
🔥 학습목표
- callback, promise, async/await 으로 fs모듈을 사용할 수 있다.
- callback, promise, async/await 으로 fetch를 이용한 네트워크 요청을 각각 구현할 수 있다.
🟩 fs 모듈 사용하기
🟣 callback
const fs = require("fs");
const getDataFromFile = function (filePath, callback) {
fs.readFile(filePath, 'utf-8', function(err, data){
if(err){
callback(err,null);
}else {
callback(null, data);
}
});
};
getDataFromFile('README.md', (err, data) => console.log(data));
module.exports = {
getDataFromFile
};
🟣 Promise
⬜ promise
const fs = require("fs");
const getDataFromFilePromise = filePath => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile(filePath, "utf-8", (err, data) => {
if(err) reject(err);
else resolve(data);
})
})
};
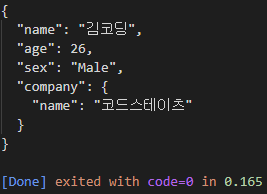
getDataFromFilePromise('part-2/files/user1.json').then(data => console.log(data));
module.exports = {
getDataFromFilePromise
};
⬜ promise chaining
const path = require('path');
const { getDataFromFilePromise } = require('./02_promiseConstructor');
const user1Path = path.join(__dirname, 'files/user1.json');
const user2Path = path.join(__dirname, 'files/user2.json');
const readAllUsersChaining = () => {
return getDataFromFilePromise(user1Path)
.then((user1)=>{
return getDataFromFilePromise(user2Path)
.then((user2)=>{
return [user1, user2].map(val=>JSON.parse(val));
})
})
}
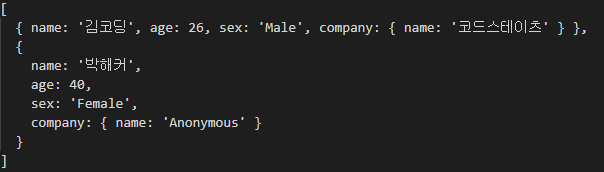
readAllUsersChaining().then((data)=>console.log(data));
module.exports = {
readAllUsersChaining
}
🟣 Promise.all
const { resolve, parse } = require('path');
const path = require('path');
const { getDataFromFilePromise } = require('./02_promiseConstructor');
const user1Path = path.join(__dirname, 'files/user1.json');
const user2Path = path.join(__dirname, 'files/user2.json');
const readAllUsers = () => {
return Promise.all([
getDataFromFilePromise(user1Path),
getDataFromFilePromise(user2Path),
])
.then(([user1, user2]) => {
return `[${user1}, ${user2}]`;
})
.then(text => {
return JSON.parse(text);
})
}
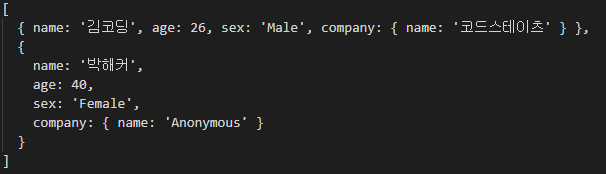
readAllUsers().then((data)=>console.log(data));
module.exports = {
readAllUsers
}
🟣 async/await
const path = require('path');
const { getDataFromFilePromise } = require('./02_promiseConstructor');
const user1Path = path.join(__dirname, 'files/user1.json');
const user2Path = path.join(__dirname, 'files/user2.json');
const readAllUsersAsyncAwait = async () => {
let user1 = await getDataFromFilePromise(user1Path);
let user2 = await getDataFromFilePromise(user2Path);
return [JSON.parse(user1), JSON.parse(user2)];
}
readAllUsersAsyncAwait().then((data)=>console.log(data));
module.exports = {
readAllUsersAsyncAwait
}
🟩 fetch API
으아... 이번 페어 과제는 페어분과 정말 시간과 정성을 들여 겨우 해결하고 잘못 이해했던 부분을 파악했다.
한땀한땀 과정을 ppt로 정리해보니, 내가 Promise 비동기 함수에 대해 첫단추부터 완전히 잘못 끼운 채 착각 중이었다.
정말 차근차근, 순서대로 반환값을 콘솔에 찍어보니 이보다 단순할 수가 없었다 ㅎㅎ... 민망했다.
🟣 Promise_basicChaining
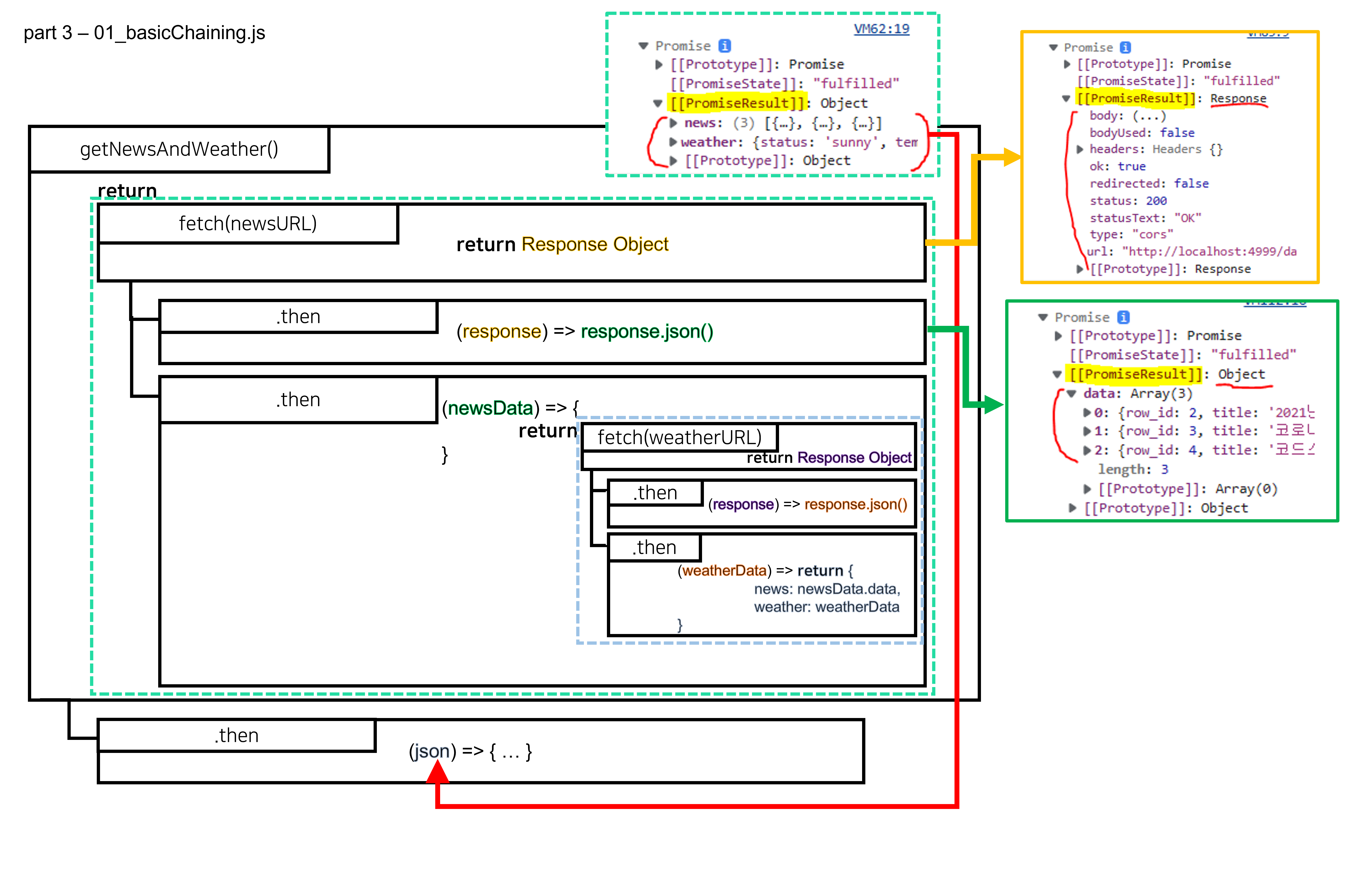
function getNewsAndWeather() {
return fetch(newsURL)
.then(resp => resp.json())
.then(json1 => {
return fetch(weatherURL)
.then(resp => resp.json())
.then(json2 => {
return {
news: json1.data,
weather: json2
}
});
})
}
if (typeof window === 'undefined') {
module.exports = {
getNewsAndWeather
}
}
🟣 Promise.all
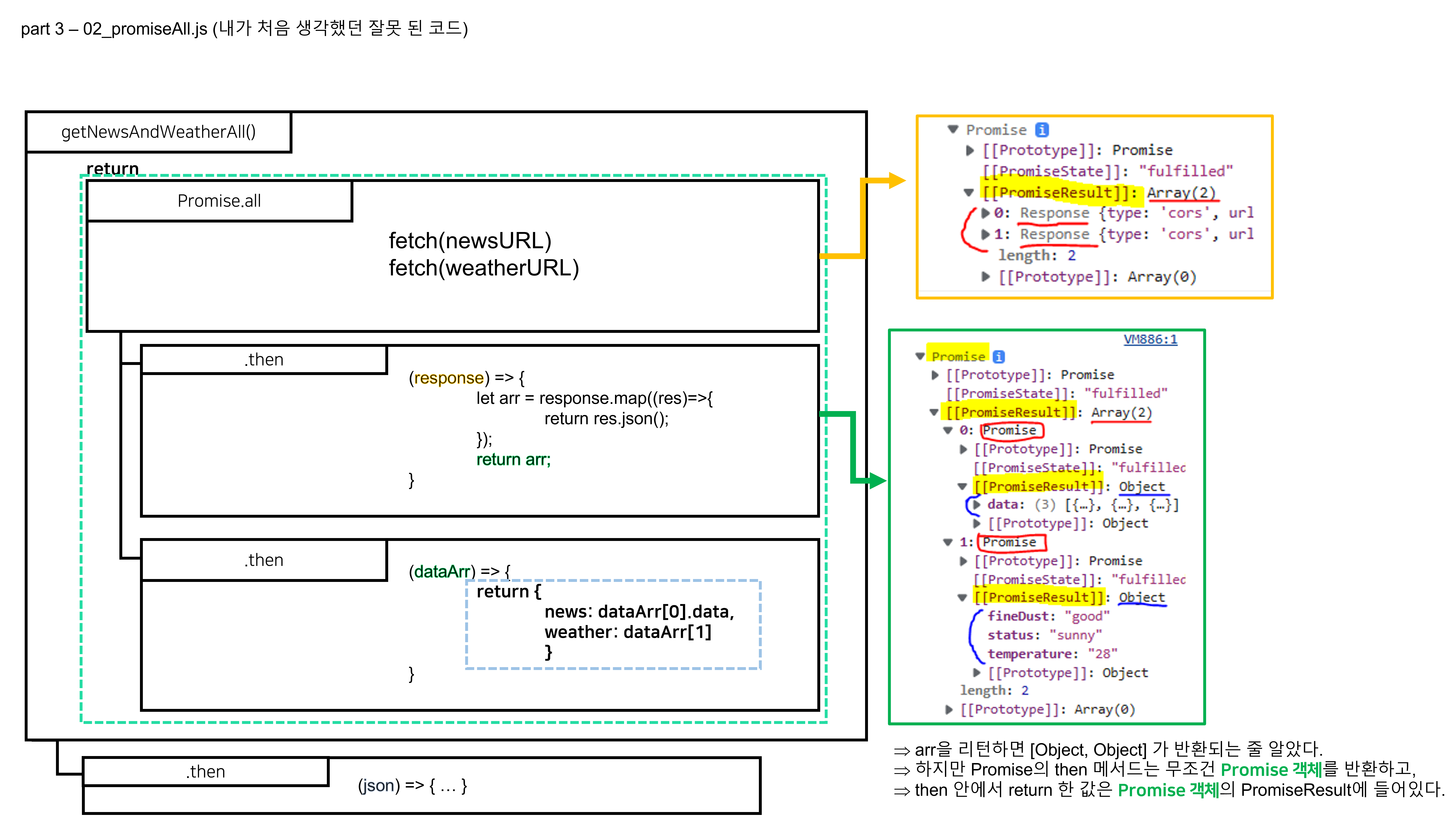
⬜ 내가 처음 잘못 생각했던 코드(와 그 이유)
function getNewsAndWeatherAll() {
return Promise.all([
fetch(newsURL),
fetch(weatherURL)
])
.then((response)=>{
let arr = response.map((res)=>{
return res.json();
});
return arr;
})
.then((dataArr) => {
return {
news: dataArr[0].data,
weather: dataArr[1]
}
})
}
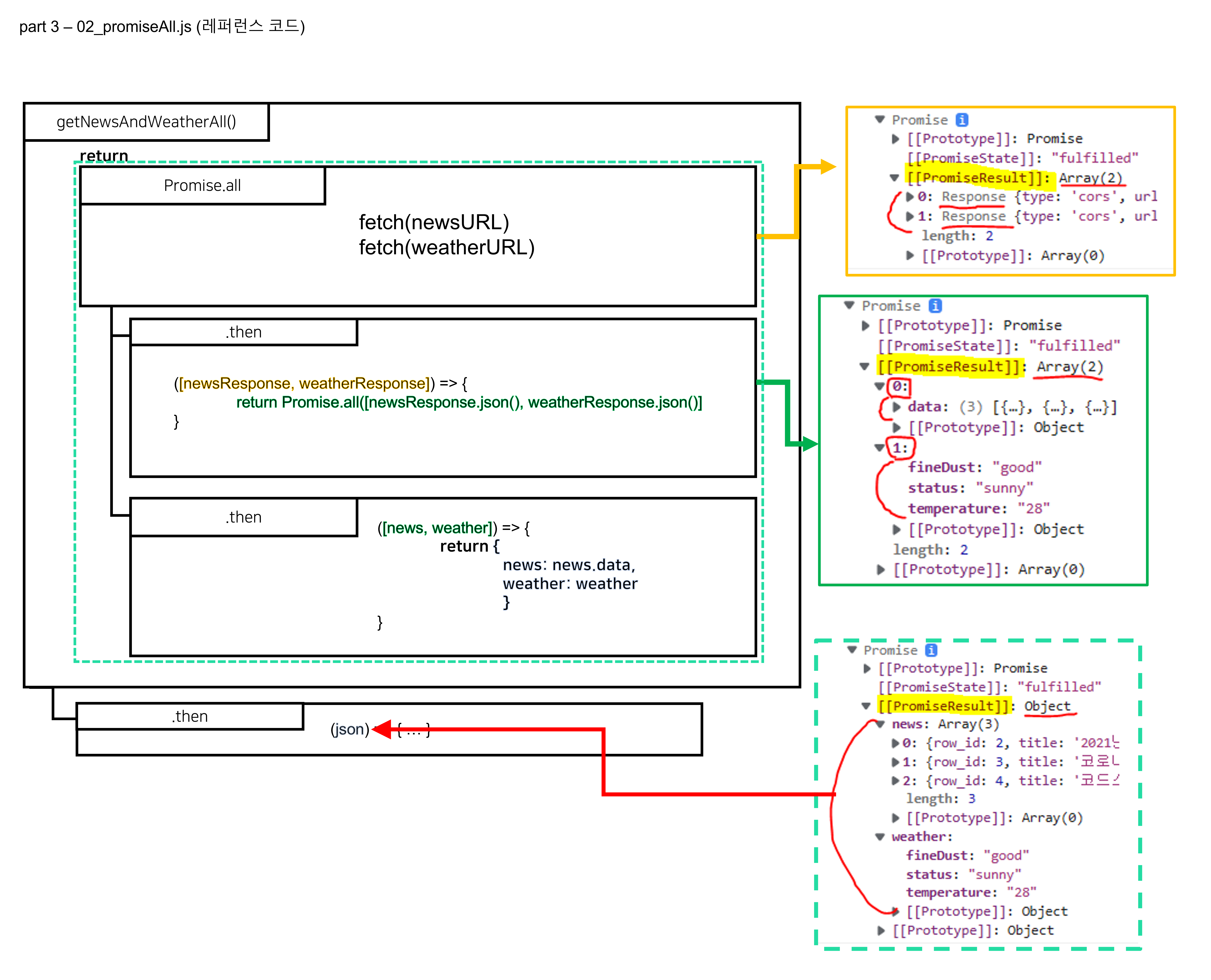
⬜ 래퍼런스 코드
function getNewsAndWeatherAll() {
return Promise.all([
fetch(newsURL),
fetch(weatherURL)
])
.then(([newsResponse, weatherResponse]) => {
return Promise.all([newsResponse.json(), weatherResponse.json()])
})
.then(([news, weather]) => {
return {
news: news.data,
weather: weather
}
})
}
if (typeof window === 'undefined') {
module.exports = {
getNewsAndWeatherAll
}
}
🟣 async/await
async function getNewsAndWeatherAsync() {
let json1 = await fetch(newsURL).then(resp => resp.json());
let json2 = await fetch(weatherURL).then(resp => resp.json());
return {
news: json1.data,
weather: json2
}
}