
1. Java의 Collection Framework란?
- 자바에서 컬렉션 프레임워크(collection framework)란 다수의 데이터를 쉽고 효과적으로 처리할 수 있는 표준화된 방법을 제공하는 클래스의 집합을 의미한다.
- 데이터를 저장하는 자료 구조와 데이터를 처리하는 알고리즘을 구조화하여 클래스로 구현해 놓은 것이다.
- 자바의
interface를 사용하여 구현된다.
1-1. Collection Framework의 장점
- List, Set, Map 등의 인터페이스를 제공하고, 이를 구현하는 클래스를 제공하여 일관된 API 를 사용할 수 있다.
- 고정적인 저장 공간을 제공하는 배열과 달리 가변적인 저장 공간을 제공한다.
- 자료구조, 알고리즘을 구현하기 위한 코드를 직접 작성할 필요 없이, 이미 구현된 컬렉션 클래스를 목적에 맞게 선택하여 사용하면 된다.
1-2. Collection Framework 사용법
1-2-1. List
// ArrayList 예시
// List<타입 파라미터> 객체명 = new ArrayList<타입 파라미터>(초기 저장용량);
List<Integer> number = new ArrayList<Integer>(); // 초기 용량은 객체 10개
List<String> name = new ArrayList<String>(50);1-2-2. Set
// HashSet 예시
// HashSet<타입 파라미터> 객체명 = new HashSet<타입 파라미터>(초기 저장용량);
HashSet<String> coffee = new HashSet<String>();
HashSet<Integer> price = new HashSet<Integer>(30);1-2-3. Map
// HashMap 예시
// Map<Key, Value> map = new HashMap<Key, Value>();
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
2. Java Collection Framework interface의 종류
인터페이스 간의 상속관계 그림
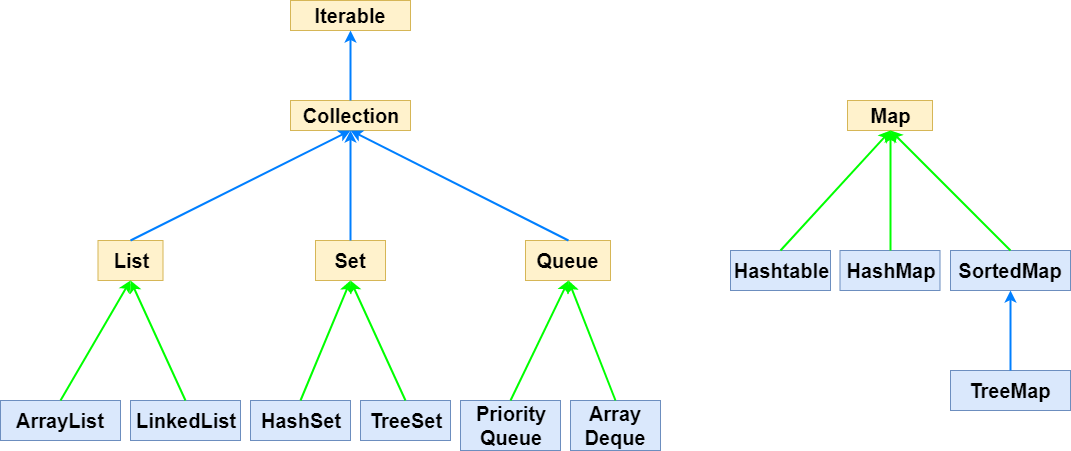
1. 리스트 ( List )
- List Interface(리스트 인터페이스)는 대표적인 선형 자료구조로,
주로 순서가 있는 데이터를 목록으로 이용할 수 있도록 만들어진 인터페이스다.- List를 통해 구현된 클래스들은 '동적 크기'를 갖으며 배열처럼 사용할 수 있게 되어있다. (배열의 기능 + 동적 크기 할당 = List)
2. 집합 ( Set )
- 순서가 없으며, 데이터를 중복하여 저장할 수 없다. 집합 연산 (합집합, 교집합, 차집합 등) 을 지원한다.
3. 맵 ( Map )
- Key-value 쌍으로 데이터를 저장한다. 순서가 존재하지 않으며, Key가 중복될 수 없다.
2-1. < List interface >를 구현하는 클래스
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
- Vector
< List interface >에 선언된 대표적인 메소드
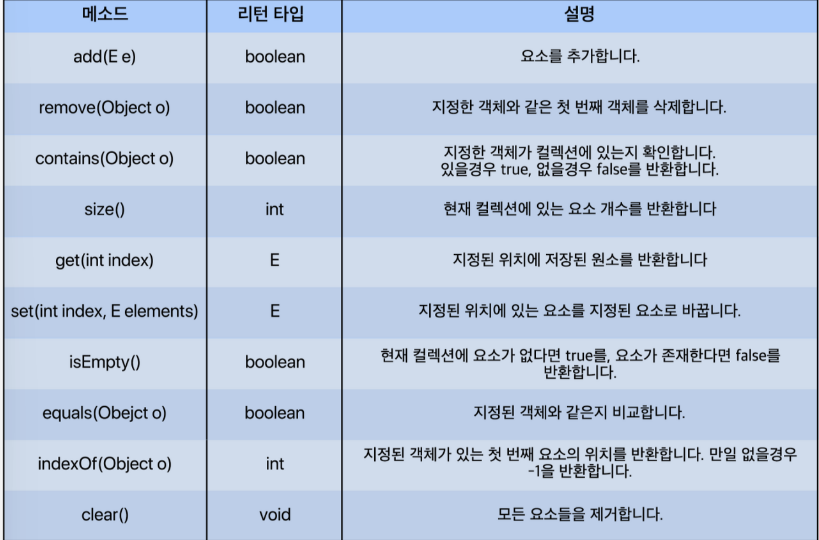
< ArrayList > 실습 코드
// student라는 ArrayList를 만들고 객체를 추가해 인덱스값과 해당 인덱스에 저장된 객체를 출력하는 코드
public class ArrayListPractice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> student = new ArrayList<String>();
student.add("2210 박우빈");
student.add("2212 백서진");
student.add("2111 원설아");
int size = student.size(); // size == 3
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
String str = student.get(i);
System.out.println(i + " : " + str); // 출력
}
student.remove(0); // 0번 인덱스의 객체 삭제
}
}
// 출력
// 0 : 2210 박우빈
// 1 : 2212 백서진
// 2 : 2111 원설아2-2. < Set interface >를 구현하는 클래스
- HashSet
- LinkedHashSet
- TreeSet
< Set Interface에 선언된 대표적인 메소드 >
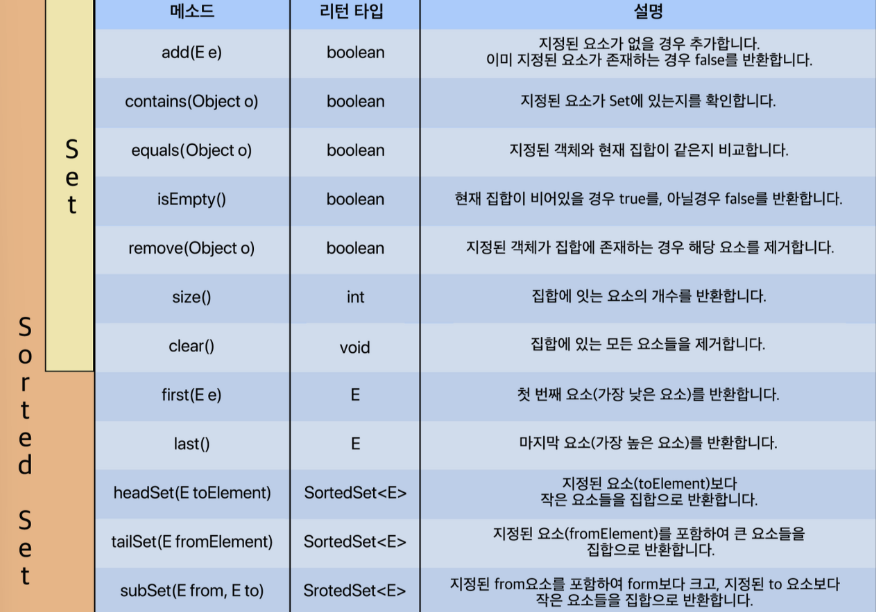
< HashSet > 실습 코드
public class HashSetPractice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> sport = new HashSet<String>();
coffee.add("baseball");
coffee.add("soccer");
coffee.add("basketball");
coffee.add("swimming");
coffee.add("running");
Iterator it = sport.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
// 출력
// baseball
// soccer
// basketball
// swimming
// running
}2-3. < Map interface >를 구현하는 클래스
< Map interface >에 선언된 대표적인 메소드
- HashMap
- TreeMap
- Hashtable
- Properties
public class HashMapPractice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("빨", 1);
map.put("주", 2);
map.put("노", 3);
map.put("초", 4);
map.put("파", 5);
map.put("남", 6);
map.put("보", 7);
System.out.println("총 entry 수 : " + map.size());
System.out.println("빨 : " + map.get("빨"));
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
Iterator<String> keyIterator = keySet.iterator();
while(keyIterator.hasNext()){
String key = keyIterator.next();
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " : " + value);
}
}
}
// 출력:
// 총 entry 수 : 7
// 빨 : 1
// 보 : 7
// 빨 : 1
// 노 : 3
// 초 : 4
// 남 : 6
// 주 : 2
// 파 : 53. 정리
- C언어의 경우 표준 라이브러리에서는 이러한 자료구조를 지원하지 않지만, Java에서는 Collection Framework로 위에서 설명한 자료구조 뿐만 아니라 매우 많은 자료구조를 지원하기 때문에 사용하기 편리하고, 재사용성이 높다.
Collection interface에는List,Set,Map등이 있다.