논리적 개념
동시성이란
여러 작업을 동시에 다루는 것. 즉, 한 사람이 여러 일을 동시(concurrency) 에 처리(여러 작업 간 스위칭 발생)
"""
Concurrency Programming
동시성 프로그래밍 기법과 결과 비교
"""
import time
"Sync Programming"
import requests
def sync_fetcher(session: requests.Session, url: str) -> str:
with session.get(url) as res:
return res.text
def sync_crawler():
urls = ["https://naver.com", "https://google.com", "https://instagram.com"]
with requests.Session() as session:
res = [sync_fetcher(session, url) for url in urls]
return res
"Concurrency - Coroutine"
import aiohttp, asyncio
async def fetcher(session: aiohttp.ClientSession, url: str) -> str:
async with session.get(url) as res:
return await res.text()
async def coroutine_crawler():
urls = ["https://naver.com", "https://google.com", "https://instagram.com"]
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
# 동시에 세 사이트에 request 요청을 수행함
# 단일 스레드 내 비동기 동작
res = await asyncio.gather(*[fetcher(session, url) for url in urls])
return res병렬성이란
한 번에 여러 작업을 병렬적(Parallelism)으로 처리하는 것. 즉, 여러 사람이 여러 일을 각각 동시(at the same time)에 처리
"Parallelism - Multi Threading"
from typing import Tuple
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def multi_fetcher(params: Tuple[requests.Session, str]) -> str:
session, url = params
with session.get(url) as res:
return res.text
def multi_crawler():
urls = ["https://naver.com", "https://google.com", "https://instagram.com"]
executor = ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=3)
# max_workers는 사용할 Thread 개수
with requests.Session() as session:
params = [(session, url) for url in urls]
# 다중 스레드를 만들어 비동기 처리 하는 코드
res = list(executor.map(multi_fetcher, params))
return res세 가지 코드 결과 비교
if __name__ == "__main__":
s = time.time()
sync_crawler()
print(f"sync crawler execution time: {time.time() - s} s")
s = time.time()
asyncio.run(coroutine_crawler())
print(f"coroutine crawler execution time: {time.time() - s} s")
s = time.time()
multi_crawler()
print(f"multi-thread crawler execution time: {time.time() - s} s")결과 비교
| 방식 | 결과(s) | 비고 |
|---|---|---|
| concurrency | 0.83 | |
| parallelism | 0.92 | 적절한 max_workers를 지정하더라도동시성(concurrency) 방식이 비교 우위이다. |
| sync | 1.31 |
GIL
GIL 설명을 하기 전에 몇 가지 단어 정의부터 확인하고 넘어가야 한다.
Mutex(뮤텍스)
뮤텍스란 한 프로세스의 내부에서 여러 스레드의 임계구역 제어를 위해 사용하는 객체를 뜻한다. 서로 다른 스레드가 공유 자원(데이터, 클래스 등)에 접근할 때 해당 자원을 점유하고 있는 스레드가 뮤텍스를 풀어줘야 접근이 가능해진다.
Garbage Collection(GC, 가비지 컬렉션)
가비지 컬렉션은 메모리 관리 기법의 하나로 프로그램이 동적으로 할당했던 메모리 영영 중에서 필요 없게 된 영역을 해제하는 기능이다.
Race Condition(레이스 컨디션)
레이스 컨디션이란 두 개 이상의 프로세스가 공통 자원을 병행적으로(concurrently) 읽거나 쓰는 동작을 할 때, 공유 자원에 대한 접근이 어떤 순서에 따라 이루어졌는지에 따라 그 실행 결과가 같지 않고 달라지는 상황을 말한다.
What is GIL
Global Interpreter Lock(GIL)으로 한 번에 한 개의 스레드만을 강제하는 CPython 인터프리터 기반 파이썬 정책이다.
파이썬은 어떤 객체가 호출될 때 동적 메모리 할당 후 참조 횟수를 센다. 이때 참조 횟수가 0이 되면 해당 객체를 메모리에서 삭제시키는 GC(가비지 컬렉션)가 동작하고 이러한 특징으로 인해 파이썬이 병행적 상황에서 인터프리터가 동시에 실행될 때 레이스 컨디션이 발생할 수 있다. 그러므로 CPython에서는 GIL이 일종의 뮤텍스 역할을 하여 여러 스레드에서 동시에 공유 자원에 접근할 수 없게 한다.
이에 따라 아래 사진(1)과 같이 멀티 스레딩 상황에서 context switching이 발생하고 때에 따라 코루틴보다 느린 결과를 도출할 수 있다.
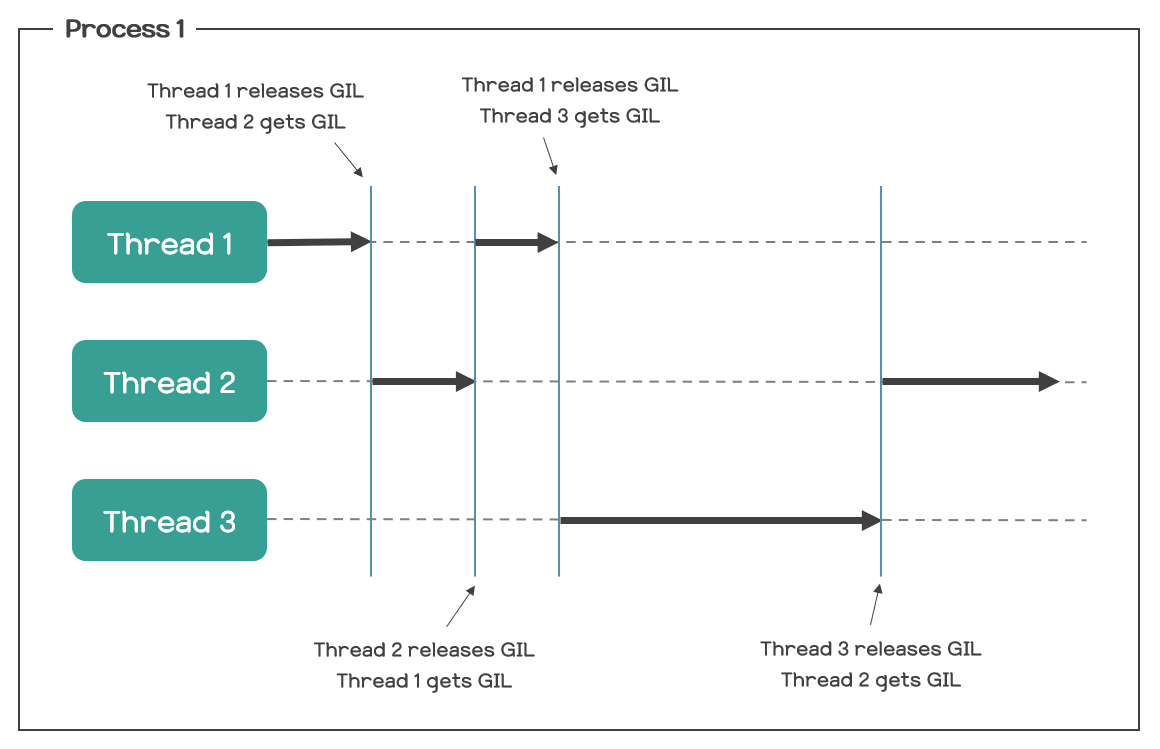
결론
파이썬 멀티 스레딩은 병렬 연산(Parallelism) 보다 동시성(Concurrency) 개념을 적용하여 I/O bound 코드에서 유용하게 사용 할 수 있다.
