2020.08.21 배열 함수 수정
2021.01.06 변수 축약 ,구조 분해 할당 , 비구조화 할당
2021.01.22 함수 function default parameter , function ..rest
변환 convert
string to int
const numberString = "15";
const number = parseInt(numberString , 10);int to string
const num = 15;
const n = num.toString();int to string reverse
const number = 123;
const number_reverse = [...number].reverse().join('');
console.log(number_reverse); // 321 ( string ) string reverse
const string = "smilejakdu"
const string_reverse = string.split("").reverse().join("");
console.log(string); // "smilejakdu"
console.log(string_reverse); // "udkajelims"배열에 새 항목 추가하기 - push()
const objects = [{name:'멍멍이'} , {name:'야옹이'}];
objects.push({
name : '멍뭉이'
});
console.log(objects);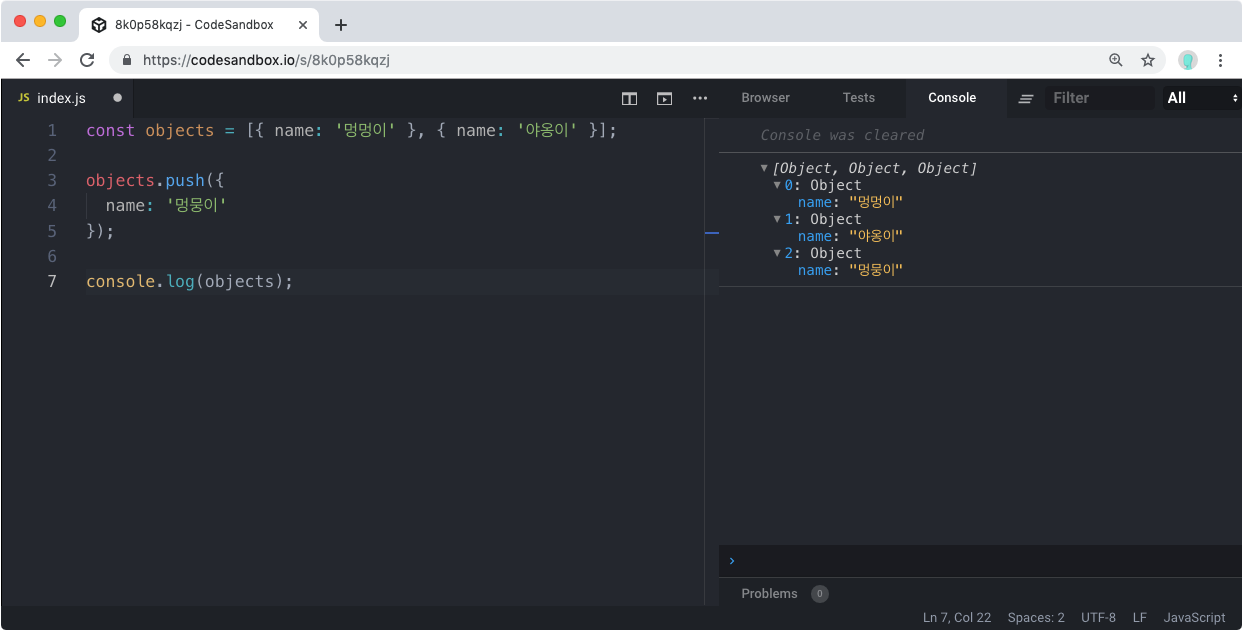
배열을 추가하기 되면 뒤에 추가가 된다.
그러면 앞에 추가할려면 ??
배열 값 앞에서 꺼내기
const numbers = [10,20,30,40,50];
const value = numbers.shift();
console.log(value); // 10
console.log(numbers); // [20,30,40]
배열 값 앞에 추가. - unshift
test = new Array;
test = ['456' , '789']
test.unshift('123');
console.log(test);
// ['123' , '456' , '789']배열의 크기 알아내기 - length
const objects = [{name:'멍멍이'} , {name : '야옹이'}];
console.log(objects.length);
objects.push({
name : '멍뭉이'
});
console.log(objects.length);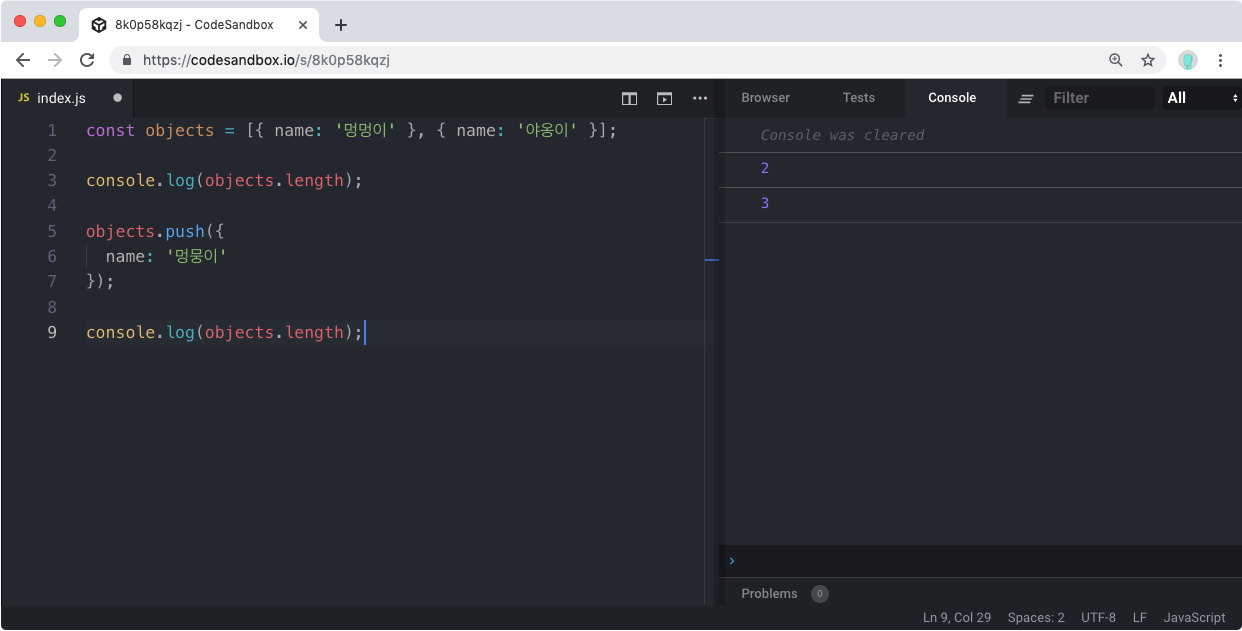
배열의 항목 빼기 - pop()
const objects = [{name:'멍멍이'} , {name:'야옹이'}];
console.log(objects);
objects.pop();
console.log(objects);배열 요소 조작
배열 이어 붙이기 - concat()
let arr1 = [1,2,3];
let arr2 = [4,5,6];
let result = arr1.concat(arr2); // [1,2,3,4,5,6]구조분해 할당
구조분해 할당은 정말 많이 사용하는 것 같다.
[a, b, ...rest] = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
console.log(a); // 10
console.log(b); // 20
console.log(rest); // [30, 40, 50]
({a, b, ...rest} = {a: 10, b: 20, c: 30, d: 40});
console.log(a); // 10
console.log(b); // 20
console.log(rest); // {c: 30, d: 40}구조분해 default 값 설정
const a , b ;
[a = 5 , b = 10] = [1];
console.log(a); // 1
console.log(b); // 10Spread Operator
let sample_array = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
let sample_string = 'string_test'
console.log(sample_array)
// [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
console.log(...sample_array)
// 1 2 3 4 5 6
console.log(sample_string)
// string_test
console.log(...sample_string)
// s t r i n g _ t e s t
let obj1 = {last_name : 'kim', first_name : 'brian'}
let obj2 = {hobby : 'puzzle', office_number : 501}
let obj3 = {...obj1, ...obj2}
console.log(obj3)
// {last_name: "kim", first_name: "brian", hobby: "puzzle", office_number: 501}비구조화 할당
let obj = {
name: '윤자이',
age: 26,
bag: {
item_1: '지갑',
item_2: '전공서적',
},
};
const { name, bag: { item_1 } } = obj
console.log(name) // 윤자이
console.log(item_1) // 지갑배열의 특정index 자르기 - slice()
let arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6];
arr1.slice(2); // [3,4,5,6]
arr1.slice(2,4); // [3,4];- 첫번째 인자 : 자라낼 위치의 인덱스 숫자 지정
- 두번째 인자 : 가리키는 인덱스의 바로 앞요소를 지정
배열을 string 으로 - join()
let string_list = [1,2,3,4,5,6];
string_list.join('-'); // '1-2-3-4-5-6'요소 포함 여부 검색 - includes()
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6];
arr.includes(3): // true일치하는 요소 index 반환 - indexOf()
- 첫번째 인자 : 찾는요소
- 두번째 인자 : 검색을 시작하는 인덱스 번호
- 해당 값이 없으면 -1 을 반환
- 해당하는 요소 하나만 반환
let arr [ 1,2,'s','m','i','l','e',2,4,5];
arr.indexOf('s') //2역순으로 검색 - lastIndexOf()
- 배열의 끝에서 검색
let arr =객체 검색 index 반환 - findIndex()
const todos=[
{
id:1,
text:'asdfasdf',
done : true,
},
{
id:2,
text:'zxcvasdf',
done:true,
},
{
id:3,
text:'asdfxcv23f',
done:true,
},
{
id:4,
text:'avdvlkwev',
done:false
}
]
const index = todos.findIndex(todo => todo.id ===3);
console.log(index); // 2findIndex 는 찾고자 하는 값에 index 를 가르쳐 줍니다.
findIndex 는 객체라던지 그러한 조건들이 있을때 , 사용합니다.
객체 검색 객체 반환 - find()
const todos=[
{
id:1,
text:'asdfasdf',
done : true,
},
{
id:2,
text:'zxcvasdf',
done:true,
},
{
id:3,
text:'asdfxcv23f',
done:true,
},
{
id:4,
text:'avdvlkwev',
done:false
}
]
const index = todos.find(todo => todo.id ===3);
console.log(index); // Object {id: 3, text: "asdfxcv23f", done: true}find 라는 함수는 객체를 반환한다.
검색후 리스트 반환 - filter()
filter method 는 주어진 함수의 테스트를 통과하는
모든 요소를 모아 새로운 배열로 반환합니다.
const numbers = [1,2,3,4,5];
const filtered = numbers.filter(n => n > 3);
console.log(filtered); // [4,5]
const filtered = numbers.filter(n => n!==3);
console.log(filtered); // [1,2,4,5]
const todos=[
{
id:1,
text:'asdfasdf',
done : true,
},
{
id:2,
text:'zxcvasdf',
done:true,
},
{
id:3,
text:'asdfxcv23f',
done:true,
},
{
id:4,
text:'avdvlkwev',
done:false
}
]
const tasksNotDone = todos.filter(todo => todo.done ===true);
console.log(tasksNotDone);
/*
[Object, Object, Object]
0: Object
id: 1
text: "asdfasdf"
done: true
1: Object
id: 2
text: "zxcvasdf"
done: true
2: Object
id: 3
text: "asdfxcv23f"
done: true
*/
map()
map method 는 배열 내의 모든 요소 각각에 대하여
주어진 함수를 적용한 결과를 모아 새로운 배열을 반환합니다.
const array = [1,3,5,7,9]
const map_test = array.map(x => x*2);
console.log(map_test); // [ 2, 6, 10, 14, 18 ]Array.from
Array.from() 메소드는 유사 배열 객체나 반복 가능한 객체를 얕게 복사해서
새로운 Array 객체를 만듭니다.
console.log(Array.from('foo'));
// expected output: Array ["f", "o", "o"]
console.log(Array.from([1, 2, 3], x => x + x));
// expected output: Array [2, 4, 6]
set()
set 객체는 자료형에 관계 없이
원시 값과 객체 참조 모두 유일한 값( 중복 x ) 을 저장할 수 있습니다.
const array = [1,2,3,3,1,1,4,5,6]
const result = Array.from(new Set(array));
console.log(result); // [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ]Math.max()
Math.max() 함수는 0 이상의 숫자 중 가장 큰 숫자를 반환합니다.
const array = [1,2,3,4,5]
const max = Math.max(...array);
console.log(max); // 5Math.min()
Math.min() 함수는 주어진 숫자들 중 가장 작은 값을 반환합니다.
const array = [1,2,3,4,5]
const min = Math.min(...array);
console.log(min); // 1Math.floor()
Math.floor() 함수는 주어진 숫자와 같거나 작은 정수 중에서 가장 큰 수를 반환 합니다.
즉 다시 얘기해서 버림을 한다
console.log(Math.floor(5.6)); // 5forEach()
forEach() 메소드는 주어진 함수를 배열 요소 각각에 대해 실행합니다.
const array = [1,2,3,4,5];
array.forEach(element => console.log(element));
/**
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
*/함수
함수란 ??
하나의 특정한 작업을 수행하도록 설계된 독립적인 블록입니다.
변수에 이름이 있듯이 , 함수도 이름이 존재합니다.
함수 이름을 부르면 , 함수 내에 있는 코드가 실행됩니다.
함수를 불러 실행시키는 것을 함수를 호출한다 라고 얘기합니다.
선언적 function
function hello1(){
console.log('hello1');
}
console.log(hello1 , typeof hello1);
// [Function: hello1] function
function hello3(name){
return `hello3 ${name}`;
}
console.log(hello3('jakdu')); // hello3 jakdu
const hello1 = function(){
console.log('hello1');
}
console.log(hello1 , typeof hello1); // [Function: hello1] function
익명 함수를 만들어 변수에 할당
const hello2 = function(name) {
console.log('hello2' , name);
}
const hello3 = function(name){
return `hello3 ${name}`;
}둘의 차이점은 무엇일까 ??
hello1();
hello2();
hello3();
function hello1() {
console.log('hello1');
}
var hello2 = function(){
console.log('hello2'); // hello2 is not a function
}
const hello3 = function() {
console.log('hello3'); // hello3 is not defined
};
선언적 function 에서는 에러 없이 출력이 되지만 ,
익명 함수에서는 에러를 출력하게 된다.
생성자 함수
함수라는것이 결국에는 객체의 한 형태이며 ,
new 를 사용해서 객체를 만드는방법이 있기 때문에 가능합니다.
const hello = new Function();매개변수에 따라서 생성자에 넣어 주면 됩니다.
const sum = new Function('a' , 'b' , 'c' , 'return a + b + c ');
console.log(sum(1,2,3)); // 6생성자 함수를 이용하여 새로운 객체를 만들어 내는 방법은 ??
function Person(name , age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
const p = new Person('jakdu' , 20);
console.log(p , p.name , p.age); // Person { name: 'jakdu', age: 20 } jakdu 20
const a = new Person('iu' , 19);
console.log(a , a.name , a.age); // Person { name: 'iu', age: 19 } iu 19default parameters
function showMessage(message , from = 'unkown'){
console.log(`${message} by ${from}`);
}
showMessage('hi');
// hi by unkownrest parameters
function printAll(...args){
for (const arg of args){
console.log(arg);
}
}
args.forEach((arg) => console.log(arg));
printAll('test' , 'test2' , 'test3');
// test
// test2
// test3그러면 function 과 new Function() 의 차이는 ?
global.a = 2
{
const a = 1;
const test = new Function('return a');
console.log(test()); // 2
}위에서 출력을 하게 되면 2 가 출력이 된다 .
어찌된거지 ??
global.a = 2
{
const a = 1;
const test = new Function('return a');
console.log(test());
}
{
const a = 3;
const test = function () {
return a ;
}
console.log(test()); // 3
}arrow function
() =>{ ... } // 매개변수가 없는 경우
x => { ... } // 매개변수가 1 개인 경우 , 소괄호 생략 가능
( x , y ) => { ... } // 매개변수가 2개 이상인 경우 , 소괄호 생략 불가const hello1 = () => {
console.log('hello1');
};
const hello2 = (name)=>{
console.log('hello2' , name);
};
const hello3 = (name , age) =>{
console.log('hello3' , name , age);
};
const hello4 = name =>{
return `hello4 ${hello4}`;
};
const hello5 = namne => `hello5 ${name}`;function Person(name , age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
const p = new Person('jakdu' , 20);
console.log(p , p.name , p.age); // Person { name: 'jakdu', age: 20 } jakdu 20
const a = new Person('iu' , 19);
console.log(a , a.name , a.age); // Person { name: 'iu', age: 19 } iu 19
const Cat = (name , age)=>{
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
const c = new Cat('cat ' , 1); // Person { name: 'iu', age: 19 } iu 19
함수 안에서 함수를 만들어 리턴
function plus(base) {
return function(num){
return base + num;
};
};
const plus5 = plus(5);
console.log(plus5(10)); // 15
const plus7 = plus(7);
console.log(plus7(8)); // 15
함수를 호출할 때 , 인자로 함수를 사용
function hello(c){
console.log('hello');
c();
}
hello(function(){
console.log('콜백');
});
// hello
// 콜백콜백함수
조건에 맞는 요소가 하나라도 있는지 - some()
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
arr.some((x) => {
return x % 2 === 0;
} //=> 배열에 짝수가 하나라도 있기 때문에 true
배열의 모든 요소가 조건에 맞아야 true 를 반환 - every()
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5];
arr.every((x) => {
return x % 2 === 0;
} //=> 배열의 모든 요소가 짝수가 아니라 false
객체 (object )
객체는 함수 , 클래스 로 틀을 만드는것이다.
그 틀에서 object 를 하나씩 만들어서 사용하게 된다.
이러한 객체를 인스턴스 라고도 한다.
생성자 함수
function 틀(){} => new 틀()
생성자 함수로 객체 만들기function A(){}
const a = new A();
console.log(a , typeof a); // A {} object
console.log(A()); // undefinedlist insert 리스트 더하기
a = [1,2,3,4]
b = 5
todo_list = [...a , b]
console.log(todo_list)
// [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]todolist delete
const {todo_list} = this.state;
const index = todo_list.findIndex((todo_item)=>todo_item.id ===id);
todo_list : [
...todo_list.slice(0 , index),
...todo_list.slice(index+1 , todo_list.length),
]문자열
charAt()
const sample = "hello";
const result = sample.charAt(1);
console.log(result); // eIndexOf() / lastIndexOf()
const sample = "hello jakdu good morning"
const result_indexOf = sample.indexOf("good");
const result_lastindexOf = sample.lastIndexOf("jakdu");
console.log(result_indexOf); // 12
console.log(result_lastindexOf); // 6replace()
const sample = "hello jakud good morning";
const result = sample.replace("hello" , "hi");
console.log(result);
// hi jakud good morning
substring() / substr()
const sample = "hello world";
const result_substring = sample.substring(0,5);
const result_substr = sample.substr(6,5);
console.log(result_substring); // hello
console.log(result_substr); // worldsplit()
const sample = "hello/world";
const result = sample.split("/");
console.log(result); // [ 'hello', 'world' ]concat()
const sample1 = "hello";
const sample2 = "world";
console.log(sample1.concat(sample2));
// helloworld