이벤트 처리
DOM의 이벤트 처리 방식과 비슷하지만...
- 카멜 케이스(camelCase) 를 사용
{ }속의 이벤트 처리 함수(이벤트 핸들러, Event handler)로 전달
onChange
이 속성이 들어간 태그의 값이 바뀔 때마다 발생하는 이벤트
function NameForm() {
const [name, setName] = useState("");
const handleChange = (e) => {
setName(e.target.value);
}
return (
<div>
<input type="text" value={name} onChange={handleChange}></input>
<h1>{name}</h1>
</div>
)
};
onClick
클릭 하였을 때 발생하는 이벤트
function NameForm() {
const [name, setName] = useState("");
const handleChange = (e) => {
setName(e.target.value);
}
return (
<div>
<input type="text" value={name} onChange={handleChange}></input>
<button onClick={alert(name)}>Button</button>
<h1>{name}</h1>
</div>
);
};위와 같이 onClick에서 함수를 바로 실행시켜 버린다면
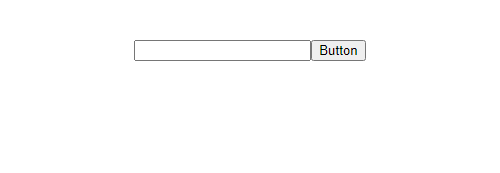
State가 바뀔 때마다 새로 렌더링 되면서
onClick에 있는 함수가 그 때마다 실행되어버린다
함수를 실행한 것이 아닌 함수 자체를 넣어준다
onClick내에서 익명 함수로 전달
<button onClick={() => alert(name)}>Button</button>- 함수 자체를 전달
const handleClick = () => {
alert(name);
};
...
<button onClick={handleClick}>Button</button>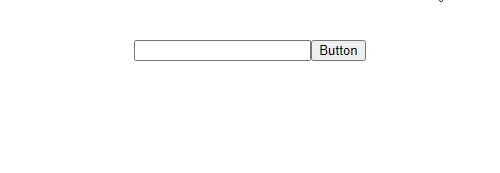
버튼을 눌렀을 때만 함수가 작동한다
<select>에서 활용
<select> : dropdown 목록을 만드는 태그
function App() {
const [choice, setChoice] = useState("apple");
const fruits = ["apple", "orange", "pineapple", "strawberry", "grape"];
const options = fruits.map((fruit) => {
return <option value={fruit}>{fruit}</option>;
});
const handleFruit = (event) => {
setChoice(event.target.value);
};
return (
<div className="App">
<select onChange={handleFruit}>{options}</select>
<h3>{choice}</h3>
</div>
);
}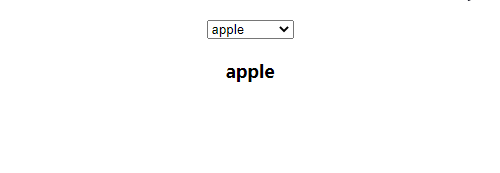
<select>태그 안에 목록 내용이 들어 있다- 선택할 수 있는 옵션은
<option>태그로 감싼다
-<option value={fruit}>{fruit}</option>
value속성 →event.target.value
뒤의 텍스트는 목록을 열었을 때 보여질 내용
- 여러 개인 경우map을 활용한다
팝업(pop up) 활용
팝(pop)하고 튀어나오는(up) 웹페이지 표시방법을 가리킨다. 새창을 표시하기 위해 기존페이지를 전환하는 방식이 아닌, 새로운 웹창을 하나 더 추가시키는 기능
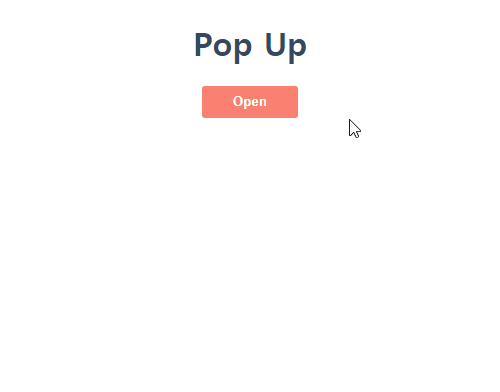
App.js
function App() {
const [showPopup, setShowPopup] = useState(false);
const togglePopup = () => {
setShowPopup(!showPopup)
};
return (
<div className="App">
<h1>Pop Up</h1>
<button className="open" onClick={togglePopup}>Open</button>
{showPopup ? (
<div className="popup">
<div className="popup_inner">
<h2>Success!</h2>
<button className="close" onClick={togglePopup}>
Close
</button>
</div>
</div>
) : null}
</div>
);
}팝업 창을 위해 css도 같이 넣으면
App.css
.App {
font-family: sans-serif;
text-align: center;
}
.App > h1 {
color: #34495e;
}
.open {
width: 6rem;
height: 2rem;
border: none;
border-radius: 3px;
background-color: salmon;
color: white;
font-weight: bolder;
}
.popup {
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
margin: auto;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
}
.popup_inner {
position: absolute;
left: 25%;
right: 25%;
top: 25%;
bottom: 25%;
margin: auto;
background: white;
}
.popup_inner > h2 {
position: absolute;
left: 25%;
right: 25%;
top: 25%;
bottom: 25%;
margin: auto;
color: #34495e;
}
.close {
position: absolute;
left: 25%;
right: 25%;
top: 40%;
bottom: 25%;
margin: auto;
width: 6rem;
height: 2rem;
border: none;
border-radius: 3px;
background-color: salmon;
color: white;
font-weight: bolder;
outline: none;
}