BFS
다차원 배열에서 각 칸을 방문할 때 너비를 우선으로 방문하는 알고리즘.
예시
- 시작하는 칸을 큐에 넣고 방문 표시를 남김
- 큐에서 원소를 꺼내어 그 칸에 상하좌우로 인접한 칸에 대해
3번 진행 - 해당 칸을 이전에 방문했다면 아무 것도 하지 않고, 처음 방문했다면 방문했다는 표시를 남기고 해당 칸을 큐에 삽입.
- 큐가 빌 때까지
2번을 반복
-> 모든 칸이 큐에 1번씩 들어가므로 시간복잡도는 칸이 N개 일 때 O(N)임.
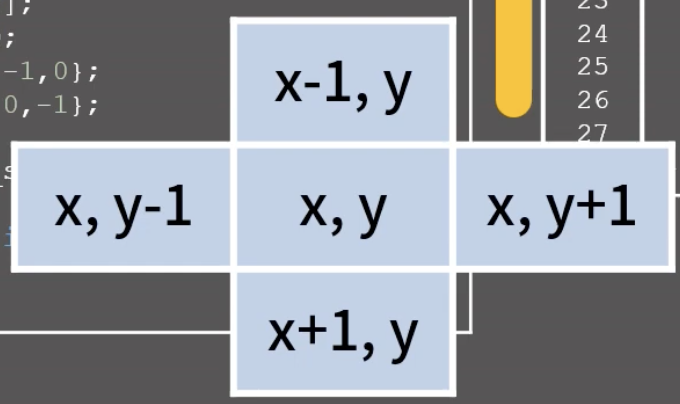
- x: 행
- y: 열
BFS 기본 코드
public static void bfs(int node, boolean[] visited) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue.offer(node);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
node = queue.poll();
if(visited[node]) continue;
visited[node] = true;
for(int nextNode:nodeList[node]) {
queue.add(nextNode);
}
}
}BOJ 1926: 그림
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1926
- 상하좌우로 연결된 그림의 크기 찾기
- 도화지에 있는 모든 그림 찾아내기
2번 -> 이중 for문으로 각 칸이 BFS의 시작점이 될 수 있는지를 체크해준다.
정답코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
// 행, 열
int n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int[][] board = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
board[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(board));
// 2. 맵에서 모든 그림 찾기 -> 이중 for문으로 bfs 시작점 찾아내기
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
// 방문처리
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
// 상하좌우 이동
int[] dx = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 0, -1, 1};
// 그림 개수
int picture = 0;
// 그림 최댓값
int mx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 1 && !visited[i][j]) { // 그림 시작점 && 방문체크!(bfs 하기 전)
picture += 1;
// 1. 상하좌우로 연결된 그림 찾기-> bfs 수행
q.offer(new int[]{i, j});
visited[i][j] = true; // 방문처리
int cur_area = 0; // 현재 그림 면적
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
cur_area++;
int[] cur = q.poll();
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int nx = cur[0] + dx[d];
int ny = cur[1] + dy[d];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m) {
if (!visited[nx][ny] && board[nx][ny] != 0) {
q.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
visited[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
}
}
mx = Math.max(mx, cur_area);
} else { // 그림 아닐 때
continue;
}
}
}
System.out.println(picture + " " + mx);
}
}응용1-거리 측정
bfs에서 상하좌우로 탐색할때, 현재까지의 경로의 길이 + 1 하면서 다음 좌표로 탐색 가능.
이러한 성질을 이용해 거리를 측정할 수 있다.
BOJ 2178: 미로 탐색
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2178
거리를 저장할 dist 배열을 두고, -1로 초기화하면 따로 방문배열을 둘 필요가 없다.
정답코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
// 행, 열
int n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int[][] board = new int[n][m];
// 거리 배열
int[][] dist = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
dist[i][j] = -1; // -1 로 초기화함으로서 방문 배열 따로 두지 x
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String line = br.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
board[i][j] = line.charAt(j) - '0';
}
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(board));
// bfs 수행하면서 거리 저장
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
int[] dx = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 0, -1, 1};
// 시작점을 큐에 넣는다
q.offer(new int[]{0, 0}); // board: 0-based
// 시작점을 방문 체크한다!
dist[0][0] = 1;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = q.poll();
int cx = cur[0];
int cy = cur[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = cx + dx[i];
int ny = cy + dy[i];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m) {
if (dist[nx][ny] == -1 && board[nx][ny] == 1) {
q.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
// 거리 갱신(현재까지의 거리 + 1)
dist[nx][ny] = dist[cx][cy] + 1;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(dist[n - 1][m - 1]);
}
}
응용2-시작점이 여러개일때
BOJ 7576: 토마토
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7576
토마토 상자.
보관 후 하루가 지나면 익은 토마토들의 인접한 곳에 있는 익지 않은 토마토들도 익는다.
인접: 상하좌우
-> 최소 며칠이 지나면 모든 토마토가 익게 되는지?
예외처리
-
모든 토마토가 익어있는 상태라면 0 출력
->입력받은 board에 0이 없다면! -
모든 토마토가 익지 못한다면 -1 출력
->bfs를 모두 돌았는데도 0이 남아있는 경우
board에서 1인 모든 좌표에서 BFS 돌아야 함.
-> 1인 좌표를 모두 Queue에 넣고 bfs 수행한다.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
// 행, 열
int m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int[][] board = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
board[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(board));
// # 예외처리1: 모든 토마토 익었는지 체크/ 익은 토마토를 큐에 넣는다
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
// 거리 배열
int[][] dist = new int[n][m];
int[] dx = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 0) {
cnt++;
dist[i][j] = -1; // -1로 초기화해준다
} else if (board[i][j] == 1) {
q.offer(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
}
if (cnt == 0) {
System.out.println(0);
return;
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = q.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = cur[0] + dx[i];
int ny = cur[1] + dy[i];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m && dist[nx][ny] == -1 && board[nx][ny] == 0) {
q.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
dist[nx][ny] = dist[cur[0]][cur[1]] + 1; // 거리 +1
board[nx][ny] = 1; // 토마토 익기
}
}
}
// bfs를 모두 돌았는데도 0이 남아있는 경우
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 0) {
System.out.println(-1);
return;
}
ans = Math.max(ans, dist[i][j]); // 다 익을 때 까지 걸리는 날짜
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}결론적으로, 문제에서 익지 않은 토마토가 익은 토마토가 될때까지라는 표현을 썼지만 시작점에서 모든 지점으로의 거리를 구하는 문제였다.
응용3-시작점이 두 종류일때
BOJ 4179:불!
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/4179
지훈: J
불: F
불: 상하좌우 확산, 수직/수평 이동(=상하좌우)
지훈: 수직/수평 이동(=상하좌우)
불과지훈모두 움직여야 함.- 불 확산은 상하좌우 for 문 4방향 + dx, dy로 처리
- 불, 지훈 둘다 움직임 + 지훈이가 불이 도달하기 전에 미로를 탈출 해야 함.
- 미로 탈출 조건: 미로 가장자리 공간(n,m)
→ 지훈, 불 모두 bfs를 수행해준다
먼저 지훈이는 신경쓰지 말고 불에 대한 BFS를 수행해 미리 각 칸에 전파되는 시간을 다 구해둔다.
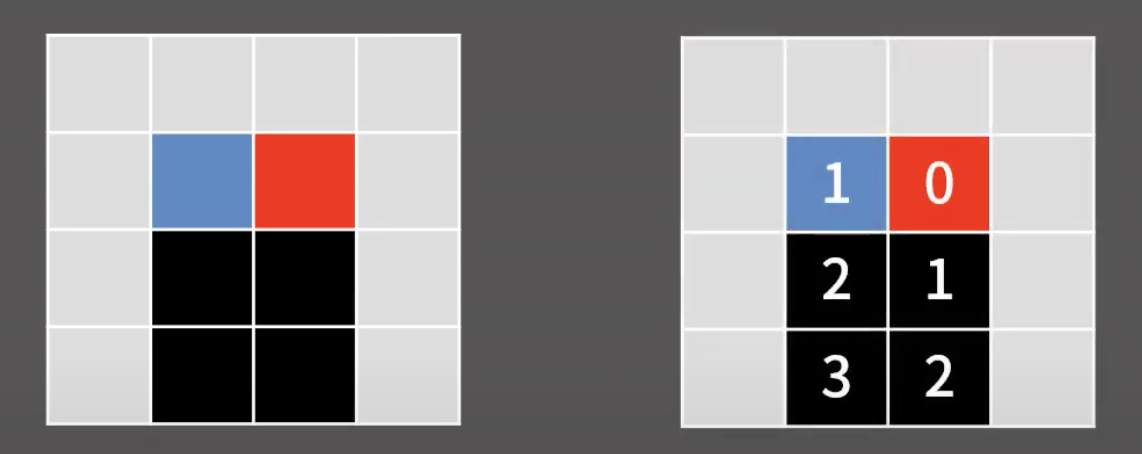
위 사진과 같이 불이 전파되는 시간을 구해둔다.
그 다음 지훈이에 대한 BFS를 돌리며 지훈이를 이동시킨다.
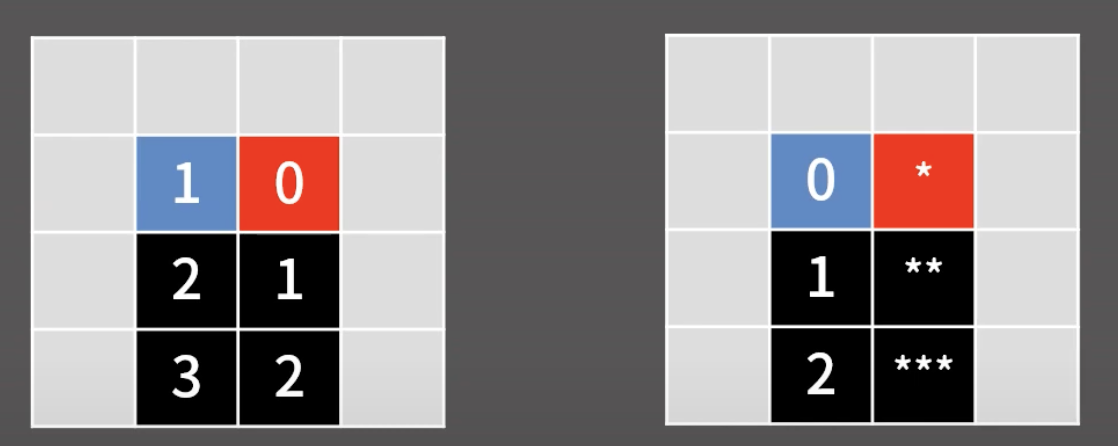
이때, 지훈이가 이동하는 데 걸리는 시간 > 불 이동 시간 이라면 해당 칸은 가지 못한다!(사진에서 *, ** , *** 로 표현된 칸)
원래 BFS 구현에선 큐 안에서 (nx, ny)를 살펴볼 때 방문했는지 여부를 vis[nx][ny]가 true인지 혹은 dist[nx][ny]가 0 이상인지 확인하고, 이미 방문한 칸이라면 continue 함.
-> 이 문제에선 추가로 해당 칸에 불이 붙은 시간을 확인해서 필요에 따라 continue하면 됨
정답코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
// 행, 열
int n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
char[][] board = new char[n][m]; // #: 벽, J: 지훈, F: 불, .: 이동 가능칸
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String li = br.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
board[i][j] = li.charAt(j);
}
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(board));
Queue<int[]> fq = new LinkedList<>(); // 불 dfs 용 큐
Queue<int[]> jq = new LinkedList<>(); // 지훈 dfs 용 큐
int[][] fdis = new int[n][m]; // 불 전파 시간 저장용
int[][] jdis = new int[n][m]; // 지훈이 이동 시간 저장용
int[] dx = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 0, -1, 1};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
fdis[i][j] = -1;
jdis[i][j] = -1;
if (board[i][j] == 'F') {
fq.offer(new int[]{i, j});
fdis[i][j] = 0; // 현재 지점은 방문 처리해줘야
} else if (board[i][j] == 'J') {
jq.offer(new int[]{i, j});
jdis[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// 불 bfs
while (!fq.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = fq.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = cur[0] + dx[i];
int ny = cur[1] + dy[i];
// 범위 내, 방문 x, 갈 수 있다면
if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m || fdis[nx][ny] != -1 || board[nx][ny] == '#') continue;
fq.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
fdis[nx][ny] = fdis[cur[0]][cur[1]] + 1;
}
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(fdis));
// 지훈 bfs
while (!jq.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = jq.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = cur[0] + dx[i];
int ny = cur[1] + dy[i];
// 범위 벗어났다면 -> 탈출한거!
if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m) {
System.out.println(jdis[cur[0]][cur[1]] + 1); // 현재 + 1
return;
}
if (jdis[nx][ny] != -1 || board[nx][ny] == '#') continue;
// 지훈 이동 시간 > 불 이동 시간이라면 해당 칸 가지 못함!
if (fdis[nx][ny] != -1 && jdis[cur[0]][cur[1]] + 1 >= fdis[nx][ny]) continue;
jq.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
jdis[nx][ny] = jdis[cur[0]][cur[1]] + 1;
}
}
// 여기까지 왔다면,, 탈출 실패
System.out.println("IMPOSSIBLE");
}
}