지금까지 Process : “단일 스레드로 실행 중인 프로그램”로 가정했다.
하지만, “다중 스레드”를 포함할 수 있지 않을까?
Thread
- a lightweight process = LWP , CPU를 점유하는 가장 기본적인 단위
- 쓰레드 ID(thread ID), PC(Program counter), 레지스터 세트(Register set), 스택(Stack) 으로 구성되어있다.
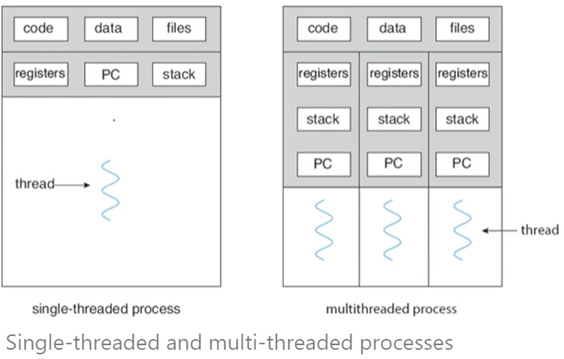
The benefits of multithreaded programming (멀티스레드 프로그래밍의 장점)
-
응답성(Responsiveness)
싱글 스레드의 경우, 작업이 끝나기 전까지 새로운 사용자에게 응답을 하지 않는다.
반면 멀티스레드의 경우, 실시간으로 사용자에게 응답할 수 있다.
-
자원 공유(Resource sharing)
프로세스는 공유 메모리(shared-memory) or 메시지 패싱(message-passing)을 이용해서 자원을공유할 수 있지만, 스레드는 Code, Data, File, Memory…를 공유하여 효율적이다.
-
경제성(Economy)
프로세스를 새로 생성하는 비용보다 스레드를 새로 생성하는 게 훨씬 싸다.
(Context switching의 오버헤드 또한 스레드가 더 경제적이다.)
-
확장성(Scalability)
싱글 스레드인 경우 한 프로세스는 오직 한 프로세서에서만 수행 가능하다. 반면 멀티 스레드인 경우 한 프로세스를 여러 프로세서에서 수행할 수 있으므로 훨씬 효율적이다.
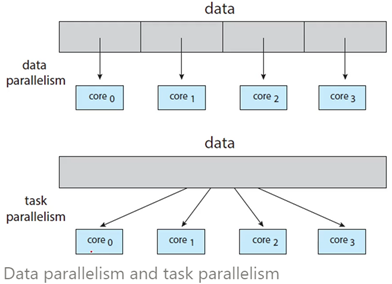
Multi-threading in a “Multicore” system
동시성(Concurrency) 향상을 위해 다중 코어를 보다 효율적으로 사용할 수 있다.
→ Single-core : threads will be interleaved over time. (Time Sharing)
→ multiple cores : some threads can run in parallel.
( ex) 4개의코어, 4개의 스레드가 있을 때, 각각의 코어에 1개의 스레드를 배치하면, Context Switch 없이 실행 가능)

Programming Challenges in Multicore systems.
-
Identifying tasks: find areas can be divided into separate tasks.
→ ex) Merge sort : 한 구역을 정렬하는 동안, 다른 구역은 정렬되지 않고 있다. (의존적)
⇒ 병렬적으로(Parallel) 할 수 있는 작업, 다른 작업에 의존하는지(Dependency) 찾아내야한다.
-
Balance : ensure the tasks to perform equal work of equal value.
→ 같은 value를 지니는 작업은, 같은 양을 실행하도록 한다.
-
Data splitting : data also must be divided to run on separate cores.
-
Data dependency : ensure that the execution of tasks is synchronized to accommodate the data dependency
→ 작업해야할 데이터들끼리 잘 동기화가 되도록 한다. ex) Merge sort
-
Testing and debugging : single-thread에 비해 훨씬 복잡하다
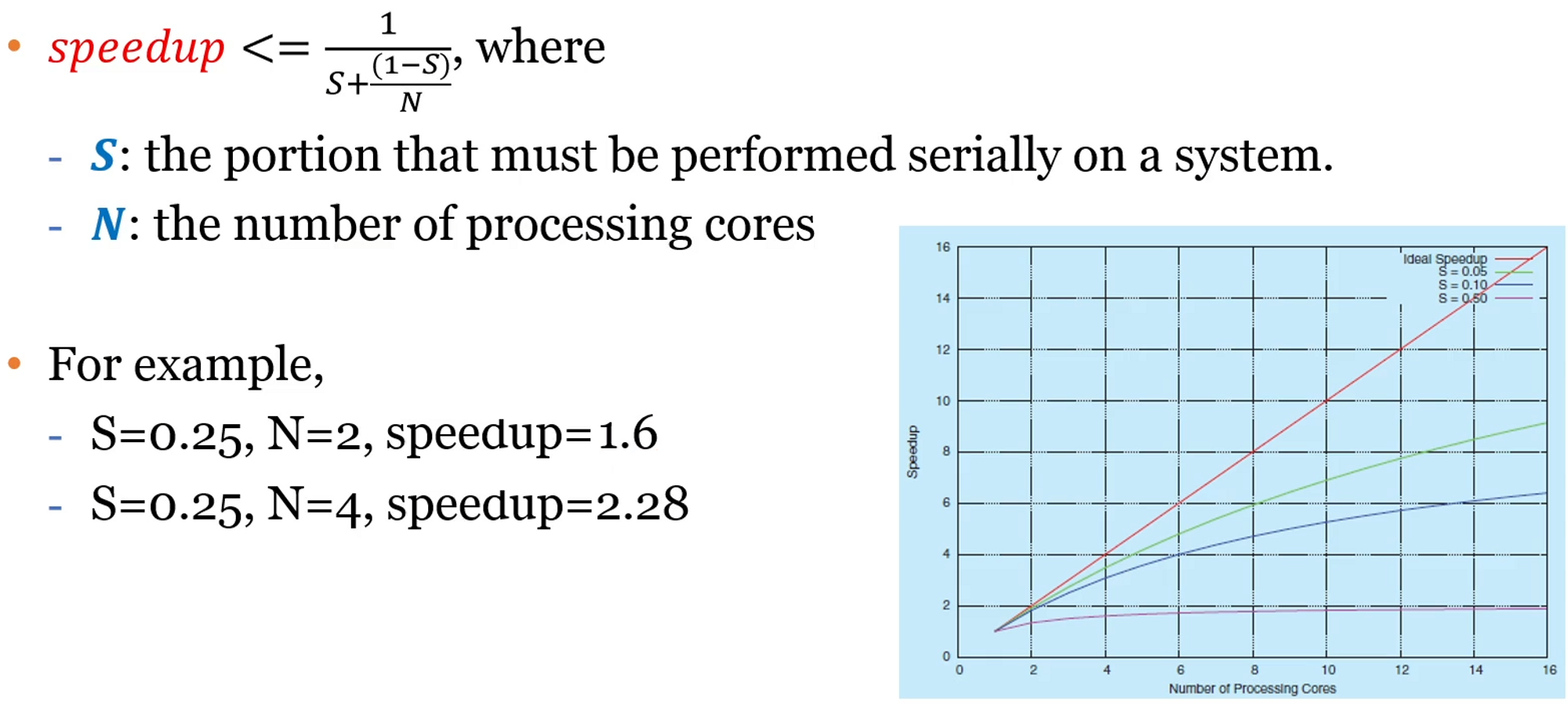
Amdahl’s Law(암달의 법칙):
- 코어가 무조건 많을수록 좋을까? → Serial(연속적인)한 프로그램이 있을 경우 그렇지 않다.
참고 :
Silberschatz et al. 『Operating System Concepts』. WILEY, 2020.
