10번째-강의
프로세스간 통신 (Inter-Process Communications (IPC))
하나의 프로세스안에 스레드들이 공존하기 때문에 전역변수를 설정하면 특별히 공유하기 위한 메커니즘이 불필요 하다.
하지만, 프로세스끼리는 독립된 주소와 리소스를 사용하기 때문에 공유하기 위한 기능이 필요한데 이것이 IPC임.
프로세스간 Communications & Synchronization
목적 : 전송, 공유, 이벤트 전달, Resource Sharing & 동기화, Control
어떻게 ?
2가지 모델이 있음.
- Message Passing
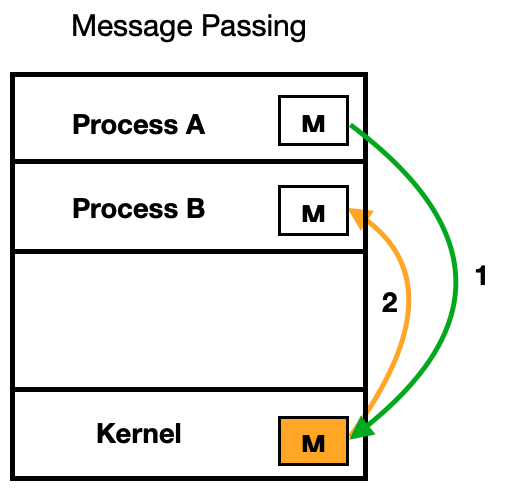
프로세스간 직접 전달이 불가능 하므로 User계층에 있는 Kernel을 이용해 Msg를 전달한다.
- 메커니즘
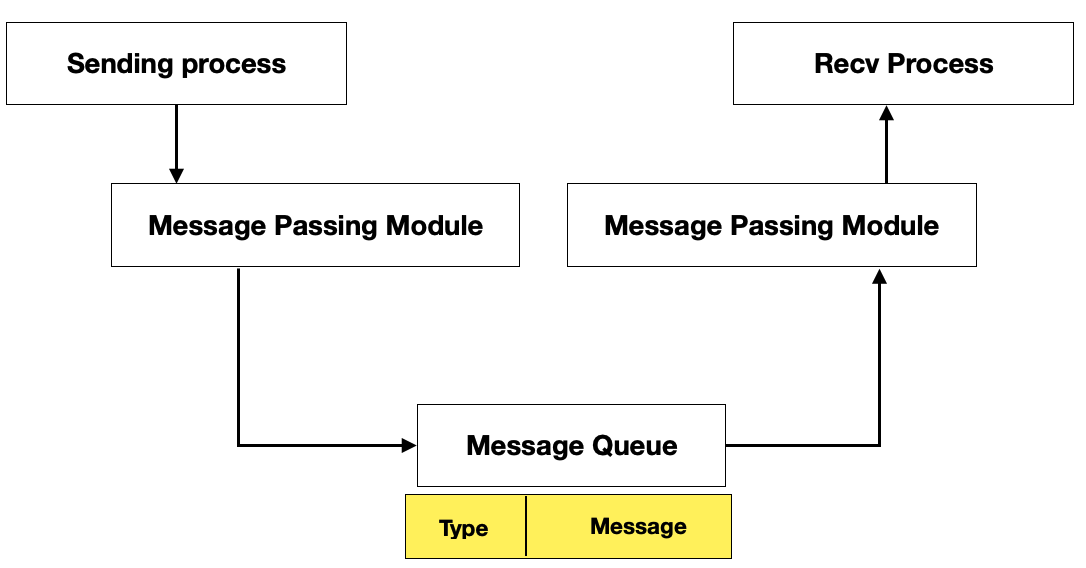
- Message Queue
- Pipes
- Mailboxes
- Sockets
- Shared Memory : 특정메모리(share)를 정의
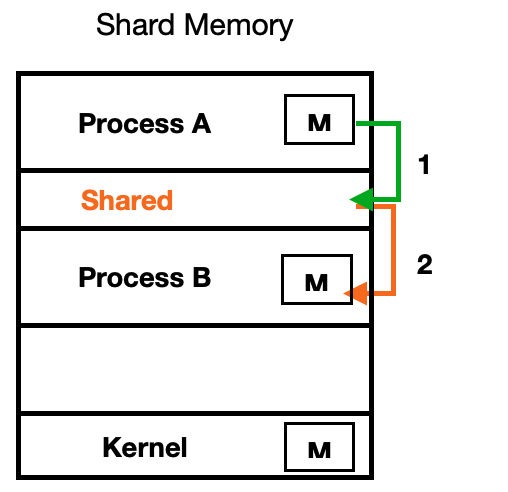
IPC 예제
-
동기화를 위한 Primitives
Ex )
Semaphore -> Thread간의 동기화. Processr간의 동기화는 IPC
Debugging
Event Notification - UNIX signals
-
2가지 Primitives
- Send(destination, msg) or Send((msg))
- Receive(source msg) or receive(msg)
-
사이즈는 변할수도 고정될수도 있다.
Message Passing
Send <----------> Receive
- communication Link를 만든다.
- 보내고자 , 받고자 하는 메시지 생성
방법
-
Direct OR Indirect
-
Symmetric OR Asymmetric
-
Automatic buffering OR Explicit Buffering
: 메시지를 위해 필요햔 것을 buffer에 넣는데, 이때의 buffer size를 관리
-
Send-by-Copy OR Send-by-Reference
: 메모리가 매우 클 경우 시간이 오래걸린다. 이럴땐 Send-by-Reference (C언어의 Pointer와 같은 개념)
-
Fixed OR Variable message size
Direct Communication & Indirect Communication
Direct Communication
: 직접 상대방을 지명
Q->P 가정하면, Send(P,messge), Receive(Q,messge)
조건
- 두 프로세스 모두 살아있는 상태여야 함.
- Communication Link는 자동적으로 만들어짐 (직접 지명하니까)
- 상대방의 ProcessID를 정확히 알아야 함.
Indirect Communication
: 직접 지명하지 않는다.
Q---> mailBox ---> P
mailBox가 존재.-> unique한 ID를 가져야 한다. 즉, 프로세스마다 하나씩 있어야 한다.
direct와 차이점 ?
- Q는 P가 준비가 되었든 아니든 상관없이 보낼 수 있다.
- 다른 프로세스와 공유가 쉽다.
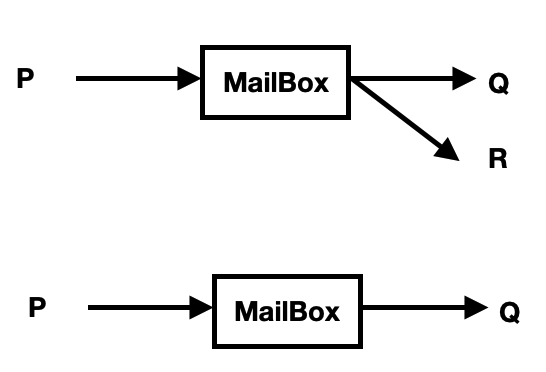
만약 receive 프로세스가 두개가 동시에 온다면 ?
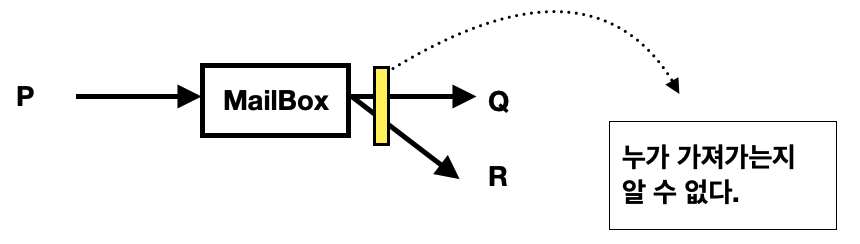
해결책
-
두개의 프로세스만 메일박스를 사용가능하도록 정의. (P--->Q, P---.R)
-
동시 access가 접근 불가능 하도록한다.
--> Process간 동기화가 필요하다 (lock. ...)
Symmetric Communication
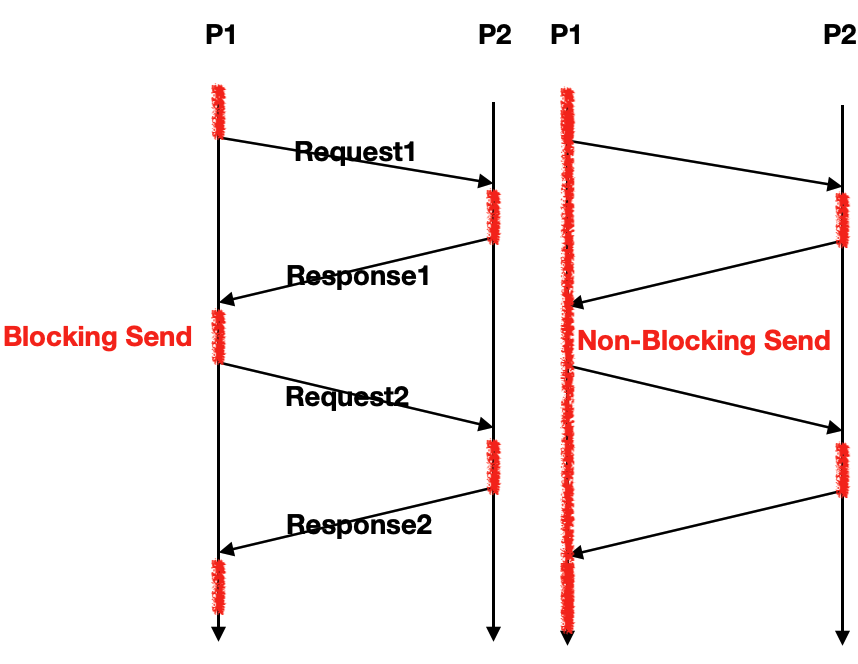
Symmetric = blocking = synchronous
Sender && Receiver 모두 blocking상태가 되도록 한다.
: 보내고나면 응답이 올때까지 block
특징
Function Call과 유사함
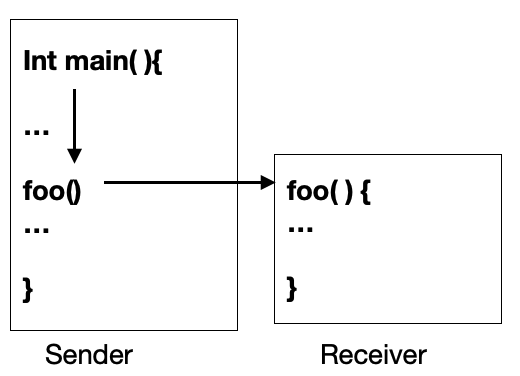
main함수 진행 중 foo 함수를 호출하면 main함수는 foo함수가 종료될 때까지 정지한다.
Non-Blocking (asynchronous)
의미 : Sender가 보내는 작업을 하고 멈추지 않고 계속적으로 동작하게 된다.
차이점
Message Queue
Send_message.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MSGSZ 128
typedef struct msgbuf
{
long mytype;
char mtext[MSGSZ];
} message_buf;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int msgId;
int msgflag = IPC_CREAT | 0666;
key_t key;
message_buf sbuf;
size_t buf_length;
key = 1234;
if ((msgId = msgget(key, msgflag)) < 0)
{
perror("msgget");
exit(1);
}
sbuf.mytype = 1;
(void)fprintf(stderr, "msgget : msgget succeeded: msgid = %d\n", msgId);
(void)strcpy(sbuf.mtext, "Did you get this?");
(void)fprintf(stderr, "msggget : msgget succeededd : msgid = %d\n", msgId);
buf_length = strlen(sbuf.mtext) + 1;
if (msgsnd(msgId, &sbuf, buf_length, IPC_NOWAIT) < 0)
{
printf("%d, %ld, %s, %zu \n", msgId, sbuf.mytype, sbuf.mtext, buf_length);
perror("msgsnd");
exit(1);
}
else
{
printf("Message : \"%s\" Send\n", sbuf.mtext);
}
exit(0);
return 0;
}
recv_msg.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MSGSZ 128
typedef struct msgbuf
{
long mytype;
char mtext[MSGSZ];
} message_buf;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int msgId;
key_t key;
message_buf sbuf;
key = 1234;
// if ((msgId = msgget(key, msgflag)) < 0)
// {
// perrpr("msgget");
// exit(1);
// }
if (msgrcv(msgId, &sbuf, MSGSZ, 1, 0) < 0)
{
perror("msgrcv");
exit(1);
}
printf("%s\n", sbuf.mtext);
exit(0);
return 0;
}Pipe
- FIFO buffer
- File I/O 형태와 동일한 모양
- Asynchronous
- 양방향, Arrayg형태
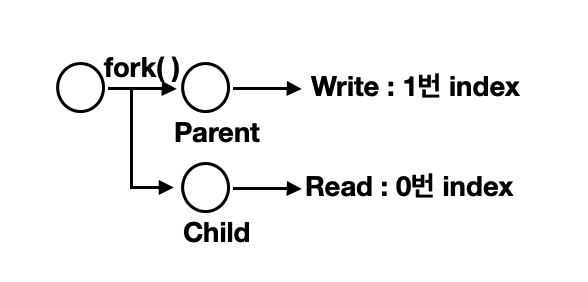
- read-write pipe
- 0번 idx : read , 1번 idx : write
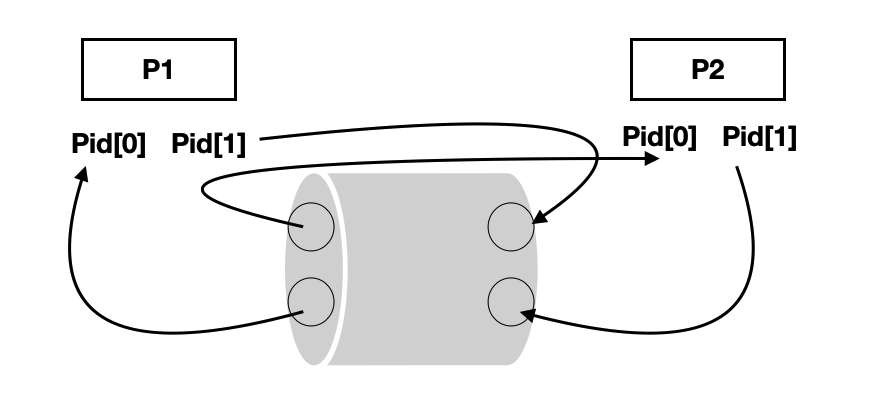
pipe.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
char *message = "Do u see this msg ?";
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
char buf[1024];
int fd[2];
pipe(fd);
if (fork() != 0)
{
write(fd[1], message, strlen(message) + 1);
}
else
{
read(fd[0], buf, 1024);
printf("Got this from Parent! : &s\n", buf);
}
return 0;
}- Fork() : 동일한 자식 프로세스 생성