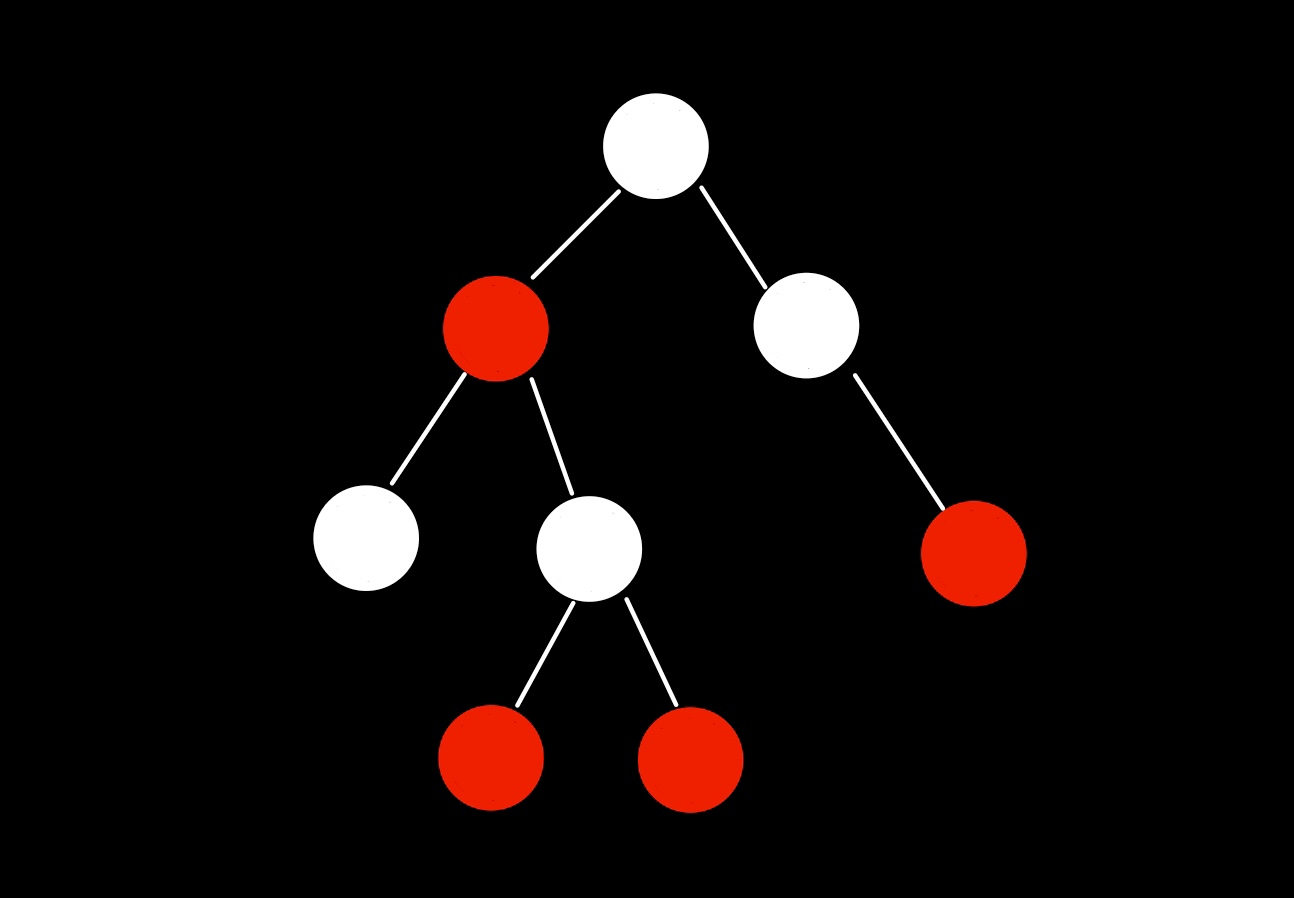
레드블렉 트리는 균형이진트리의 한 종류다.
AVL트리와 많이 비교된다.
레드블랙 트리 규칙
전제
- 각 노드는 레드 또는 블랙이다.
- 루트 노드는 블랙이다.
- 모든 nil 노드는 블랙이다.
- 레드 노드의 자식 노드는 블랙이다. (레드는 연속될 수 없다.)
- 어떤 노드든 모든 nil노드까지의 블랙 노드 수는 동일하다. (black height)
+ 삽입되는 노드의 색은 항상 레드로 한다.
Search
specific value search
tree_search(x, k)
if x == NIL or key[x] == k // if target x is NIL or key of x is the searching key
return x // return target
if k < key[x] // if searching key is less then target key
return tree_search(left[x], k) // search in left subtree
else // if searching key is greater than target key
return tree_search(right[x], k) // search in right subtree
minimum search
이진트리의 성질을 갖고 있으므로 계속 왼쪽으로 따라 들어가면 된다.
tree_min()
while left[x] != NIL // check if left child of the target x is NIL
do x = left[x] // if not NIL, make left child the next target
return x // when target x's left child is NILLmaximum search
마찬가지로 오른쪽으로 따라 들어가면 된다.
tree_max()
while right[x] != NIL // check if left child of the target x is NIL
do x = right[x] // if not NIL, make left child the next target
return x // when target x's left child is NILLSuccessor
석세서 개념은 삭제 개념에서 나오게 되는데,
다음 그 자리를 어떤 노드가 계승하는가에 대한 것이다.
해당 노드의 값보다 큰 노드들 중 가작 작은 값의 노드가 석세서이다.
tree_successor(x)
if right[x] != NIL // if right subtree exists
return tree_min(right[x])
y = p[x] // if right subtree does not exist, set y the parent of x to find successor among ancestors
while y != NIL and x == right[y] // find until root node and while x is being right child
do x = y // make parent new target x
y = p[y] // make grandparent new parent of new x
return ypredecessor
석세서와 반대, right <-> left
Rotation
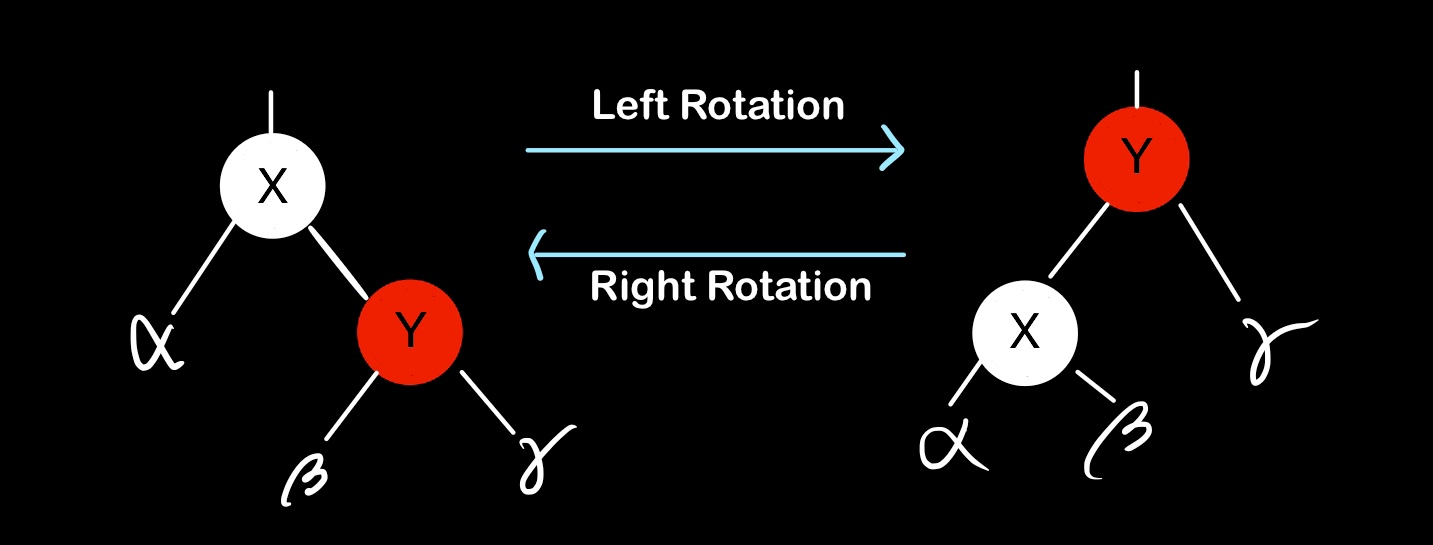
Left rotation
only when y == right[x] && y != NIL
left_rotate(RBT, x):
y = right[x] // set y
right[x] = left[y] // turn y's left subtree into x's right
p[left[y]] = x // link y's left child's parent to x
p[y] = p[x] // link x's parent to y
if p[x] == nil[RBT] // if x is the root node
then root[RBT] = y // make y the new root node
else if x == left[p[x]] // if x has a parent, and x is left node of the parent
then left[p[x]] = y // make y new left node of x's ex-parent
else
right[p[x]] = y // make y right node of x's ex-parent
left[y] = x // now make x left node of y
p[x] = y // and y becomes parent of x
Right rotation
left rotation을 반대로 해주면 right rotation
right_rotate(RBT, x):
y = left[x]
left[x] = right[y]
p[right[y]] = x
p[x] = p[y]
if p[x] == nil[RBT]
then root[RBT] = y
else if x == right[p[x]]
then right[p[x]] = y
else
left[p[x]] = y
right[y] = x
p[x] = y Insert
insert(RBT, z)
y = nil[RBT] // y is the follower of x
x = root[RBT] // set target x = root
while x != nil[RBT] // until target reaches nil node
do y = x // put y in target x's place, so y steps down to x's place
if key[z] < key[x] // if key of z is less than x's
then x = left[x] // x steps down to the left
else // if key of z is greater than x's
x = right[x] // x steps down to the right
p[z] = y // when x reaches nil node, y becomes the parent of z
if y == nil[RBT] // if there is no node in the tree
then root[RBT] = z // z become the root node
else if key[z] < key[y] // if key of z is less than parent node y
then left[y] = z // z becomes left child of y
else // if kye of z is greater than parent node y
right[y] = z // z becomes right child of y
left[z] = nil[RBT] // since z is the vaild end node, it should have nill node of left
right[z] = nil[T] // add right nil node
color[z] = RED // <ONLY RB TREE> new node is red
RB_insert_fixup(RBT, z) // <ONLY RB TREE> make the tree stick to the rule
이때 레드 노드가 삽입된 것이므로
1. 각 노드는 레드 또는 블랙이다 => 만족
2. 루트 노드는 블랙이다 => 레드면 블랙으로 바꾸면 됨
3. 모든 nil 노드는 블랙이다 => 만족
4. 레드 노드의 자식 노드는 블랙이다 => 연속된 레드가 올 가능성
5. 어떤 노드든 모든 nil노드까지의 블랙 노드 수는 동일하다 => 레드이므로 만족
따라서 RB_insert_fixup에서는 2번 조건일때는 단순히 black으로 바꿔주면 되므로 주로 4번 조건에 대한 경우만 신경써주면 된다.
4번 조건에 대한 불만족 경우의 수는 6가지다. 그런데 case 1,2,3과 case 4,5,6은 left-right 경우로 대칭적이다. 따라서 case 4,5,6에는 case 1,2,3의 로직을 그대로 활용하면 된다.
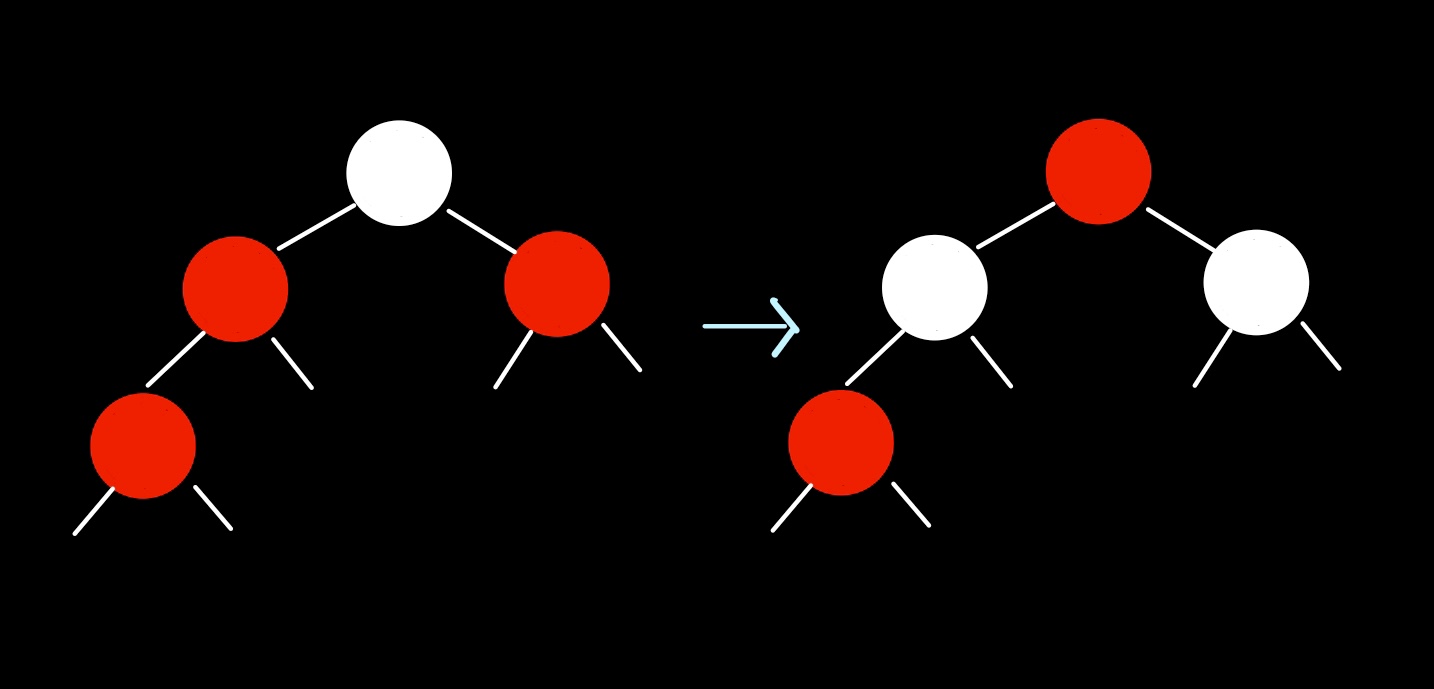
CASE 1
z의 uncle이 red일 때
(a) z가 left child일 경우
(b) z가 right child일 경우
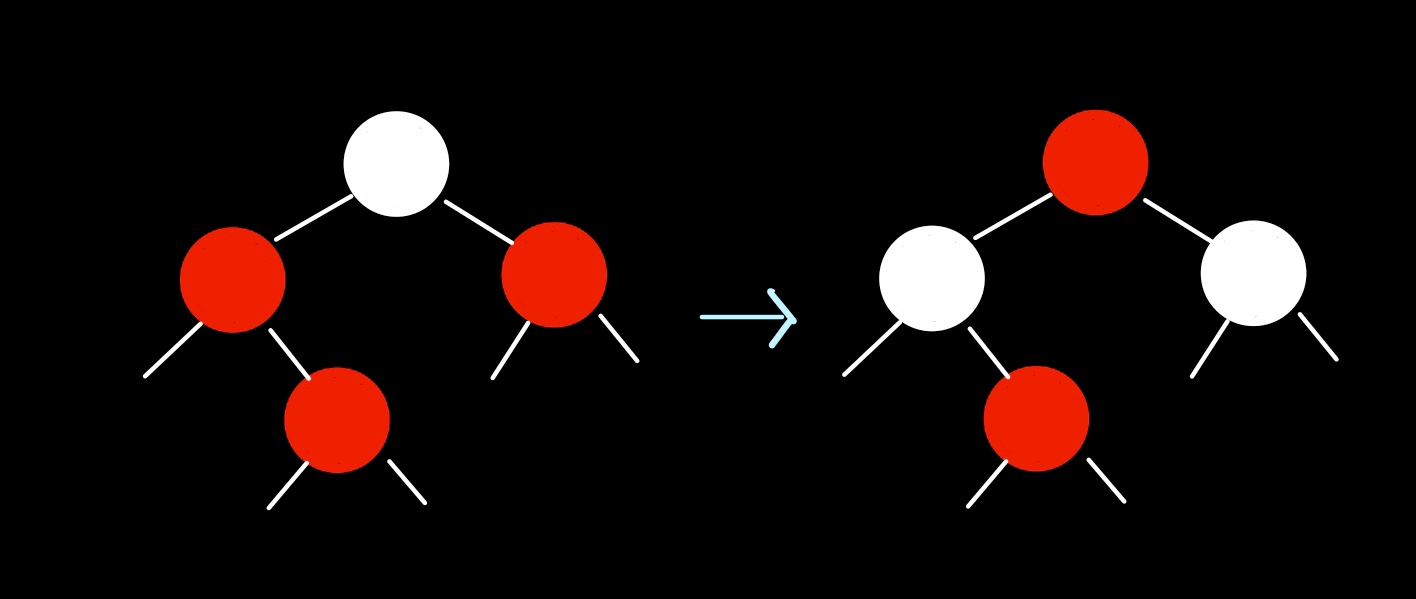
할아버지 노드의 색(black->red)과 부모 노드 및 uncle의 색(red -> black)을 바꿔준다.
4번 규칙 위반이 할아버지 노드로 이전될 수 있지만, 반복해서 루트 노드까지 위반 내용을 해결해주면 된다.
CASE 2,3
z의 uncle이 black(nil 포함)일 때
(a) z가 right child => CASE 2
(b) z가 left child => CASE 3
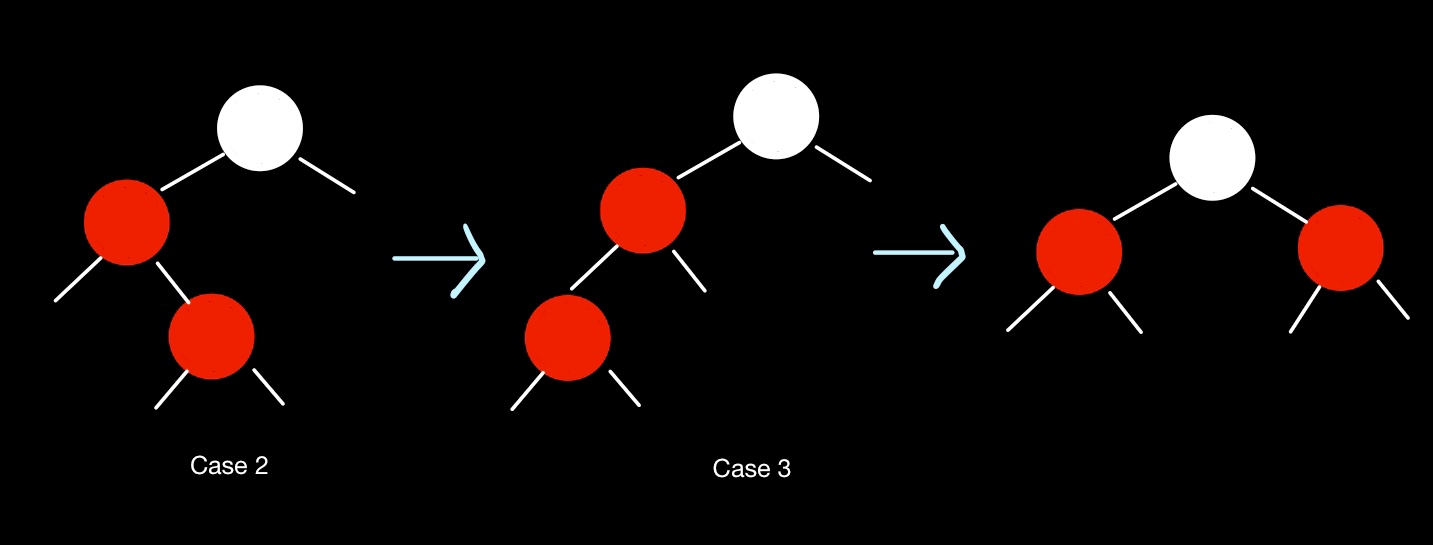
CASE 3인 상태로 만들어서 할아버지 노드 중심 right rotation + 할아버지 색과 right rotation 끝 노드의 색을 바꾸는 것으로 해결
CASE 2는 left rotation을 통해 CASE 3로 만들어서 같은 방법으로 해결
RB_insert_fixup(RBT, z)
while p[z] != NIL && color[p[z]] == RED // while RED is successive
if p[z] == left[p[p[z]]] // CASE 1,2,3
y = right[p[p[z]]] // y is uncle node of z
if color[y] == RED // CASE1 : if the unclude is RED
color[p[z]] = BLACK // parent of z becomes BLACK
color[y] = BLACK // uncle node y becomes BLACK
color[p[p[z]] = RED // grandparent of z becomes RED
z = p[p[z]] // grandparent becomes new z to solve problem
else // CASE2, CASE3: if the uncle is BLACK
if z == right[p[z]] // CASE2 : if z is the right child
z = p[z] // z steps up
left_rotate(RBT, z) // left rotation
color[p[z]] = BLACK // CASE3 : if z is the left child
color[p[p[z]]] = RED // grandparent becomes RED
right_rotate(RBT, p[p[z]]) // right rotation
else
/* ---------------------------------- */
/* == the same logic as CASE 1,2,3 == */
/* symmtric as to z is on th right */
/* ---------------------------------- */
color[root[RBT]] = BLACK // make root node BLACKDelete
자식 노드가 없는 경우 => 그냥 삭제
자식 노드가 한개인 경우 => 자식 노드를 부모 위치로 옮겨옴
자식 노드가 두개인 경우 => successor가 해당 자리를 계승
delete(RBT, z) // z will be deleted
if left[z] == nil[T] or right[z] == nillT] // if z has only one child
then y = z // z will be deleted
else // z has two childs
y = tree_successor(z) // successor of z node will be deleted
if left[y] != nil[RBT] // if y has a child
then x = left[y] // set y's left child as x
else // if y has no child
x = right[y] // set y's right child as x
p[x] = p[y] // make x's parent y(deleted)'s parent
if p[y] == nil[RBT] // if y is root node
then root[RBT] = x // x becomes new root node
else if y == left[p[y]] // if y is left child
then left[p[y]] = x // x becomes the left child of the parent of deleted y
else // if y is right child
right[p[y]] = x // x becomes the right child of the parent of deleted y
if y != z // if z's successor is deleted
then key[z] = key[y] // copy y(successor)'s data into z (z's ex-data is deleted)
if color[y] == BLACK // if deleted node is BLACK (deletion of RED node is no problem)
then RB_delete_fixup(RBT, x) // fixup the rule
return y삭제 시 삭제된 노드의 색이 RED일 경우는 문제가 안 됨 -> black height는 그대로
그러나 삭제된 노드가 BLACK일 경우 문제가 됨 -> RB_delete_fixup(RBT, x)
- 각 노드는 레드 또는 블랙이다 => 만족
- 루트 노드는 블랙이다 => 레드면 블랙으로 바꾸면 됨
- 모든 nil 노드는 블랙이다 => 만족
- 레드 노드의 자식 노드는 블랙이다 => 삭제된 노드의 자식노드를 레드에서 블랙으로 변경
- 어떤 노드든 모든 nil노드까지의 블랙 노드 수는 동일하다 => extra black 개념으로 해결
extra black을 가진 노드가 black -> doubly black 노드
extra black을 가진 노드가 red -> red & black 노드
이 상태를 해결하는 기본적인 아이디어는
extra black을 부모 노드로 계속 이전하는 것임
-> red & black 상태가 되면 black 노드로 만듦
-> 루트 노드가 doubly black 상태가 되면 extra black을 제거
(이 때 현재 상태를 보는 노드의 형제 노드는 NIL 노드가 아니라는 조건이 있어야 한다.)
총 8가지 CASE가 있지만, Case 1,2,3,4와 5,6,7,8은 left-right 대칭이다.
Case 1
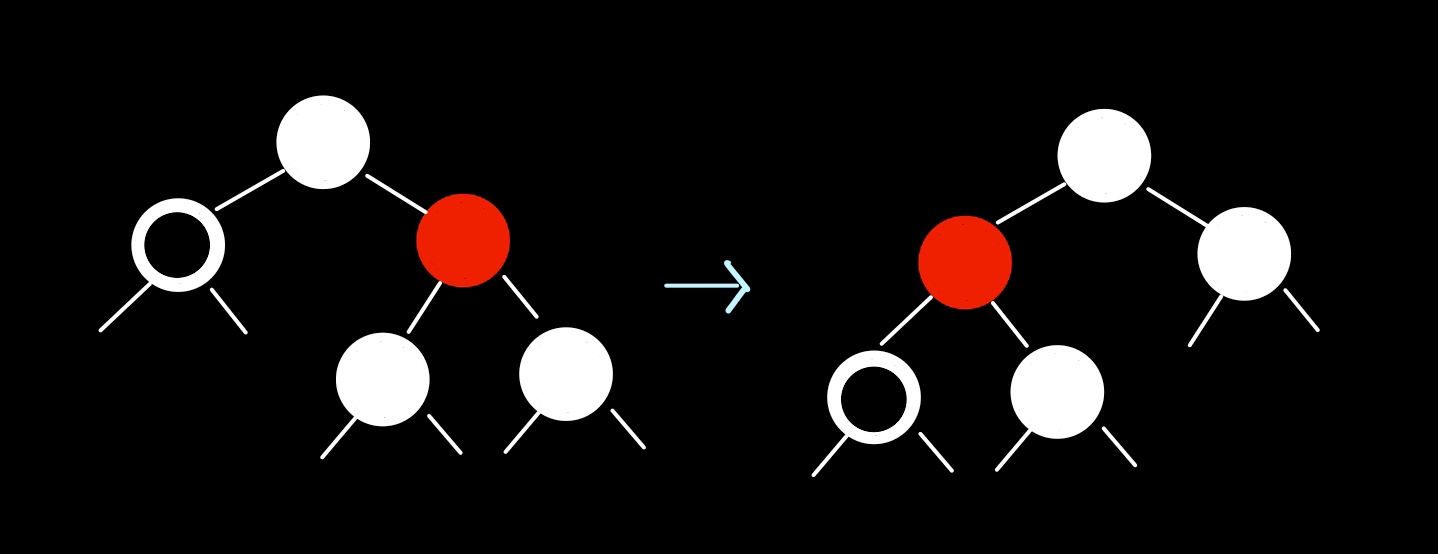
uncle노드가 레드일 때를 Case 1이라고 하고, left rotation + 색 변경을 통해 uncle 노드를 블랙인 경우로 만든다. 이후 extra black을 이전시키면 된다. (Case 2,3,4)
Case 2
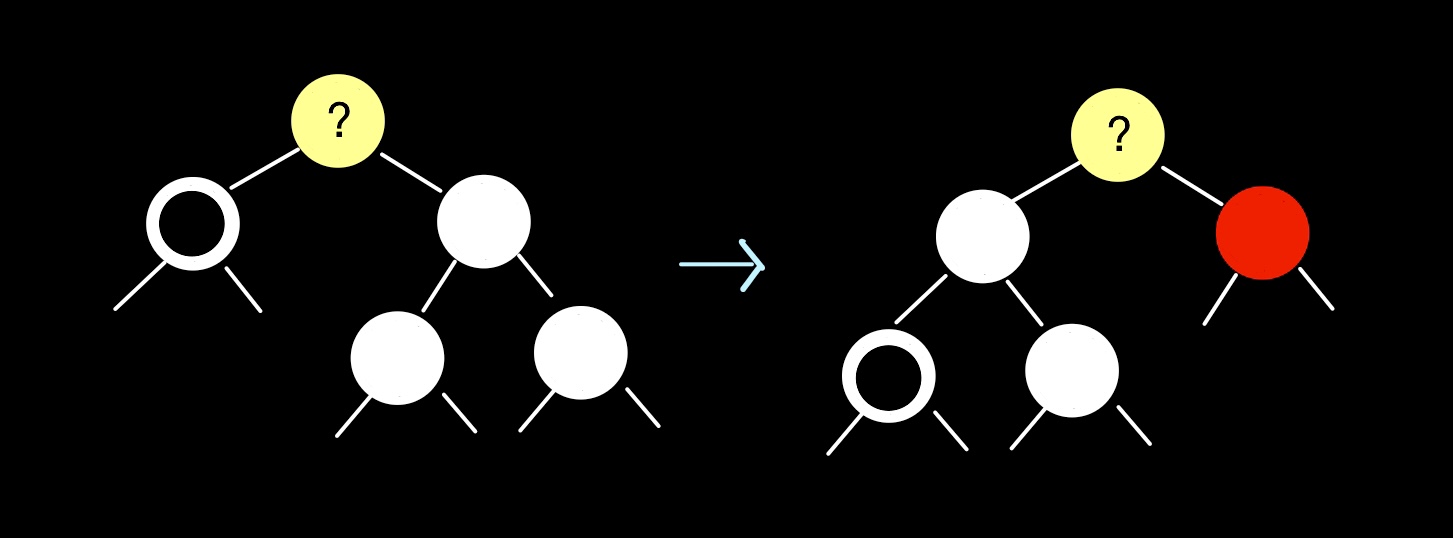
doubly black과 그냥 블랙에서 블랙을 하나씩 차감하고 레드 또는 블랙인 부모는 블랙을 하나 더해준다. 그러면 부모 노드는 doubly black 또는 red & black 이 된다.
Case 3
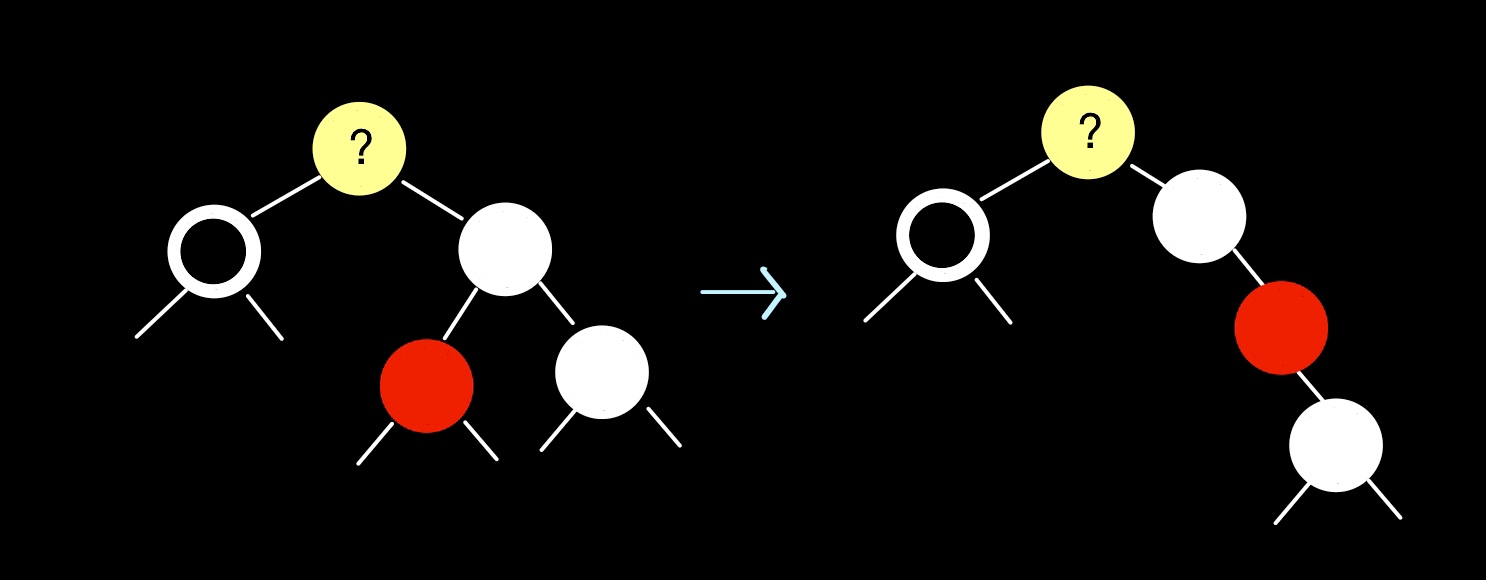
Case 4로 만들어 준다. uncle 노드를 레드로, uncle의 왼쪽 자식을 블랙으로 바꾼 뒤 right rotation을 진행한다.
Case 4
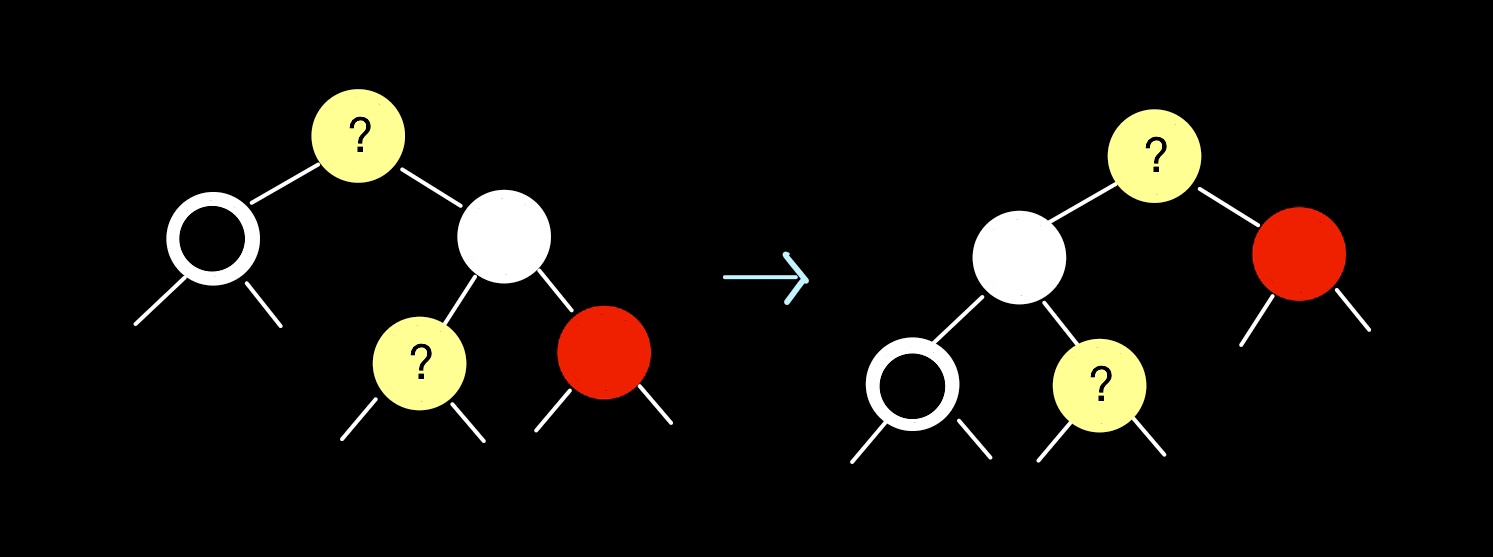
uncle 노드와 부모 노드의 색을 서로 바꿔준 뒤 left rotation을 진행한다.
모든 과정이 끝나면 black height를 맞춰주기 위해 doubly black의 extra black을 부모노드로 계속해서 이전한다.
RB_delete_fixup(RBT, x)
while x != root[T] and color[x] == BLACK
if r == left[p[x]]
w = right[p[x]]
if color[w]= RED
color[w] + BLACK // CASE 1
color[p[x]] < RED
left_rotate(RBT, P[x])
w = right[p[r]]
if color[left[w]] == BLACK and color[right[w]] == BLACK
color[w] = RED // CASE 2
x = p[x]
else if color[right[w]] == BLACK
color[left[w]] = BLACK // CASE 3
color[w] = RED
right_rotate(RBT, w)
w = right[p[x]]
color[w] = color[p[x]] // CASE 4
color[p[x]] = BLACK
color[right[w]] = BLACK
left_rotate(RBT, p[x])
x = root[RBT]
else
/* ---------------------------------- */
/* == the same logic as CASE 1,2,3,4 */
/* symmtric as to z is on th right */
/* ---------------------------------- */
color[x] = BLACK참고로 아래 웹페이지에서 레드블랙 트리를 테스트 해볼 수 있다.
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/RedBlack.html
