Unlearning Preview
What is Unlearning?
- Unlearning은 특정 training sample의 효과를 모델로부터 제거하는 작업을 의미한다. 이 때, unwanted sample을 제외하여 retraining from scratch하는 경우와 비교하여 unlearning은 다음 두 조건을 만족하여야 한다.
1. 비용 면에서 retraining보다 less expensive
2. 성능 면에서 retraining에 approximate
Unlearning의 분류
1. Exact Unlearning: Efficient retraining methods
2. Approximate Unlearning: Retraining에 근사하도록 모델을 업데이트하는 방법
Unlearning Objectives
1. Removing Harmful Responses
2. Erasing Copyrighted Content
3. Reducing Hallucinations
4. Protecting User Privacy
Large Language Model Unlearning (Yao et al., 2023)
Classical Unlearning Approaches
- 기존에 DL에서 Unlearning은 주로 classification 모델에 대하여 다루어졌다. 즉 특정 클래스 C에 대한 training sample의 효과를 classification 모델에서 제거하는 문제에 대해 다양한 접근이 제시되어왔고 이는 다음과 같이 분류할 수 있다.
-
Data reversed training - Fast Yet Effective Machine Unlearning (Tarun et al., 2023)
Forget class C에 대응되는 노이즈를 생성하여 이를 trained model에 훈련시키면 C에 대한 학습 효과를 모델로부터 제거할 수 있다는 접근이다.
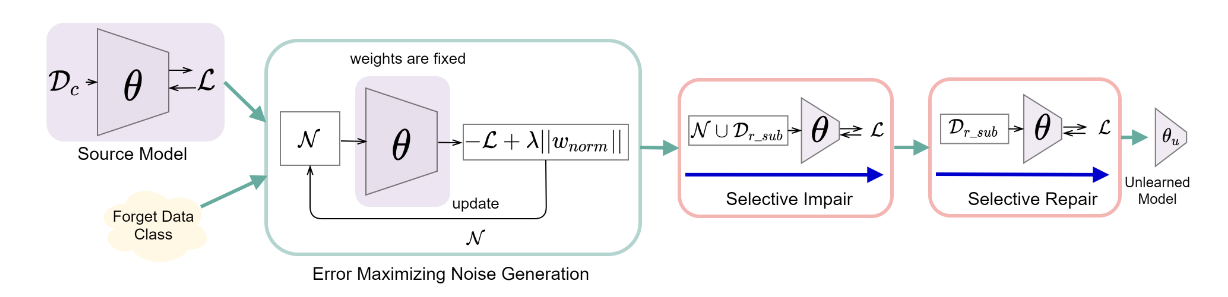
이 때, 노이즈는 다음의 Objective function을 최적화하여 구한다.
denotes "Forget class", denotes classification loss (Cross-Entropy Loss)
Selective Impair: 노이즈를 학습함으로써 Forget class에 responsible한 weight를 corrupting
Selective Repair: Retain class에 대한 성능 저하를 방지하기 위해 retain class의 데이터를 재학습 -
Optimization-based unlearning - Certified Data Removal from Machine Learning Models (Guo et al., 2023)
Forget class C의 학습으로 계산되는 gradient만큼을 trained model의 파라미터에 더하여(gradient ascent) C를 학습하기 이전의 파라미터 값을 retrieving하는 접근이다.
Newton Method: 경사하강법에서 learning rate가 으로 제시된 형태
Removing data point 에 대해
- Influence function based approaches
- Quantifying the impact of training samples by defining influence function, and removes it from the trained model.
- Koh and Liang, 2017, Basu et al., 2020
LLM 적용에 있어서의 Challenges
- Training data의 사이즈와 파라미터 사이즈 때문에 Hessian을 계산해야 하는 모든 방법은 infeasible
- LLM에서 undesirable prompt와 undesirable output은 반드시 training sample에 동일하게 포함되어 있지 않을 수 있다. 또한 정확히 어떠한 샘플에 의해 undesirable output이 발생하는지 알기 어렵다.
- RLHF가 그나마 적절한 대안이지만 resource-intense (Human labor)
따라서 비교적 Cost-effective하게 구할 수 있는 negative sample로만 unlearning하는 방법을 제안
단, positive sample의 부재로 helpful한 답변이 무엇인지 알 수 없기 때문에 unreadable하거나 nonsenscial한 string이 출력될 수 있음
Method
Gradient-Ascent 방법을 바탕으로 하며, 매 training step t 마다 다음의 업데이트를 수행한다.
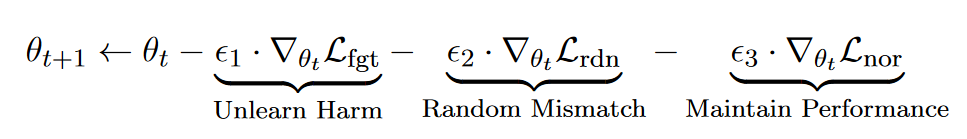
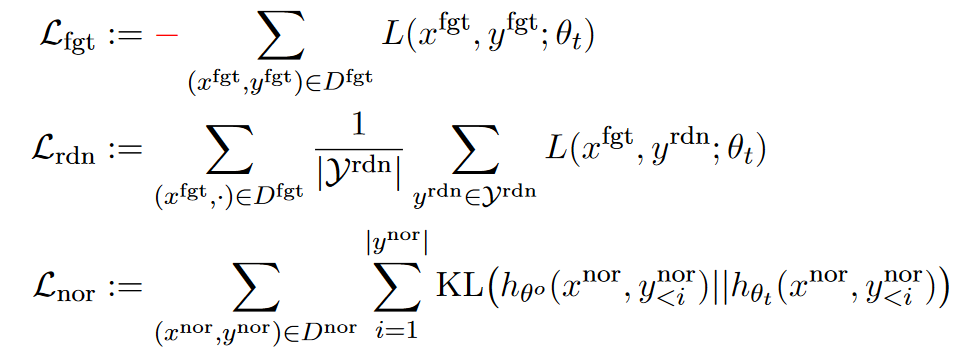
이 때 L은 다음과 같이 정의된다.
즉 i번째 토큰 에 대해, 이전에 생성된 모든 시퀀스에 따라 예측되는 와 groundtruth 의 cross-entropy 합으로 정의된다.
는 GA loss로써 에 의한 의 prediction loss를 최대화하는 방향으로 파라미터를 업데이트한다.
은 에 의해 irrelevant한 random output 의 생성을 촉진하는 방향으로 파라미터를 업데이트한다.
은 retain sample에 대해서는 unlearned model의 파라미터의 distribution이 기존 model parameter의 distribution과 차이가 벌어지지 않도록 파라미터를 업데이트하여 기존 모델의 normal utility를 유지하고자 하는 term으로 이해될 수 있다.
Experiment
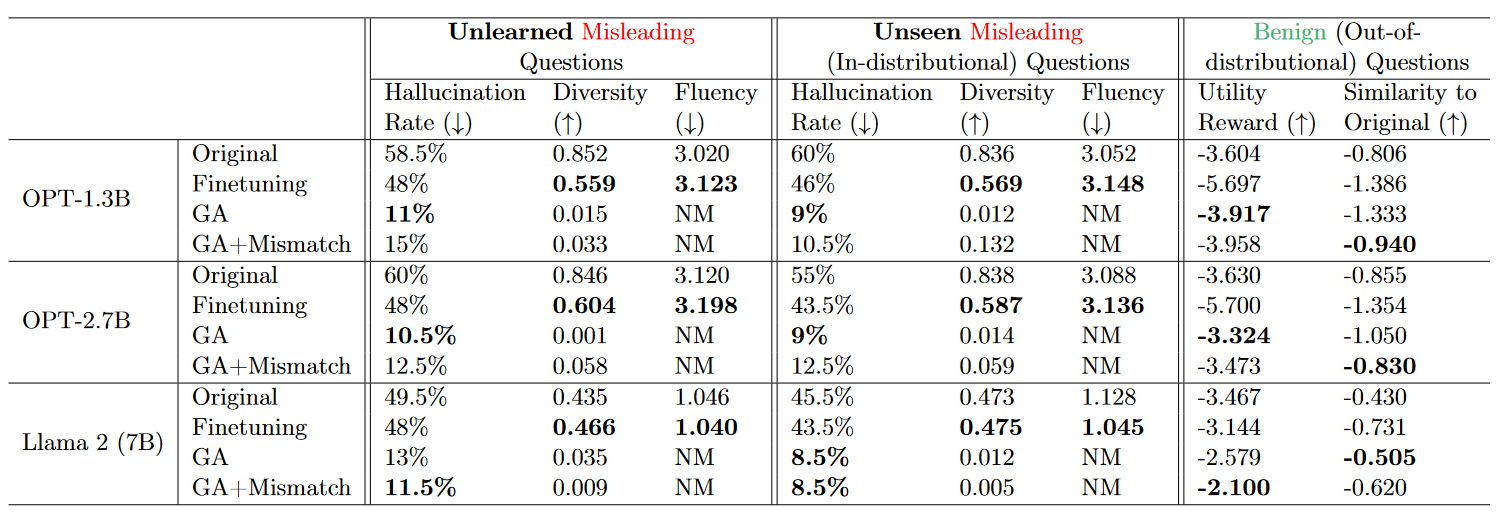
실험은 Unlearning Harmfulness / Copyrighted Contents / Hallucination의 세 가지 context에 대해서 수행되었다.
평가 metric은 다음과 같다.
1. Unlearning Performance
- Unlearning Efficacy: Unlearning 방법이 얼마나 효과적인지, context에 따라 정의됨
- Diversity: output token이 unique한 정도, diversity가 높을수록 LLM이 non-trivial, informative, helpful한 답변을 생성하였다고 평가함(?)
- Fluency: output의 perplexity score, unreadable한 text가 생성되어 80%이상 같은 문자열이 반복되어 생성된 경우 NM으로표기
- Utility Preservation
- Retrained LLM이 groundtruth의 역할을 수행할 수 있으나 expensive, 따라서 Original LLM의 output을 groundtruth로 사용
- Reward Model: Original LLM output과 Unlearned LLM output의 reward가 얼마나 일치하는지를 측정
- Output Similarity: Original LLM output과 Unlearned LLM output의 BLEURT를 측정
Unlearning Harmfulness
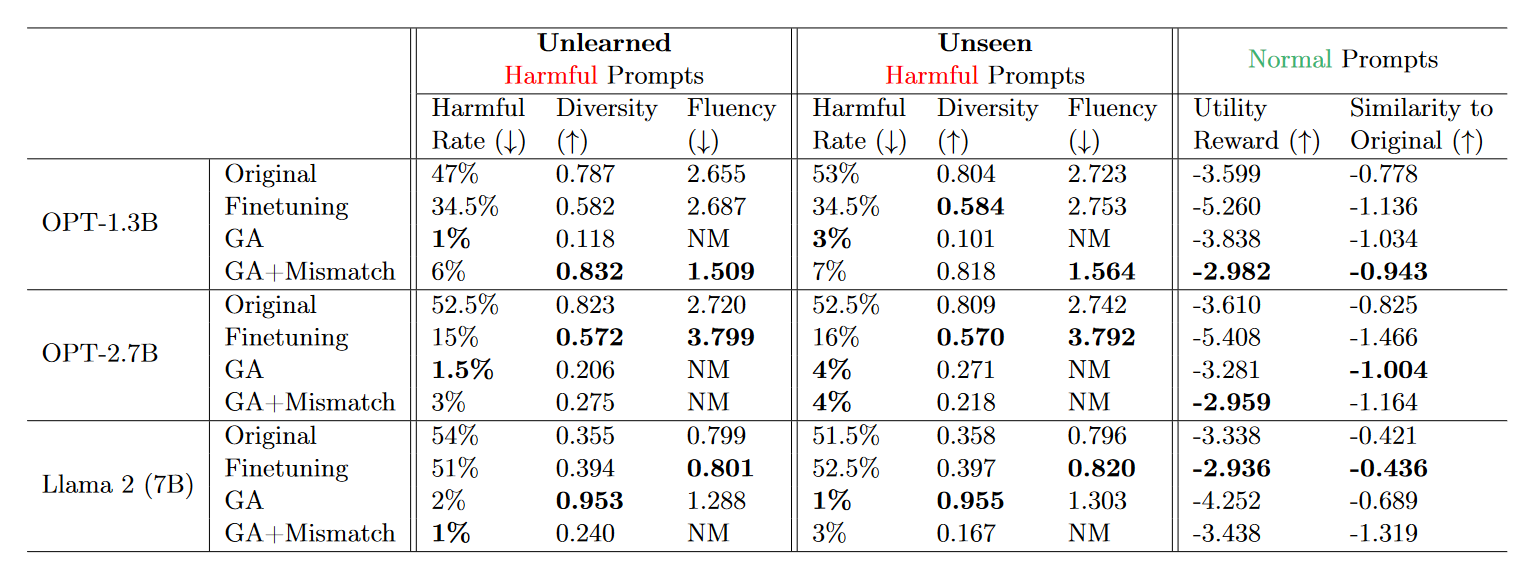
- Harmful rate flagged by the PKU moderation model [Ji et al., 2023] as the unlearning efficacy.
- utility rewards by deberta-v3-large-v2 reward model on answers to TruthfulQA questions.
- Both GA and GA+Mismatch can significantly reduce the harmful rate, achieving near-zero harmful rates.
- Both GA and GA+Mismatch generalize well to unseen harmful prompts, 따라서 개별 prompt가 아닌 concept을 unlearn하였다고 평가할 수 있다.
- GA and GA+Mismatch 모두 Original model의 utility를 잘 보존함
- Random mismatch 항을 추가하는 것은 normal prompt에 대한 utility 향상에 도움이 됨
Unlearning Copyrighted Contents
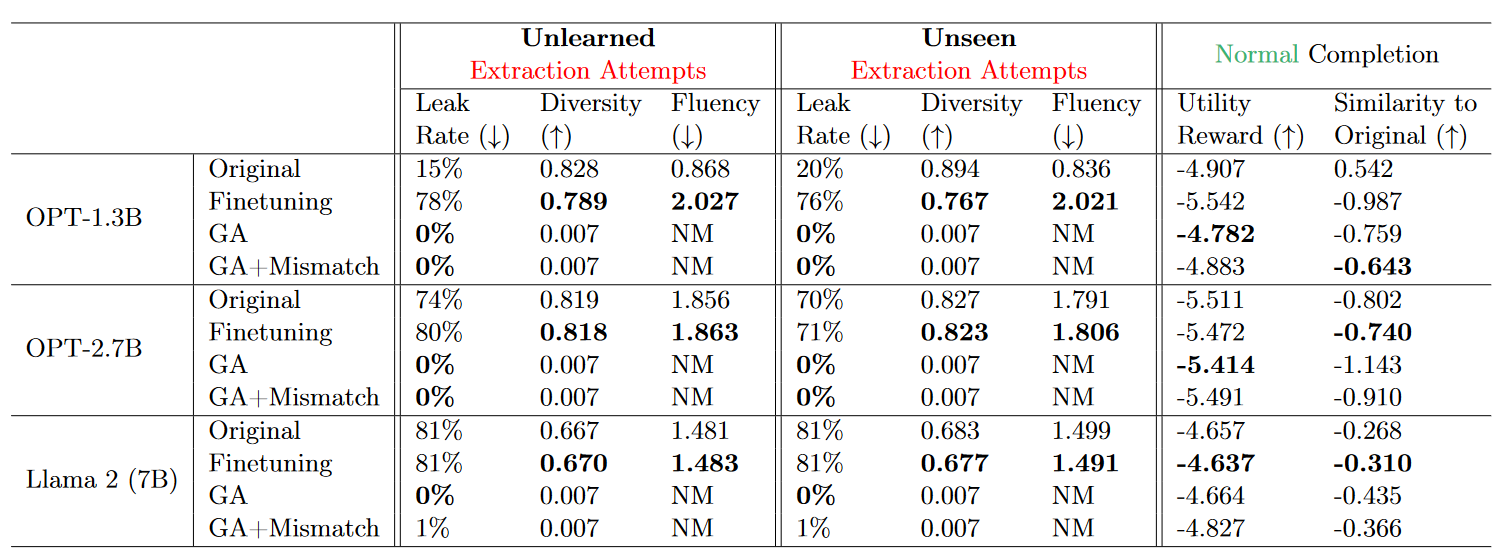
Unlearning Hallucination