
Page Header
Stores metadata about a page like
- Flag for page contents
- Layout
- Number of cells
- Cell offset pointing to empty space
ex) MySQL (InnoDB) - # of Heap Records and Level
Magic Number
is a multi-byte block containing constant values stored in either file header or page header
- contains information like
- Page type
- Page version
- Used for authentication and sanity checks
- Offset is valid if it matches with magic number
- ex) 50 41 47 45 (Hex value of a page)
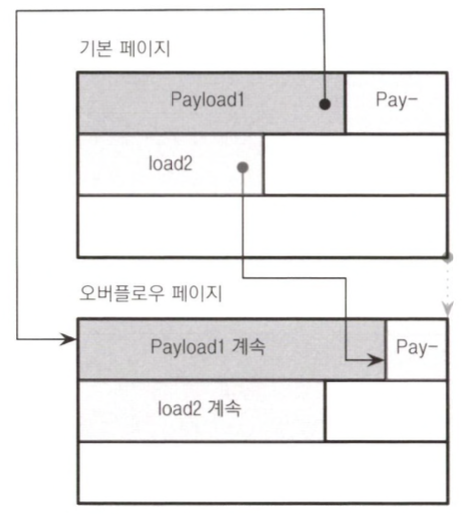
Overflow Page
A page added to primary page for implemenation of variable-length pages
- Primary page refers to original page where overflow page was added
- Stores fixed-size of bytes in primary key first
- fixed-size = node size / fanout
- always
max_payload_byteof bytes left
- Stores rest of data in overflow page
- Each record in primary page points to it
- Might need multiple overflow pages to store a data
Pointers
Sibling Link
- Pros
- Easy access to a sibling node
- Cons
- Requires additional update for sibling offset
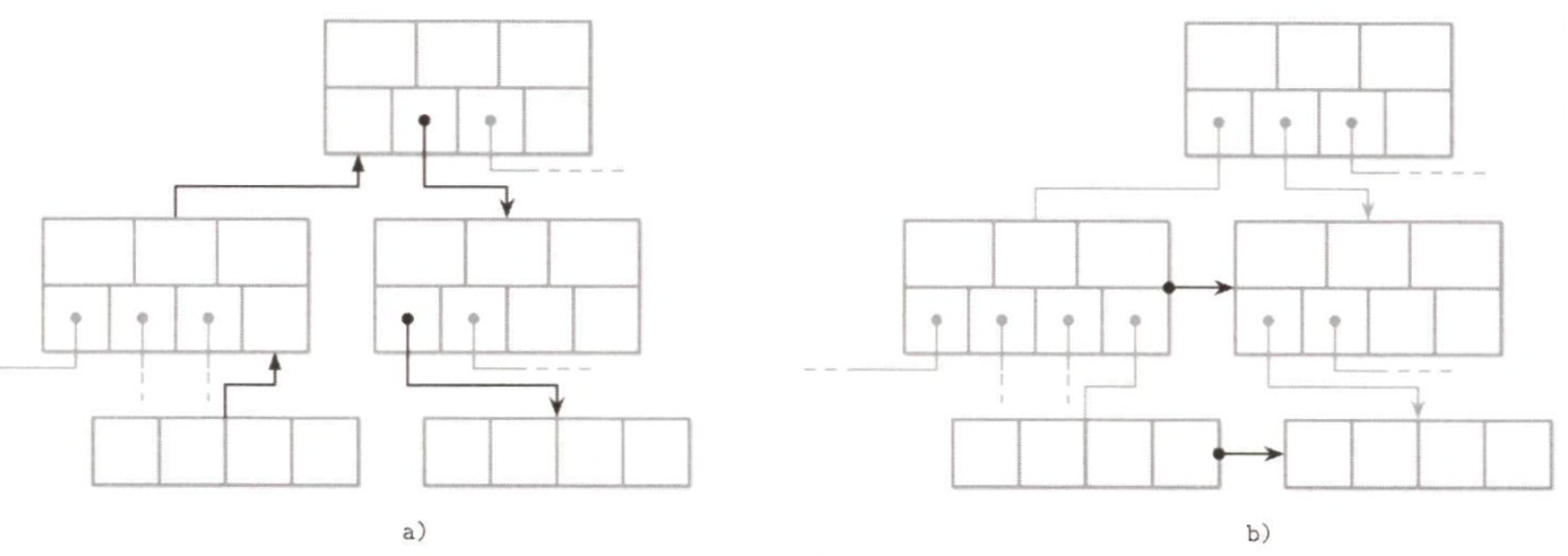
Right-most Pointer
- can be stored separately from other keys and pointers
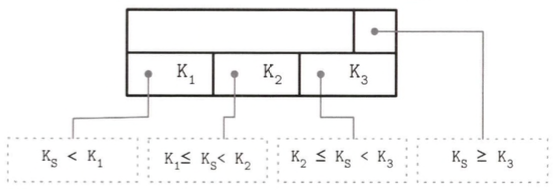
High Key
A key having the highest value in the current node's subtree
- (N+1) keys and (N+1) pointers
- Reduces search cost from inifinity to high key

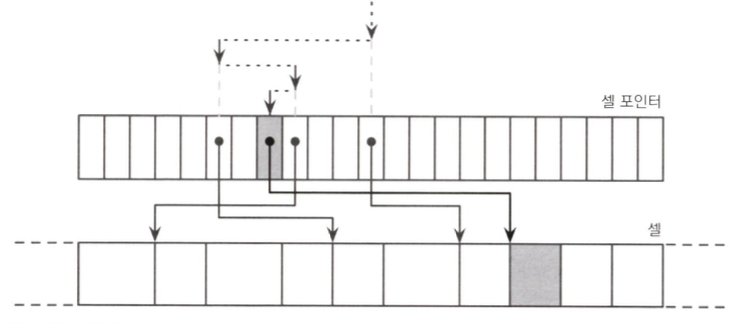
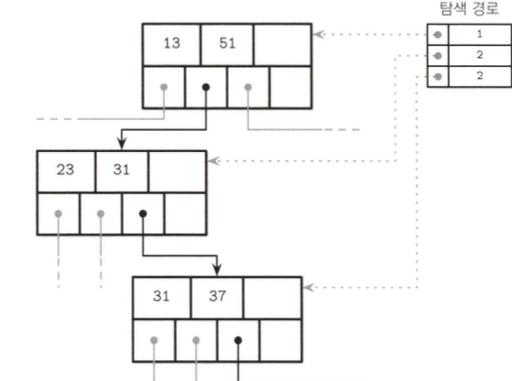
Binary Search
B-tree uses binary search for a specific key search in a node
- Returns a number
- Positive - A given key exists
- Negative - Doesn't exist
- Returns insert location of first large key of given key
- Searches cell offset list
- which is sorted logically
- whereas cell is stored by insert order
Mere and Split
Happens from current nodes to upper-level nodes
- Requires traversal to root node
- by storing parent node
- by storing search path
Rebalancing
Tries to reduce the possibility of split or merge operations by load-balancing among sibiling nodes (B*tree)
- Enhances the efficiency of probe process
- Low tree height
- Low number of pages to be traversed
Optimizing of auto-increment
All inserts are done in right-most leaf node
- Fast path (PostgreSQL)
- If a given key is greater than the first key in right most page && enough space,
- Insert without extra search process
- Quick balance (SQLite)
- If right most node has no space,
- Assigns a new node instead of rebalancing
- Bulk Loading
- Composes all leaf nodes first
- Adds already-prepared child pointer and key to parent nodes
Compression
Most databases provide a compression algorithm to save disk space due to the overhead of storing raw data
- High compression rate
- Reduces data size and accesses more data at once
- but, uses more RAM and CPU cycle in decompression process
Page-level compression
- File-level is inefficient
- Re-compression is required once file update
- is recommended to have page size same with block size
- Block is data transfer unit
- If block contains several pages partially,
- unused page would be decompressed

Page Compaction
is a compaction process in order to
- remove fragmentation by de-allocating dead cell space
- re-order cells in logical order in a page
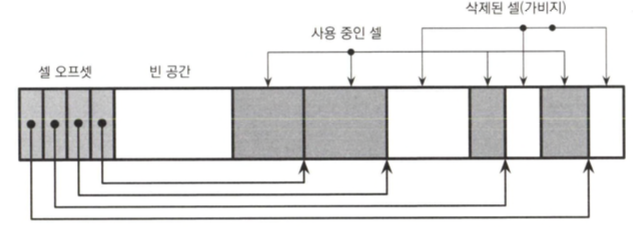
- Garbage Cell
- Unable to be accessed
- It is inefficient to pad it with 0s,
- Because it would be overwritten with new data

A strolling magician and walk around magician add a unique, interactive flair to events by mingling with guests and performing up-close magic tricks. Unlike stage magicians, these performers don’t require a set stage or formal setup; they carry their magic in their hands, moving through the crowd to entertain smaller groups at a time. This style allows guests to experience magic in a personal and engaging way, creating memorable moments. The spontaneity of a strolling magician and walk around magician adds an element of surprise and excitement, making them perfect for parties, weddings, corporate events, and gatherings of all kinds.