문제
풀이
요구사항
파이프가 놓여져있는 상태에 따라 아래와 같이 움직일 수 있다.
가로 - 오른쪽, 오른쪽 아래
세로 - 아래, 오른쪽 아래
대각선 - 오른쪽, 아래, 오른쪽 아래
또한 이동할 위치에 벽이 있으면 이동하지 못한다.
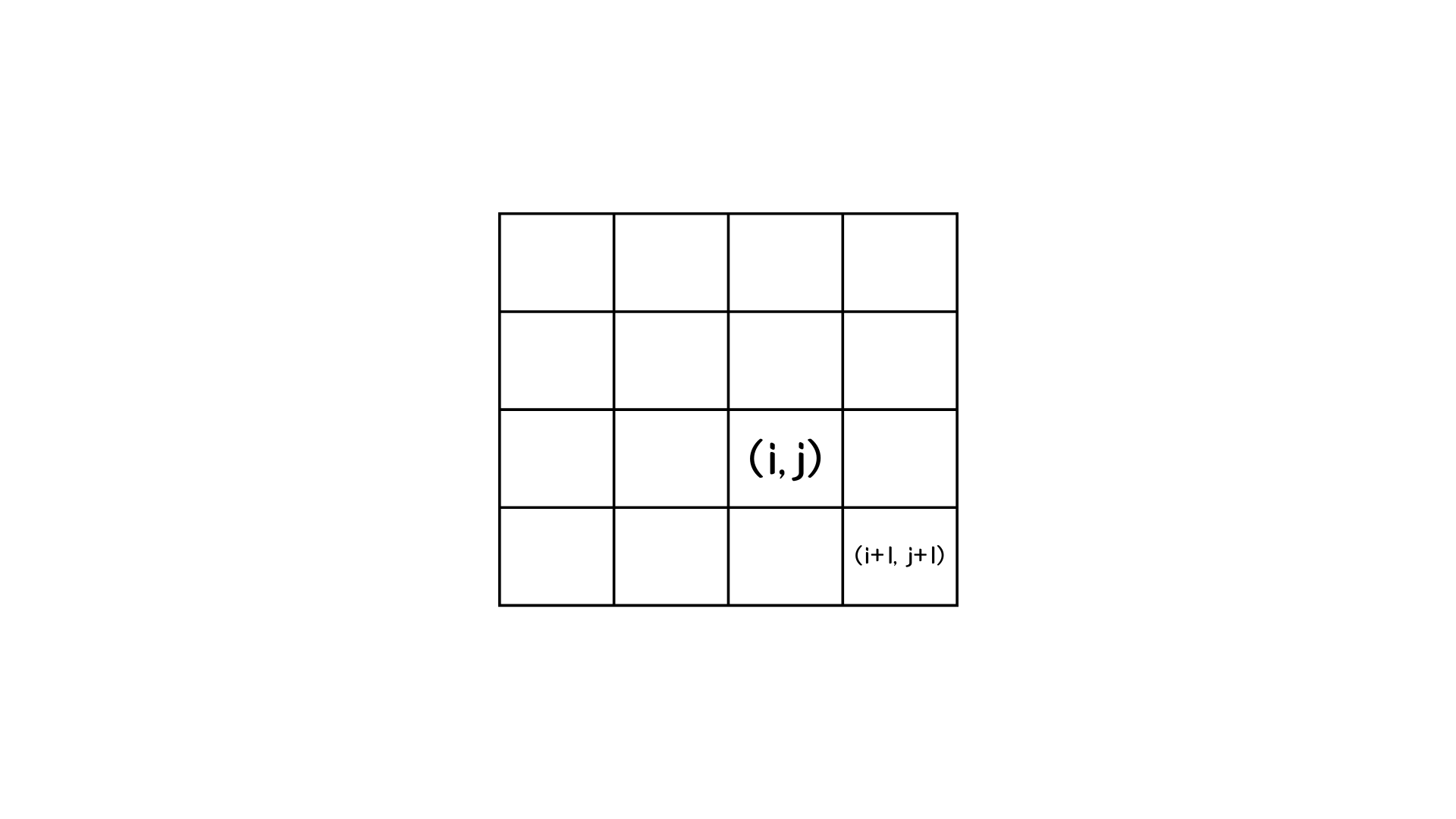
처음에 파이프는 가로 방향으로 놓여있고, (1,1)(1,2)이렇게 두 칸의 공간을 차지한다.
파이프가 (N,N)에 도달할 수 있는 경우의 수를 구하시오
해결방안
완전탐색
현재 파이프의 상태 (가로, 세로, 대각선) 을 저장해놓는다.
파이프에 상태에 따라 오른쪽, 아래, 오른쪽 아래를 확인하며 벽이 아니거나 범위를 벗어나지 않을 경우에 이동한다. (재귀함수)
(N,N)에 도달하면 카운트를 하나 증가시키고 재귀를 탈출한다.
시간 복잡도는
DP
가로, 세로, 대각선으로 이동했을 때 각 칸에 도달할 수 있는 경우의 수를 저장하기 위해 2차원 dp 배열 3개를 만든다.
const d1 = Array.from({ length: N }, () => Array(N).fill(0)); // 가로
const d2 = Array.from({ length: N }, () => Array(N).fill(0)); // 세로
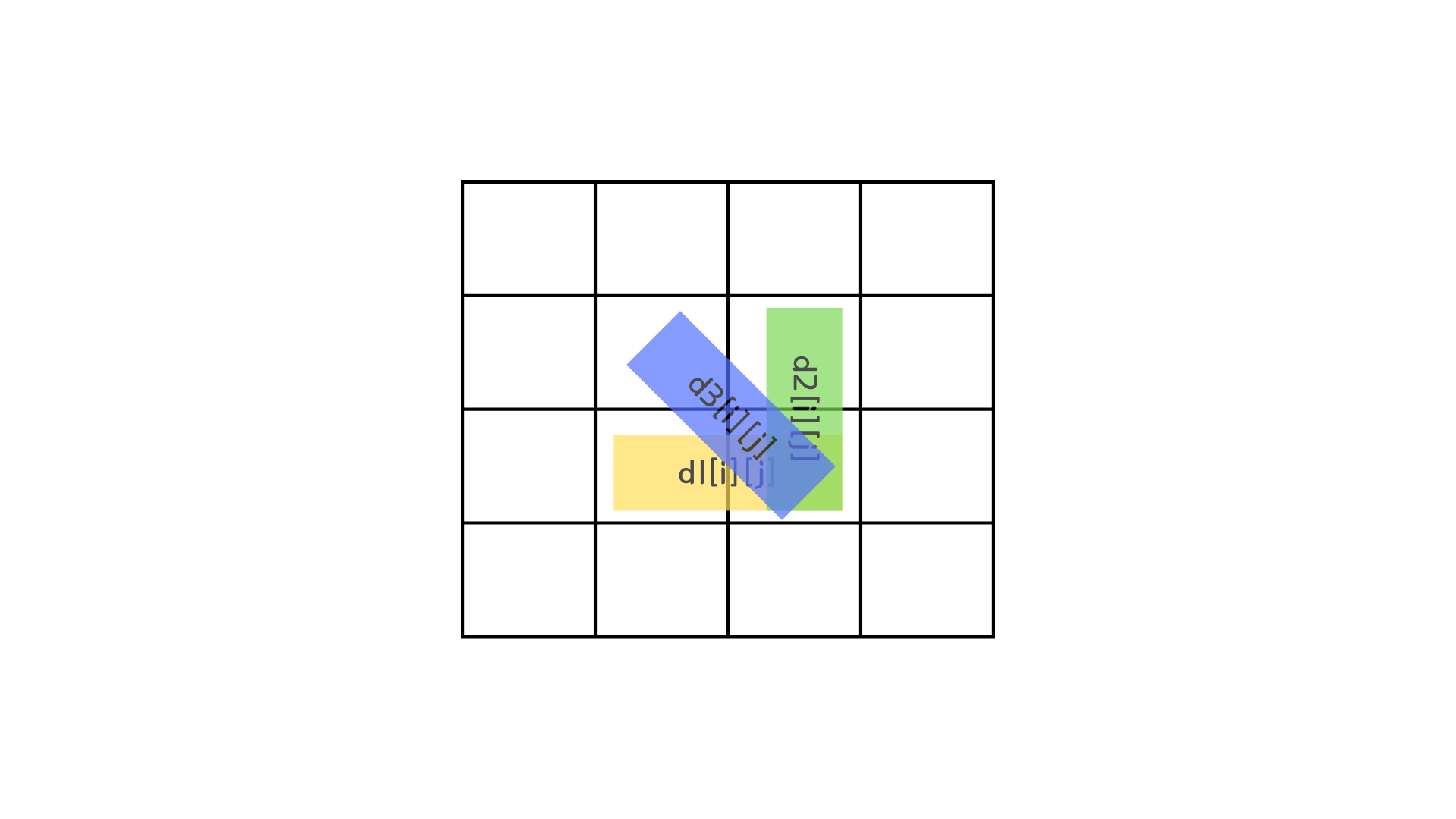
const d3 = Array.from({ length: N }, () => Array(N).fill(0)); // 대각선입력으로 들어온 2차원 배열을 순회하며 현재 칸에서 대각선으로 이동할 수 있는지, 오른쪽을 이동할 수 있는지, 아래로 이동할 수 있는지 확인한다.
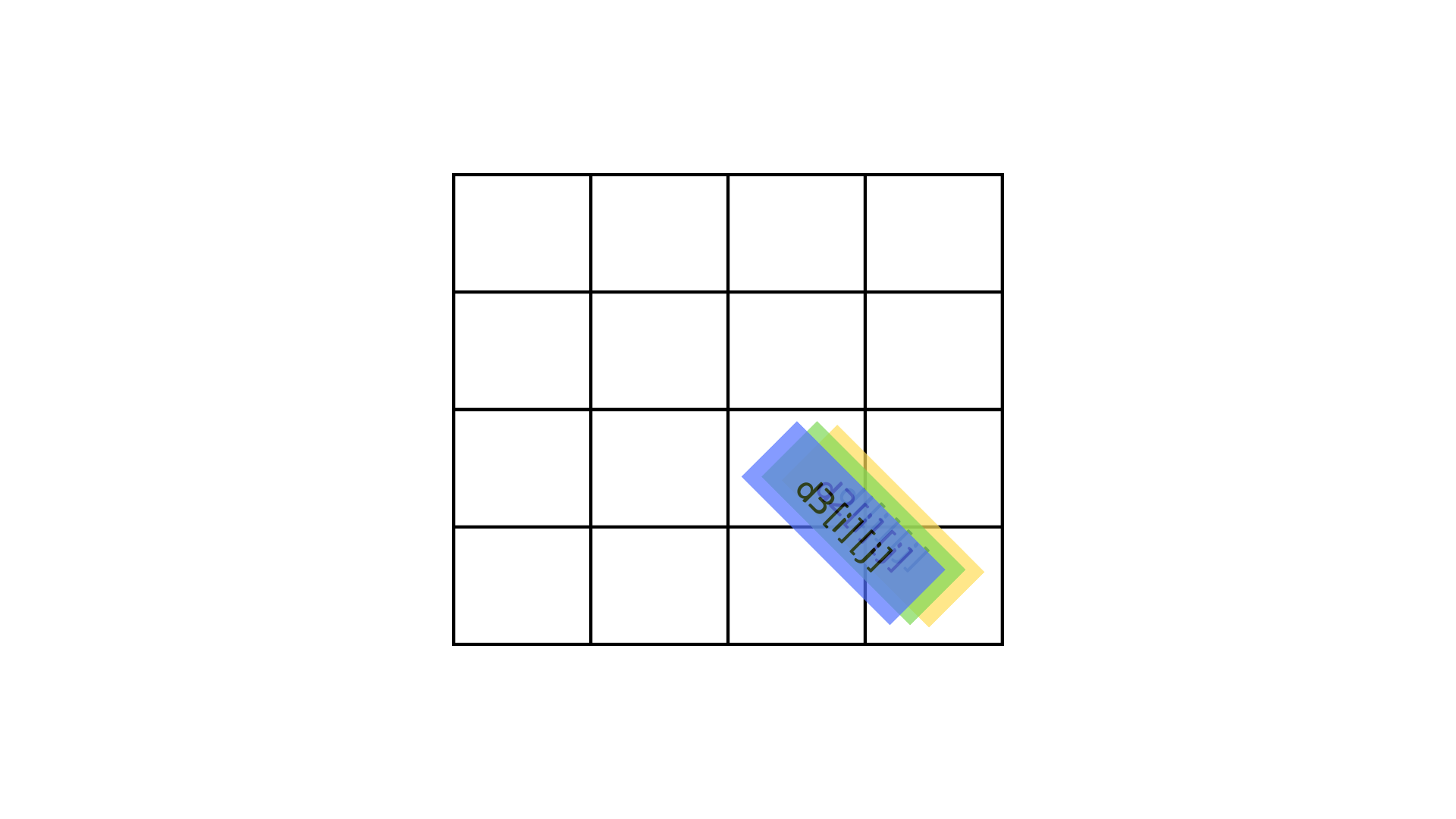
대각선으로 이동할 수 있을 경우 d3[i+1][j+1] += d1[i][j] + d2[i][j] + d3[i][j] 이런식으로 [i+1][j+1]칸으로 이동할 수 있는 경우의 수를 누적해주면 된다.
이 코드가 의미하는 바는 아래 그림을 보면 이해할 수 있을 것이다.
시간 복잡도는 이다.
코드
완전탐색
const filePath = process.platform === 'linux' ? '/dev/stdin' : './Javascript/input.txt';
const input = require('fs').readFileSync(filePath).toString().trim().split('\n');
const N = +input[0];
const map = input.slice(1).map((e) => e.split(' ').map(Number));
let state = 'horizontal';
let answer = 0;
function bruteforce(state, y, x) {
// 범위를 벗어날 경우
if (y > N - 1 || x > N - 1) return;
// (N,N)에 도달했을 경우
if (y === N - 1 && x === N - 1) {
answer++;
return;
}
// 가로
if (state === 'horizontal') {
if (map[y][x + 1] === 0) bruteforce(state, y, x + 1);
if (map[y + 1] !== undefined && map[y + 1][x + 1] === 0 && map[y][x + 1] === 0 && map[y + 1][x] === 0) bruteforce('diagonal', y + 1, x + 1);
}
// 세로
else if (state === 'vertical') {
if (map[y + 1] !== undefined && map[y + 1][x] === 0) bruteforce(state, y + 1, x);
if (map[y + 1] !== undefined && map[y + 1][x + 1] === 0 && map[y][x + 1] === 0 && map[y + 1][x] === 0) bruteforce('diagonal', y + 1, x + 1);
}
// 대각선
else {
if (map[y][x + 1] === 0) bruteforce('horizontal', y, x + 1);
if (map[y + 1] !== undefined && map[y + 1][x] === 0) bruteforce('vertical', y + 1, x);
if (map[y + 1] !== undefined && map[y + 1][x + 1] === 0 && map[y][x + 1] === 0 && map[y + 1][x] === 0) bruteforce(state, y + 1, x + 1);
}
}
bruteforce(state, 0, 1);
console.log(answer);DP
const filePath = process.platform === 'linux' ? '/dev/stdin' : './Javascript/input.txt';
const input = require('fs').readFileSync(filePath).toString().trim().split('\n');
const N = +input[0];
const d1 = Array.from({ length: N }, () => Array(N).fill(0)); // 가로
const d2 = Array.from({ length: N }, () => Array(N).fill(0)); // 세로
const d3 = Array.from({ length: N }, () => Array(N).fill(0)); // 대각선
const map = input.slice(1).map((e) => e.split(' ').map(Number));
function isValid(y, x) {
return y >= 0 && x >= 0 && y < N && x < N && !map[y][x];
}
d1[0][1] = 1;
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j < N; j++) {
// 대각선으로 갈 수 있다면
if (isValid(i, j + 1) && isValid(i + 1, j) && isValid(i + 1, j + 1)) {
d3[i + 1][j + 1] += d1[i][j] + d2[i][j] + d3[i][j];
}
// 가로로 갈 수 있다면
if (isValid(i, j + 1)) {
d1[i][j + 1] += d1[i][j] + d3[i][j];
}
// 세로로 갈 수 있다면
if (isValid(i + 1, j)) {
d2[i + 1][j] += d2[i][j] + d3[i][j];
}
}
}
const answer = d1[N - 1][N - 1] + d2[N - 1][N - 1] + d3[N - 1][N - 1];
console.log(answer);

