문제를 이해하고 있다면 바로 풀이를 보면 됨
전체 코드로 바로 넘어가도 됨
마음대로 번역해서 오역이 있을 수 있음
Problem
이진 트리가 주어졌을 때, 최소 깊이를 구해라.
최소 깊이는 루트 노드에서 가장 가까운 리프 노드까지의 최단 경로에 있는 노드의 개수를 의미한다.
리프는 자식이 없는 노드이다.
Example
#1
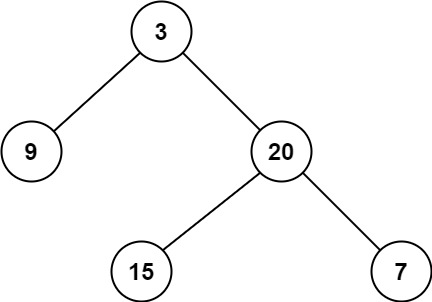
Input: root = [3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7]
Output: 2
#2
Input: root = [2, null, 3, null, 4, null, 5, null, 6]
Output: 5
Constraints
- 트리에 있는 노드의 숫자는 0에서 10^5 범위 안에 있다.
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solved
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int depth = 1;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int levelSize = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node.left == null && node.right == null) return depth;
if(node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);
}
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
}큐를 이용해서 BFS로 문제를 해결했다.
큐에 root를 추가하고 깊이를 1로 한다.
이후 while문을 통해 큐가 비어있지 않을 때까지 반복한다.
큐의 사이즈만큼 반복문을 실행하는데, 이때 양쪽 리프가 없다면 depth를 반환한다.
각 리프가 존재할 경우엔 큐에 리프를 추가하고, depth를 증가시킨다.