서문
안녕하세요. 마이다스인에서 인재 채용 플랫폼 잡다의 웹 프론트엔드 개발을 담당하고 있는 배준형입니다.
잡다에서는 React-Query 라이브러리를 사용하여 Data Fetching을 처리하고 있는데요. 로딩 상태는 useQuery에서 반환하는 isLoading, isFetching 값을 활용하여 관리하고 있습니다.
이를 Suspense를 이용해 간단하게 처리하려 했으나 의도한 대로 동작하지 않았고, suspense 옵션을 true로 설정한 useQuery(v5에서는 useSuspenseQuery)가 여러 개 존재하면 waterfall 방식으로 순차 실행되는 문제가 있었습니다.
useQueries를 사용하거나 기존처럼 isLoading, isFetching으로 처리하면서 suspense 옵션을 사용하지 않으면 query들이 병렬로 실행되는 것처럼 보이는데요. 왜 suspense를 사용하면 순차 실행될까요? 그리고 Suspense는 어떻게 자식 요소들의 Data Fetching 완료를 알 수 있을까요?
의도한 대로 동작하지 않는 코드들을 통해 Suspense의 작동 원리가 궁금해졌고, 이에 대해 알아본 내용을 공유하고자 합니다.
Suspense
Suspense 컴포넌트를 사용하면 하위 항목이 로딩을 완료할 때까지 대체 fallback을 표시할 수 있습니다.
<Suspense fallback={<Loading />}>
<SomeComponent />
</Suspense>여기서 로딩이 완료되었다(finished loading)는 것은 정확히 무엇을 의미할까요?
React 공식 문서에 따르면 Suspense는 다음 3가지 경우에 대해서만 활성화됩니다.
- Suspense를 도입한 데이터 소스
lazy를 사용한 지연 로딩 컴포넌트use를 통해 읽은 Promise value
반면 Effect나 Event Handler에서 발생하는 Data Fetching은 감지하지 못합니다.
로딩이 완료되었다(finished loading)는 의미를 추론해보면,
- Suspense를 도입한 Data Fetching의 경우 Data Fetching이 완료되었을 때
lazy지연 로딩 컴포넌트의 경우 컴포넌트 로딩이 완료되었을 때use를 사용한 Promise value의 경우 Promise가 Settled 되었을 때
를 의미하는 것으로 보입니다.
2개 이상의 Suspense 컴포넌트 로딩
만약 하나의 Suspense로 여러 요소를 감싸고 있다면, Suspense 내부는 단일 단위로 취급됩니다. 아래 코드처럼 2개의 자식 요소 중 하나라도 로딩 중이라면 fallback이 표시되고, 모든 요소가 준비되면 한번에 렌더링됩니다.
<Suspense fallback={<Loading />}>
<Biography />
<Panel>
<Albums />
</Panel>
</Suspense>Suspense가 중첩되어 있으면 어떨까요? 컴포넌트가 Suspends 된다면 가장 가까운 상위 Suspense 컴포넌트의 fallback이 표시됩니다.
<Suspense fallback={<BigSpinner />}>
<Biography />
<Suspense fallback={<AlbumsGlimmer />}>
<Panel>
<Albums />
</Panel>
</Suspense>
</Suspense>만약 Biography, Albums 둘 다 Suspend된다면,
Suspense컴포넌트에 의해Biography가 먼저 로딩을 시도합니다.- 그 동안
Albums는 Data Fetching을 시도하지 않고, 렌더링도 이루어지지 않습니다. Biography의 렌더링 준비가 완료되면 BigSpinner 대신Biography와Albums를 감싸고 있는Suspense가 렌더링됩니다.Biography가 렌더링 되어있는 상태에서Albums가 로딩을 시도하고, 완료되면AlbumsGlimmer를Albums가 대체합니다.
순서로 컴포넌트가 표시됩니다. 이 때 Suspense 하나로 모든 요소를 감쌀 때와 중첩되게 Suspense를 사용하는 경우 동작이 다른데요.
Suspense 하나만 사용 시
<Suspense fallback={<Loading />}>
<Biography />
<Panel>
<Albums />
</Panel>
</Suspense>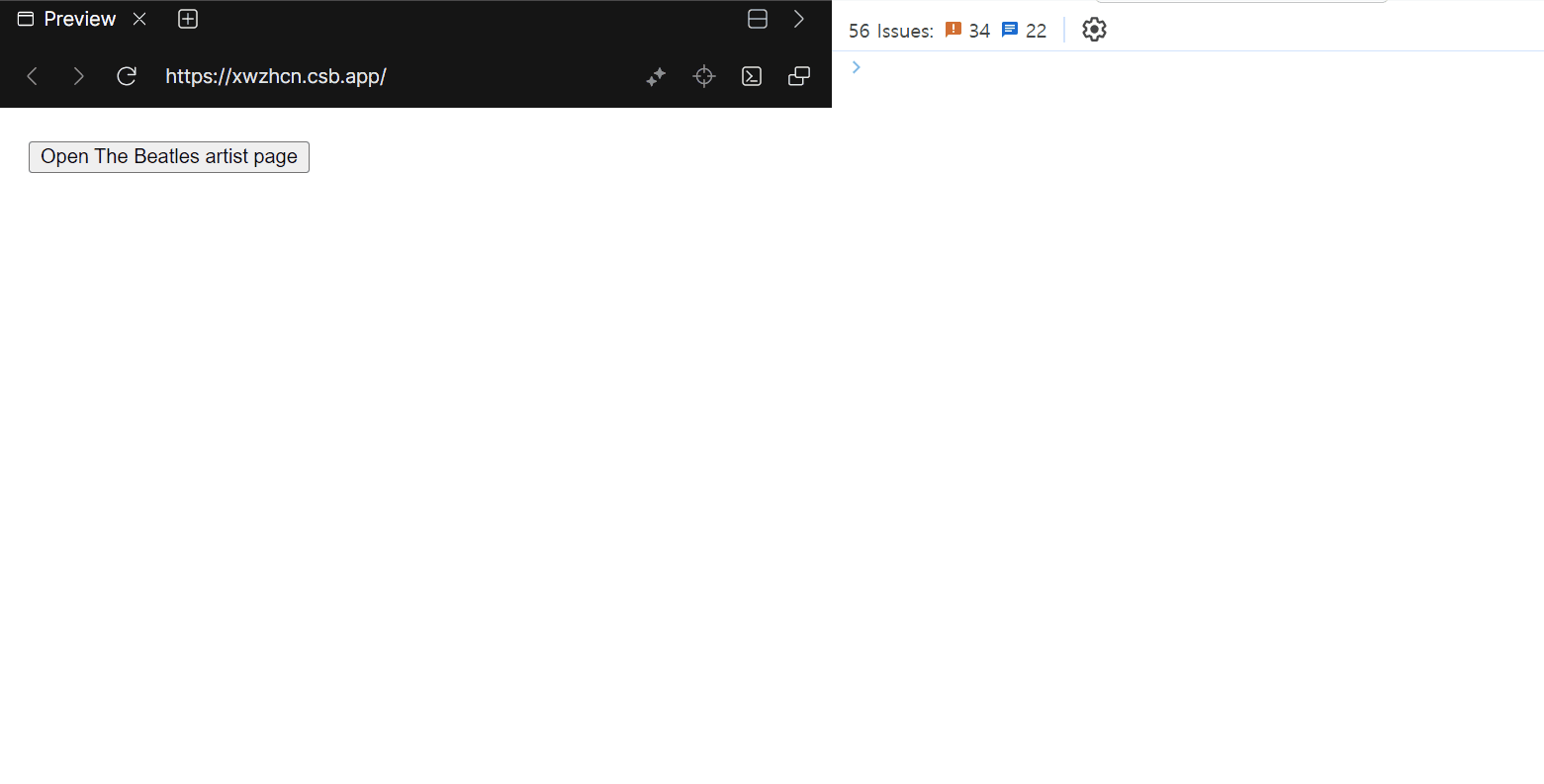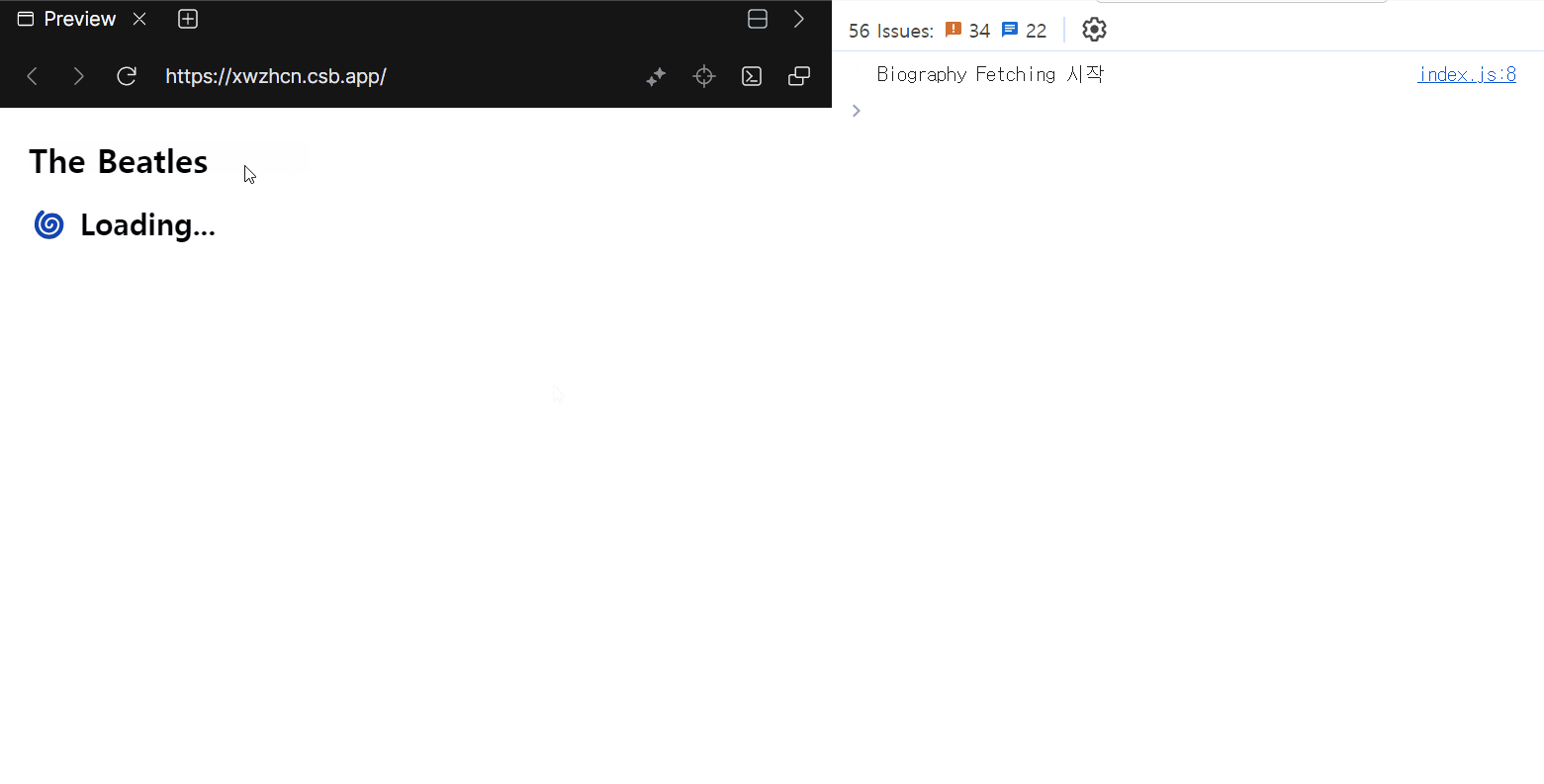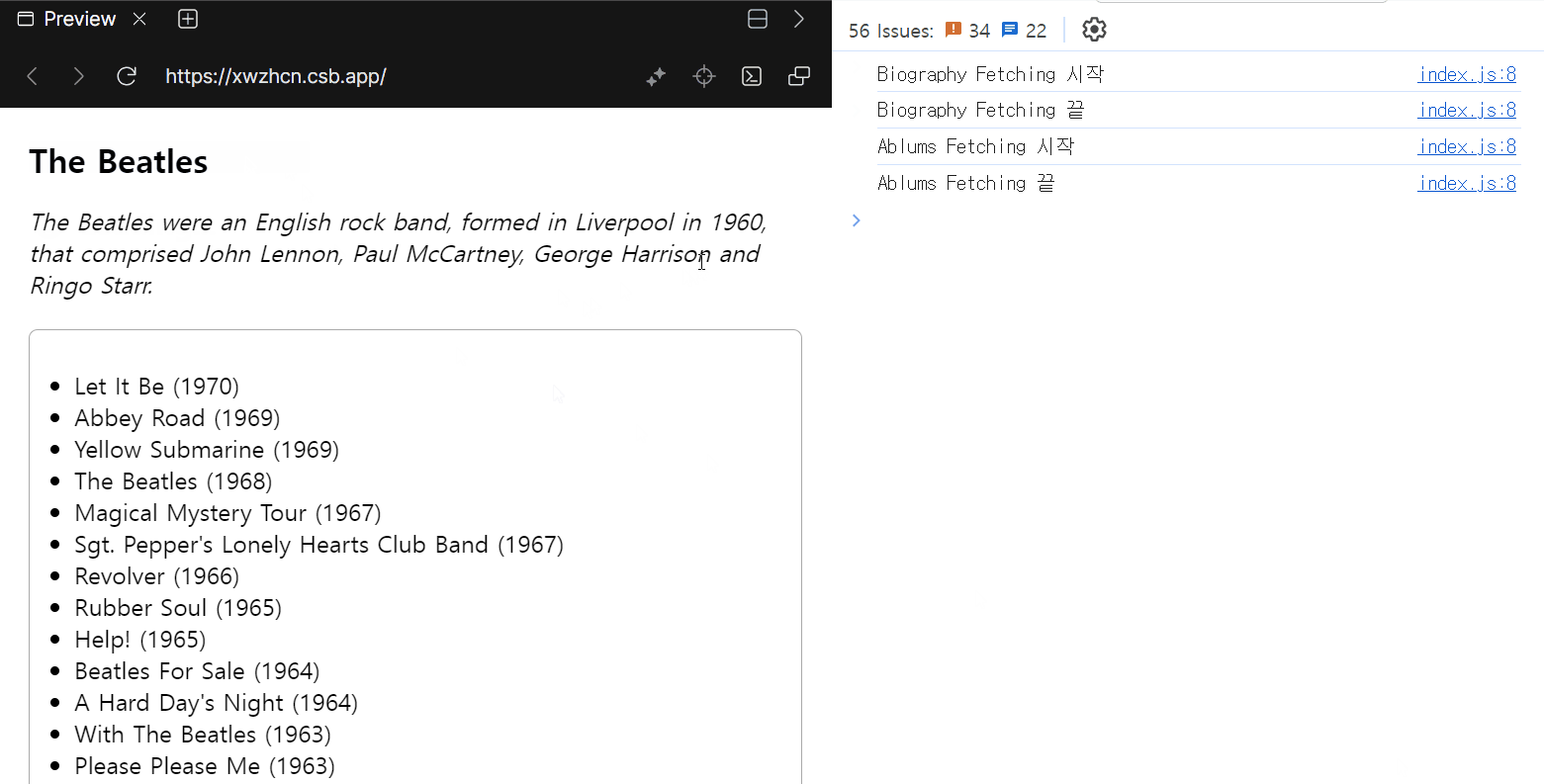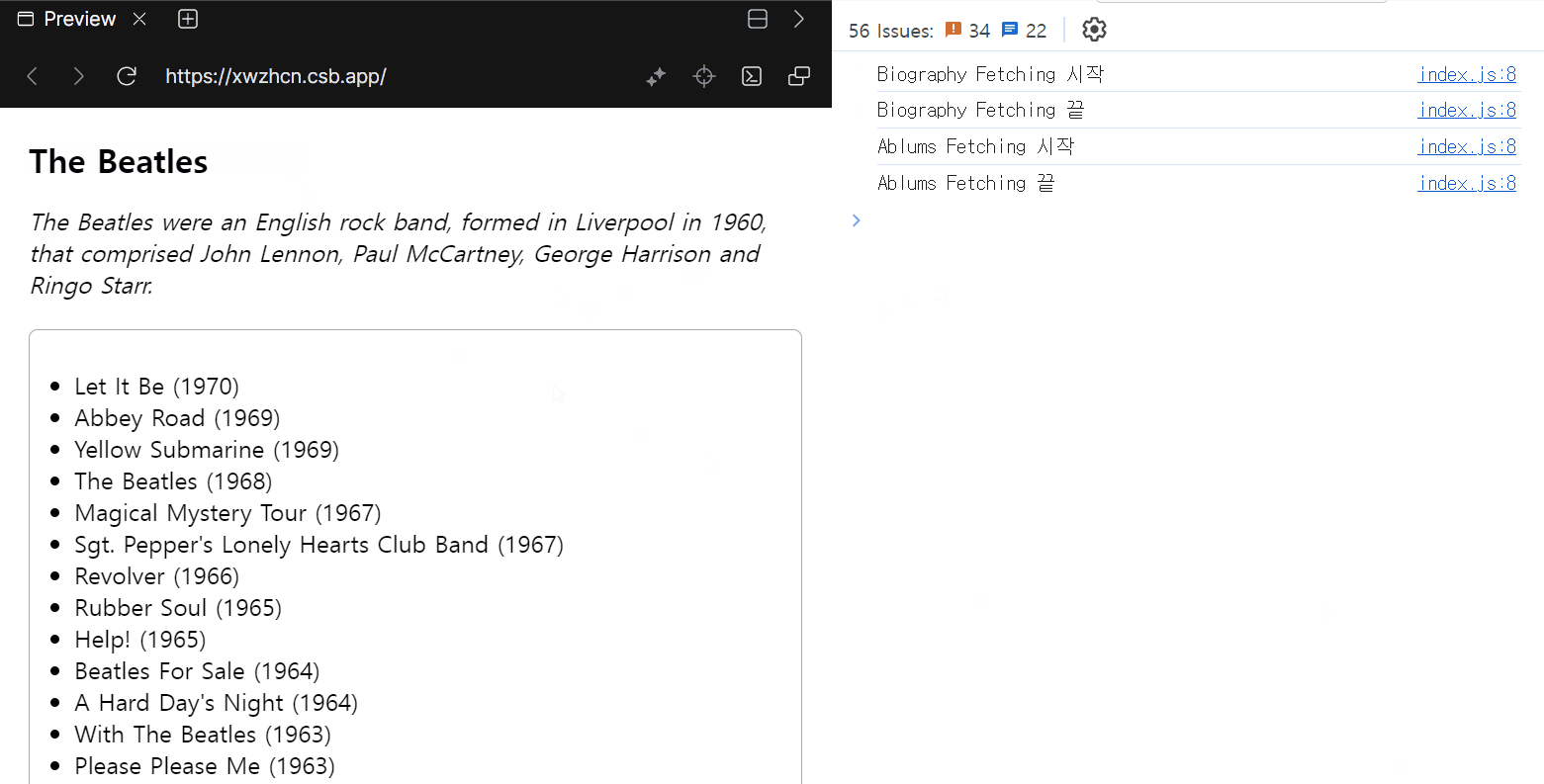
- 모든 요소가 로딩이 완료되어야 children이 렌더링 됩니다.
중첩 Suspense 사용 시
<Suspense fallback={<BigSpinner />}>
<Biography />
<Suspense fallback={<AlbumsGlimmer />}>
<Panel>
<Albums />
</Panel>
</Suspense>
</Suspense>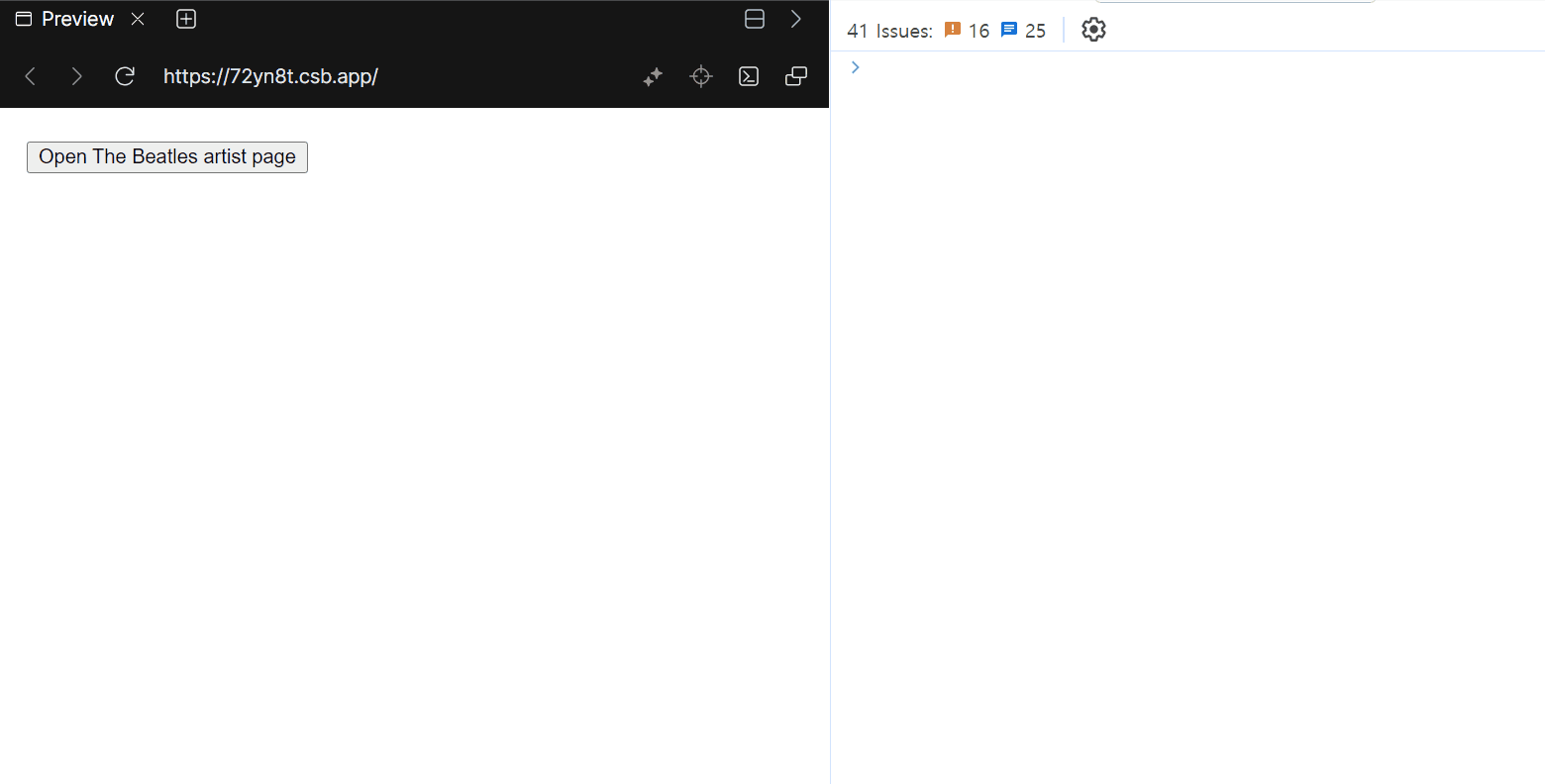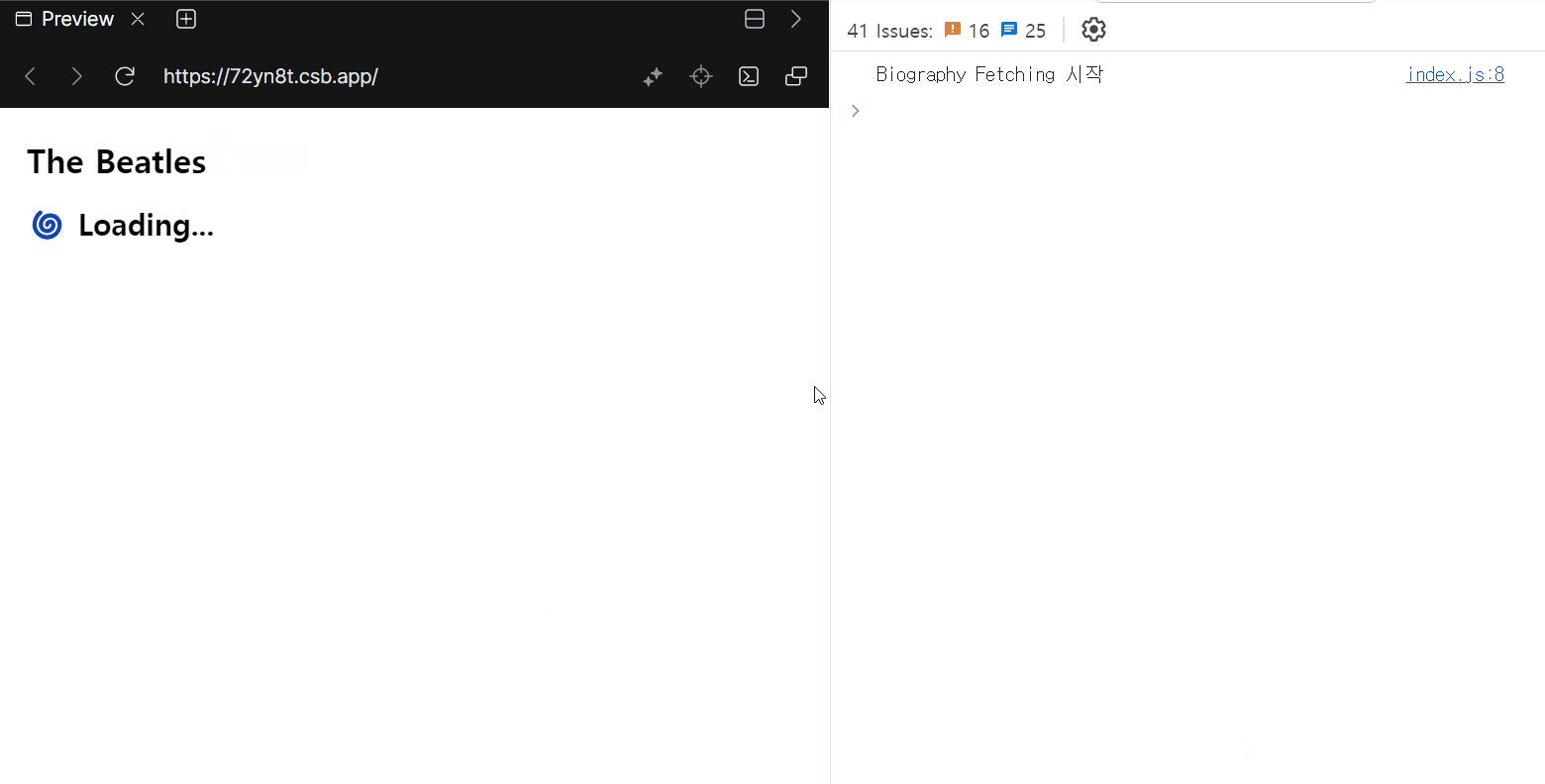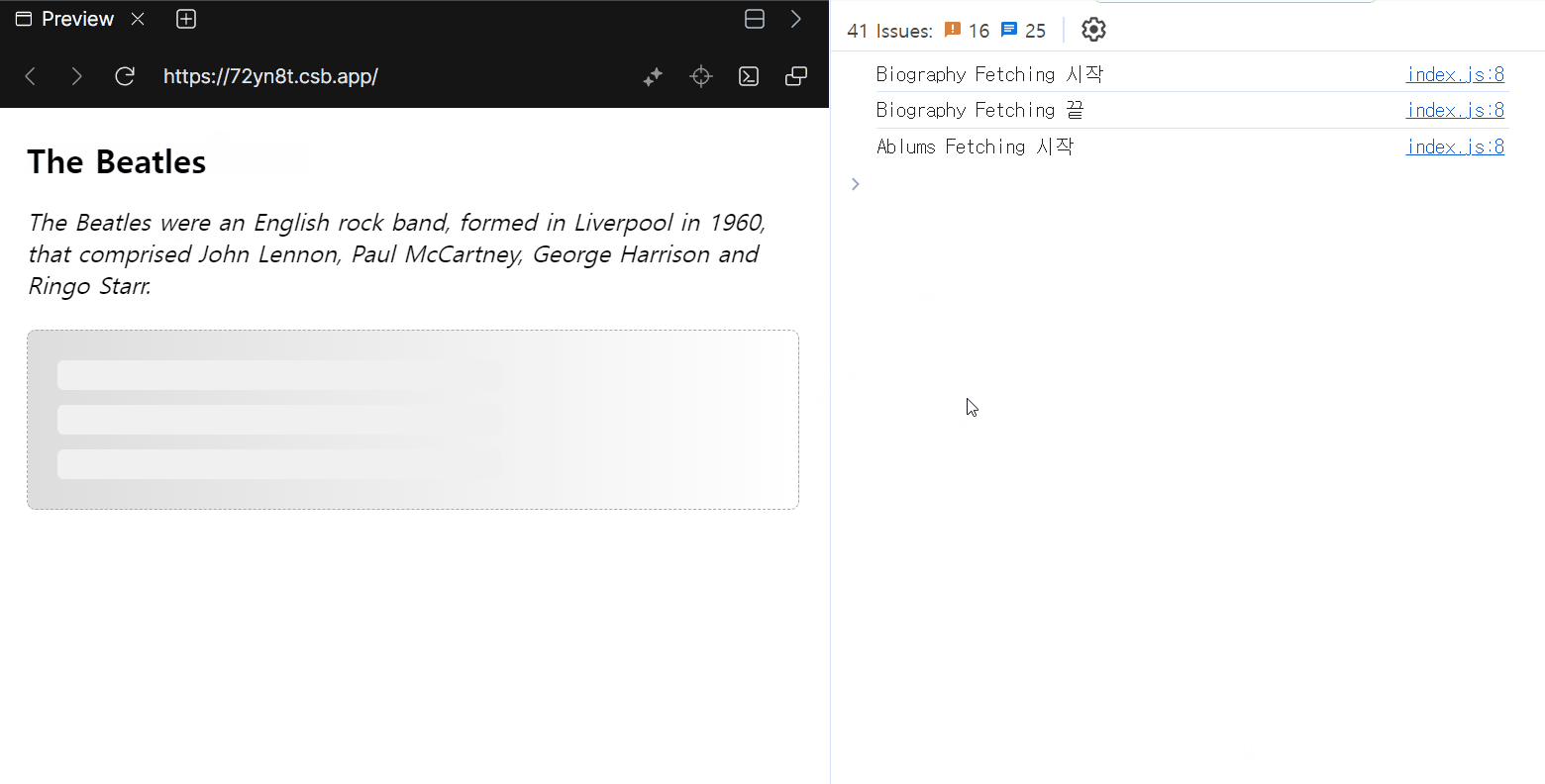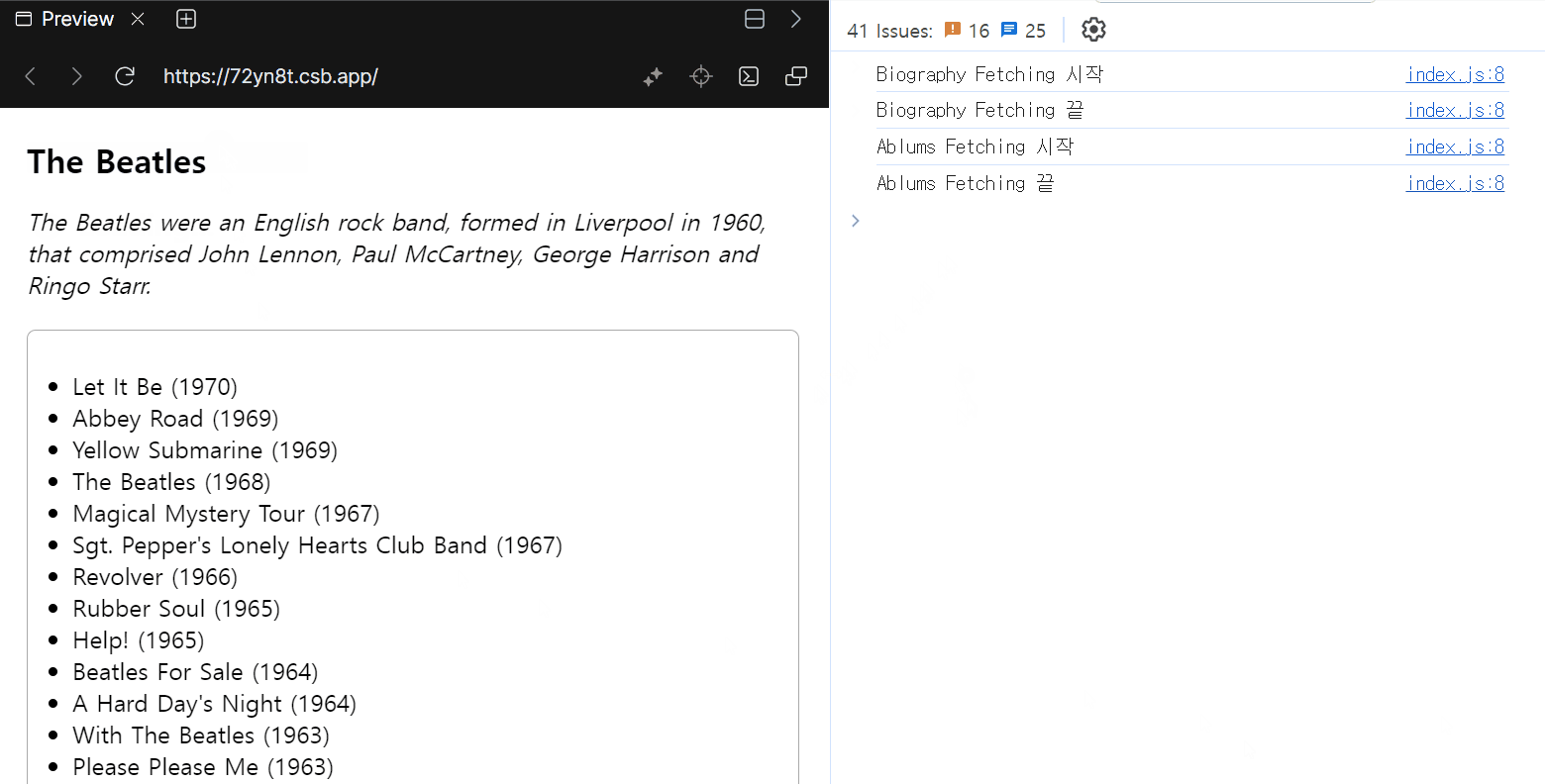
- Suspense를 감싼 요소가 하위 요소로 있는 경우 각 Suspend 상태는 독립적으로 동작합니다.
children을 한 번에 보여주느냐, 준비된 요소부터 바로 보여주느냐 차이는 있지만, Data Fetching은 여전히 순차적으로 이루어지는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
중첩된 Suspense를 먼저 렌더링 시
<Suspense fallback={<BigSpinner />}>
<h1>{artist.name}</h1>
<Suspense fallback={<AlbumsGlimmer />}>
<Panel>
<Albums artistId={artist.id} />
</Panel>
</Suspense>
<Biography artistId={artist.id} />
<Biography2 artistId={artist.id} />
</Suspense>- 임의로
Biography2컴포넌트를 추가했고, Albums는 3초, Biography는 1.5초, Biography2는 2.5초 소요되는 것으로 가정했습니다. - 중첩 Suspense를 가장 위에 배치하고, 하단 2개 컴포넌트는 Suspense로 감싸지 않았습니다.
결과는 어떨까요?
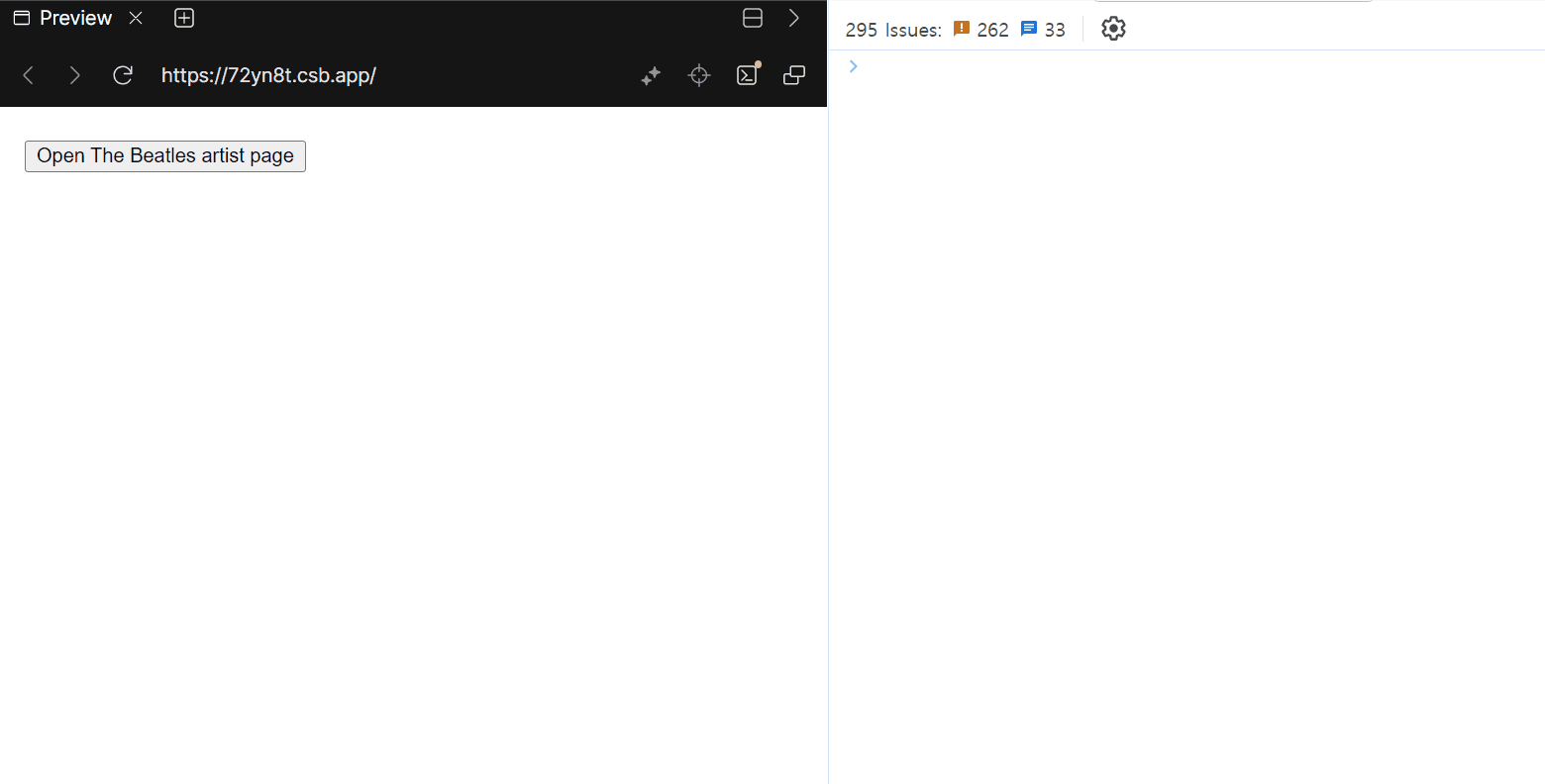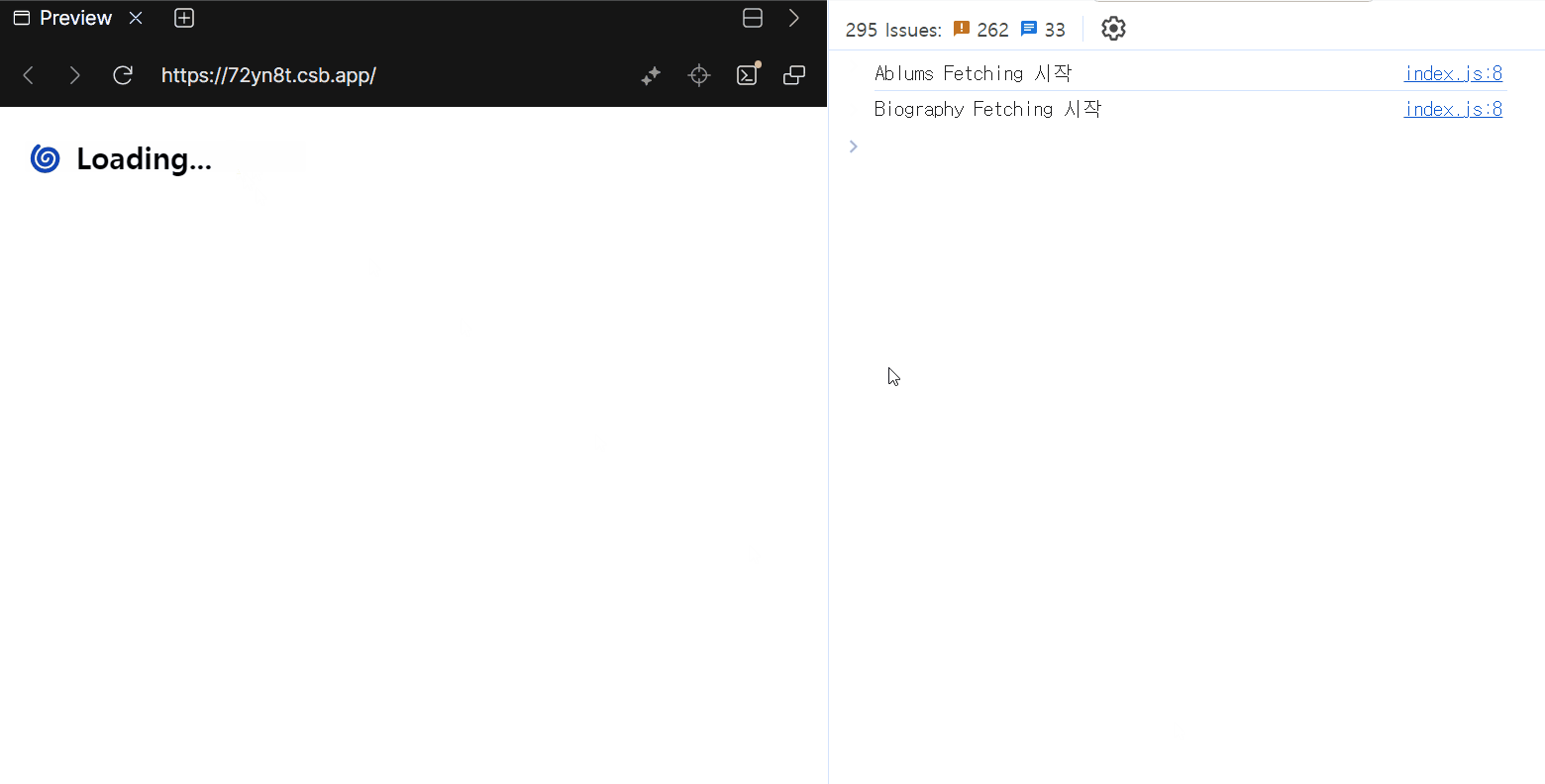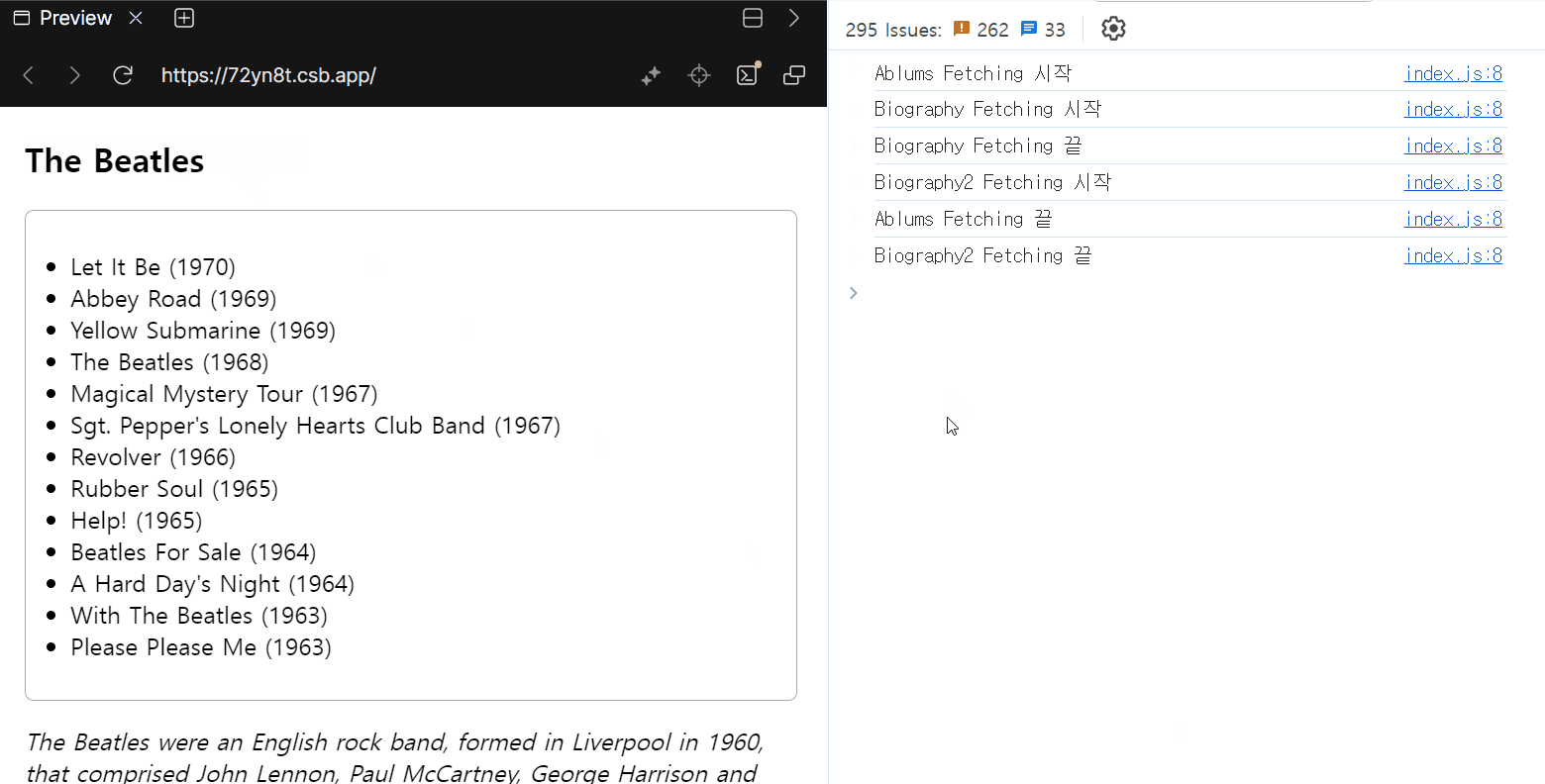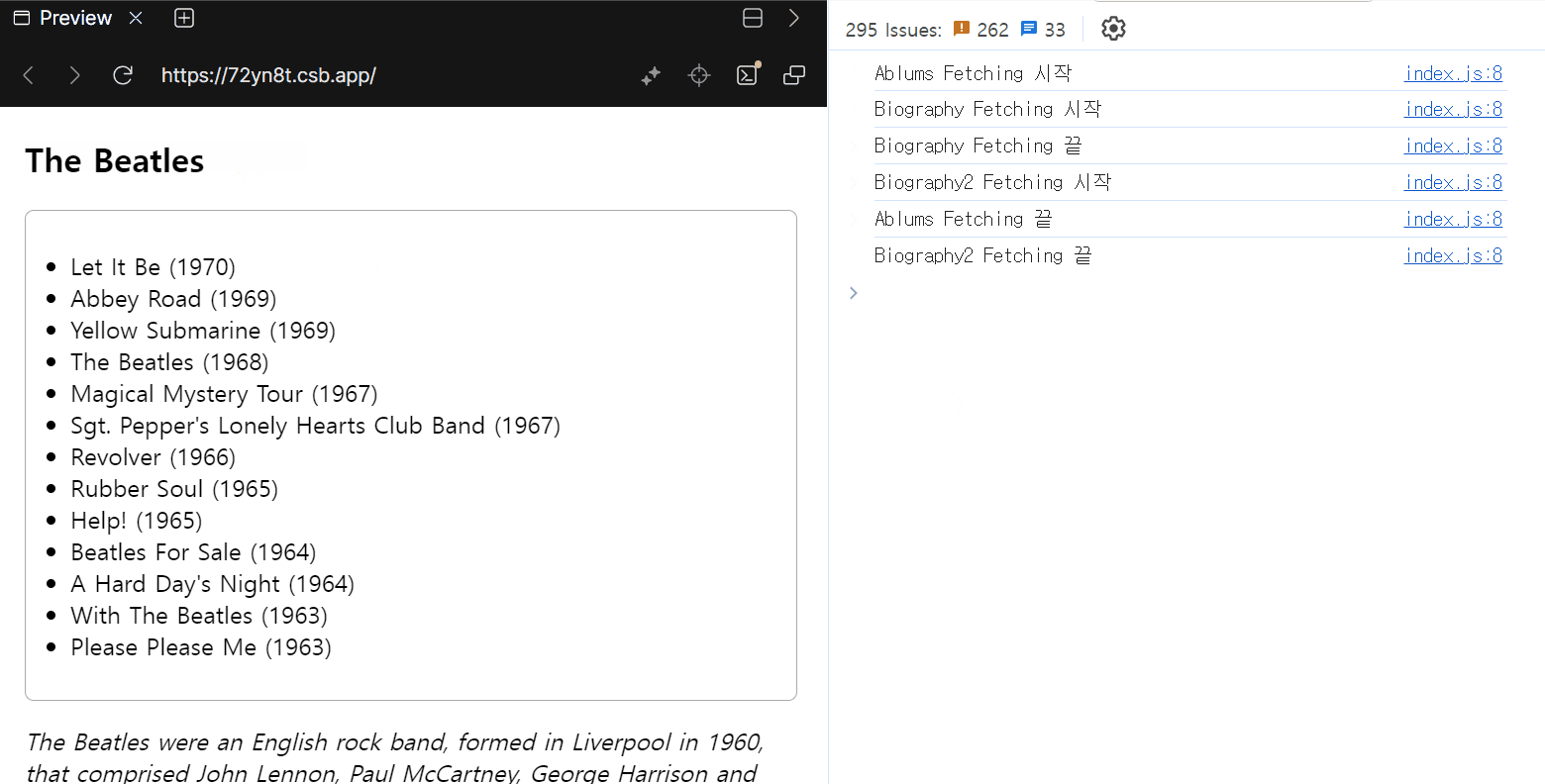
Albums와Biography는 동시에 로딩됩니다.Biography와Biography2는 순차 실행됩니다.Albums로딩이 완료되어도Biography2로딩이 끝나지 않아 화면에 표시되지 않습니다.
Albums와 Biography가 동시에 실행된 건 서로 다른 Suspense 경계에 있기 때문이고, Biography와 Biography2가 순차 실행된 건 같은 Suspense 경계 안에 있기 때문입니다.
Biography2는 Biography와 같은 Suspense 경계에 있어, Biography 로딩이 끝나고 데이터가 표시될 때까지 렌더링되지 않습니다.
각 컴포넌트에 Suspense 적용 시
그럼 각 컴포넌트를 별도 Suspense로 감싸면 어떻게 될까요?
export default function ArtistPage({ artist }) {
return (
<>
<h1>{artist.name}</h1>
<Suspense fallback={<BigSpinner />}>
<BiographyAndAlbums artist={artist} />
</Suspense>
</>
);
}
function BiographyAndAlbums({ artist }) {
return (
<>
<Suspense fallback={<BigSpinner />}>
<Biography artistId={artist.id} />
</Suspense>
<Suspense fallback={<AlbumsGlimmer />}>
<Panel>
<Albums artistId={artist.id} />
</Panel>
</Suspense>
<Suspense fallback={<BigSpinner />}>
<Biography2 artistId={artist.id} />
</Suspense>
</>
);
}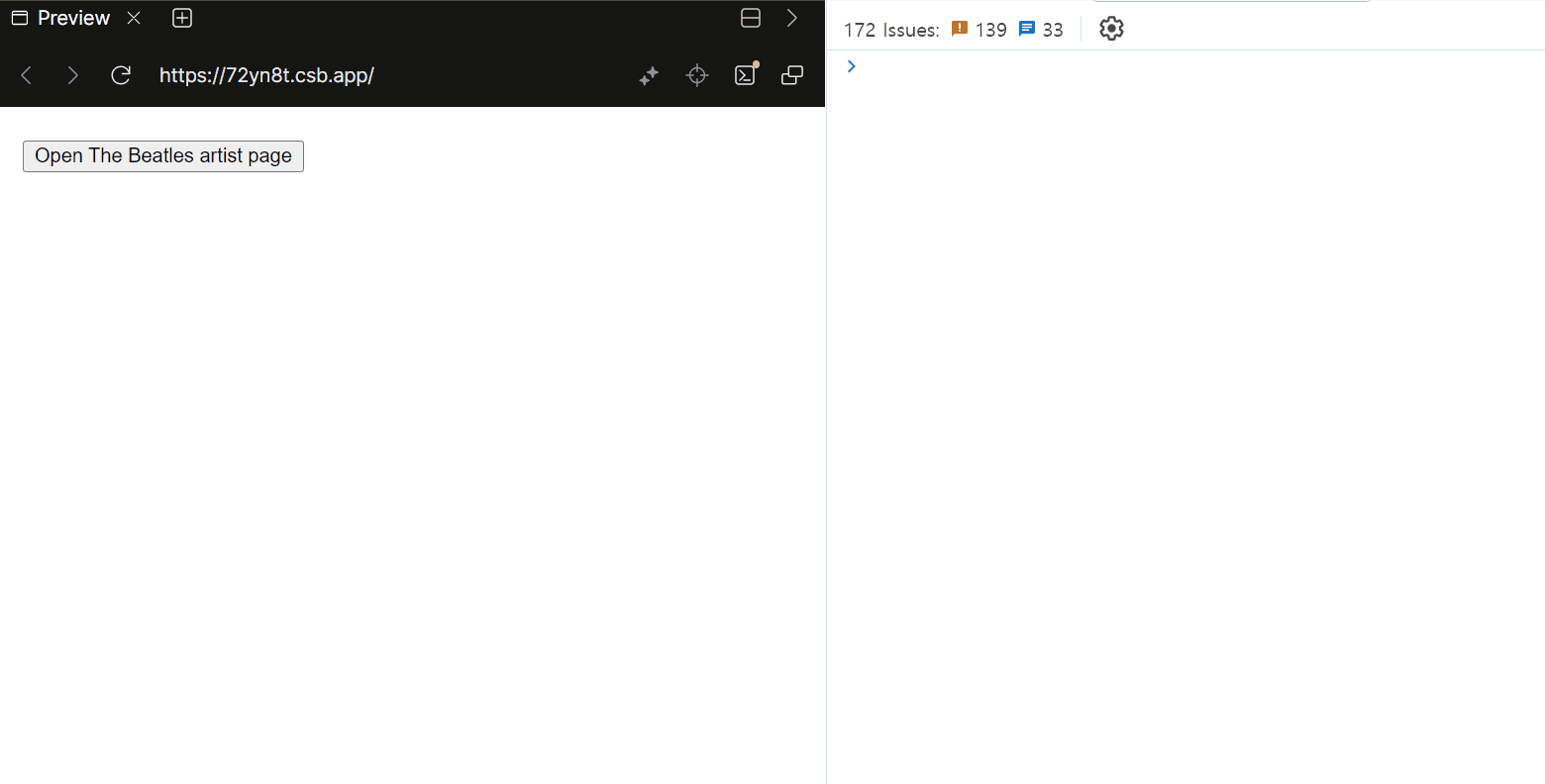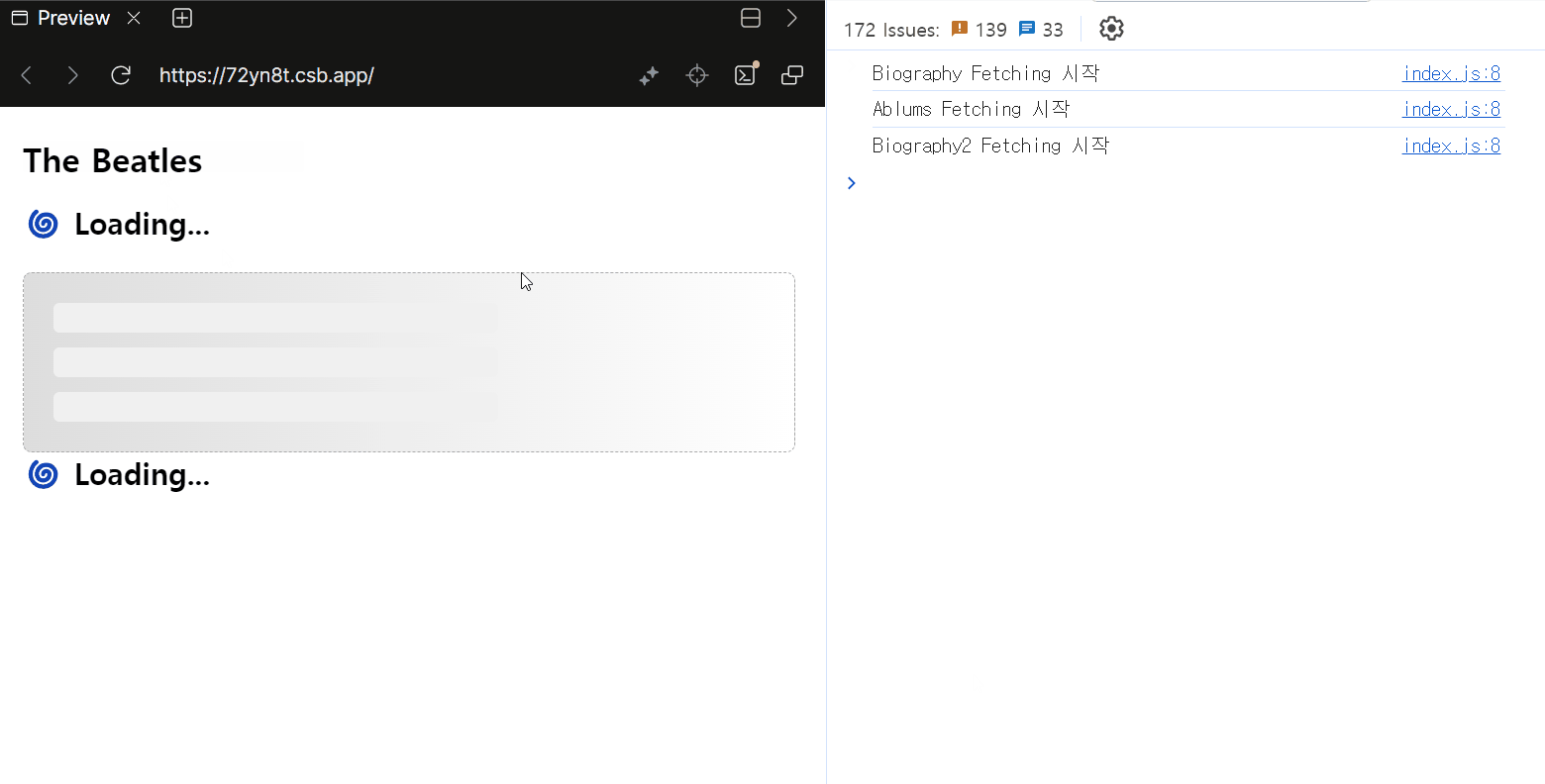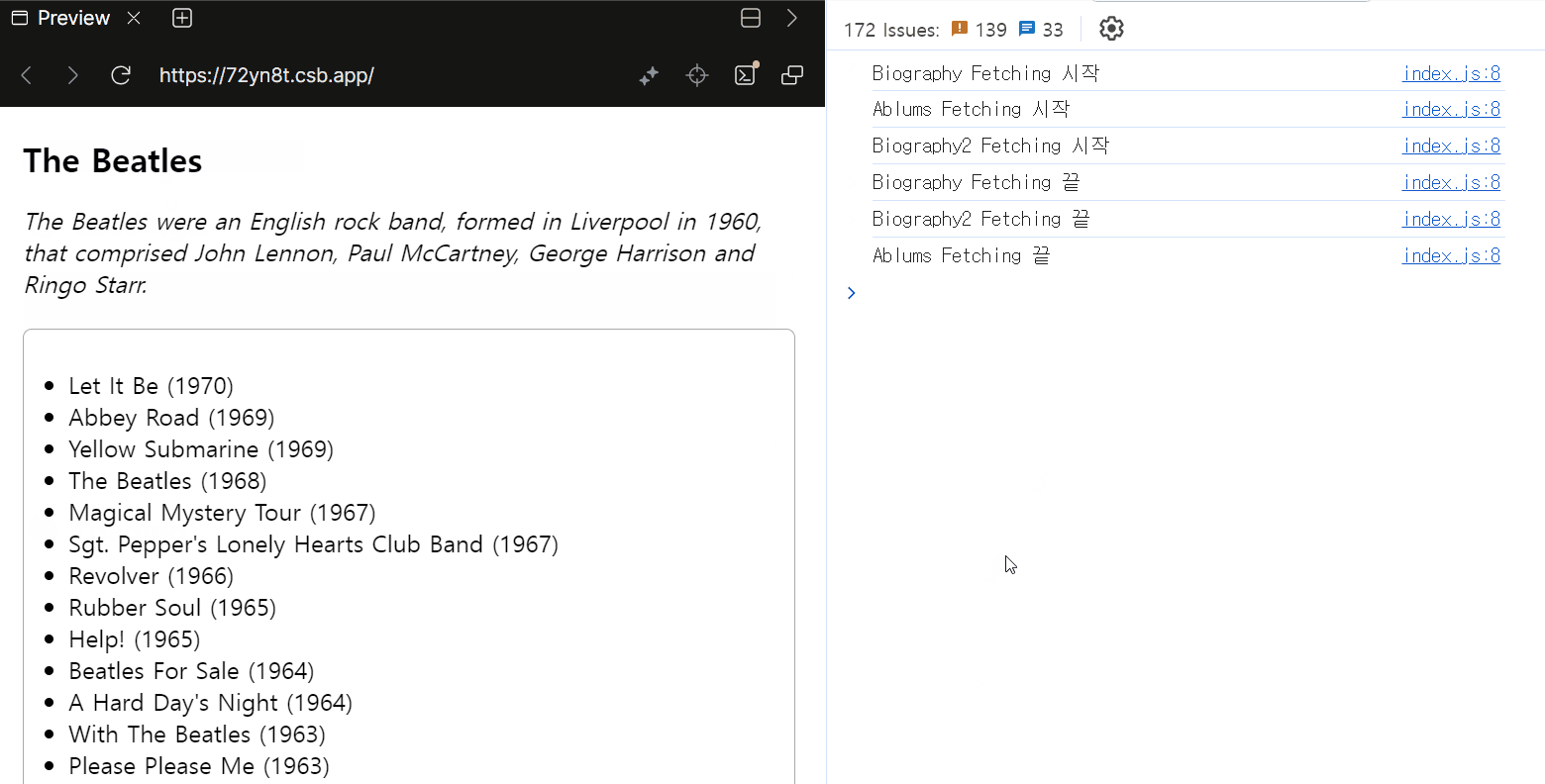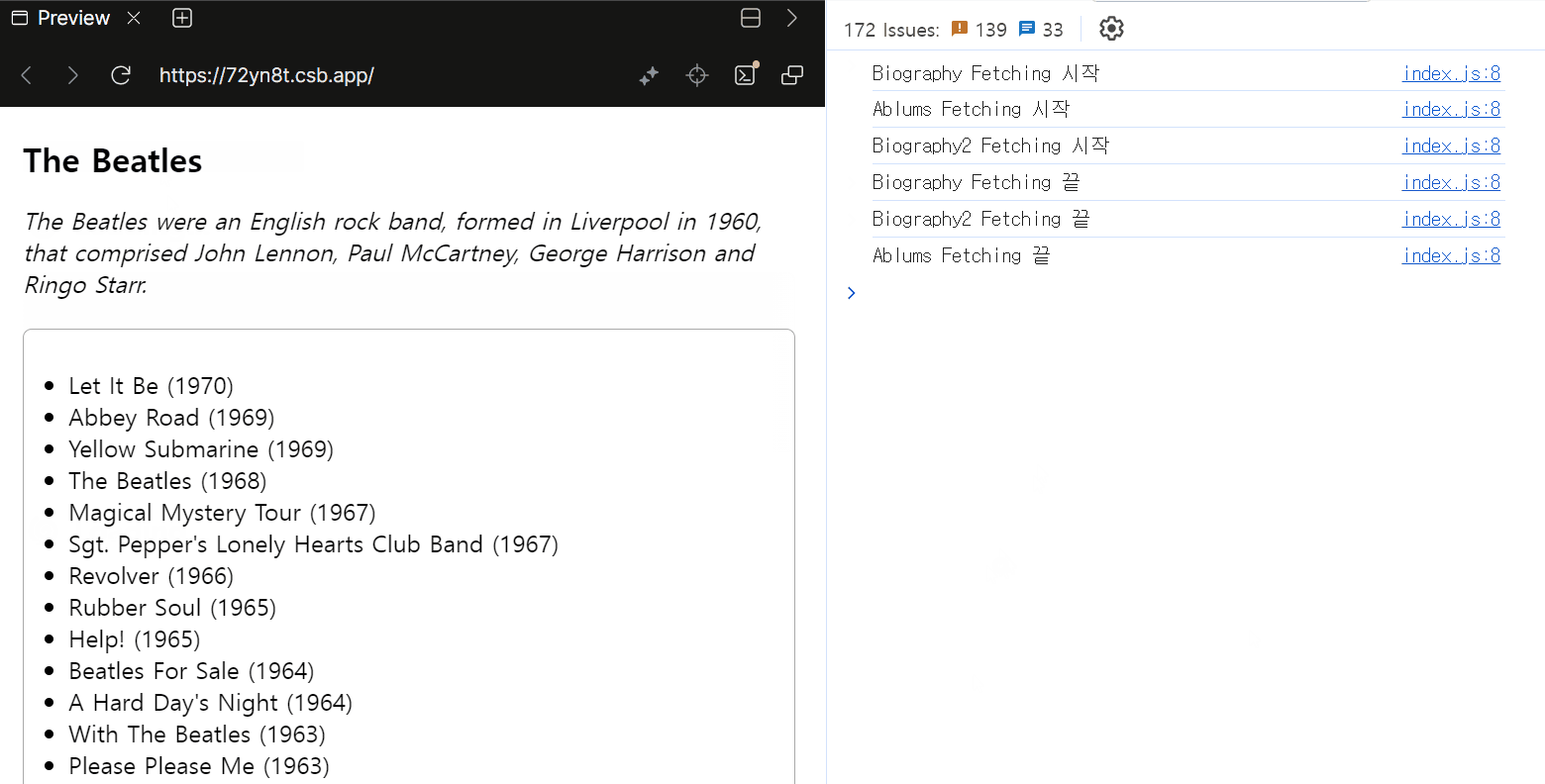
우선 가장 상위의 부모 역할 Suspense 경계의 fallback은 동작하지 않았습니다. 이는 컴포넌트가 Suspends되면 가장 가까운 상위 Suspense 컴포넌트의 fallback이 표시되기 때문인데, 위 경우 모든 컴포넌트가 Suspense 경계를 가지고 있으므로 가장 상위의 Suspense 컴포넌트의 fallback은 표시되지 않습니다.
결과적으로 각 요소들이 모두 동시에 로딩되는데요. 이 경우 각 컴포넌트가 각자의 Suspense 경계를 갖기 때문에 동시에 로딩되는 것으로 보입니다. 이에 따라 준비가 완료된 요소부터 개별적으로 렌더링 되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
Suspense 컴포넌트를 어떻게 쓰는지에 따라 결과가 조금씩 달라지는 것을 확인했는데요. 왜 이런 차이가 발생하는 것일까요?
Suspense 코드 뜯어보기
여기부터는 React 코드를 보면서 추론한 내용이며, 실제 동작과는 다를 수 있습니다.
React 16부터 Fiber Reconciler가 도입되었고, Fiber는 가상 DOM과 실제 DOM을 연결하는 데이터 구조를 갖습니다. Fiber는 React가 UI를 업데이트하는 데 필요한 정보를 담은 객체이며, Fiber Reconciler는 컴포넌트 변경 사항을 파악하고 DOM을 업데이트하는 역할을 합니다.
Fiber Reconciler가 컴포넌트의 변경 사항을 파악하고 DOM을 업데이트할 때 하나의 작업 단위(unitOfWork)를 기준으로 작업을 수행하며, 한 번에 하나의 Fiber를 처리합니다. 그리고 하나의 작업은 beginWork, completeWork 함수에 의해 처리됩니다.
beginWork는 unitOfWork를 기준으로 재귀적으로 호출하여 Fiber 트리를 순회하며 Fiber 노드를 생성하거나 업데이트하고, completeWork는 beginWork 이후에 호출되어 unitOfWork의 작업을 완료하는 역할을 합니다.
performUnitOfWork
function performUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): void {
// ...
const current = unitOfWork.alternate;
setCurrentDebugFiberInDEV(unitOfWork);
let next;
if (enableProfilerTimer && (unitOfWork.mode & ProfileMode) !== NoMode) {
startProfilerTimer(unitOfWork);
next = beginWork(current, unitOfWork, entangledRenderLanes);
stopProfilerTimerIfRunningAndRecordDelta(unitOfWork, true);
} else {
next = beginWork(current, unitOfWork, entangledRenderLanes);
}
resetCurrentDebugFiberInDEV();
unitOfWork.memoizedProps = unitOfWork.pendingProps;
if (next === null) {
// If this doesn't spawn new work, complete the current work.
completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork);
} else {
workInProgress = next;
}
ReactCurrentOwner.current = null;
}
performUnitOfWork 함수는 주어진 unitOfWork를 처리합니다.
startProfilerTimer / setCurrentDebugFiberInDEV 같은 함수들이 있지만, 핵심은 beginWork 함수를 호출하고, beginWork 함수의 결과에 따라 다음 작업 단위를 결정하는 것입니다.
beginWork
function beginWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
if (__DEV__) {
// ...
}
if (current !== null) {
const oldProps = current.memoizedProps;
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
if (
oldProps !== newProps ||
hasLegacyContextChanged() ||
// ...
) {
// ...
} else {
// ...
}
// ...
workInProgress.lanes = NoLanes;
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent: { ... }
case LazyComponent: { ... }
case FunctionComponent: { ... }
case ClassComponent: { ... }
// ...
case SuspenseComponent:
return updateSuspenseComponent(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
// ...
}
throw new Error(
`Unknown unit of work tag (${workInProgress.tag}). This error is likely caused by a bug in ` +
'React. Please file an issue.',
);
}current Fiber Node가 null이 아닌 경우 이미 마운트된 상태인 경우를 처리합니다.
- 그 경우 이전 props와 새로운 props를 비교하거나 Context가 변경되었는지 확인하고, 변경이 이루어졌다면 컴포넌트가 업데이트 되어야 함을 표시합니다.
이후 Fiber Node의 tag 값에 따라 다양한 컴포넌트 타입을 처리하고, SuspenseComponent의 경우 updateSuspenseComponent 함수를 호출합니다.
updateSuspenseComponent
function updateSuspenseComponent(
current: null | Fiber,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes,
) {
const nextProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
// ...
let showFallback = false;
const didSuspend = (workInProgress.flags & DidCapture) !== NoFlags;
if (
didSuspend ||
shouldRemainOnFallback(current, workInProgress, renderLanes)
) {
// ...
showFallback = true;
}
// ...
if (current === null) {
// Initial mount
// ...
const nextPrimaryChildren = nextProps.children;
const nextFallbackChildren = nextProps.fallback;
if (showFallback) {
pushFallbackTreeSuspenseHandler(workInProgress);
const fallbackFragment = mountSuspenseFallbackChildren(
workInProgress,
nextPrimaryChildren,
nextFallbackChildren,
renderLanes,
);
// ...
return fallbackFragment;
} else if ( ... ) {
} else {
pushPrimaryTreeSuspenseHandler(workInProgress);
return mountSuspensePrimaryChildren(
workInProgress,
nextPrimaryChildren,
renderLanes,
);
}
} else {
// This is an update.
// ...
}
}updateSuspenseComponent는 beginWork에서 Fiber Node의 tag가 SuspenseComponent일 때 컴포넌트를 처리합니다.
showFallback을 false로 둔 뒤 조건에 따라 true로 변경하면서 fallback 컴포넌트 표시 여부를 결정합니다.
nextPrimaryChildren은 주 컴포넌트를, nextFallbackChildren은 fallback 컴포넌트를 나타내는데,
showFallback이 true이면
pushFallbackTreeSuspenseHandler함수를 호출하여 fallback 트리를 처리mountSuspenseFallbackChildren함수를 호출하여 fallback 컴포넌트를 마운트
showFallback이 false이면
pushPrimaryTreeSuspenseHandler함수를 호출하여 주 컴포넌트 트리를 처리mountSuspensePrimaryChildren함수를 호출하여 주 컴포넌트를 마운트
처리 됩니다.
그럼 언제 showFallback이 true가 될까요?
언제 showFallback이 true가 될까
let showFallback = false;
const didSuspend = (workInProgress.flags & DidCapture) !== NoFlags;
if (
didSuspend ||
shouldRemainOnFallback(current, workInProgress, renderLanes)
) {
// Something in this boundary's subtree already suspended. Switch to
// rendering the fallback children.
showFallback = true;
workInProgress.flags &= ~DidCapture;
}didSuspend: 현재 컴포넌트가 suspend 상태인지 확인합니다.workInProgress.flags & DidCapture가NoFlags와 다르다는 건workInProgress.flags에DidCapture플래그가 설정되어 있다는 의미로, 이는 컴포넌트가 suspend 상태임을 나타냅니다.
shouldRemainOnFallback: 현재 컴포넌트가 fallback UI를 계속 보여줘야 하는지 결정합니다. 이미 fallback을 보여주고 있다면 fallback 상태를 유지해야 할 수 있습니다.
현재 작업 중인 workInProgress Fiber의 flags에 DidCapture가 설정되어 있으면 fallback UI를 보여주게 됩니다.
그럼 DidCapture Flag는 언제 설정될까요?
언제 DidCapture Flag가 설정될까
markSuspenseBoundaryShouldCapture
function markSuspenseBoundaryShouldCapture(
suspenseBoundary: Fiber,
returnFiber: Fiber,
sourceFiber: Fiber,
root: FiberRoot,
rootRenderLanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
// ...
if ((suspenseBoundary.mode & ConcurrentMode) === NoMode) {
// Legacy Mode일 때
if (suspenseBoundary === returnFiber) {
suspenseBoundary.flags |= ShouldCapture;
} else {
suspenseBoundary.flags |= DidCapture;
sourceFiber.flags |= ForceUpdateForLegacySuspense;
// ...
return suspenseBoundary;
}
}
// Concurrent Mode일 때
suspenseBoundary.flags |= ShouldCapture;
suspenseBoundary.lanes = rootRenderLanes;
return suspenseBoundary;
}이 함수는 Suspense 경계(boundary)가 일시 중단된 예외를 캡처해야 하는지 판단합니다. Legacy Mode와 Concurrent Mode에서 다르게 동작하는데요.
- Legacy Mode:
ReactDom.render를 통해 React App을 구성한다면 Legacy Mode입니다.- 렌더링과 업데이트가 동기적으로 처리
- 렌더링이 끝날 때까지 인터랙션이 제한됨
- Concurrent Mode:
ReactDOM.createRoot를 통해 React App을 구성한다면 Concurrent Mode입니다.- 렌더링과 업데이트가 비동기적으로 처리
- 렌더링 작업을 작은 단위로 쪼개어 처리하고, 우선순위에 따라 작업을 중단하고 재개할 수 있음
결국 markSuspenseBoundaryShouldCapture 함수는 조건에 따라 DidCapture 또는 ShouldCapture flag를 설정하고, Suspense 경계 Fiber를 반환합니다.
beginWork()에서 SuspenseComponent일 때 workInProgress Fiber의 flag가 DidCapture인 경우 fallback을 보여주기로 했습니다. 그 조건에 ShouldCapture flag는 사용되지 않았는데요.
Concurrent Mode일 때는 DidCapture 대신 ShouldCapture flag만 설정하고 있습니다. 코드를 더 살펴보겠지만, 이는 ShouldCapture flag가 활성화 되어 있을 때 어딘가에서 DidCapture flag를 활성화 시켜줄 것으로 추정됩니다.
renderRootConcurrent
function renderRootConcurrent(root: FiberRoot, lanes: Lanes) {
// ...
outer: do {
try {
if (
workInProgressSuspendedReason !== NotSuspended &&
workInProgress !== null
) {
// ...
const unitOfWork = workInProgress;
const thrownValue = workInProgressThrownValue;
resumeOrUnwind: switch (workInProgressSuspendedReason) {
case SuspendedOnError: { ... }
case SuspendedOnData: {
const thenable: Thenable<mixed> = (thrownValue: any);
if (isThenableResolved(thenable)) {
workInProgressSuspendedReason = NotSuspended;
workInProgressThrownValue = null;
replaySuspendedUnitOfWork(unitOfWork);
break;
}
// ...
const onResolution = () => {
if (
workInProgressSuspendedReason === SuspendedOnData &&
workInProgressRoot === root
) {
// Mark the root as ready to continue rendering.
workInProgressSuspendedReason = SuspendedAndReadyToContinue;
}
ensureRootIsScheduled(root);
};
thenable.then(onResolution, onResolution);
break outer;
}
case SuspendedOnImmediate: { ... }
case SuspendedOnInstance: { ... }
case SuspendedAndReadyToContinue: { ... }
// ...
}
if (__DEV__ && ReactCurrentActQueue.current !== null) {
// ...
} else {
workLoopConcurrent();
}
break;
} catch (thrownValue) {
handleThrow(root, thrownValue);
}
} while (true);
// ...
}renderRootConcurrent 함수는 Concurrent Mode에서 루트를 렌더링하는 역할을 수행합니다.
SuspendedOnData: 작업 단위가 데이터를 기다리는 동안 일시 중단된 경우입니다. 데이터가 해결되면 작업 단위를 재생(replay)하고, 그렇지 않으면 작업 루프가 데이터가 해결될 때까지 기다립니다.SuspendedAndReadyToContinue: 데이터가 해결되면 작업 단위를 재생하고, 그렇지 않으면 작업 단위를 풀어내고 일반 작업 루프로 돌아갑니다.
switch 문 조건 중 SuspendedOnData 부분에선 작업 단위가 데이터를 기다리는 동안 일시 중단된 경우를 처리합니다. thenable.then(onResolution, onResolution); 부분에서 onResolution 콜백이 전달되는데, 이 콜백은 데이터가 준비되었을 때 호출됩니다.
thenable.then 에서 호출된 onResolution 콜백에선 workInProgressSuspendedReason값을 SuspendedAndReadyToContinue로 설정하며, 데이터가 준비되었으므로 작업을 계속할 준비가 되었음을 나타냅니다.
이렇게 되면 다음 렌더링 주기에 작업 루프가 재개되면서 SuspendedAndReadyToContinue case로 실행되며, 아래 로직들이 실행됩니다.
case SuspendedAndReadyToContinue: {
const thenable: Thenable<mixed> = (thrownValue: any);
if (isThenableResolved(thenable)) {
// The data resolved. Try rendering the component again.
workInProgressSuspendedReason = NotSuspended;
workInProgressThrownValue = null;
replaySuspendedUnitOfWork(unitOfWork);
} else {
// Otherwise, unwind then continue with the normal work loop.
workInProgressSuspendedReason = NotSuspended;
workInProgressThrownValue = null;
throwAndUnwindWorkLoop(unitOfWork, thrownValue);
}
break;
}주석의 설명에 따라 데이터가 준비된 경우라면 replaySuspendedUnitOfWork 함수를 호출하여 중단된 작업을 다시 시도하여 렌더링을 재개하고, 데이터가 준비되지 않은 경우라면 throwAndUnwindWorkLoop 함수를 호출하여 스택을 풀어내고(unwind) 정상적인 작업 루프로 돌아갑니다.
데이터가 아직 준비되지 않아 fallback을 보여줘야되는 경우는 else 문에 해당합니다. 그리고 이 throwAndUnwindWorkLoop 함수에서 조건에 따라 예외를 처리하고 스택을 풀어내는 과정에서 ShouldCapture flag가 설정되어 있을 때 이를 DidCapture로 변경하는 작업이 이루어집니다.
throwAndunwindWorkLoop
function throwAndUnwindWorkLoop(unitOfWork: Fiber, thrownValue: mixed) {
// ...
try {
// Find and mark the nearest Suspense or error boundary that can handle
// this "exception".
throwException(
workInProgressRoot,
returnFiber,
unitOfWork,
thrownValue,
workInProgressRootRenderLanes,
);
} catch (error) {
workInProgress = returnFiber;
throw error;
}
if (unitOfWork.flags & Incomplete) {
unwindUnitOfWork(unitOfWork); // 아직 완료되지 않은 Fiber에 대해 여기서 unwindUnitOfWork 호출
} else {
completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork);
}
}function unwindUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): void {
let incompleteWork: Fiber = unitOfWork;
do {
// ...
const next = unwindWork(current, incompleteWork, entangledRenderLanes);
// ...
} while (incompleteWork !== null);
// ...
}function unwindWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
// ...
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case ClassComponent: { ... }
case HostRoot: { ... }
case HostHoistable
case HostSingleton:
case HostComponent: { ... }
case SuspenseComponent: {
// ...
const flags = workInProgress.flags;
if (flags & ShouldCapture) { // flag에 ShouldCapture가 설정되어 있으면
workInProgress.flags = (flags & ~ShouldCapture) | DidCapture; // ShouldCapture flag를 제거하고, DidCapture flag를 설정합니다.
// Captured a suspense effect. Re-render the boundary.
if (
enableProfilerTimer &&
(workInProgress.mode & ProfileMode) !== NoMode
) {
transferActualDuration(workInProgress);
}
return workInProgress;
}
return null;
}
// ...
default:
return null;
}
}renderRootConcurrent함수에서 호출된 throwAndUnwindWorkLoop 함수 내부에서 unwindUnitOfWork → unwindWork 함수가 호출되는데요. unwindWork 함수에서 ShouldCapture flag가 설정되어 있는 경우 ShouldCapture flag를 제거하고 DidCapture flag를 설정하게 됩니다.
이런 과정에 의해 beginWork() 함수에서 호출된 updateSuspenseComponent() 함수에서 flag의 DidCapture 활성화 여부를 확인하여 showFallback 값을 true로 설정한 다음 fallback을 보여주는 것이죠.
지금까지 정리
지금까지의 흐름을 정리하자면
renderRootConcurrent함수를 호출하여 Concurrent 렌더링을 수행- do while 문 내부에서 reason 값이
SuspendedOnData인 경우 액션을 수행한 다음onResolution함수에 의해 값을SuspendedAndReadyToContinue로 변경 - 다음 렌더링 주기에
renderRootConcurrent함수에 의해 다시 do while 문 작업을 수행하고, 이번엔SuspendedAndReadyToContinuecase로 동작 - 만약 데이터가 준비되지 않았을 경우
throwAndUnwindWorkLoop함수를 호출 throwAndUnwindWorkLoop함수에서throwException함수를 통해 가장 가까운Suspense또는ErrorBoundary를 찾고, 예외를 처리throwException내부에서markSuspenseBoundaryShouldCapture함수를 호출하고, 조건에 따라ShouldCapture|DidCaptureflag를 설정- 이후 완료되지 않은 작업이 있다면
unwindUnitOfWork함수를 호출하여 완료되지 않았거나 오류가 발생된 Fiber에 대해 상태를 업데이트하거나 예외 처리를 수행 - 그 과정에서
unwindWork함수를 호출하고, 여기서ShouldCaptureflag가 설정되어 있는 Fiber라면DidCaptureflag로 설정 Fiber트리를 순회하면서Fiber Node를 생성 또는 업데이트 할 때performUnitOfWork함수 호출,beginWork함수 호출이 이루어지며 여기서Fiber Node의 tag값이SuspenseComponent인 경우 fallback UI를 표시할지 children을 표시할지 결정됩니다.- 그 때 Fiber의 flag의
DidCapture가 설정되어 있다면 fallback UI를 보여줌
Suspense가 순차적으로 실행되는 이유
어느 흐름으로 fallback 또는 children을 보여주는지 알게 되었습니다. 그러면, 조건에 따라 Suspense가 동작할 수 있는 컴포넌트들을 Suspense 컴포넌트로 감싸면 왜 순차적으로 호출되는지도 알아보겠습니다.
일련의 과정에 의해 unwindUnitOfWork 함수가 호출되는데, 이 함수는 Fiber 작업 단위를 처리하는 데 사용되는 함수로 throwAndUnwindWorkLoop 내부에서 호출됩니다.
function unwindUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): void {
let incompleteWork: Fiber = unitOfWork;
do {
const current = incompleteWork.alternate;
const next = unwindWork(current, incompleteWork, entangledRenderLanes);
if (next !== null) {
next.flags &= HostEffectMask;
workInProgress = next;
return;
}
// ...
} while (incompleteWork !== null);
workInProgressRootExitStatus = RootDidNotComplete;
workInProgress = null;
}do while 문에서 next 변수에 unwindWork 반환된 값을 저장하고 있습니다. 이 값이 null이 아닌 경우 해당 Fiber에 HostEffectMask flag를 설정하고 return 하여 함수를 종료합니다. unwindWork 함수의 반환값은 다음과 같은데요.
function unwindWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
// ...
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case ClassComponent: { ... }
case HostRoot: { ... }
case HostHoistable
case HostSingleton:
case HostComponent: { ... }
case SuspenseComponent: {
// ...
const flags = workInProgress.flags;
if (flags & ShouldCapture) {
workInProgress.flags = (flags & ~ShouldCapture) | DidCapture;
// Captured a suspense effect. Re-render the boundary.
if (
enableProfilerTimer &&
(workInProgress.mode & ProfileMode) !== NoMode
) {
transferActualDuration(workInProgress);
}
return workInProgress;
}
return null;
}
// ...
default:
return null;
}
}작업이 진행 중인 Fiber의 tag가 SuspenseComponent일 때, flag에 ShouldCapture가 활성화 되어 있다면 그 flag에 ShouldCapture를 제거하고 DidCapture를 활성화 하면서 해당 Fiber를 반환합니다.
결국, ShouldCapture flag가 활성화 되어 있으면 unwindUnitOfWork함수에서의 Fiber tree를 순회하면서 작업하던 do while 문을 멈추고 return 하면서 작업을 중지하는 것인데요.
Suspense 컴포넌트로 조건에 해당하는 하위 컴포넌트를 감싸고 있고, Data를 로딩중인 경우 하위 컴포넌트의 Fiber Node를 생성, 업데이트 하는 과정에서 flag가 ShouldCapture로 설정되고, 이후 수행되는 unwindUnitOfWork 함수가 return 되면서 다음 작업이 진행되지 않기에 순차적으로 Data fetching이 이루어지는 것처럼 보이게 됩니다.
다시 확인해보는 Suspense 동작
Suspense를 1개만 쓸 때
<Suspense fallback={<Loading />}>
<Biography />
<Panel>
<Albums />
</Panel>
</Suspense>
Biography의Fiber Node생성을 시도할 때 Data가 준비되지 않았다면ShouldCaptureflag가 활성화되면서 이후의 작업은 이루어지지 않습니다.ShouldCaptureflag에 의해 해당 flag는 제거되고DidCaptureflag가 활성화 되면서 Fiber tree를 순회하며Fiber Node의 생성/업데이트 처리를 실행하던 함수가 중단됩니다.- data의 준비가 완료되면
Fiber Node의 업데이트를 시도하게 되고, 그 과정에선 do while 문을 멈추지 않고 다음Fiber Node로 넘어갑니다. - 다음
AlbumsFiber Node를 생성하면서 해당 컴포넌트의 Data fetching을 시도합니다. - 2번 과정을 반복하면서 이후
Fiber Node에 대한 생성/업데이트는 이루어지지 않습니다. Albums의 Data가 준비되었다면Fiber Node를 업데이트 하면서 렌더링이 진행 됩니다.
위의 흐름으로 진행되니 Biography 컴포넌트가 준비되지 않은 상태라면 Albums의 작업을 진행하지 않기에 초기 렌더링 시에는 Albums의 Data fetching이 이루어지지 않습니다.
각 요소에 Suspense를 감싸서 사용하는 경우
export default function ArtistPage({ artist }) {
return (
<>
<h1>{artist.name}</h1>
<Suspense fallback={<BigSpinner />}>
<BiographyAndAlbums artist={artist} />
</Suspense>
</>
);
}
function BiographyAndAlbums({ artist }) {
return (
<>
<Suspense fallback={<BigSpinner />}>
<Biography artistId={artist.id} />
</Suspense>
<Suspense fallback={<AlbumsGlimmer />}>
<Panel>
<Albums artistId={artist.id} />
</Panel>
</Suspense>
<Suspense fallback={<BigSpinner />}>
<Biography2 artistId={artist.id} />
</Suspense>
</>
);
}
이 경우엔 동시에 처리되는 것처럼 동작하는 것을 확인했었죠. Suspense 컴포넌트로 각 요소를 감싸면 각각의 컴포넌트가 개별 Suspense Boundary를 갖게 됩니다.
이에 따라 각자 독립적으로 Data fetching을 시도하고 준비가 완료되는대로 개별적으로 렌더링됩니다.
최상단에 Suspense 컴포넌트로 하위 요소들을 감싸고 있긴 하지만, 하위 요소에서 발생하는 Suspend 상태는 가장 가까운 Suspense 경계를 찾으므로 개별적으로 동작하게 됩니다.
정리
Suspense를 사용할 수 있는 경우
- Relay 및 Next.js와 같은 Suspense 도입 프레임워크를 사용한 데이터 페칭
- lazy를 사용한 지연 로딩 컴포넌트 코드
- use 함수를 통해 읽는 Promise Value
Suspense를 사용할 수 없는 경우
- Effect 에서의 Data Fetching
- Event Handler 에서의 Data Fetching
Suspense를 사용할 수 있는 여러 개의 컴포넌트를 하나의 Suspense 컴포넌트로 감싸는 경우
- 일련의 과정으로
Fiber Node생성/업데이트를 시도 - 만약 데이터가 준비되지 않았다면 이어서 작업을 하는 것이 아니라 작업 종료
- 이에 따라 모든 컴포넌트가 순차적으로 실행됨
Suspense를 사용할 수 있는 여러 개의 컴포넌트를 각각 Suspense 컴포넌트로 감싸는 경우
- 이에 해당하는 모든 Suspense는 독립적인 Suspense 경계를 가짐
- 병렬적으로 실행되는 것처럼 동작하며 준비가 완료되는 컴포넌트부터 개별적으로 렌더링
위의 흐름에 따라 Suspense가 사용됩니다. 잡다 코드에는 Suspense를 사용하고 있지 않은데, 기획 요구사항에 따라 한 페이지에서 발생하는 모든 Loading이 마무리된 후에 화면을 보여주는 것으로 작업을 해야해서 부분적으로 Suspense 도입을 시도했었습니다.
그러나, Suspense가 아예 동작하지 않거나, 적절히 수정하여 동작하게 됐더라도 API 요청이 waterfall 방식으로 호출되어 느리게 동작하는 것처럼 느껴졌습니다. 이에 더 학습한 후에 적절히 Suspense를 사용하여(또는 사용하지 않고) 이를 구현하기 위해 Suspense의 동작과 코드를 확인해 보았습니다.
그러나 아직 useQueries를 사용한다거나 useQuery의 suspense옵션을 true로 주는 경우(useSuspenseQuery) 어떤 일이 일어나는지 아직 모릅니다. 이에 대한 포스팅도 이어서 진행해보면 Suspense 사용에 도움이 될 것 같습니다.
