#1978
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int N, X;
int ans = 0;
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
cin >> X;
int count = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= X; j++)
{
if (X%j == 0) //값이 나누어 떨어진다면
{
count++;
}
}
if (count == 2)
ans++;
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}#2581
//처음에 N이 소수이고 제일 작은 수 일수도 있다는 생각을 못해서 min = N으로 뒀다가 틀림... min = N+1하니까 맞았다
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int M, N;
int sum = 0;
cin >> M >> N;
int min = N+1;
for (int i = M; i <= N; i++)
{
int count = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
if (i%j == 0)
count++;
}
if (count == 2)
{
sum += i;
if(i<min)
{
min = i;
}
}
}
if (min == N+1)
cout << "-1";
else
{
cout << sum << "\n";
cout << min;
}
return 0;
}#1929
//제곱근까지만 계산하기,, 풀이 외우기,,
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int M, N;
int X;
cin >> M >> N;
for (int i = M; i <= N; i++)
{
X = sqrt(i); //제곱근
if (i == 2 || i == 3)
{
cout << i << "\n";
continue;
}
//홀수라면
if ((i % 2)!=0)
{
for (int j = 2; j <= X; j++)
{
if ((i%j) == 0) //나눠진다는 뜻 -> 소수가 아님
break;
if (j == X) //제곱근까지 나눠지지 않았다는 뜻
cout << i << "\n";
}
}
}
return 0;
}#4948
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int N;
while (1)
{
int X; //제곱근을 저장할 변수
int count = 0;
cin >> N;
if (N == 0)
break;
X = sqrt(2 * N);
//제곱근 사용해서 풀기
for (int i = N + 1; i <= 2 * N; i++)
{
if (i == 2 || i == 3)
{
count++;
continue;
}
//홀수라면
if ((i % 2) != 0)
{
for (int j = 2; j <= X; j++)
{
if ((i%j) == 0) //나눠진다는 뜻 -> 소수가 아님
break;
if (j == X) //제곱근까지 나눠지지 않았다는 뜻
count++;
}
}
}
cout << count << "\n";
}
return 0;
}#9020
// N/2-i 와 N/2+i의 합은 N이라는 걸 이용하는 문제,,
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
bool prime(int i)
{
int X = sqrt(i);
if (i == 2 || i == 3)
{
return true;
}
//홀수라면
if ((i % 2) != 0)
{
for (int j = 2; j <= X; j++)
{
if ((i%j) == 0) //나눠진다는 뜻 -> 소수가 아님
return false;
if (j == X) //제곱근까지 나눠지지 않았다는 뜻
return true;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int T, N;
cin >> T;
for (int i = 0; i < T; i++)
{
cin >> N;
for (int i = N/2; i >= 2; i--)
{
if (prime(i) && prime(N - i))
{
cout << i << " " << N - i << "\n";
break; //중앙에서부터 값을 계산하므로 처음에 출력된 값이 제일 차이가 작다.
}
}
}
return 0;
}#1085
// algorithm을 이용해서 min을 쓰는 방법도 있다
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x, y, w, h;
int min;
cin >> x >> y >> w >> h;
min = x;
if (min > y)
min = y;
if (min > h - y)
min = h - y;
if (min > w - x)
min = w - x;
cout << min;
return 0;
}#3009
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3;
int x, y;
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2 >> x3 >> y3;
if (x1 == x2)
x = x3;
else if (x1 == x3)
x = x2;
else
x = x1;
if (y1 == y2)
y = y3;
else if (y1 == y3)
y = y2;
else
y = y1;
cout << x << " " << y;
return 0;
}#4153
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x, y, z;
while (1)
{
int max;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
if (x == 0)
break;
if (x > y)
{
if (x > z)
{
if (x*x == y * y + z * z)
cout << "right" << endl;
else
cout << "wrong" << endl;
}
else
{
if (z*z == y * y + x * x)
cout << "right" << endl;
else
cout << "wrong" << endl;
}
}
else
{
if (y > z)
{
if (y*y == x * x + z * z)
cout << "right" << endl;
else
cout << "wrong" << endl;
}
else {
if (z*z == x * x + y * y)
cout << "right" << endl;
else
cout << "wrong" << endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}#3053
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double R, S1, S2;
const double pi = acos(-1);
cin >> R;
S1 = R * R * pi;
S2 = 2 * R * R;
cout << fixed;
cout.precision(6);
cout << S1 << "\n" << S2;
}#1002
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int T;
int x1, y1, r1, x2, y2, r2;
cin >> T;
for (int i = 0; i < T; i++)
{
int d, c1, c2;
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> r1 >> x2 >> y2 >> r2;
d = (x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2);
c1 = (r1 - r2) * (r1 - r2);
c2 = (r1 + r2) * (r1 + r2);
if (d == 0) // 두 원의 중심이 같을 때
{
if (r1 == r2) //두 원의 반지름도 같을 때
{
cout << "-1" << "\n";
}
else //한 원이 다른 원을 감싸고 있는 모양이므로 접점 X
{
cout << "0" << "\n";
}
}
else if (d == c1 || d == c2)
{
cout << "1" << "\n";
}
else if (c1 < d && d < c2)
{
cout << "2" << "\n";
}
else
{
cout << "0" << "\n";
}
}
}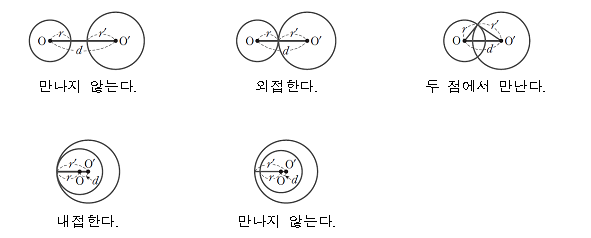
내접하는거 생각 못해서 틀렸다,.,,
