모니터 (Monitor)
모니터는 세마포 이후에 등장한 프로세스 동기화 도구이며 세마포보다 더 고수준의 개념이다.
구조
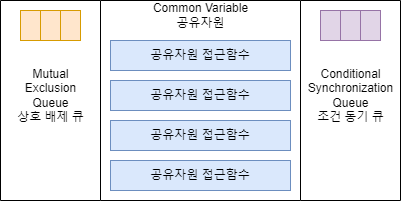
- 공유자원과 공유자원 접근함수로 이루어져있다.
- 상호 배타 큐 (Mutual Exclusion Queue)와 조건 동기 큐 (Conditional Synchronization Queue)를 갖고 있다.
- 공유자원 접근함수는 최대 1개의 쓰레만 진입할 수 있다.
- 진입한 쓰레드가 조건 동기 큐로 블록되면 새로운 쓰레드가 진입할 수 있다.
- 새로운 쓰레드는 조건 동기 큐로 블록된 쓰레드를 깨울 수 있다.
notify(): 조건 동기 큐에 있는 쓰레드 한개를 깨운다.notifyAll(): 조건 동기 큐에 있는 모든 쓰레드를 깨운다.wait(): 현재 실행중인 쓰레드를 조건 동기 큐에 삽입한다.
- 깨워진 쓰레드는 현재 실행 중인 쓰레드가 나가면 다시 진입할 수 있다.
자바 모니터 (Java Monitor)
자바의 모든 객체는 모니터가 될 수 있다.
class C {
private int value, ...;
synchronized void f() {
...
}
synchronized void g() {
...
}
void h() {
...
}
}자바에서 상호 배타 큐는 synchronized 키워드를 사용하여 지정할 수 있다.
조건 동기 큐는 wait(), notify(), notifyAll() 메소드를 사용한다.
synchronized 키워드로 선언된 f(), g() 함수는 상호 배타 함수이며, 똑같은 임계 구역을 갖는다는 의미를 갖고 있다. 따라서 f() 함수 또는 g()함수가 어떤 쓰레드를 실행중이라면, 다른 쓰레드들은 이 함수에 접근할 수 없다.
h() 함수는 일반 함수로써, 여러 쓰레드가 동시에 접근이 가능하다.
BankAccountProblem
Mutual Exclusion
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws InterruptedException {
BankAccount b = new
BankAccount();
Parent p = new Parent(b);
Child c = new Child(b);
p.start();
c.start();
p.join();
c.join();
System.out.println( "\nbalance = " + b.getBalance());
}
}
class BankAccount {
int balance;
synchronized void deposit(int amt) {
int temp = balance + amt;
System.out.print("+");
balance = temp;
}
synchronized void withdraw(int amt) {
int temp = balance - amt;
System.out.print("-");
balance = temp;
}
int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
class Parent extends Thread {
BankAccount b;
Parent(BankAccount b) {
this.b = b;
}
public void run() {
for (int i=0; i<100; i++)
b.deposit(1000);
}
}
class Child extends Thread {
BankAccount b;
Child(BankAccount b) {
this.b = b;
}
public void run() {
for (int i=0; i<100; i++)
b.withdraw(1000);
}
}+++++++++++++++++++++++------------------------------------------+++++++++++++++
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++------------------
----------------------------------------
balance = 0synchronized 키워드를 통해 모니터를 선언하여 상호 배제가 이루어졌다. 세마포보다 코드가 더 간결해진 것을 확인할 수 있다.
Ordering
모니터에서의 Ordering은 세마포의 방식과 유사하다.
2개의 프로세스 P1, P2가 있을 때 다음과 같이 실행할 수 있다.
| P1 | P2 |
|---|---|
| wait() | |
| S1 | S2 |
| notify() |
- 항상 입금을 먼저하는 경우
class BankAccount {
int balance;
synchronized void deposit(int amt) {
int temp = balance + amt;
System.out.print("+");
balance = temp;
notify();
}
synchronized void withdraw(int amt) {
while (balance <= 0)
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
int temp = balance - amt;
System.out.print("-");
balance = temp;
}
int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
++++++++++++++++++++------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------
balance = 0- 항상 출금을 먼저하는 경우
class BankAccount {
int balance;
synchronized void deposit(int amt) {
while (balance == 0)
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
int temp = balance + amt;
System.out.print("+");
balance = temp;
}
synchronized void withdraw(int amt) {
int temp = balance - amt;
System.out.print("-");
balance = temp;
notify();
}
int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
balance = 0- 입출금을 교대로 하는 경우 (P-C-P-C-P-C-...)
class BankAccount {
int balance;
boolean p_turn = true;
synchronized void deposit(int amt) {
int temp = balance + amt;
System.out.print("+");
balance = temp;
notify();
p_turn = false;
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
}
synchronized void withdraw(int amt) {
while (p_turn)
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
int temp = balance - amt;
System.out.print("-");
balance = temp;
notify();
p_turn = true;
}
int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-
balance = 0전통적 동기화 예제
생산자-소비자 문제 (Producer-Consumer Problem)
class Buffer {
int[] buf;
int size, count, in, out;
Buffer(int size) {
buf = new int[size];
this.size = size;
count = in = out = 0;
}
synchronized void insert(int item) {
while (count == size)
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
buf[in] = item;
in = (in+1)%size;
notify();
count++;
}
synchronized int remove() {
while (count == 0)
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
int item = buf[out];
out = (out+1)%size;
count--;
notify();
return item;
}
}
class Producer extends Thread {
Buffer b;
int N;
Producer(Buffer b, int N) {
this.b = b; this.N = N;
}
public void run() {
for (int i=0; i<N; i++)
b.insert(i);
}
}
class Consumer extends Thread {
Buffer b;
int N;
Consumer(Buffer b, int N) {
this.b = b; this.N = N;
}
public void run() {
int item;
for (int i=0; i<N; i++)
item = b.remove();
}
}
class Test {
public static void main(String[] arg) {
Buffer b = new Buffer(100);
Producer p = new Producer(b, 10000);
Consumer c = new Consumer(b, 10000);
p.start();
c.start();
try {
p.join();
c.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
System.out.println("Number of items in the buf is " + b.count);
}식사하는 철학자 문제 (Dining Philosopher Problem)
class Philosopher extends Thread {
int id; // philosopher id
Chopstick lstick, rstick;
Philosopher(int id, Chopstick lstick, Chopstick rstick) {
this.id = id;
this.lstick = lstick;
this.rstick = rstick;
}
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
lstick.acquire();
rstick.acquire();
eating();
lstick.release();
rstick.release();
thinking();
}
}catch (InterruptedException e) { }
}
void eating() {
System.out.println("[" + id + "] eating");
}
void thinking() {
System.out.println("[" + id + "] thinking");
}
}
class Chopstick {
private boolean inUse = false;
synchronized void acquire() throws InterruptedException {
while (inUse)
wait();
inUse = true;
}
synchronized void release() {
inUse = false;
notify();
}
}
class Test {
static final int num = 5; // number of philosphers & chopsticks
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i;
/* chopsticks */
Chopstick[] stick = new Chopstick[num];
for (i=0; i<num; i++)
stick[i] = new Chopstick();
/* philosophers */
Philosopher[] phil = new Philosopher[num];
for (i=0; i<num; i++)
phil[i] = new Philosopher(i, stick[i], stick[(i+1)%num]);
/* let philosophers eat and think */
for (i=0; i<num; i++)
phil[i].start();
}
}
