C# 형변환
- 숫자 → 숫자 (int, float)
int x = 5;
float y = 10.0f;
float float_X = (float)x; // 굳이 명시하지 않아도 됨
int int_y = (int)y;- 다른 자료형 → 문자 (숫자, bool → string)
int x = 10;
string strX = x.ToString();
float y = 10.5f;
string strY = y.ToString();
bool myBool = true;
string strBool = myBool.ToString();- 문자 → 다른 자료형
- Convert 클래스 이용
string strX = "10";
int X = Convert.ToInt32(strX);Convert 클래스의 매서드
ConvertConvert.ToInt32(); //32비트 부호 있는 정수로 변환 Convert.ToDouble(); //실수 형태로 변환 Convert.ToSingle(); //단정 밀도 부동 소수점(float)형으로 변환 Convert.ToChar(); //유니코드 형태로 변환 Convert.ToString(); //문자열로 변환 Convert.ToBooleen(); //부울 형태로 변환
- Parse() 함수 이용
string strX = "10";
int x = int.Parse(strX);Convert와 Parse() 이용 시, 변환할 수 없는 값일 경우 에러 발생!
string strX = "10xxxx"; int x = Convert.ToInt32(strX); // 에러 발생! int y = int.Parse(strX); // 에러 발생!→ TryParse() 사용
- TryParse() 함수 이용
string strX = "10";
int x;
int.TryParse(strX, out x); // x : 10TryParse()는 반환값으로 bool을 반환, 캐스팅 성공 여부 확인
string strX = "10"; int x; bool isSuccess; isSuccess = int.TryParse(strX, out x); // isSuccess : true, x : 10
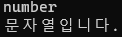
입력받은 데이터가 숫자인지 문자열인지 판단하기
string input = Console.ReadLine(); int x; bool isNumber = int.TryParse(input, out x); if(isNumber){ Console.WriteLine(x); Console.WriteLine("숫자입니다."); } else{ Console.WriteLine(input); Console.WriteLine("문자열입니다."); }
입력받은 데이터가 숫자라면 짝수인지 홀수인지 판단하기
string input = Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("입력받은 데이터 : " + input); int x; bool isNumber = int.TryParse(input, out x); if (isNumber) { int remainder = x % 2; if (remainder == 0) Console.WriteLine(x + "은(는) 짝수입니다."); else Console.WriteLine(x + "은(는) 홀수입니다."); } else Console.WriteLine("숫자가 아닙니다.");
반복문
for문
for(초기화;조건;변화){
실행 내용
}while문
while(조건){
실행 내용
}do while문
do{
실행 내용
}while(조건);입력받은 데이터로 구구단 출력하기
Console.WriteLine("출력하고 싶은 단을 입력해주세요."); string input = Console.ReadLine(); int x; bool isNum = int.TryParse(input, out x); if (!isNum) Console.WriteLine("숫자가 아닙니다."); else { for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) { Console.WriteLine(x + " x " + i + " = " + x * i); } }
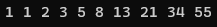
피보나치 수열 10개까지 출력하기
int first = 0; int second = 1; for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ Console.Write(second + " "); int result = first + second; first = second; second = result; }
문자열
string
참고하기 https://learn.microsoft.com/ko-kr/dotnet/csharp/programming-guide/strings/
출처 https://kukuta.tistory.com/413
String 초기화
// 초기화 없이 단순 선언 string str1; //null로 초기화 string str2 = null; //빈 스트링 객체 생성 string str3 = System.String.Empty; //문자열로 초기화 string oldPath = "C:\\Path\\To\\Somewhere"; // oldPath : C:\Path\To\Somwhere //이스케이프 문자('\')를 사용하지 않고 문자열 초기화 string newPath = @"C:\Path\To\Somewhere"; // newPath : C:\Path\To\Somwhere // var 키워드를 이용한 묵시적 스트링 객체 생성 var temp = "I'm still a strongly-typed System.String!"; // const 키워드를 이용한 상수 스트링 객체 생성 const string message5 = "You can't get rid of me!"; // 문자열 char[] letters = { 'A', 'B', 'C' }; // ABC, 문자 배열을 이용해 스트링 객체 생성 string alphabet1 = new string(letters); // BC, start번째 문자를 시작으로 count 만큼의 길이를 갖는 스트링 객체 생성 string alphabet2 = new string(letters, 1, 2); // AAA, 입력한 문자를 n번 반복하는 스트링 객체 생성 string alphabet3 = new string('A', 3);
String 클래스의 메서드
- Clone() → string을 복사할 때 사용하는 듯
string message1 = "Hello World"; string message2 = (string)message1.Clone(); // 참조를 리턴, 이제 부터 message1과 message2는 같다. Console.WriteLine(message1); // message1 : Hello World Console.WriteLine(message2); // message2 : Hello World
- Concat() → 두 개의 문자열을 결합할 때 사용
string a = "Hello"; string b = "World"; Console.WriteLine(string.Concat(a, b)); // HelloWorld
- Contains() → 지정된 문자열의 스트링 클래스에 포함 여부를 검사, True 또는 False를 리턴
string a = "HelloWorld"; string b = "World"; Console.WriteLine(a.Contains(b)); // True
- Equals() → 주어진 두 문자열이 동일한지 여부 확인. 참이면 Ture, 거짓이면 False
string a = "Hello"; string b = "World"; Console.WriteLine(a.Equals(b)); // False
- IndexOf() → 스트링 내 지정된 문자열이 처음으로 발생하는 위치 반환. 0부터 시작
string a = "Hello"; int b = a.IndexOf('o'); Console.WriteLine(b); // 4
- Insert() → 스트링 내 지정한 인덱스에 새로운 문자열 삽입. 인덱스는 0부터 시작
string a = "Hello"; string b = a.Insert(2, "_World_"); Console.WriteLine(b); // He_World_llo
- Replace() → 스트링 객체의 지정된 문자열을 다른 문자열로 치환. 첫번째 인자가 치환 대상
string a = "Hello"; string b = a.Replace("lo", "World"); Console.WriteLine(b); // helWorld
- SubString() → 스트링의 문자열 일부를 추출하는데 사용.
string a = "Hello"; string b = a.Substring(2); Console.WriteLine(b); // llo
- Length → 문자열의 길이
string a = "Hello World"; Console.WriteLine(a.Length); // 11
StringBuilder 클래스
C#에서 문자열은 한번 생성되어 메모리에 할당 되면 더 이상 변경되지 않음 → Immutable
ex) string a = "C#" → string a = "F#" 으로 변경할 경우, .Net에서는 새로운 string 객체를 생성하여 "F#"으로 초기화 후 변수 a에 할당함. → 변수 a는 다른 메모리를 갖는 객체를 가리키게 됨.
스트링 변경 작업이 빈번할 경우 성능 저하가 발생할 가능성이 있다. → 이를 보완하기 위해 StringBuilder를 사용한다.
String.text.StringBuilder 참조
StringBuilder
using System; using System.Text; // StringBuilder를 사용하기 위한 namespace namespace MySystem { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 1; i <= 26; i++) { sb.Append(i.ToString()); sb.Append(System.Environment.NewLine); } string s = sb.ToString(); Console.WriteLine(s); } } }
$ 문자열
문자열을 변수들과 다이나믹하게 결합하기 위해선 string.Format을 이용해 변수들의 결합 위치를 지정.
string str1 = string.Format("Hello {0}, {1}", "World", 123); Console.WriteLine(str1); // Hello World, 123그러나 Format 메서드 대신 문자열 앞에 $심볼을 표기해주면 변수 삽입을 다이나믹하게 할 수 있다.
string world = "World"; int num = 123; string str2 = $"Hello {world}, {num}"; Console.WriteLine(str1); // Hello World, 123