Pytorch
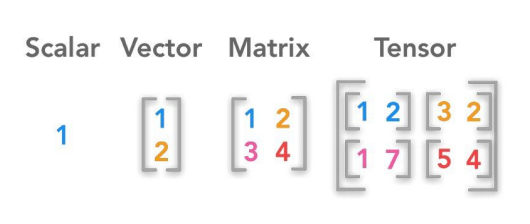
텐서
-
파이토치의 기본적인 자료구조, 스칼라, 벡터, 행렬등을 일반화
-
-

-
텐서의 크기와 랭크(차원)
-
텐서의 모양 바꾸기
x0 = torch.unsqueeze(x, 0) x1 = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) x2 = torch.unsqueeze(x, 2) print("x0.shape:", x0.shape) print("x1.shape:", x1.shape) print("x2.shape:", x2.shape) print("x0 =", x0) print("x1 =", x1) print("x2 =", x2) ## unsqueeze(x, i): tensor x에 i 번째 차원 추가x3 = torch.squeeze(torch.squeeze(x0)) print("x3 =", x3) print("x3.shape =", x3.shape) ## squeeze(x): 텐서 x에서 크기가 1인 차원 제거x4 = x.view(9) x5 = x.view(1,3,3) print("x4 =", x4) print("x5 =", x5) ## x.view([shape]): x를 [shape]의 모양으로 변환
-
행렬 연산
-
xw + b
x = torch.FloatTensor([[1,2], [3,4], [5,6]]) w = torch.randn(1,2, dtype=torch.float) b = torch.randn(3,1, dtype=torch.float) result = torch.mm(x, torch.t(w)) + b print(result)- 곱셈 : torch.mm
-
기울기 계산
w = torch.tensor(1.0, requires_grad=True) a = w*3 l = a**2 l.backward() print('l을 w로 미분한 값은', w.grad)
Linear Regression
-
학습 데이터 생성
x_train = torch.FloatTensor([[1,2], [3,2], [3,7], [1,1], [1,0]]) y_train = torch.FloatTensor([[4], [8], [23], [1], [-2]]) ## y = 2x1 + 3x2 - 4 -
w, b초기화 및 Learning Rate 설정
W = torch.rand(2,1) b = torch.rand(1,1) lr = 0.01 -
반복횟수 설정 및 w,b의 requires_grad 설정
for epoch in range(3001): W.requires_grad_(True) b.requires_grad_(True) -
Hypothesis, cost 설정
hypothesis = torch.mm(x_train, W) + b cost = torch.mean((hypothesis - y_train) ** 2) -
경사계산 및 w,b업데이트
cost.backward() with torch.no_grad() as grd: W = W - lr * W.grad b = b - lr * b.grad -
결과 출력
if epoch % 100 == 0: print( 'epoch: {}, cost: {:.6f}, W: {}, b: {}' .format(epoch,cost.item(), W.squeeze(), b)) -
결과
-
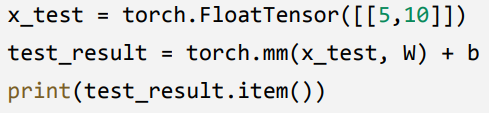
x = [5,10]일때 y값을 구하려면