용
- 블록 성격 요소를 한 줄로 배치
- width 속성이 적용되지 않으면 요소가 가지고 있는 콘텐츠만큼 너비가 자동 조정
- float되지 않는 요소 위로 배치하거나, clear 속성 사용하여 float 중지할 수 있음
-
image를 삽입하거나 layout을 위한 용도로 사용
-
속성값
- none : float 속성 적용X
- left : 대상 요소를 공중에 띄워 왼쪽에 배치하면서 다음에 오는 요소를 주변에 배치
- right : 대상 요소를 공중에 띄워 오른쪽에 배치하면서 다음에 오는 요소를 주변에 배치
-
가로 배치 방법 1️⃣
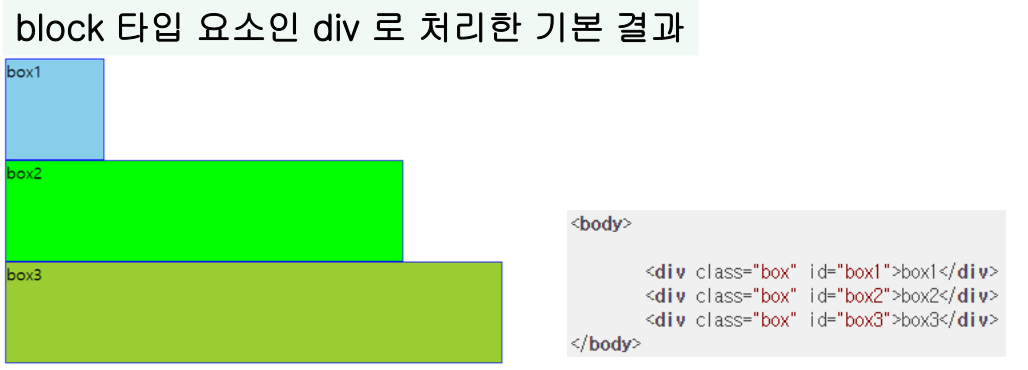
- block 타입 요소인 div로 처리한 기본 결과
- box1의 float 속성을 left로 처리한 결과
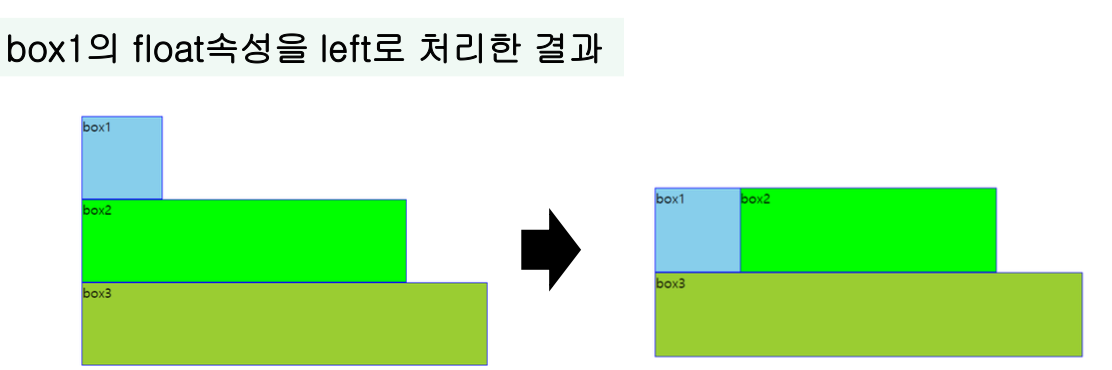
- box2의 float 속성을 right로 처리한 결과

- box3의 float 속성을 clear로 처리한 결과
- float되는 요소와 float 중지하는 요소가 따로 구현되어 혼란
- 가로로 배치된 요소들을 별도로 wrapping해서 조상 레벨에서 처리

- block 타입 요소인 div로 처리한 기본 결과
-
가로 배치 방법 2️⃣ (overflow:hidden 사용)
- 부모 태그에서 overflow:hidden 사용하면 자식 태그들의 영역 까지만 크기 확보하고, 넘는 크기는 무시
- outer 크기가 확보되고 outer는 float이 아니기 때문에 box1, box2와 무관하게 box3 배치 가능
#outer{ overflow: hidden; } -
가로 배치 방법 3️⃣ (display:flex 속성 사용)
-
부모의 display 속성으로 flex 지정하면 자식을 가로로 배치
#outer{ display: flex; } -
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>float 실습</title> <style> img { float: right; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>Float Right</h2> <p>In this example, the image will float to the right in the paragraph, and the text in the paragraph will wrap around the image.</p> <p><img src="images/pineapple.jpg" alt="Pineapple" style="width:170px;height:170px;margin-left:15px;"> Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. </p> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
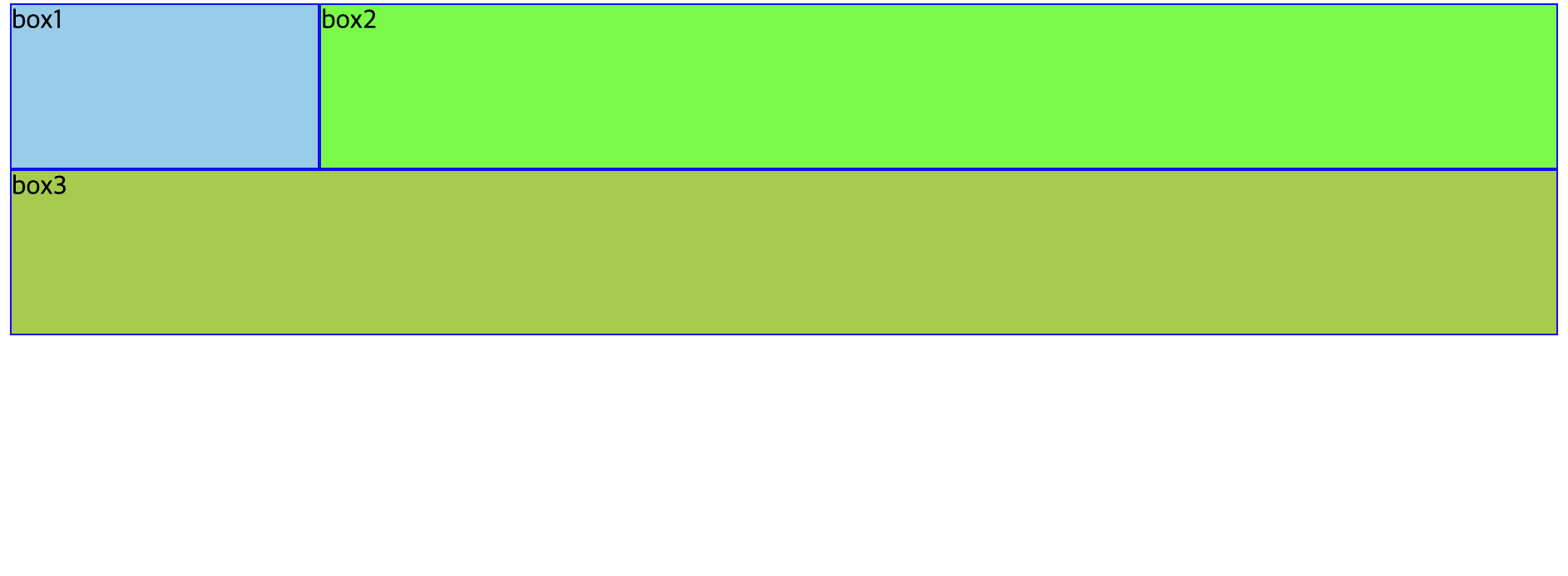
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>float overflow, hidden 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> #outer{ overflow: hidden; } .box{ box-sizing: border-box; height: 100px; border: 1px solid blue; } #box1{ float:left; background: skyblue; width: 20%; } #box2{ float:right; background: lime; width: 80%; } #box3{ background: yellowgreen; width: 100%; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="outer"> <div class="box" id="box1">box1</div> <div class="box" id="box2">box2</div> </div> <div class="box" id="box3">box3</div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋
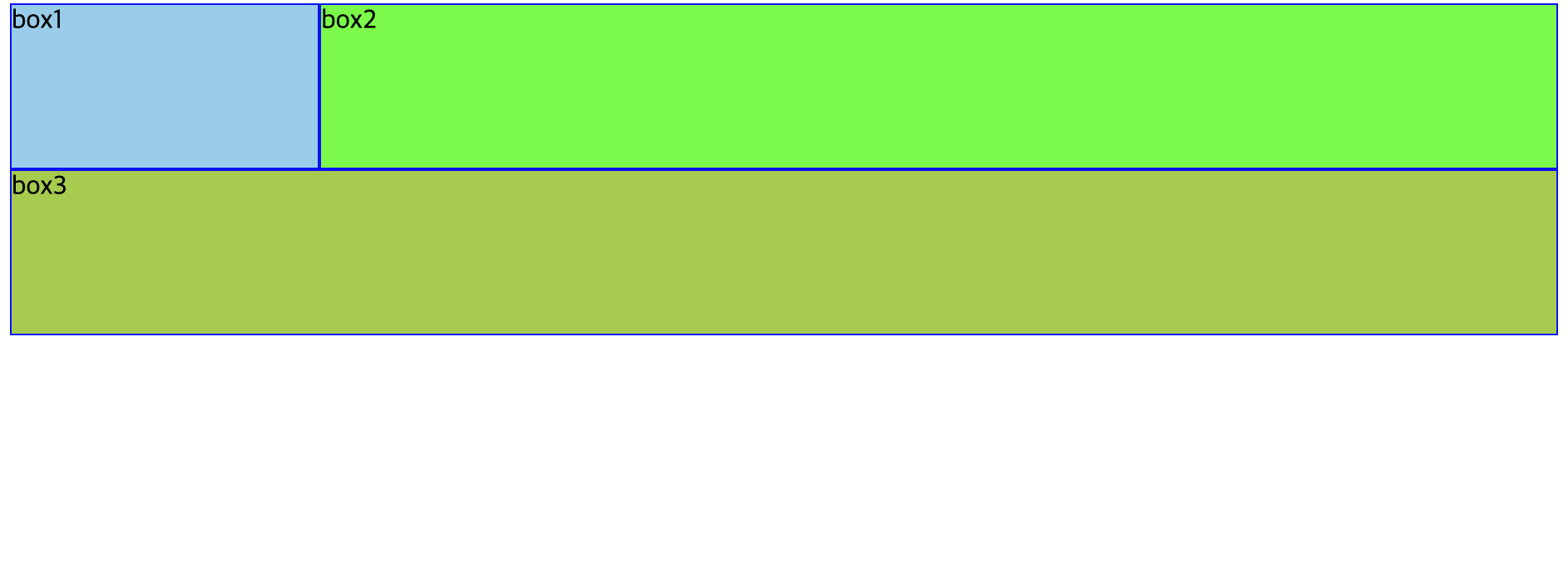

-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>float diplay_flex 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> #outer{ display: flex; } .box{ box-sizing: border-box; height: 100px; border: 1px solid blue; } #box1{ background: skyblue; width: 20%; } #box2{ background: lime; width: 80%; } #box3{ background: yellowgreen; width: 100%; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="outer"> <div class="box" id="box1">box1</div> <div class="box" id="box2">box2</div> </div> <div class="box" id="box3">box3</div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋
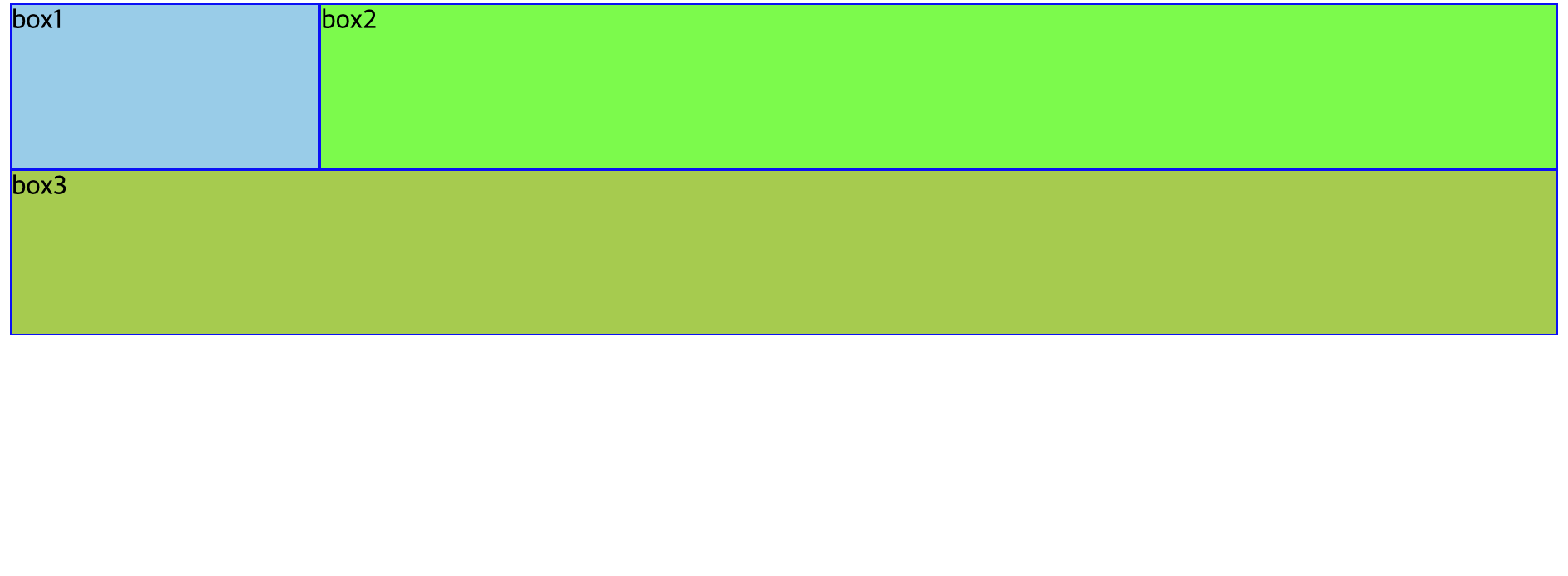

-
7) float clear 속성
-
float 속성을 해제할 때 사용하는 속성
-
float 속성이 대상 요소의 다음 요소에 영향을 줌
-
속성값
-
left : float 속성의 left 값 해제
-
right : float 속성의 right 값 해제
-
both : float 속성의 left와 right 값 해제
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>float clear 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .box{ box-sizing: border-box; height: 100px; border: 1px solid blue; } #box1{ float:left; background: skyblue; width: 20%; } #box2{ float:right; background: lime; width: 80%; } #box3{ clear:both; background: yellowgreen; width: 100%; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box" id="box1">box1</div> <div class="box" id="box2">box2</div> <div class="box" id="box3">box3</div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
6. 플렉스 박스 레이아웃
1) Flexbox
-
개념
- float 또는 positioning 없이 유연한 반응형 레이아웃 구조를 쉽게 적용하기 위한 1차원(행/열) 지정 방법
- vertical centering
- dynamic sizing
- custon ordering
-
구성요소
-
flex 모듈을 적용하기 위해서 부모/자식 관계 설정 필요
- 부모(Flex Container), 자식(Flex Item)
- Flex Container에서는 CSS로 display: flex로 반드시 지정
-
Flexbox Container 속성
- flex-direction
- flex-wrap
- flex-flow
- justify-content
- align-items
- align-content
-
Flexbox Item 속성
- order
- flex-grow
- flex-shrink
- flex-basis
- flex
- align-self
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; width: 200px; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border:1px solid white; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋
-
2) Flexbox Container 속성
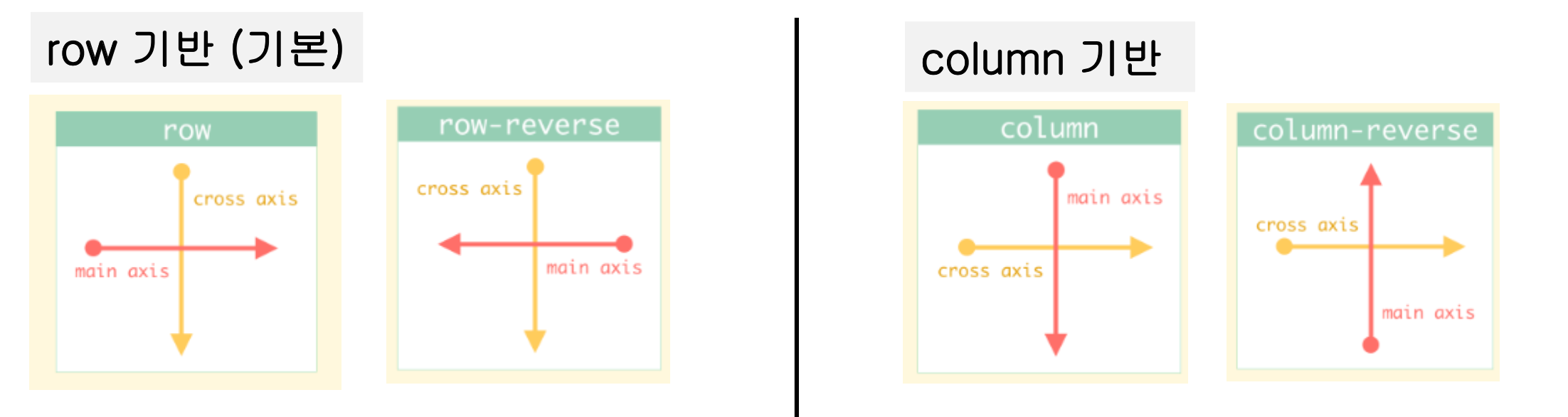
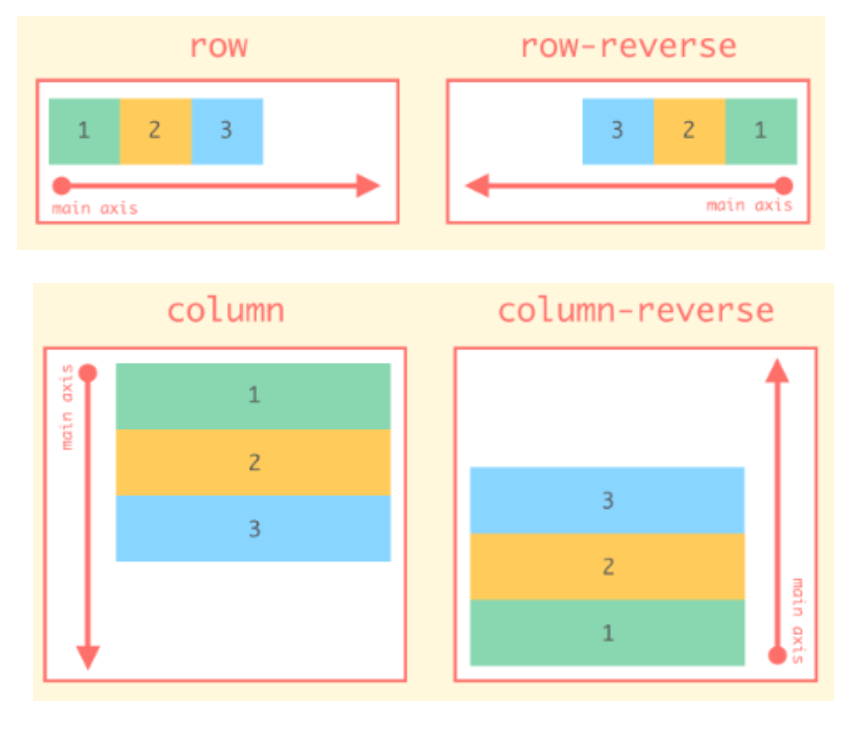
- flex-direction 속성
- 주 축과 교차 축의 2축 시스템에 의해서 작동
- 주 축 : Flex Item이 Flex Container에 배치되는 방식을 정의하는 방향
- 교차 축 : 주 축에 수직인 방향
- 주 축과 교차 축의 2축 시스템에 의해서 작동
.parent {
flex-direction : row /* default */
row-reverse
column
column-reverse
} 
- 📋 코드 📋
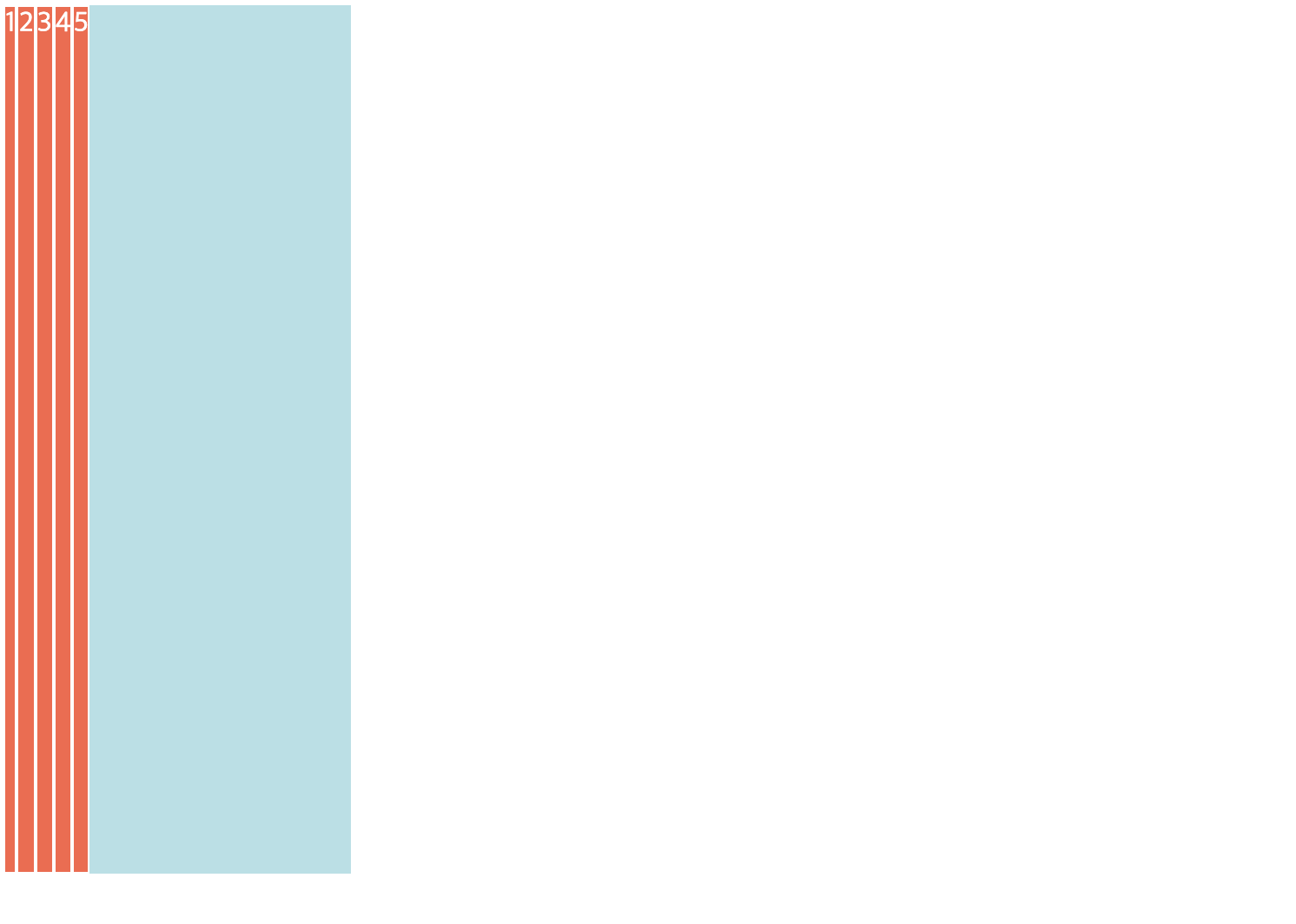
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ background-color: powderblue; width: 200px; height: 500px; display:flex; /* flexbox 축 */ flex-direction: row; /* flex-direction: row-reverse; flex-direction: column; flex-direction: column-reverse; */ } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border:1px solid white; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋

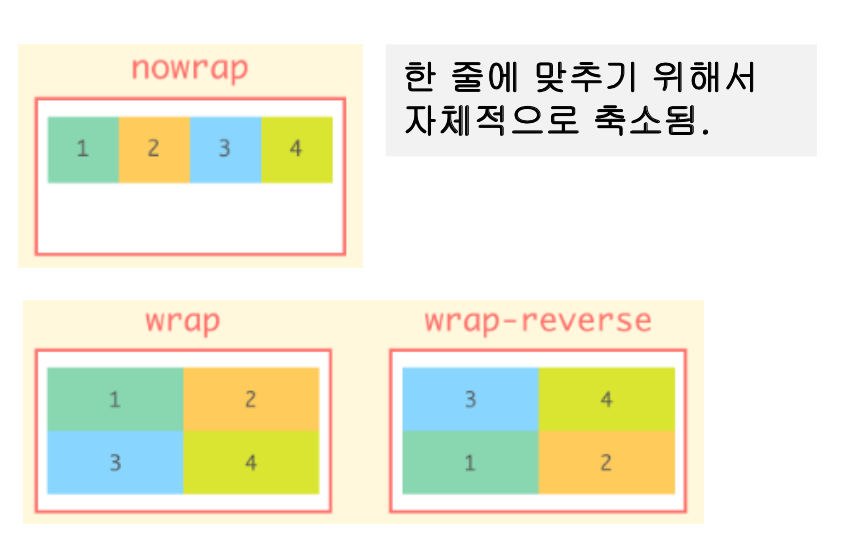
- flex-wrap 속성
- 한 줄에 맞추기 위해서 자체 축소X (줄바꿈 하지 않음)
- Flex Item의 크기를 유지하고 overflow가 Container의 여러 줄에 퍼지도록 하기 위해 사용
.parent {
flex-wrap : nowrap /* default */
wrap
wrap-reverse
}
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex wrap 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ display:flex; flex-direction: row; flex-wrap: wrap; } .item{ color:black; border: 1px solid black; width: 300px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="item" style="background-color: gray;"><article> <h2>This is the heading of the main section</h2> <p>This is a paragraph of text.</p> </article></div> <div class="item" style="background-color: white;"><aside>Here is the aside</aside></div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
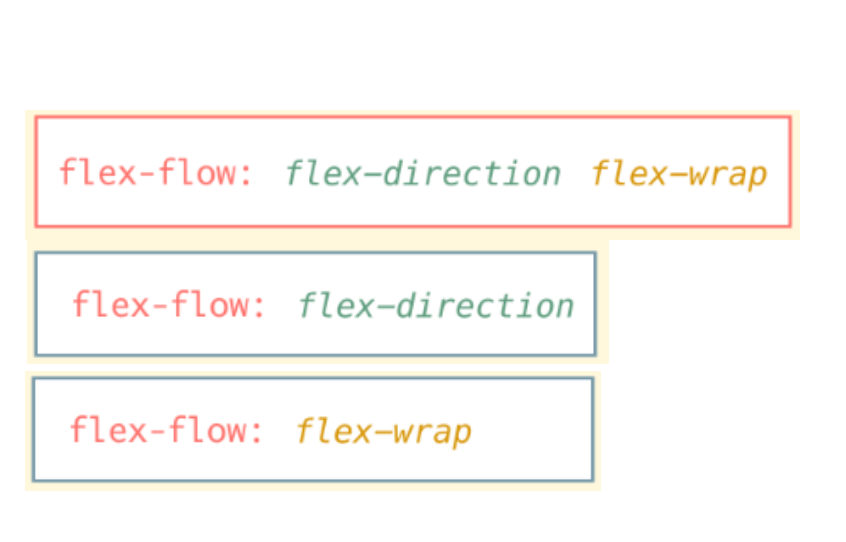
flex-flow 속성
- flex-direction 속성과 flex-wrap 속성을 모두 설정하기 위한 단축표현 방법
- 하나만 설정하면 설정하지 않은 속성은 기본값 사용
.parent {
flex-flow : row nowrap /* default */
<flex-direction> <flex-wrap>
<flex-direction>
<flex-wrap>
}
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex flow 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; /* flex-direction: row; flex-wrap: wrap; */ flex-flow: row wrap; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border: 1px solid black; width: 300px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
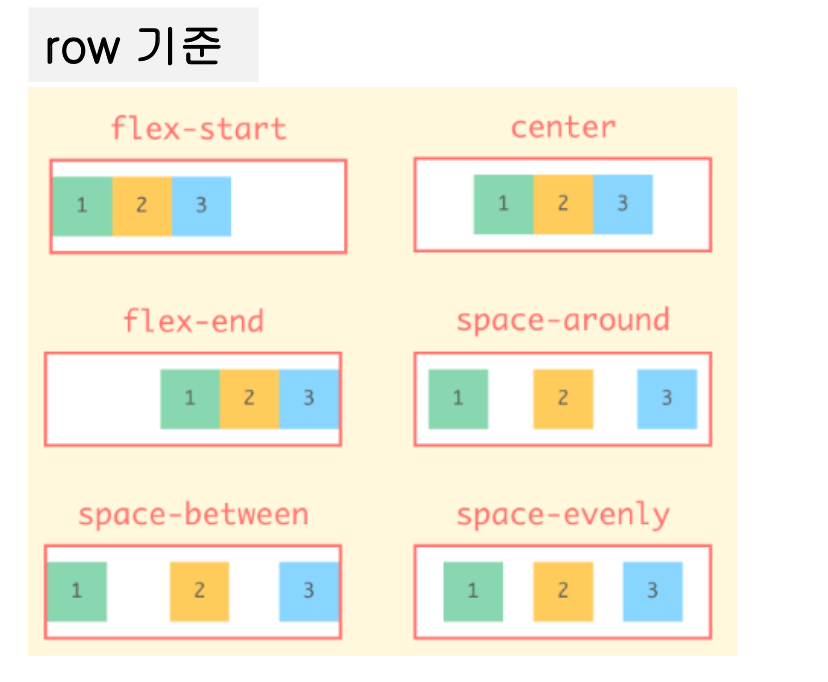
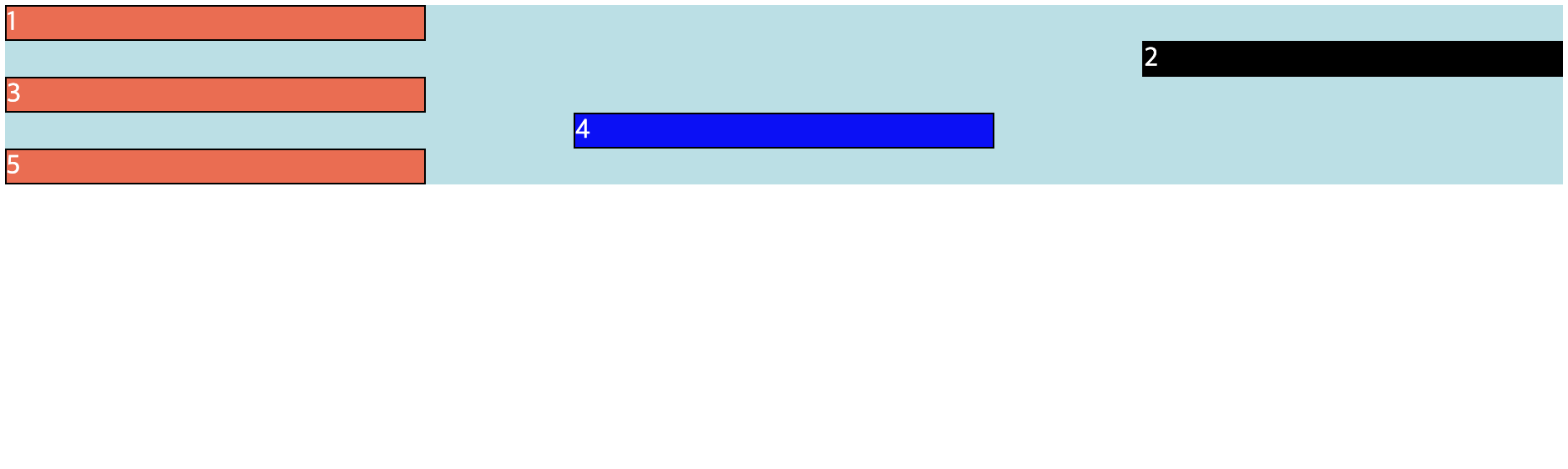
justify-content 속성
- 주 축에 대해서 정렬을 설정하는 속성 (기본은 row)
- 창 너비를 줄이거나 늘리면 Flexbox가 자동으로 계산하여 선택한 정렬 유지
.parent {
justify-content : flex-start /* default */
flex-end
center
space-around
space-between
space-evenly
}
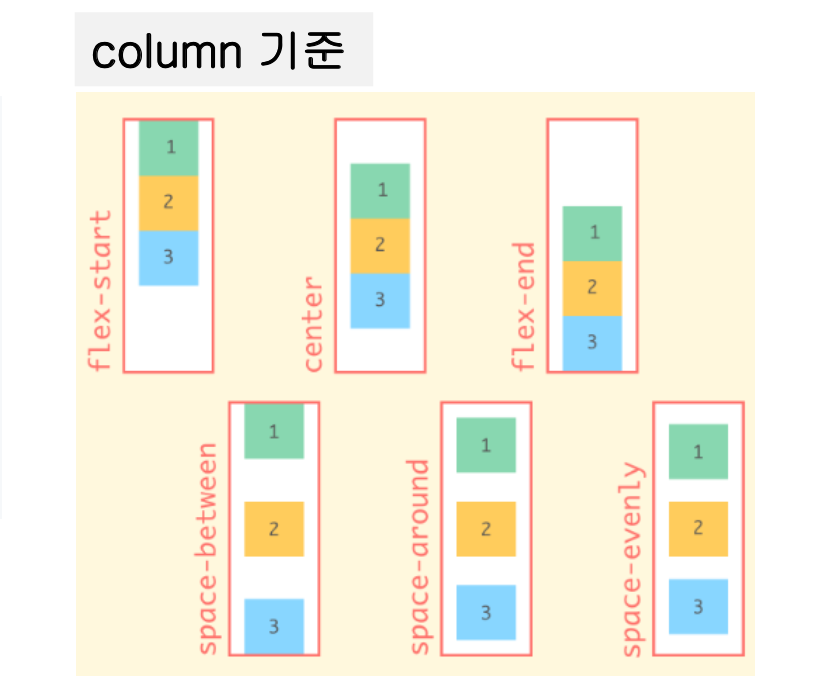
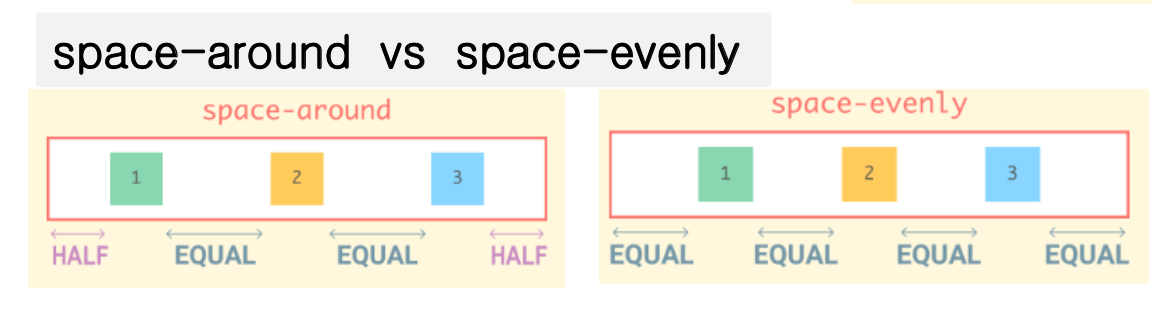
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex justify-content row 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; flex-direction: row; justify-content: flex-start; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border:1px solid white; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
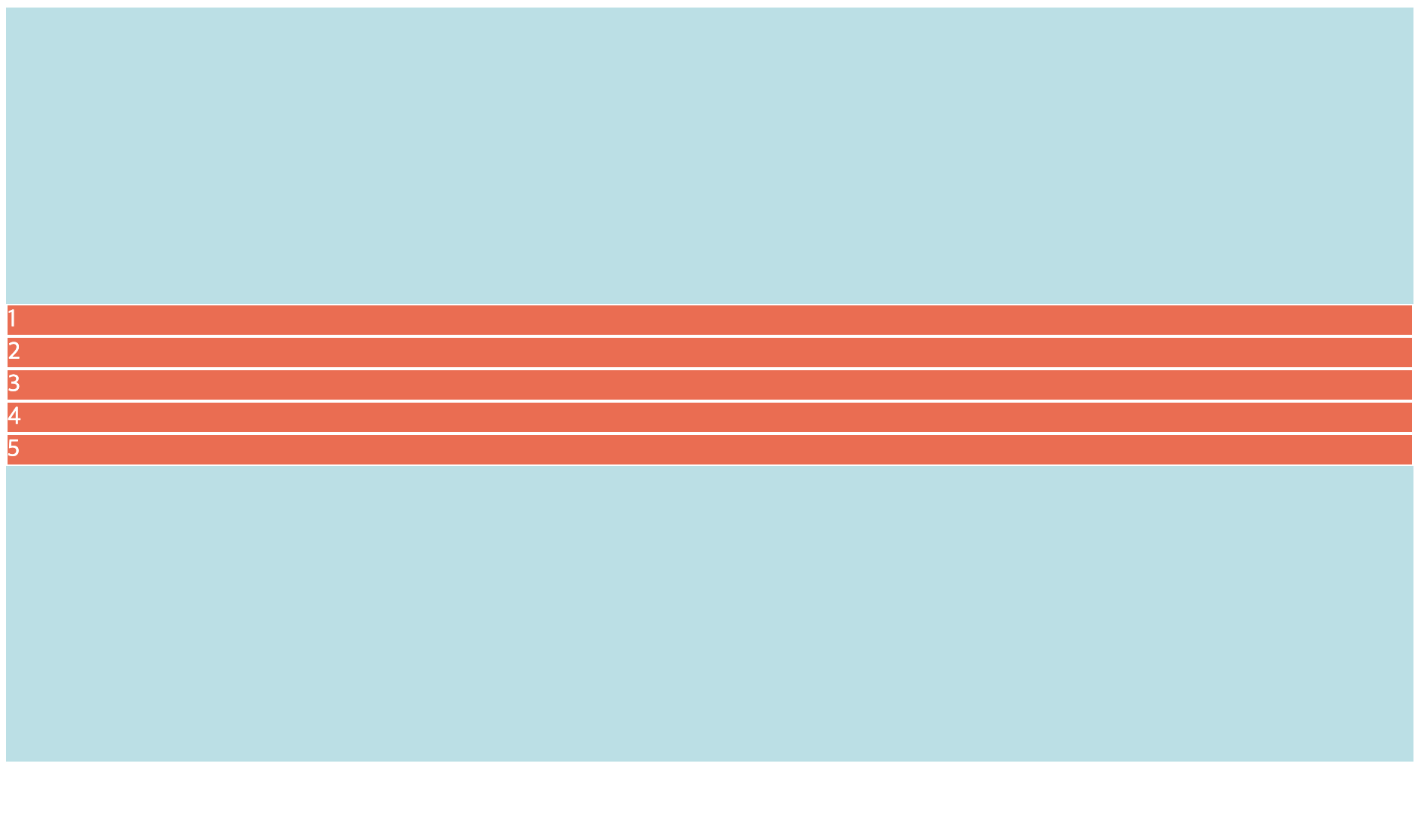
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex justify-content column 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; flex-direction: column; height: 500px; justify-content: center; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border:1px solid white; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
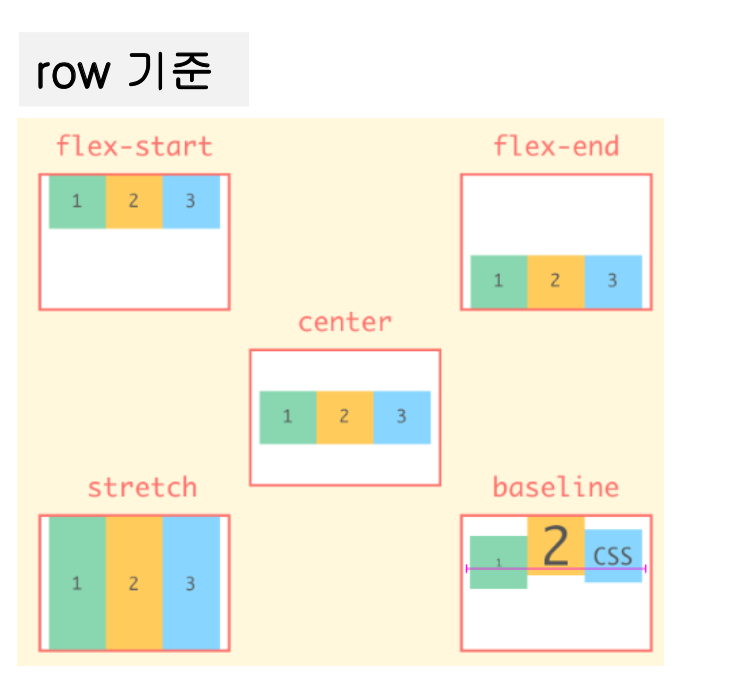
align-items 속성
- 교차 축에 대해서 정렬을 설정하는 속성
- 기본값인 stretch는 Flex Item을 늘려서 Container를 채움
.parent {
align-items : stretch /* default */
flex-start
flex-end
center
baseline
}
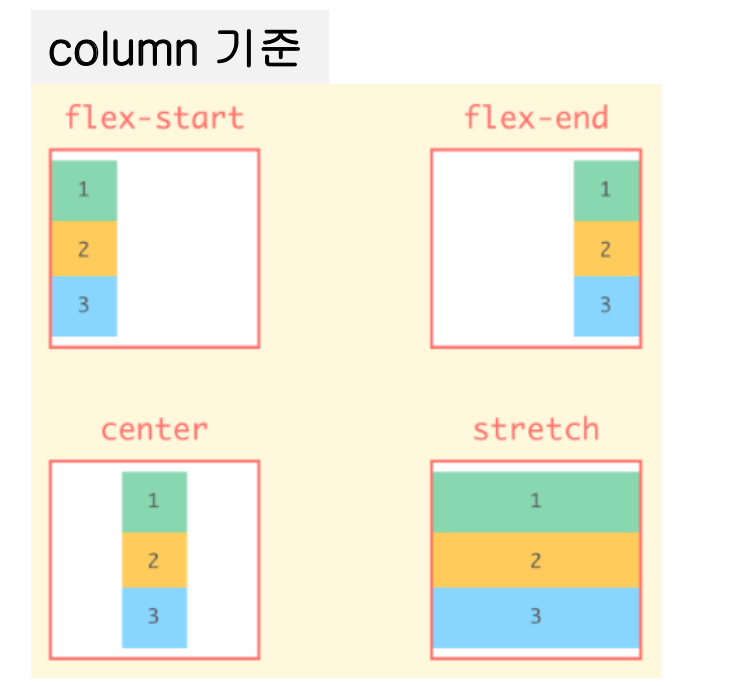
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex align-items row 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .x{ height: 500px; } .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; flex-direction: row; height: 500px; align-items: stretch; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border:1px solid white; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="x"> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex align-items column 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .x{ height: 500px; } .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; flex-direction: column; height: 500px; align-items: flex-end; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border:1px solid white; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="x"> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
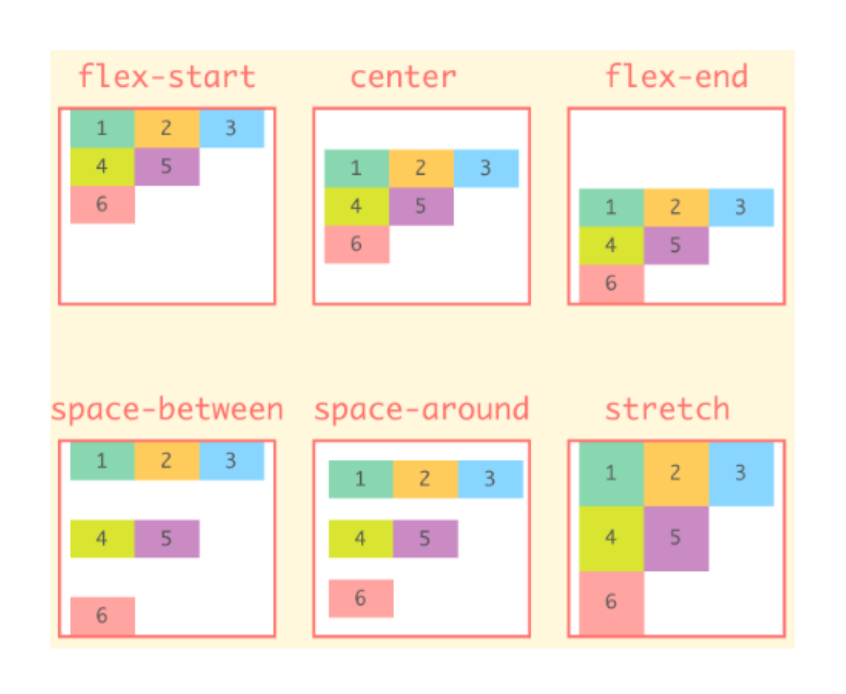
align-content 속성
- wrap된 항목에만 적용되는 속성
- 교차 축에 정렬되는 방식을 제어할 수 있음
- Flex Item이 한 줄만 있는 경우 아무런 영향 X
.parent {
align-content : stretch /* default */
flex-start
flex-end
center
space-between
space-around
}
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex align-content 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .x{ height: 500px; } .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; flex-direction: row; height: 200px; flex-wrap: wrap; /* wrap된 경우에만 적용 */ align-content: center; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border: 1px solid black; width: 300px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="x"> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋
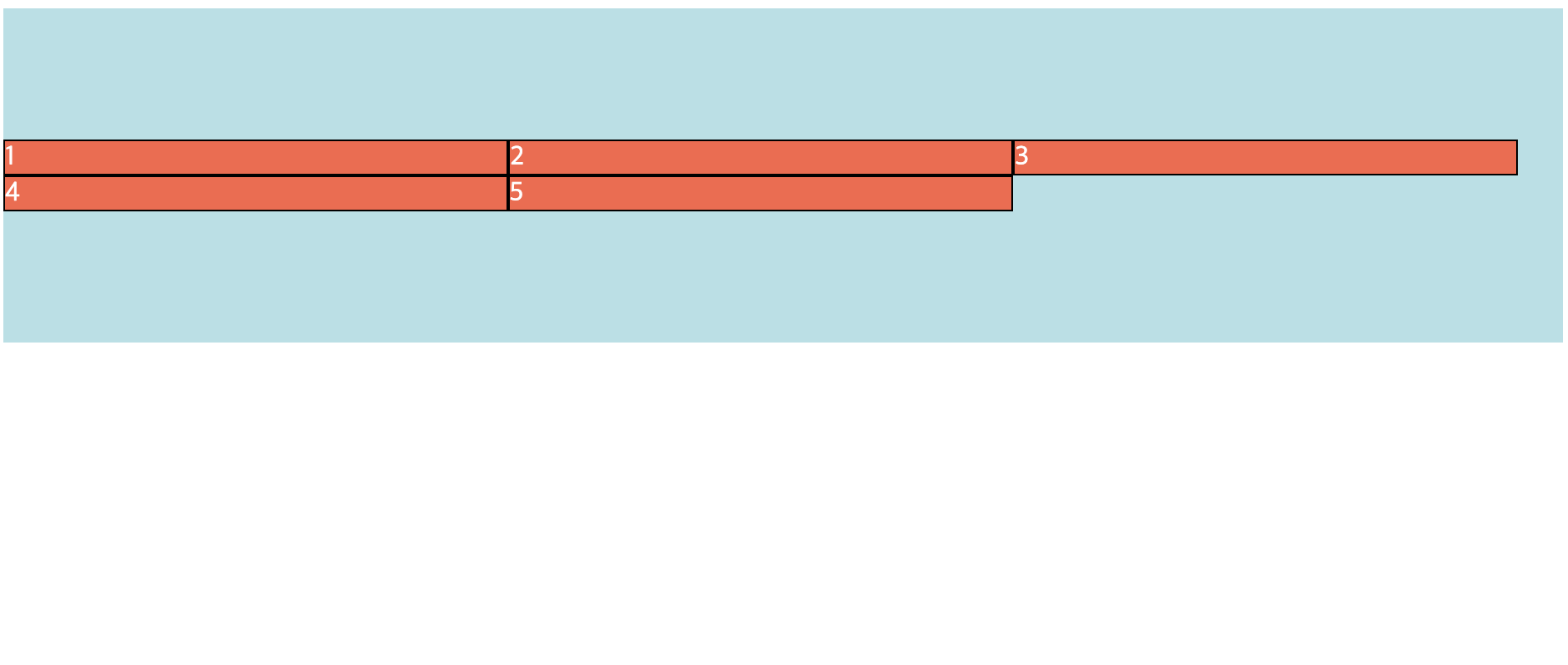
3) Flexbox Item 속성
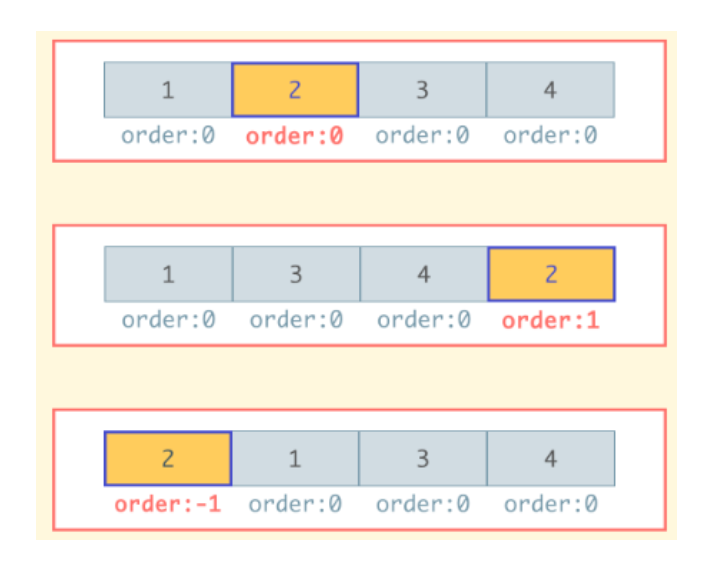
- order 속성
- Flex Item의 나타나는 순서를 변경
- 기본값은 0이고, 값이 작을수록 먼저 표시
.child {
order : 0 /* default */
<number>
}
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex order 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; flex-direction: row; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border: 1px solid black; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <!-- 5 6 4 2 1 3 --> <div class="item" style="order: 3">1</div> <div class="item" style="order: 2">2</div> <div class="item" style="order: 4">3</div> <div class="item" style="order: 1">4</div> <div class="item" style="order: -1">5</div> <div class="item" style="order: 0">6</div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
flex-basis 속성
- Flex Item의 초기 길이를 지정할 때 사용
- 지정하지 않으면 기본적으로 자신의 content 값 또는 지정된 width 값으로 설정
- flex-grow 또는 flex-shrink 속성 적용하여 flex 크기를 변경할 때 base 역할
- flex-basis와 width
- 항상 width 보다 flex-basis 설정된 값 사용
- 최소너비(min-width)와 최대너비(max-width) 설정하는 경우 width 사용
.child {
flex-basis : auto /* default */
<width>
}
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex-basis 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; flex-direction: row; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border: 1px solid black; } .item:nth-child(2){ /* 자신의 content 너비값으로 설정 (기본) */ flex-basis: auto; } .item:nth-child(3){ /* width 값으로 설정 */ flex-basis: auto; width: 150px; } .item:nth-child(4){ /* 명시된 flex-basis 값으로 설정 */ flex-basis: 250px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋
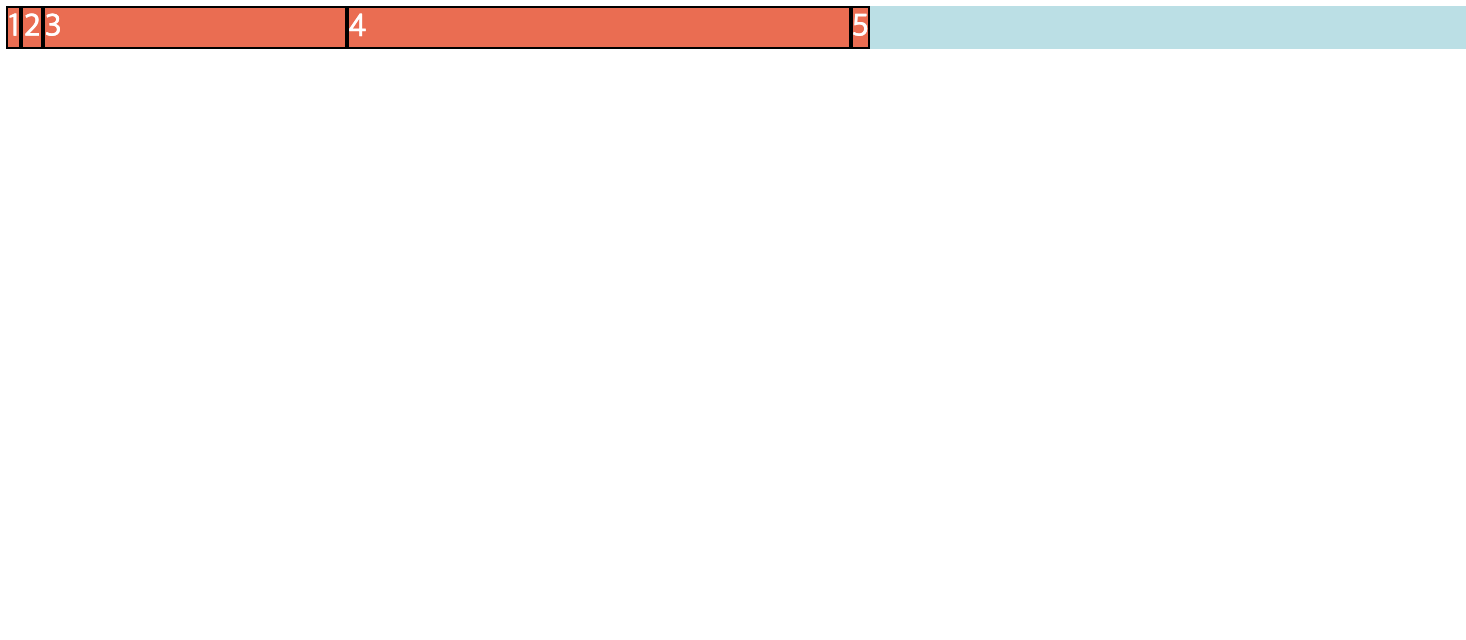
-
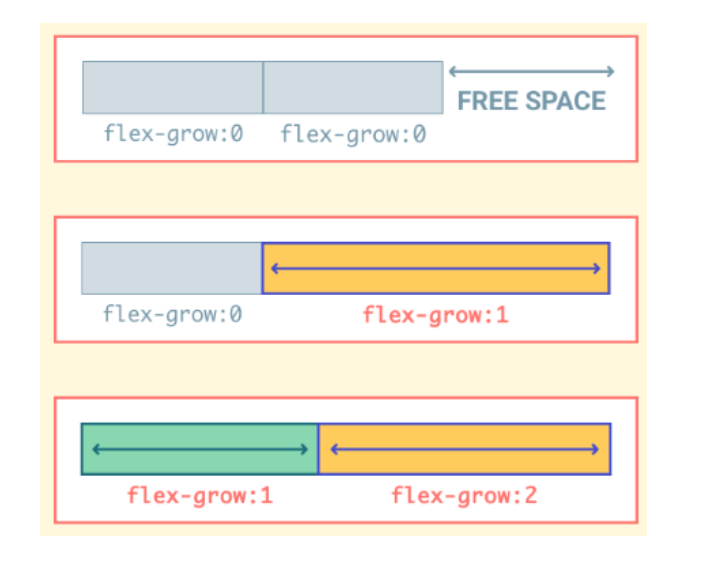
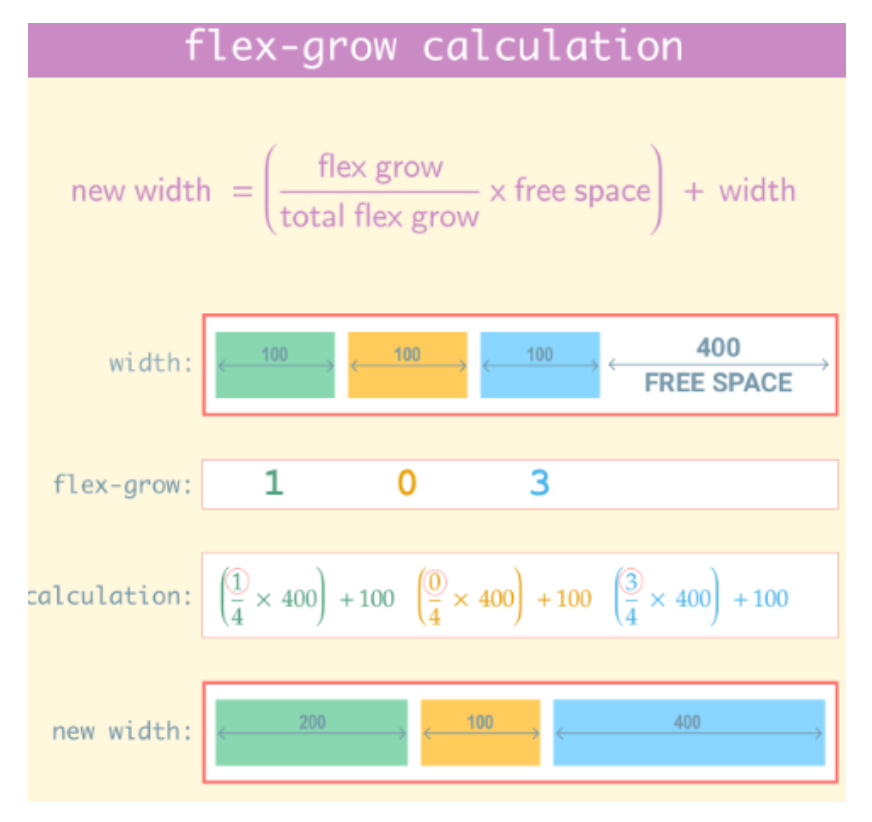
flex-grow 속성
- Flex Container에 여분의 공간이 있는 경우 일정 비율에 따라 특정 항목이 비어있는 공간을 채우도록 지정
- 필요한 경우 Flex Item이 커질 수 있음
- 기본값은 0, 숫자가 커질수록 더 빠르게 성장
.child {
flex-grow : 0 /* default */
<number>
}
-
📋 코드 📋
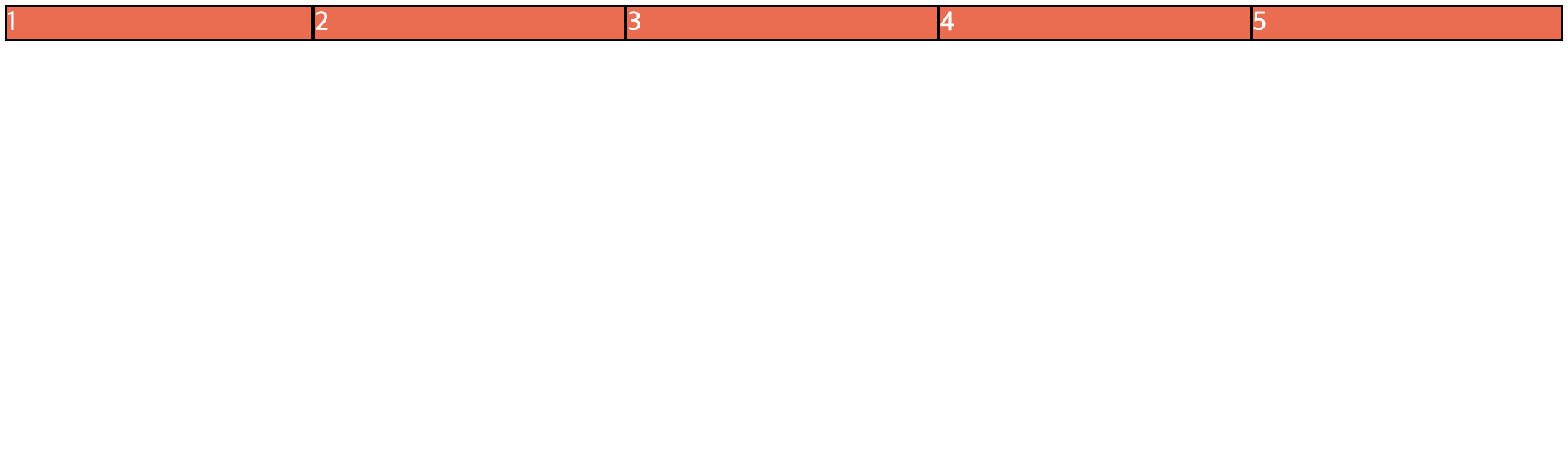
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex-grow 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; flex-direction: row; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border: 1px solid black; /* 1로 지정하면 균등하게 전체 너비를 채움 */ flex-grow: 1; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex-grow2 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; flex-direction: row; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border: 1px solid black; flex-grow: 1; } .item:nth-child(3){ /* 다른 항목보다 3배정도 빠르게 성장한다. */ flex-grow: 3; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
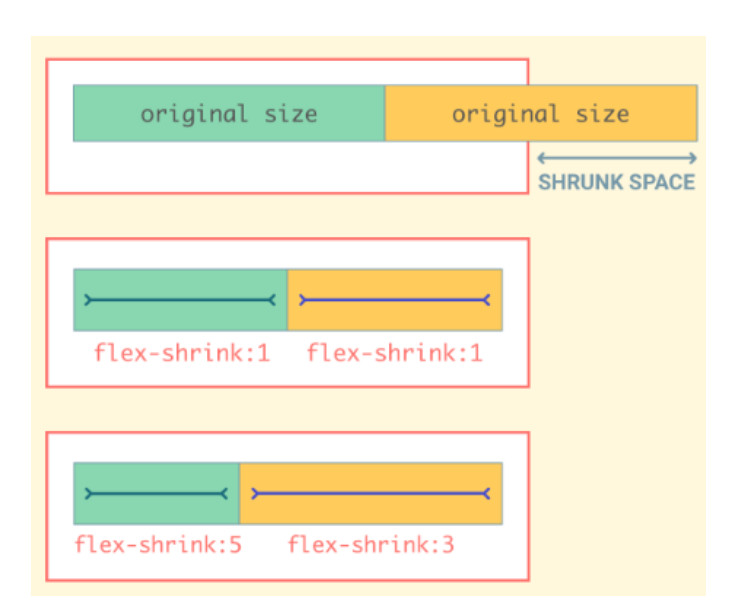
flex-shrink 속성
- flex-grow 속성과 반대
- 공간이 부족한 경우에 Flex Item이 얼마나 빨리 축소될 것인지 제어하는 속성
- 기본값은 1, 숫자가 클수록 더 많이 축소 (0으로 지정하면 축소 안됨)
.child {
flex-shrink : 1 /* default */
<number>
}
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex-shrink 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; flex-direction: row; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border: 1px solid black; width: 250px; flex-shrink: 2; } .item:nth-child(2){ background-color: black; flex-shrink: 1; /* 숫자가 클수록 더 크게 줄어든다. 다른 item은 2이기 때문에 더 빨리 축소된다.*/ } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex-shrink2 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; flex-direction: row; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border: 1px solid black; width: 250px; flex-shrink: 1; } .item:nth-child(2){ background-color: black; flex-shrink: 0; /* 숫자가 클수록 더 크게 줄어든다. 0이면 줄어들지 않는다.*/ } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
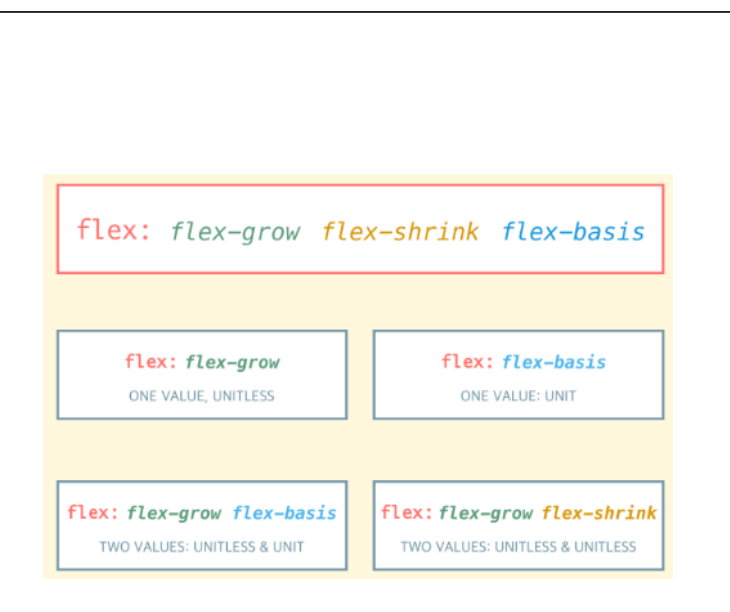
flex 속성
- flex-grow, flex-shrink, flex-basis 속성을 모두 설정하기 위한 단축 표현 방법
- 원하는 속성만 설정하면 설정하지 않은 속성은 기본값 사용
.child {
flex : 0 1 auto /* default */
<flex-grow> <flex-shrink> <flex-basis>
<flex-grow>
<flex-basis>
<flex-grow> <flex-basis>
<flex-grow> <flex-shrink>
}
-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex 단축 표현 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; flex-direction: row; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border: 1px solid black; width: 250px; } .item:nth-child(2){ background-color: black; flex: 0 0 200px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
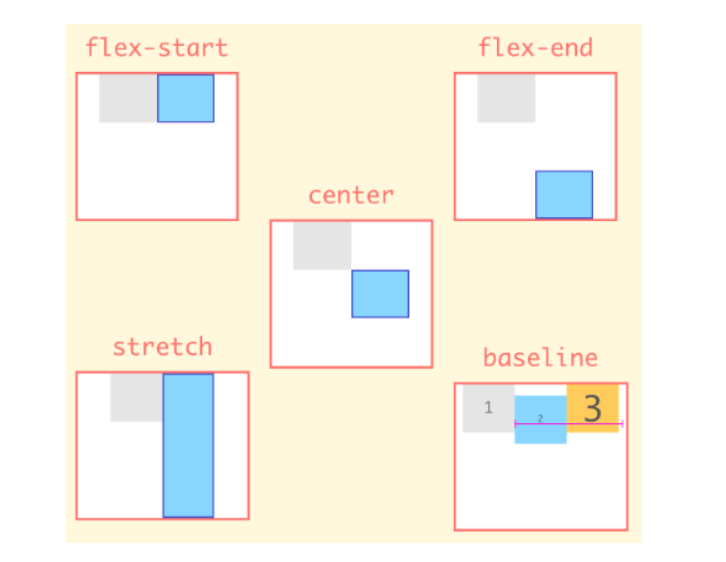
align-self 속성
- 설정된 기본 정렬 재정의
- align-items 속성은 Flex Container에서 지정 가능한 속성이기 때문에 모든 Flex Item에 적용
- 독립적으로 적용하기 위해서 align-self 속성 사용
- 설정된 기본 정렬 재정의
.child {
align-self : stretch /* default */
flex-start
flex-end
center
baseline
}
- 📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>flex align-self 실습</title> <style type="text/css"> .container{ background-color: powderblue; display:flex; flex-direction: column; } .item{ background-color: tomato; color:white; border: 1px solid black; width: 250px; } .item:nth-child(2){ background-color: black; align-self: flex-end; } .item:nth-child(4){ background-color: blue; align-self: center; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> </div> </body> </html> 📋 실행 📋
7. 반응형 웹을 위한 미디어 쿼리
1) Media Queries
- 사이트에 접속하는 미디어 타입과 특징, 해상도에 따라 스타일 속성을 적용하게 하는 기술
- @media 규칙을 적용하면 다양한 미디어 유형에 대해 다양한 스타일 규칙 적용
- 뷰포트의 너비와 높이 및 방향(가로/세로) 정보를 활용하여 반응형 App 구현
- Media Query 문법
- not/only : 모든 조건 부정 / 미디어 쿼리를 지원하는 기기만 미디어 쿼리를 해석
- mediatype : 미디어 쿼리가 적용될 미디어 타입 명시 (생략 가능)
- 생략하지 않으면 반드시 다음에 and 연산자 필요
- all (모든 기기, 생략할 경우 all로 인식)
- print (인쇄 장치)
- screen (컴퓨터 화면)
- speech (스크린 리더기)
- media feature : 미디어 쿼리가 적용될 미디어 조건
- min-width:<화면 너비> (미디어 쿼리가 적용도리 최소 너비)
- max-width:<화면 너비> (미디어 쿼리가 적용될 최대 너비)
- orientation:portrait (세로 모드, 뷰포트의 세로 높이가 가로 너비보다 큰 경우)
- orientation:landscape (가로 모드, 뷰포트의 가로 너비가 세로 높이보다 큰 경우)
@media 미디어타입 and (표현식) {
CSS 코드;
}
@media <not|only> <mediatype> and (<media feature>) <and|or|not> (<media feature>) {
/* css 코드 */
}-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <style> body { background-color: yellow; } @media screen and (max-width: 600px) { /* 최대 600px 이 되면 lightblue로 변경해라 */ body { background-color: lightblue; } } </style> </head> <body> <h1>The @media Rule</h1> <p>Resize the browser window. When the width of this document is 600 pixels or less, the background-color is "lightblue", otherwise it is "yellow".</p> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <style> div.example { background-color: yellow; padding: 20px; } @media screen and (max-width: 600px) { div.example { display: none; } } </style> </head> <body> <h2>Hide elements on different screen sizes</h2> <div class="example">Example DIV.</div> <p>When the browser's width is 600px wide or less, hide the div element. Resize the browser window to see the effect.</p> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

-
📋 코드 📋
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <text>media query 반응형</text> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <style> /* { box-sizing: border-box; } /* Create four equal columns that floats next to each other */ .column { float: left; width: 25%; padding: 20px; } /* Clear floats after the columns */ .row:after { content: ""; display: table; clear: both; } /* On screens that are 992px wide or less, go from four columns to two columns */ @media screen and (max-width: 992px) { .column { width: 50%; } } /* On screens that are 600px wide or less, make the columns stack on top of each other instead of next to each other */ @media screen and (max-width: 600px) { .column { width: 100%; } } </style> </head> <body> <h2>Responsive Four Column Layout</h2> <p><strong>Resize the browser window to see the responsive effect.</strong> On screens that are 992px wide or less, the columns will resize from four columns to two columns. On screens that are 600px wide or less, the columns will stack on top of each other instead of next to eachother.</p> <div class="row"> <div class="column" style="background-color:#aaa;"> <h2>Column 1</h2> <p>Some text..</p> </div> <div class="column" style="background-color:#bbb;"> <h2>Column 2</h2> <p>Some text..</p> </div> <div class="column" style="background-color:#ccc;"> <h2>Column 3</h2> <p>Some text..</p> </div> <div class="column" style="background-color:#ddd;"> <h2>Column 4</h2> <p>Some text..</p> </div> </div> </body> </html> -
📋 실행 📋

