📑 이번 문제는 Queue 문제이다.
문제를 풀어보기전에 일단 Queue(큐)가 무엇인지 알아보는 시간을 가져볼까 한다.
1. Queue란?
📌큐(Queue)란?
- 사전적 정의 : '대기열'로 선착순으로 줄 서는 것을 생각하면 이해하기 쉽다.
- 영어 단어 queue는 표를 사러 일렬로 늘어선 사람들로 이루어진 줄을 말하기도 하며, 먼저 줄을 선 사람이 먼저 나갈 수 있는 상황을 연상하면 된다. 나중에 집어 넣은 데이터가 먼저 나오는 스택과는 반대되는 개념이다.
- 큐(Queue)는 FIFO(First In First Out) 을 따른다. 즉 스택과는 다르게 '선입선출'이라는 개념이다. 쉽게 설명하면 가장 먼저 넣은 데이터를 가장 먼저 꺼낼 수 있는 선형 데이터 구조이다.
출처 : 위키백과
이렇게만 보면 무슨말인지 이해하기 굉장히 어렵다😅
그래서 우리는 쉬운 예로 '선착순'을 생각하면 쉽다.
예를 들어 비행기를 타기위해 일렬로 줄을 선다면 맨 앞에 있는 사람은 1등으로 줄을 섰을 것이고,가장 먼저 비행기에 탑승할 것이다.
이 개념이 Queue(큐)이다.
그림을 통해 Queue를 자세하게 살펴 보겠다.
2. Linear Queue(선형 큐)
Queue의 맨 앞을 Front, 맨 뒤를 Rear이라고 하고 큐에서 기본적으로 사용되는 연산을 알아보자
📌 Queue의 연산
- enqueue(): 큐의 Rear에 요소 삽입
- dequeue(): 큐의 Front에 있는 요소 삭제
- isFull(): 큐가 가득 찼는지 검사
- isEmpty(): 큐가 비었는지 검사
- front(): 큐의 Front에 있는 값 출력
- back(): 큐의 Rear에 있는 값 출력
이러한 과정으로 Linear Queue가 진행된다. 이제 이것을 코드로 작성해 보겠다.
2-1. Java
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Queue {
private int front;
private int rear;
private int maxSize;
private Object[] queueArray;
//Queue 생성
public Queue(int maxSize){
this.front = 0;
this.rear = -1;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.queueArray = new Object[maxSize];
}
//Queue 비었는지 확인
public boolean empty(){
return (front == rear+1);
}
//Queue 꽉 찼는지 확인
public boolean full(){
return (rear == maxSize-1);
}
//Queue에 item 입력
public boolean enqueue(Object item){
if(full()){
System.out.println("Queue is FULL!!");
return false;
}
queueArray[++rear] = item;
return true;
}
//Queue 가장 먼저들어온 데이터 출력
public Object dequeue(){
if(empty()){
System.out.println("Queue is EMPTY!!");
return null;
}else{
Object item = queueArray[front];
queueArray[front] = null;
front++;
return item;
}
}
//Queue 출력
public void printQueue(Queue queue){
if(!empty()){
for(int i = 0; i<maxSize; i++ ){
if(queue.queueArray[i] == null){
System.out.print("|\t\t");
}else{
System.out.print("|\t"+ queue.queueArray[i]+ "\t");
}
}
System.out.println(" |");
}else{
System.out.println("큐 비어있음");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream a = System.in;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(a);
System.out.println("큐 SIZE 입력 : ");
int size = sc.nextInt();
Queue arrayQueue = new Queue(size); //create queue
boolean flag = true;
while(flag){
menu();
String s = sc.next();
switch(s){
case "1":
System.out.print("ENQUEUE : ");
String data = sc.next();
arrayQueue.enqueue(data);
break;
case "2":
System.out.println("DEQUEUE : " + arrayQueue.dequeue());
break;
case "3":
arrayQueue.printQueue(arrayQueue);
break;
case "q":
case "Q":
flag = false;
break;
}
}
}
public static void menu(){
System.out.println("1. enQueue");
System.out.println("2. deQueue");
System.out.println("3. QUEUE");
System.out.println("Q. 종료");
}
}참고링크 : https://hahahoho5915.tistory.com/11?category=653539
2-2. Python
파이썬에서는 List의 특성상 굳이 Front가 필요하지 않기 때문에 사용하지 않아도 된다!
def enqueue(x):
global rear
rear += 1
queue.insert(rear, x)
def dequeue():
global rear
if isEmpty() == False:
rear -= 1
return queue.pop(0)
else:
print("queue is Empty")
def peek():
return queue[0]
def isSize():
return len(queue)
def isEmpty():
if rear == -1:
return True
else:
return False
def init():
global rear
rear = -1
queue.clear()
##-------------------- test Code --------------------
rear = -1
queue = []
init()
enqueue(1)
print(queue)
print('-'*10)
enqueue(2)
print(queue)
print('-'*10)
print(isSize())
print('-'*10)
print(dequeue())
print('-'*10)
print(queue)
print('-'*10)
print(peek())
print('-'*10)
enqueue(4)
print(queue)
print('-'*10)
print(peek())
print('-'*10)
init()
print(queue)참고링크 : https://wisetrue.tistory.com/228
2-3. Linear Queue의 문제점
일반적인 선형 큐는 rear이 마지막 index를 가르키면서 데이터의 삽입이 이루어집니다.
문제는 rear이 배열의 마지막 인덱스를 가르키게 되면 앞에 남아있는 (삽입 중간에 Dequeue 되어 비어있는 공간) 공간을 활용 할 수 없게 됩니다.
이 방식을 해결하기 위해서는 Dequeue를 할때 front를 고정 시킨 채 뒤에 남아있는 데이터를 앞으로 한 칸씩 당기는 수밖에 없습니다.
또 다른 방안으로는 Circular Queue(원형 큐)를 사용하는 방법이 있습니다.
3. Circular Queue(원형 큐)
📌Circular Queue의 원칙
- 배열 queue[MAX_QUEUE_SIZE]를 원형으로 취급한다.
ex) rear == MAX_QUEUE_SIZE - 1 이라면, queue[0]이 빈 경우에 queue[0]에 삽입- 최대 원소 수 : MAX_QUEUE_SIZE가 아니라 MAX_QUEUE_SIZE - 1 이다.
ex) front == rear 일 경우, 포화상태인지 공백 상태인지 구분하기 위해 하나의 공간은 항상 비워둔다.
아래의 그림을 통해 쉽게 이해 할 수 있다.
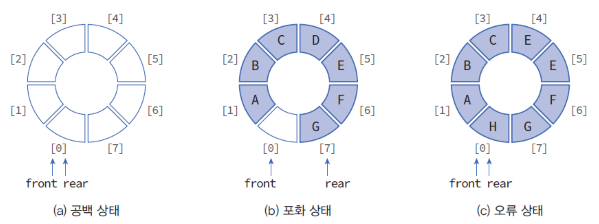
삽입되는 과정은 아래와 같다.
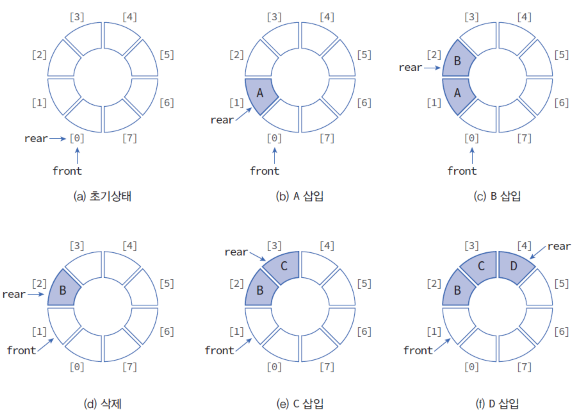
이를 바탕으로 코드를 작성해 보고자 한다.
3-1. Java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Circular_queue {
private int[] array;
private int capacity;
private int rear = 0, front = 0;
private char flag = 0;
public ArrayCircularQueue_2(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.array = new int[capacity];
}
public ArrayCircularQueue_2() {
this.capacity = 5;
this.array = new int[capacity];
}
public int size() {
return (capacity * flag + (rear - front));
}
public boolean isFull() {
return size() == capacity;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
public void enqueue(int data) {
if (isFull())
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
this.array[rear] = data;
this.rear = (this.rear + 1) % capacity;
if (front >= rear) flag = 1;
else flag = 0;
}
public int dequeue() {
if (isEmpty())
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
int data = this.array[front];
this.array[front] = 0;
this.front = (this.front + 1) % capacity;
if (front > rear) flag = 1;
else flag = 0;
return data;
}
public int peek() {
return this.array[front];
}
@Override public String toString() {
return Arrays.toString(array) + " , size : " + size();
}
}참고링크 : https://gusdnd852.tistory.com/241
3-2. Python
def enqueue(x):
global rear
if isFull()==False:
rear = (rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE
queue.insert(rear, x)
def dequeue():
global front, rear
if isEmpty() == False:
front = (front + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE
returnValue = queue[front]
queue[front] = " "
return returnValue
else:
print("queue is Empty")
def peek():
return queue[0]
def isSize():
return len(queue)
def isEmpty():
if rear == front:
return True
else:
return False
def isFull():
if front == (rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE:
print("queue is full")
return True
else:
return False
def init():
global front, rear
front = -1
rear = -1
queue.clear()
##-------------------- test Code --------------------
MAX_QUEUE_SIZE = 7
front = -1
rear = -1
queue = []
init()
enqueue(1)
print(queue)
enqueue(3)
print(queue)
dequeue()
print(queue)
enqueue(5)
print(queue)
enqueue(8)
print(queue)
enqueue(7)
print(queue)
enqueue(9)
print(queue)
enqueue(11)
print(queue)
enqueue(4)
print(queue)
dequeue()
print(queue)
참고링크 : https://wisetrue.tistory.com/229?category=783925
4. 10845번 풀이
4-1. Java
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int[] q = new int[100000];
static int size = 0;
static int front = 0;
static int back = 0;
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
while(N-- > 0) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " ");
switch(st.nextToken()){
case "push": push(Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken())); break;
case "pop" : pop(); break;
case "size" : size(); break;
case "empty" : empty(); break;
case "front" : front(); break;
case "back" : back(); break;
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
static void push(int n) {
q[back] = n;
back++;
size++;
}
static void pop() {
if(size == 0) {
sb.append(-1).append('\n');
}
else {
sb.append(q[front]).append('\n'); // 맨 앞의 원소를 출력
size--;
front++; // front가 가리키는 위치 1 증가
}
}
static void size() {
sb.append(size).append('\n');
}
static void empty() {
if(size == 0) {
sb.append(1).append('\n');
}
else sb.append(0).append('\n');
}
static void front() {
if(size == 0) {
sb.append(-1).append('\n');
}
else {
sb.append(q[front]).append('\n'); // 맨 앞의 원소 출력
}
}
static void back() {
if(size == 0) {
sb.append(-1).append('\n');
}
else {
sb.append(q[back - 1]).append('\n'); // 맨 뒤의 원소 출력
}
}
}4-2. Python
import sys
N = int(sys.stdin.readline())
queue = []
for i in range(N):
cmd = sys.stdin.readline().split()
if cmd[0] == "push":
queue.insert(0, cmd[1])
##print(queue)
elif cmd[0] == "pop":
if len(queue) != 0: print(queue.pop())
else: print(-1)
elif cmd[0] == "size":
print(len(queue))
elif cmd[0] == "empty":
if len(queue) == 0: print(1)
else : print(0)
elif cmd[0] == "front":
if len(queue) == 0: print(-1)
else: print(queue[len(queue) -1])
elif cmd[0] == "back":
if len(queue) == 0: print(-1)
else: print(queue[0])오늘은 Queue중 Linear와 Circular에 대해 알아보았다.
최대한 직접 구현하는 방법을 찾아서 하느라 좀 애를 먹었던 것 같다.
나중에 기회가 된다면 Deque와 LinkedList를 사용한 구현도 코드를 올려볼 예정이다!
아직 Queue의 종류 중 Priority Queue(우선순위 큐)는 학습하지 않았다.
Priority Queue의 구현 방법은 총 3가지가 있는데 첫째 배열기반, 둘째 연결리스트 기반, 셋째
힙기반이 있다.
그래서 이건 백준 문제중 Heep(힙)관련된 문제를 풀때 다루어볼 생각이다😁
문제 풀이말고 코드는 https://github.com/chanI95/Study.git에 있다.

