비동기 프로그래밍(4)
오늘은 then chain을 제거하는 방법에 대해 소개하겠다.
const moveLeftPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(() => console.log('left'))
const moveRightPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(() => console.log('right')
})
moveRightPromise
.then(res => {
res()
return moveLeftPromise
})
.then(res => {
res()
return moveRightPromise
})
.then(res => {
res()
return moveLeftPromise
})
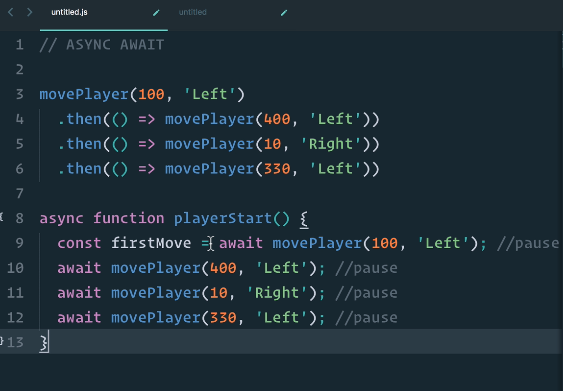
.then(res => res())promise가 중첩되면 이렇게 then, then, then, then이 계속 생기는데 이걸 then chain이라고 부른다고 했었다.
Async & Await
: ES8에 도입된 최신 비동기처리 기법이다. 최신 기법인만큼 , 비동기 코드를 작성하기도 쉽고, 가독성도 제일 좋다.
먼저, OOP에서 설명했던 prototype과 class의 관계를 떠올려보자. 자바스크립트에서 class는 prototype을 기반으로 동작하는 syntactic sugar라고 했었다.
갑자기 이 이야기를 꺼내는 이유는 async & await 또한 promise를 기반으로 동작하는 syntactic sugar 문법이기 때문에 생각이났다.
prototype에 비해 class 문법이 편리했던 것처럼 async 문법도 마찬가지이다.
그러니까 이번에 확실하게 async를 익혀보자. 위 promise를 async로 바꿔보겠다.
const moveLeftPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(() => console.log('left'))
})
const moveRightPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(() => console.log('right'))
})
async function test() {
const right1 = await moveRightPromise
const right2 = await moveRightPromise
const left1 = await moveLeftPromise
const left2 = await moveLeftPromise
right1()
left1()
right2()
left2()
}
test()
// 실행 결과 : right left right left
async 함수 안에서 비동기 코드가 동작한다.
이렇게 async 함수를 사용하면 비동기 코드를 마치 동기 코드와 같은 모양으로 작성할 수 있다.
이제, promise와 async를 비교해보자.
promise에서는 오른쪽 (then) 왼쪽 (then) 오른쪽 (then) 왼쪽 ...
이런 방식으로 비동기 작업의 순서를 보장하는 코드를 작성했다.
반면에 async에서는 await를 이용해 resolve 값을 받아올 수 있으며,
비동기 작업들의 작업 순서는 코드를 작성한 순서와 동일하다.
다음에는 비동기 작업을 처리하는 심화된 방법을 소개하겠다.
