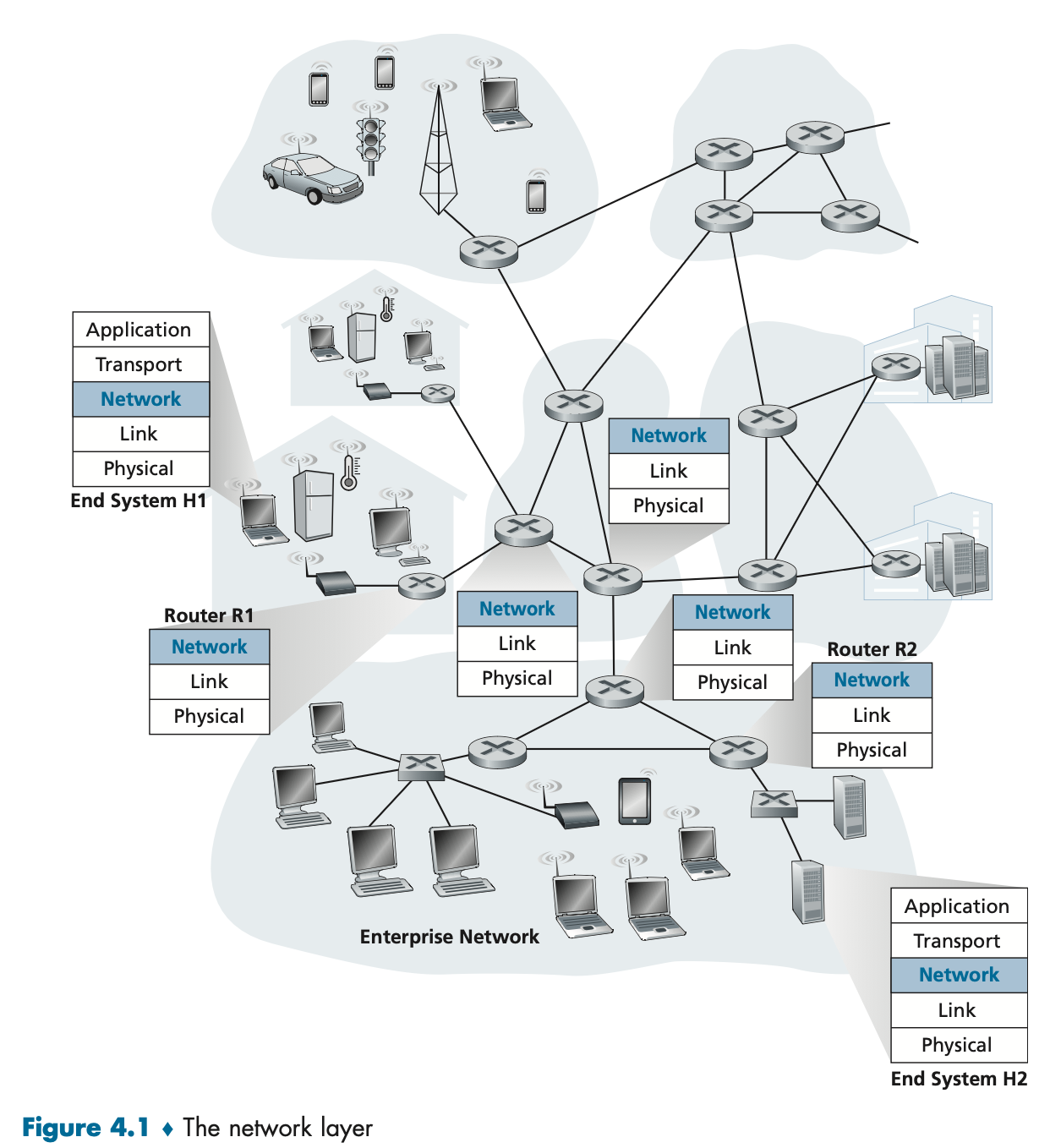
4.1.1 Forwarding and Routing: The Data and Control Planes
Forwarding: Router local action of moving the packet from input link interface to the output link interface.
Routing: Network-wide process that determining end to end route taken by packets using a routing algorithm.
Forwarding table receives key from the packet header and indicates the outgoing link interface.
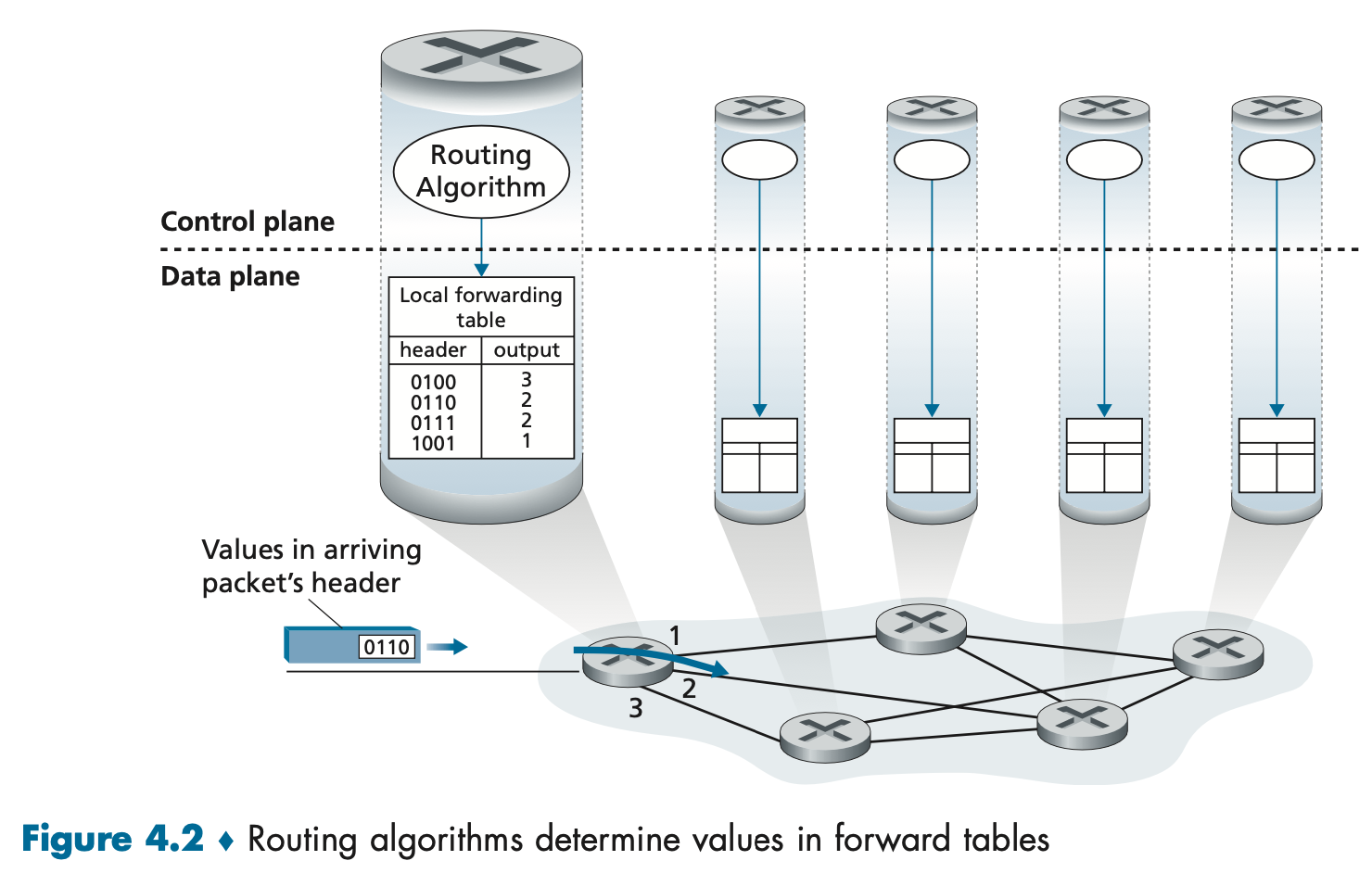
Header to Output link interface
Control Plane: The Traditional Approach
Q. How was forwarding table constructed to begin with?
A. Fig.4.2 Routing algorithm runs through every router and computes value for forwarding table by exchangingmessages between routers. (5.2~5.4)
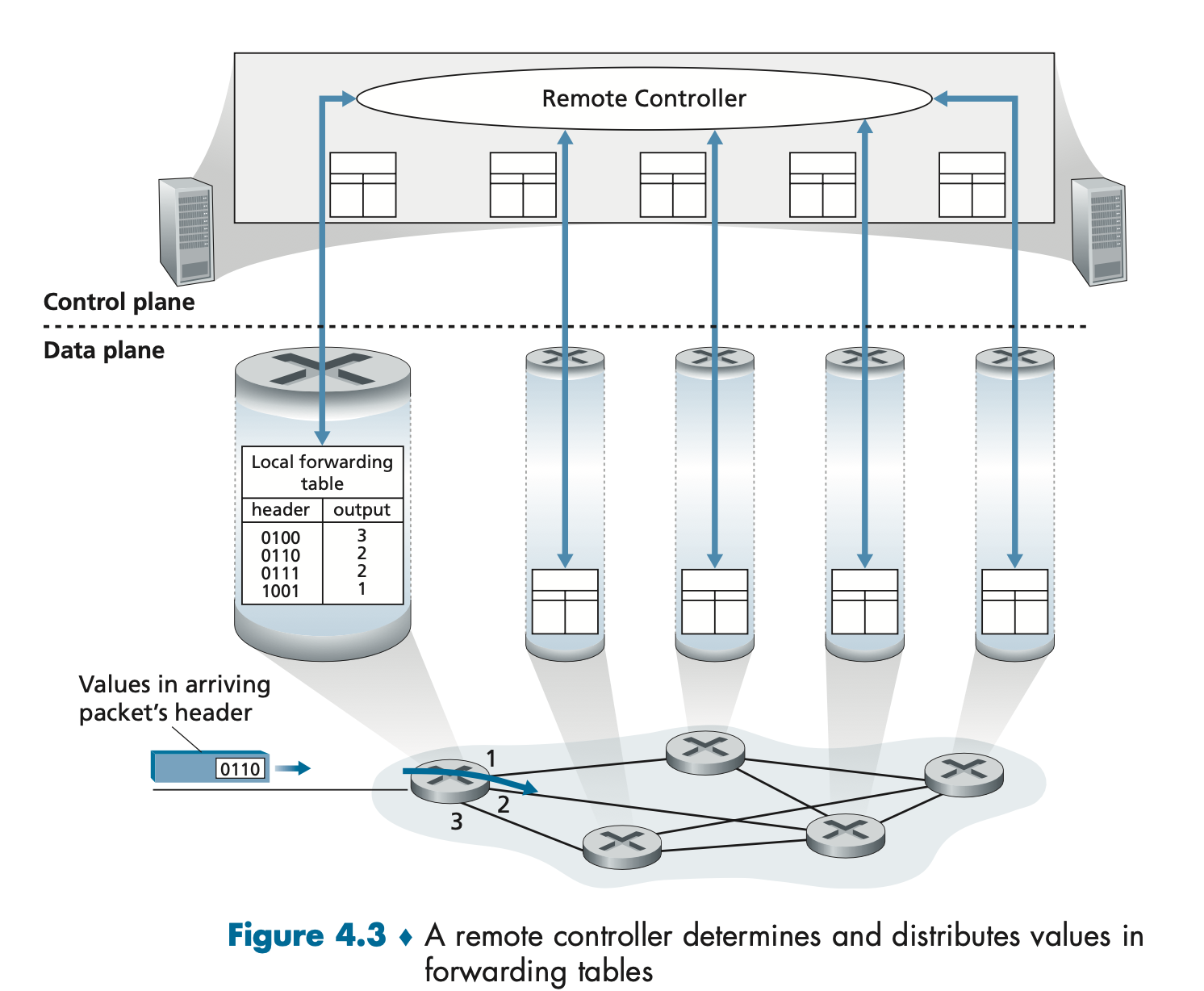
Control Plane: The SDN Approach
Control-plane routing function is separated from physical router. Router performs forwarding only, RC computes and distrubutes FW tables.
Therefore, SDN, the network is software defined since the controller for computing fw tables is implemented in sw (5.5).
4.1.2 Network Service Model
💡 Network service model defines the characteristics of end to end delivery.Possible services:
Guaranteed delivery: Guarantees packet sent by source will arrive at destination.
Guaranteed delivery w/ bounded delay: Guarantees delivery within a specific delay bound (i.e. 100ms)
In-Order packet delivery: packets arrives at the destination in order that they were sent.
Guarnateed minimal bandwidth: emulates transmission link behavior( i.e. 1Mbps)
Security: encryption/decryption of datagrams.
The internet provides **best-effort service.** There are ATM network architecture (in-order, bounded delay, minimal bandwidth), and other mode developed architectures but Internet’s basic best effort service with bandwidth provisioning and applicaiton level protocols (DASH) is proven good enough to support wide range of applications (Netflix, Zoom, etc)
