난이도 ⭐️⭐️
작성 날짜 2025.06.16
고민 내용
프로젝트를 진행하던 중, 카톡과 같은 SNS의 채팅방 채팅 메시지 캡처 사진을 상대방과 나로 구분하고 각 내용을 추출해야 하는 요구사항이 있었다.
🤔 서버 개발만 공부해온 내가 이미지 처리 문제를 해결할 수 있을까..?
찾아보기
디지털 영상 처리 수업으로 해결하기
생각해보니까 작년 초 학교에서 <디지털 영상 처리>라는 수업을 수강한 적이 있었다. 그곳에서 배운 몇 가지 기술과, 해당 과목의 프로젝트에서 사용했던 pytesseract를 이용하면 글자 추출이 가능하지 않을까?
전략은 이렇다.
- 가우시안 블러를 이용해 이미지 전처리
- 적절한 Threshold를 설정해 이진화
- 외곽선을 찾아 일정 기준을 넘는 것들만 수집
- 왼쪽이면 상대방, 오른쪽이면 내 메시지로 판단
- 테서랙트로 텍스트 추출
img = cv2.imread('./samples/test.png')
# 회색조 변환 + 블러
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (3, 3), 0)
# 이진화
thresh = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(blur, 255,
cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,
cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV, 11, 2)
# show_img(thresh)
# 외곽선 찾기
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 말풍선 필터링
balloons = []
for cnt in contours:
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
if 100 < x < 120 or 720 < x + w < 750 :
if 50 < w < 1000 and 50 < h :
balloons.append((x, y, w, h))
# y 기준 정렬
balloons.sort(key=lambda b: b[1])
# 말풍선 추출 및 OCR
for (x, y, w, h) in balloons:
roi = img[y:y+h, x:x+w]
gray = cv2.cvtColor(roi, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Otsu threshold
_, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
resized = cv2.resize(binary, None, fx=2, fy=2, interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
text = pytesseract.image_to_string(resized, lang='kor+eng', config='--psm 6')
print(text.strip())
# 결과 확인 시 활성화
# show_img(resized)
# cv2.imwrite('resized'+str(x)+'x'+str(y)+'y'+str(w)+'w'+str(h)+'.jpg', resized)이미지 처리 테스트
이제 실제 카톡 이미지로 테스트해보자!


망했다.
일단 '메시지'가 무엇인지 정의하기도 어렵고,
다양한 카톡 테마와 인스타 dm 등등 여러 메시지를 대응하는 것에도 어려움이 있었던 것이 문제도 존재했다.
좀더 고도화된 기술이 필요하다...
- 내가 원하는 객체를 인식할 수 있어야 한다.
- 특정 색상, 위치에 의존하지 않아야 한다.
YOLO
해결책은 딥 러닝.
그중에서도 실시간성을 가져 빠르게 서빙 가능하고, 경량화된 YOLO를 선택하였다.
또한, '나'와 '상대방'의 메시지를 분류하기 위한 Segmentation이 가능하면서 가벼운 YOLOv8이 필요하다고 생각하였다.
데이터 셋을 찾아보자
문제는 데이터 셋!
구글에서 '카톡 짤'을 검색해서 하나하나 저장하고 Label Studio로 라벨링 하다 현타가 와서 구글링을 시작
'Text Message Object Detection'으로 검색을 하니 데이터셋이 하나 딱 나오더라
https://universe.roboflow.com/text-message/text-message
요런 걸루
무려 라벨링된 데이터 2천 장!
근데 내가 원하는 건 상대의 톡과 내 톡이 구분되어야 한다.
이건 할 수 없이 수작업으로 진행해주었다.
label-studio-converter import yolo \
-i ./test \
-o test_annotations.json \
--image-root-url "/data/local-files/?d=test/images" \
--to-name "image" \
--from-name "label"Storage에 먼저 사진 업로드 (동기화)

모든 데이터셋을 전부 수정하는 것은 시간이 부족해 238장만 수정했다.
Label Studio의 조금 마음에 안드는 점은 나는 내가 선택한 파일만 export 하고 싶은데 그냥 프로젝트 전체 다 받아야 한다는 점이다...
여튼 json으로 export 하면 모든 데이터셋이 나온다.
python 코드를 짜서 내가 수정한 id 값만 걸러주었다.
filter_data.py
import json
def filter_labeled_data(input_file, output_file, target_ids):
"""
Label Studio export 파일에서 특정 ID들만 필터링하여 새 파일로 저장
"""
with open(input_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = json.load(f)
# ID가 target_ids 범위에 있는 항목들만 필터링
filtered_data = []
for item in data:
item_id = item.get('id')
if item_id and is_target_id(item_id, target_ids):
filtered_data.append(item)
# 필터링된 데이터를 새 파일로 저장
with open(output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(filtered_data, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
print(f"Original: {len(data)} items")
print(f"Filtered: {len(filtered_data)} items")
print(f"Saved to: {output_file}")
def is_target_id(item_id, target_ranges):
"""ID가 지정된 범위에 있는지 확인"""
for start, end in target_ranges:
if start <= item_id <= end:
return True
return False
# 사용 예시
if __name__ == "__main__":
input_file = "project-1-at-2025-06-16-08-01-6fcb70fe.json"
output_file = "filtered_labeled_data.json"
# 작업 완료한 ID 범위: 1~51, 8604~8823
target_id_ranges = [
(1, 51),
(8604, 8823)
]
filter_labeled_data(input_file, output_file, target_id_ranges)그 다음에는 json을 YOLO 형식의 txt 파일로 바꿔준다.
이미지 파일 명과 동일한 이름으로 맞춰준다.
마찬가지로 python 코드로 해결하였다.
convert_to_yolo.py
import json
import os
from pathlib import Path
from urllib.parse import urlparse, parse_qs
def convert_labelstudio_to_yolo(json_file, output_dir="yolo_labels"):
"""
Label Studio export JSON을 YOLO 형식으로 변환
"""
# 출력 디렉토리 생성
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 클래스 매핑 (Label Studio 라벨 -> YOLO 클래스 ID)
class_mapping = {
"MyMessage": 0,
"OtherMessage": 1
}
# JSON 파일 로드
with open(json_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = json.load(f)
converted_count = 0
for item in data:
# data.image 경로에서 실제 파일명 추출
image_path = item.get('data', {}).get('image', '')
if not image_path:
# fallback으로 file_upload 사용
image_path = item.get('file_upload', '')
if not image_path:
continue
# URL 파라미터에서 파일명 추출
filename = extract_filename_from_path(image_path)
if not filename:
continue
# 확장자를 .txt로 변경
txt_filename = Path(filename).stem + '.txt'
txt_path = os.path.join(output_dir, txt_filename)
# 어노테이션 정보 추출
annotations = item.get('annotations', [])
if not annotations:
continue
yolo_lines = []
for annotation in annotations:
results = annotation.get('result', [])
for result in results:
if result.get('type') != 'rectanglelabels':
continue
# 원본 이미지 크기
original_width = result.get('original_width')
original_height = result.get('original_height')
if not original_width or not original_height:
continue
# 라벨 정보
value = result.get('value', {})
rectanglelabels = value.get('rectanglelabels', [])
if not rectanglelabels:
continue
label = rectanglelabels[0]
if label not in class_mapping:
continue
class_id = class_mapping[label]
# Label Studio 좌표 (percentage) -> YOLO 좌표 변환
x_percent = value.get('x', 0)
y_percent = value.get('y', 0)
width_percent = value.get('width', 0)
height_percent = value.get('height', 0)
# YOLO 형식: center_x, center_y, width, height (모두 0-1 범위)
center_x = (x_percent + width_percent / 2) / 100
center_y = (y_percent + height_percent / 2) / 100
width_norm = width_percent / 100
height_norm = height_percent / 100
# YOLO 라인 생성
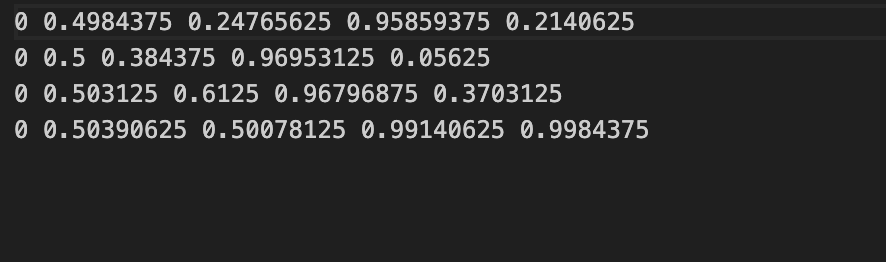
yolo_line = f"{class_id} {center_x:.6f} {center_y:.6f} {width_norm:.6f} {height_norm:.6f}"
yolo_lines.append(yolo_line)
# YOLO 텍스트 파일 저장
if yolo_lines:
with open(txt_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(yolo_lines))
converted_count += 1
print(f"Converted: {filename} -> {txt_filename}")
# 클래스 정보 파일 생성
classes_path = os.path.join(output_dir, 'classes.txt')
with open(classes_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for label, class_id in sorted(class_mapping.items(), key=lambda x: x[1]):
f.write(f"{label}\n")
print(f"\n변환 완료!")
print(f"총 {converted_count}개 파일 변환됨")
print(f"출력 디렉토리: {output_dir}")
print(f"클래스 정보: {classes_path}")
def extract_filename_from_path(image_path):
"""
이미지 경로에서 실제 파일명 추출
"""
if not image_path:
return None
# URL 파라미터가 있는 경우 처리
if '?' in image_path:
# URL 파싱
parsed_url = urlparse(image_path)
query_params = parse_qs(parsed_url.query)
# 'd' 파라미터에서 파일 경로 추출
if 'd' in query_params:
file_path = query_params['d'][0]
# 파일 경로에서 마지막 파일명만 추출
filename = os.path.basename(file_path)
return filename
# 일반적인 경우: 경로에서 파일명 추출
filename = os.path.basename(image_path)
return filename
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 변환 실행
convert_labelstudio_to_yolo("filtered_labeled_data.json", "yolo_labels")
마지막으로, 사진 데이터가 학습을 위해 정확히 구성되어있는지 체크하는 데이터 정합성 검증 코드가 필요하다.
사진과 YOLO 파일이 이름이 맞지 않거나, 누락된 파일이 있거나 하는 문제를 찾아내야 한다.
verify_yolo_conversion.py
import os
import json
import shutil
from pathlib import Path
from urllib.parse import urlparse, parse_qs
def copy_matching_images(yolo_dir="yolo_labels", images_dir="test/images", output_dir="yolo_images"):
"""
YOLO 라벨 파일과 일치하는 이미지 파일들을 복사
"""
print("=== 이미지 파일 복사 시작 ===\n")
# 출력 디렉토리 생성
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
# YOLO 라벨 파일 목록 가져오기 (classes.txt 제외)
if not os.path.exists(yolo_dir):
print(f"❌ YOLO 디렉토리가 존재하지 않습니다: {yolo_dir}")
return
txt_files = [f for f in os.listdir(yolo_dir) if f.endswith('.txt') and f != 'classes.txt']
print(f"YOLO 라벨 파일 수: {len(txt_files)}")
# 이미지 디렉토리 확인
if not os.path.exists(images_dir):
print(f"❌ 이미지 디렉토리가 존재하지 않습니다: {images_dir}")
return
copied_count = 0
missing_count = 0
for txt_file in txt_files:
# txt 파일명에서 확장자 제거
base_name = Path(txt_file).stem
# 이미지 파일 찾기 (jpg 우선, 없으면 png)
image_filename = None
source_path = None
# JPG 파일 먼저 확인
jpg_filename = base_name + '.jpg'
jpg_path = os.path.join(images_dir, jpg_filename)
if os.path.exists(jpg_path):
image_filename = jpg_filename
source_path = jpg_path
else:
# PNG 파일 확인
png_filename = base_name + '.png'
png_path = os.path.join(images_dir, png_filename)
if os.path.exists(png_path):
image_filename = png_filename
source_path = png_path
if source_path:
# 대상 경로
target_path = os.path.join(output_dir, image_filename)
# 파일 복사
shutil.copy2(source_path, target_path)
copied_count += 1
print(f"✅ 복사됨: {image_filename}")
else:
missing_count += 1
print(f"⚠️ 누락된 이미지: {base_name}.jpg 또는 {base_name}.png")
print(f"\n=== 복사 완료 ===")
print(f"복사된 이미지: {copied_count}개")
print(f"누락된 이미지: {missing_count}개")
print(f"출력 디렉토리: {output_dir}")
def verify_yolo_conversion(json_file, yolo_dir="yolo_labels"):
"""
YOLO 변환 결과 검증
"""
# JSON 파일 로드
with open(json_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = json.load(f)
print("=== YOLO 변환 결과 검증 ===\n")
# 통계 정보
total_images = len(data)
converted_files = 0
total_annotations = 0
class_counts = {"MyMessage": 0, "OtherMessage": 0}
for item in data:
# data.image 경로에서 실제 파일명 추출
image_path = item.get('data', {}).get('image', '')
if not image_path:
# fallback으로 file_upload 사용
image_path = item.get('file_upload', '')
if not image_path:
continue
# URL 파라미터에서 파일명 추출
filename = extract_filename_from_path(image_path)
if not filename:
continue
txt_filename = Path(filename).stem + '.txt'
txt_path = os.path.join(yolo_dir, txt_filename)
# YOLO 파일 존재 확인
if os.path.exists(txt_path):
converted_files += 1
# 라인 수 카운트
with open(txt_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
line_count = len([line for line in lines if line.strip()])
total_annotations += line_count
# 원본 JSON에서 클래스별 카운트
annotations = item.get('annotations', [])
for annotation in annotations:
results = annotation.get('result', [])
for result in results:
if result.get('type') == 'rectanglelabels':
rectanglelabels = result.get('value', {}).get('rectanglelabels', [])
for label in rectanglelabels:
if label in class_counts:
class_counts[label] += 1
else:
print(f"⚠️ 누락된 파일: {txt_filename} (원본: {filename})")
print(f"총 이미지 수: {total_images}")
print(f"변환된 파일 수: {converted_files}")
print(f"총 어노테이션 수: {total_annotations}")
print(f"MyMessage: {class_counts['MyMessage']}개")
print(f"OtherMessage: {class_counts['OtherMessage']}개")
# 샘플 파일 내용 출력
print("\n=== 샘플 YOLO 파일 내용 ===")
yolo_files = [f for f in os.listdir(yolo_dir) if f.endswith('.txt') and f != 'classes.txt']
if yolo_files:
sample_file = yolo_files[0]
sample_path = os.path.join(yolo_dir, sample_file)
print(f"\n파일: {sample_file}")
with open(sample_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
content = f.read().strip()
print(content[:200] + "..." if len(content) > 200 else content)
def extract_filename_from_path(image_path):
"""
이미지 경로에서 실제 파일명 추출
"""
if not image_path:
return None
# URL 파라미터가 있는 경우 처리
if '?' in image_path:
# URL 파싱
parsed_url = urlparse(image_path)
query_params = parse_qs(parsed_url.query)
# 'd' 파라미터에서 파일 경로 추출
if 'd' in query_params:
file_path = query_params['d'][0]
# 파일 경로에서 마지막 파일명만 추출
filename = os.path.basename(file_path)
return filename
# 일반적인 경우: 경로에서 파일명 추출
filename = os.path.basename(image_path)
return filename
if __name__ == "__main__":
verify_yolo_conversion("filtered_labeled_data.json", "yolo_labels")
# 이미지 파일 복사 실행
copy_matching_images("yolo_labels", "test/images", "yolo_images")
이제 하나의 폴더에 요런 구조로 정리해둔다.
이제 학습만 시키면 끝
YOLO 학습시키기
train_yolo.py
from ultralytics import YOLO
import torch
import os
def verify_label_format():
"""
라벨 파일 형식 검증
"""
print("=== 라벨 형식 검증 ===")
labels_dir = "yolo_test/labels"
if not os.path.exists(labels_dir):
print(f"❌ 라벨 디렉토리가 없습니다: {labels_dir}")
return False
label_files = [f for f in os.listdir(labels_dir) if f.endswith('.txt') and f != 'classes.txt']
if not label_files:
print("❌ 라벨 파일이 없습니다.")
return False
# 처음 5개 라벨 파일 검사
valid_files = 0
empty_files = 0
for i, label_file in enumerate(label_files[:5]):
sample_file = os.path.join(labels_dir, label_file)
print(f"\n검사 중: {label_file}")
try:
with open(sample_file, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
if not lines or all(not line.strip() for line in lines):
print(f" ❌ 빈 파일입니다.")
empty_files += 1
continue
print(f" 라벨 라인 수: {len([l for l in lines if l.strip()])}")
# 첫 번째 라벨 라인 확인
for line_num, line in enumerate(lines):
line = line.strip()
if not line:
continue
parts = line.split()
print(f" 라인 {line_num+1}: {line}")
if len(parts) != 5:
print(f" ❌ 잘못된 형식! {len(parts)}개 컬럼 (5개여야 함)")
return False
try:
class_id = int(parts[0])
x, y, w, h = map(float, parts[1:5])
print(f" 클래스: {class_id}")
print(f" 좌표: x={x:.3f}, y={y:.3f}, w={w:.3f}, h={h:.3f}")
# 좌표 범위 확인
if not (0 <= x <= 1 and 0 <= y <= 1 and 0 <= w <= 1 and 0 <= h <= 1):
print(f" ❌ 좌표가 0-1 범위를 벗어남!")
return False
# 클래스 ID 확인
if class_id not in [0, 1]:
print(f" ❌ 잘못된 클래스 ID: {class_id} (0 또는 1이어야 함)")
return False
except ValueError as e:
print(f" ❌ 숫자 변환 오류: {e}")
return False
break # 첫 번째 라인만 확인
valid_files += 1
except Exception as e:
print(f" ❌ 파일 읽기 오류: {e}")
return False
print(f"\n검증 결과:")
print(f" 유효한 파일: {valid_files}")
print(f" 빈 파일: {empty_files}")
if empty_files > 0:
print("⚠️ 빈 라벨 파일이 있습니다. 이는 정상적일 수 있습니다.")
return valid_files > 0
def create_dataset_yaml():
"""
YOLO 데이터셋 설정 파일 생성 (yolo_test 구조 사용)
"""
# 절대 경로 사용
project_path = os.path.abspath(".")
yaml_content = f"""# Chat Message Detection Dataset
path: {project_path}/yolo_test
train: images
val: images
# Classes
nc: 2
names: ['MyMessage', 'OtherMessage']
"""
with open('chat_data.yaml', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(yaml_content)
print("✅ chat_data.yaml 파일이 생성되었습니다.")
print(f"데이터셋 경로: {project_path}/yolo_test")
def clean_cache():
"""
잘못된 캐시 파일 삭제
"""
print("=== 캐시 파일 정리 ===")
cache_files = [
"yolo_test/images.cache",
"yolo_test/labels.cache",
"yolo_images.cache",
"yolo_labels.cache",
"runs/train/yolov8n_chat_debug/train.cache",
"runs/train/yolov8n_chat_debug/val.cache",
"runs/train/yolov8n_chat_stable/train.cache",
"runs/train/yolov8n_chat_stable/val.cache"
]
for cache_file in cache_files:
if os.path.exists(cache_file):
os.remove(cache_file)
print(f"✅ 삭제됨: {cache_file}")
print("캐시 파일 정리 완료")
def train():
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
if not os.path.exists("chat_data.yaml"):
print("❌ chat_data.yaml 파일이 없습니다.")
return
model.train(
data="chat_data.yaml",
epochs=100, # 에폭 복구
imgsz=640,
batch=4, # 배치 크기 증가 (표준 구조로 안정화)
name="yolov8n_chat_final", # 새로운 실험명
project="runs/train",
exist_ok=True, # 기존 폴더 덮어쓰기 허용
# 학습률 설정
lr0=0.001,
lrf=0.01,
# 데이터 증강 (정상 구조이므로 일부 활성화)
augment=True,
degrees=5.0, # 약간의 회전
translate=0.1, # 약간의 이동
scale=0.3, # 약간의 스케일
shear=0.0, # 전단 비활성화 (텍스트 특성상)
perspective=0.0, # 원근 비활성화
flipud=0.0, # 상하 뒤집기 비활성화
fliplr=0.5, # 좌우 뒤집기 활성화
mosaic=0.5, # 모자이크 감소
mixup=0.0, # 믹스업 비활성화
copy_paste=0.0, # 복사-붙여넣기 비활성화
# 검증 설정
val=True,
split=0.2, # 20% 검증 데이터
patience=30, # patience 증가
# 저장 설정
save=True,
save_period=25, # 25 에폭마다 저장
plots=True,
verbose=True,
# 하드웨어
device='0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu',
workers=2, # 워커 수 증가
# 안정성
amp=False, # Mixed Precision 비활성화 (안정성)
seed=42,
# 추가 안정성 옵션
rect=False, # 직사각형 훈련 비활성화
cache=False, # 캐시 비활성화 (첫 실행 시)
)
def verify_data_structure():
"""
데이터 구조 검증 (yolo_test 구조)
"""
print("=== 데이터 구조 검증 ===")
images_dir = "yolo_test/images"
labels_dir = "yolo_test/labels"
if not os.path.exists(images_dir):
print(f"❌ 이미지 디렉토리가 없습니다: {images_dir}")
return False
if not os.path.exists(labels_dir):
print(f"❌ 라벨 디렉토리가 없습니다: {labels_dir}")
return False
image_files = [f for f in os.listdir(images_dir) if f.lower().endswith(('.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png'))]
label_files = [f for f in os.listdir(labels_dir) if f.endswith('.txt') and f != 'classes.txt']
print(f"이미지 파일 수: {len(image_files)}")
print(f"라벨 파일 수: {len(label_files)}")
# 매칭 확인
matched = 0
mismatched = []
for img_file in image_files:
img_name = os.path.splitext(img_file)[0]
label_file = img_name + '.txt'
if label_file in label_files:
matched += 1
else:
mismatched.append(img_file)
print(f"매칭된 파일 쌍: {matched}")
if mismatched:
print(f"매칭되지 않은 이미지 파일들 (처음 5개):")
for miss in mismatched[:5]:
print(f" - {miss}")
if matched < 200:
print("⚠️ 학습에 충분한 데이터가 부족할 수 있습니다.")
return matched > 0
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(f"CUDA 사용 가능: {torch.cuda.is_available()}")
print(f"PyTorch 버전: {torch.__version__}")
# 0. 캐시 파일 정리
clean_cache()
# 1. 데이터 구조 검증
if not verify_data_structure():
print("❌ 데이터 구조에 문제가 있습니다.")
exit(1)
# 2. 라벨 형식 검증
if not verify_label_format():
print("❌ 라벨 형식에 문제가 있습니다.")
exit(1)
# 3. 데이터셋 설정 파일 생성
create_dataset_yaml()
# 4. 학습 시작
print("\n=== 최종 학습 시작 ===")
train()
print("\n=== 학습 완료 ===")
print("모델 결과는 'runs/train/yolov8n_chat_final' 디렉토리에서 확인할 수 있습니다.")- CUDA/PyTorch 버전 확인
- 캐시 파일 삭제 → 깨끗한 시작
- 데이터 구조 확인 (폴더/파일 매칭 확인)
- 라벨 형식 확인 (YOLO txt 형식, 값 검증)
- 데이터셋 yaml 생성
- YOLO 학습 실행
- 완료 메시지 출력
계속 코드를 수정하면서 테스트를 돌렸는데, 이게 데이터 검증 문제로 중간에 학습이 끊기는 문제가 있어서 검증 파이프라인을 추가했다.
이로써 테스트 데이터셋의 변경에도 자동화 형태로 문제 없이 진행할 수 있었다.
학습 결과
100 epochs completed in 1.672 hours.
Optimizer stripped from runs/train/yolov8n_chat_final/weights/last.pt, 6.2MB
Optimizer stripped from runs/train/yolov8n_chat_final/weights/best.pt, 6.2MB
Validating runs/train/yolov8n_chat_final/weights/best.pt...
Ultralytics 8.3.155 🚀 Python-3.12.0 torch-2.7.1 CPU (Apple M1 Pro)
Model summary (fused): 72 layers, 3,006,038 parameters, 0 gradients, 8.1 GFLOPs
Class Images Instances Box(P R mAP50 mAP50-95): 100
all 238 1221 0.995 0.999 0.995 0.885
MyMessage 219 599 0.996 1 0.995 0.893
OtherMessage 225 622 0.993 0.998 0.995 0.876
Speed: 0.5ms preprocess, 119.1ms inference, 0.0ms loss, 0.5ms postprocess per image238개의 데이터 셋, Mac M1 로컬로 1.7시간 돌려서
mAP50: 99.499%
mAP50-95: 89.953%
Precision: 99.907%
Recall: 99.99%
좋은 수치의 모델을 뽑아냈다! (라고 GPT가 평가해줬다)
이제 테스트를 돌려보자
YOLO 테스트
detect_yolo.py
from ultralytics import YOLO
import cv2
import os
from pathlib import Path
def run_detection():
"""
학습된 YOLO 모델로 채팅 메시지 탐지 실행
"""
print("=== 채팅 메시지 탐지 시작 ===")
# 모델 로드
model_path = "runs/train/yolov8n_chat_final/weights/best.pt"
if not os.path.exists(model_path):
print(f"❌ 모델 파일을 찾을 수 없습니다: {model_path}")
return
model = YOLO(model_path)
print(f"✅ 모델 로드 완료: {model_path}")
# 테스트 이미지 폴더 확인
test_dir = "test_images"
if not os.path.exists(test_dir):
print(f"❌ 테스트 이미지 폴더를 찾을 수 없습니다: {test_dir}")
print("📁 test_images/ 폴더를 생성하고 테스트할 이미지를 넣어주세요.")
return
# 이미지 파일 확인
image_files = [f for f in os.listdir(test_dir) if f.lower().endswith(('.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png', '.bmp'))]
if not image_files:
print(f"❌ {test_dir} 폴더에 이미지 파일이 없습니다.")
return
print(f"📸 발견된 이미지 파일: {len(image_files)}개")
# 탐지 실행
results = model.predict(
source=test_dir,
imgsz=640,
conf=0.25, # 신뢰도 임계값 (0.25 = 25%)
iou=0.45, # IoU 임계값
save=True, # 결과 이미지 저장
save_txt=True, # 감지 결과 텍스트 저장
save_conf=True, # 신뢰도도 텍스트에 저장
show_labels=True, # 라벨 표시
show_conf=True, # 신뢰도 표시
verbose=True # 상세 출력
)
# 결과 분석
total_detections = 0
my_messages = 0
other_messages = 0
for result in results:
if result.boxes is not None:
detections = len(result.boxes)
total_detections += detections
# 클래스별 카운트
for box in result.boxes:
class_id = int(box.cls[0])
if class_id == 0: # MyMessage
my_messages += 1
elif class_id == 1: # OtherMessage
other_messages += 1
print("\n=== 탐지 결과 요약 ===")
print(f"📊 총 탐지된 메시지: {total_detections}개")
print(f"💬 내 메시지: {my_messages}개")
print(f"👥 상대방 메시지: {other_messages}개")
print(f"📁 결과 위치: runs/detect/predict/")
print("✅ 탐지가 완료되었습니다!")
def test_single_image(image_path):
"""
단일 이미지 테스트 함수
"""
if not os.path.exists(image_path):
print(f"❌ 이미지 파일을 찾을 수 없습니다: {image_path}")
return
model_path = "runs/train/yolov8n_chat_final/weights/best.pt"
model = YOLO(model_path)
results = model.predict(
source=image_path,
imgsz=640,
conf=0.25,
save=True,
show=True, # 결과를 화면에 표시
verbose=True
)
# 결과 출력
for result in results:
if result.boxes is not None:
print(f"📸 {image_path}에서 {len(result.boxes)}개의 메시지를 탐지했습니다.")
for i, box in enumerate(result.boxes):
class_id = int(box.cls[0])
confidence = float(box.conf[0])
class_name = "MyMessage" if class_id == 0 else "OtherMessage"
print(f" {i+1}. {class_name} (신뢰도: {confidence:.2f})")
else:
print(f"📸 {image_path}에서 메시지를 탐지하지 못했습니다.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 폴더 전체 테스트
run_detection()
# 단일 이미지 테스트 예시 (필요시 주석 해제)
# test_single_image("test_images/sample.jpg")
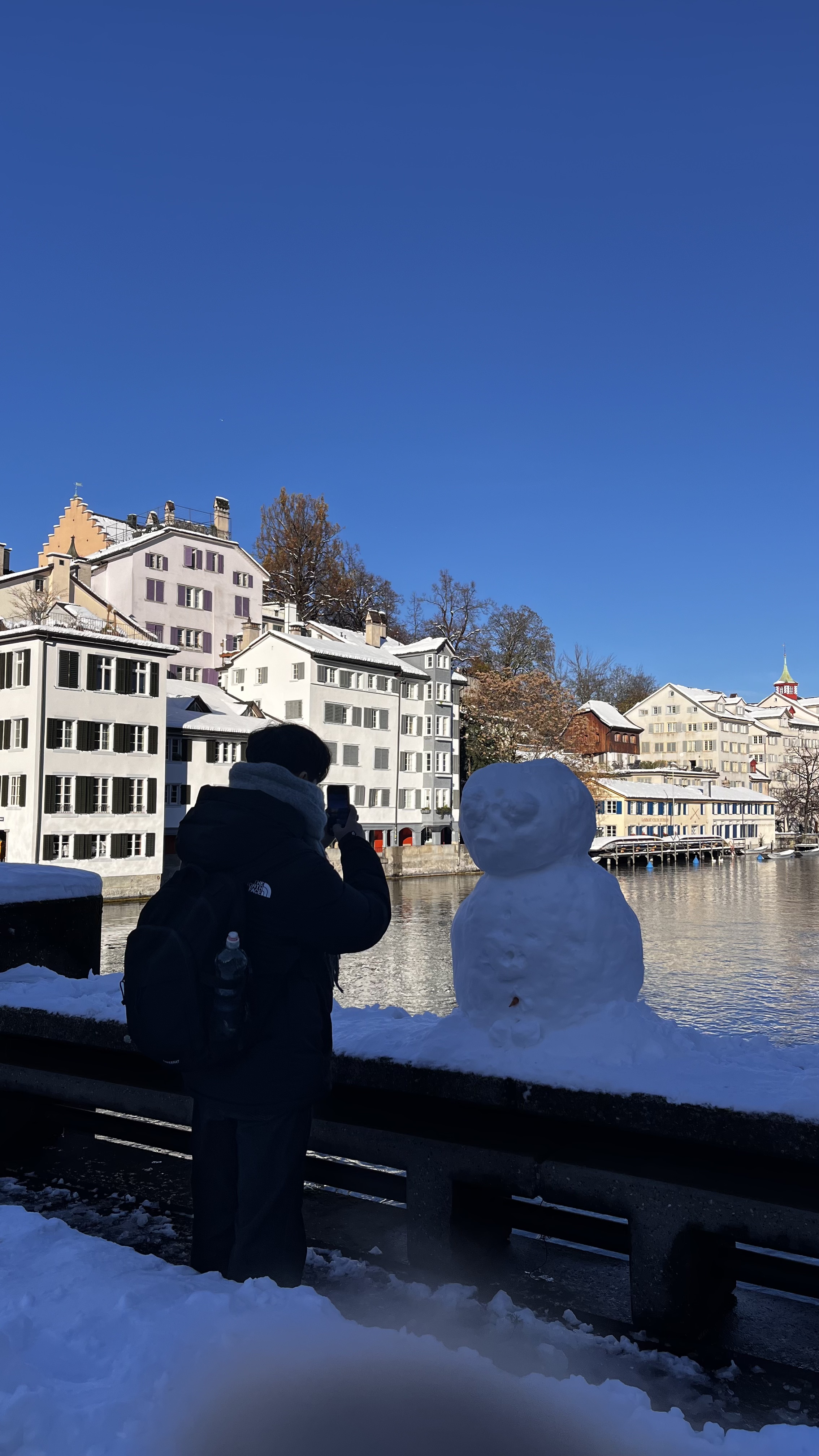
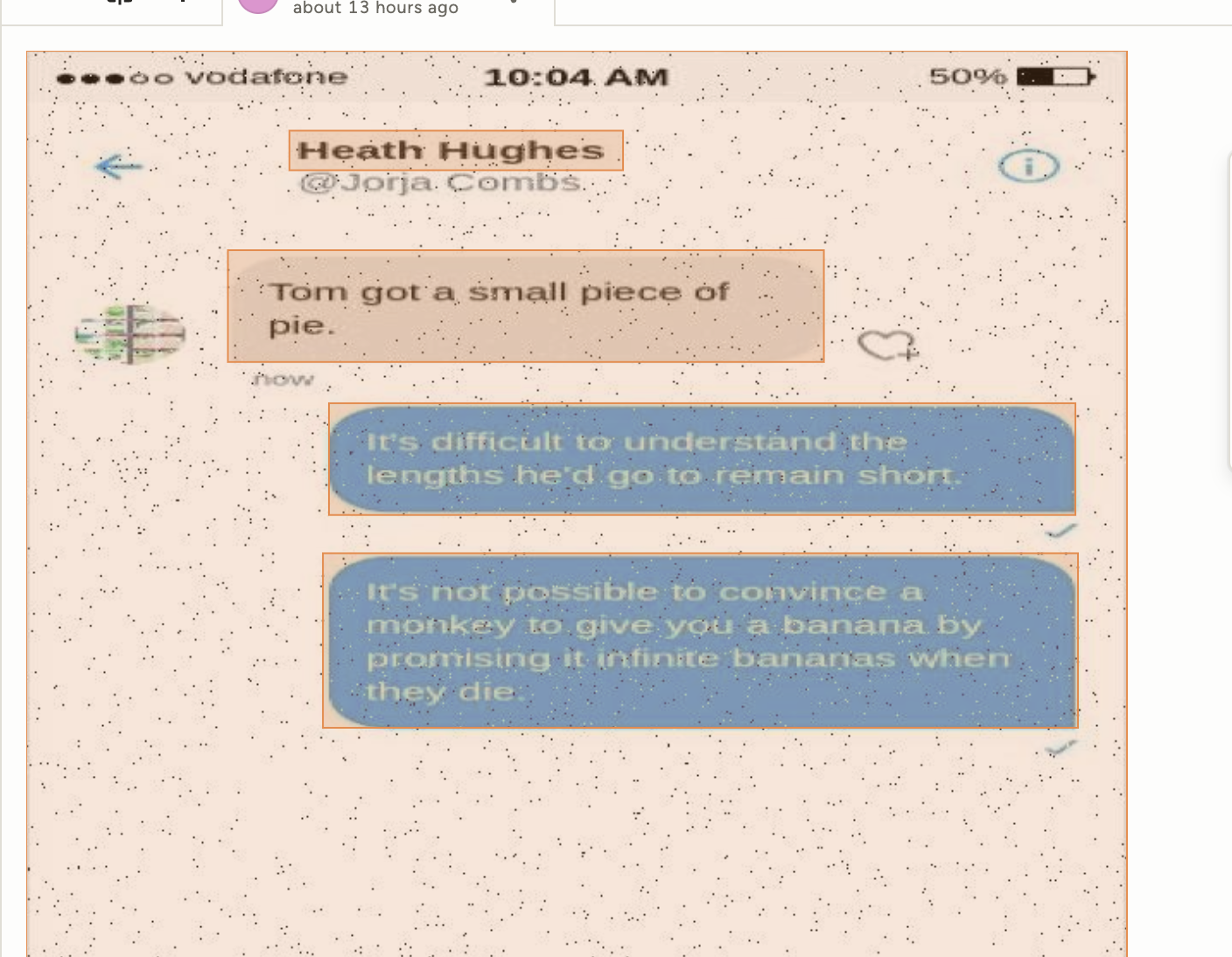
인터넷에서 구한 카톡 싸움 짤을 돌려보자
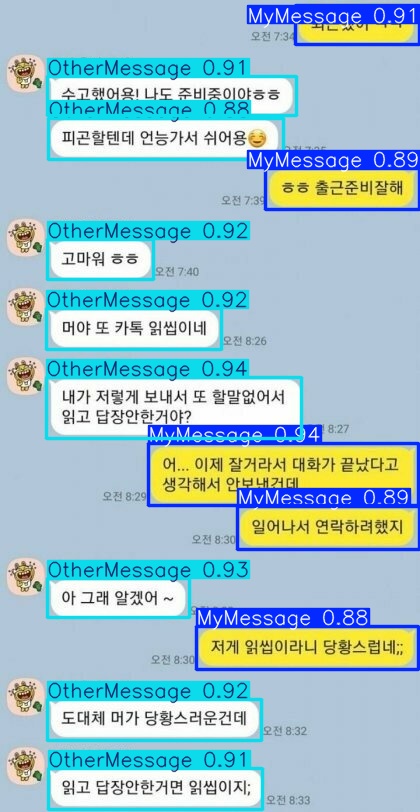
메시지 영역을 정확하게 판단하고
상대 메시지와 내 메시지를 구별해낸다!
결론
딥러닝 관련 기술을 사용해본 것이 처음이라, 비효율적인 접근 방식일지도 모르고, 더 나은 방법이 있을 것이라고 생각한다. 이건 사용해보면서 더 알아가야겠다.
결론
그래도 문제 해결을 위해 내가 아는 모든 방법을 동원하였고, 결국 해결 방법을 찾아냈다는 사실이 뿌듯하다. 앞으로도 단순히 스프링 개발자가 아니라 '비즈니스 문제를 기술로 해결하는 사람'이 되고 싶다!
