논문정보
Introduction
배경
- performance는 증가하였으나 interpretability를 잃음
- 우리가 직관적으로 믿고 중요하다고 여기는 것들을 모델도 실제로 배우고 있는지 vs 복잡한 co-occurrence 통계학을 모델링 한 것인지 모름
- 이를 파헤치기 위한 연구는 실험 기반이나 네트워크 분석
- 언어 모델의 lower layer 들은 국소한 문법적 관계를 인코딩하고, high layer 들은 더욱 복잡한 의미적 관계를 포착함 (Peters, 2018)
- 본 연구는 probing tasks (Tenny, 2019)를 확장함
의의
- 전통 NLP pipeline의 공통적인 요소들에 대한 분석
: task 들의 전통적인 계층 구조가 인코딩 시에 반영됨 (POS tagging -> parsing -> NER -> semantic roles -> coreference) - 어떻게 각각의 문장들이 BERT 내부의 각 레이어에서 분석되는지 질적으로 연구
: 모호한 의사 결정을 연기하거나 higher layer 의 정보를 기반으로 잘못된 의사 결정을 수정
Model
Edge Probing
- structured-prediction task 들을 공통된 format 에 맞춰 수행할 수 있도록 framework를 제시
- 표준적인 benchmark dataset 을 활용하여 학습하였으며, F1 score 로 평가됨
BERT
- Tenney (2019) 와 동일한 BERT 구조를 사용하였으며, 가중치는 모두 freeze 하여 task 들을 수행하는 동안 fine-tuning 되지 않도록 함
- input token:
- a set of activation vectors of the encoder layer:
- 은 문맥 정보가 반영되지 않은 word embedding
- layer 마다 가중합을 적용하여 token 당 하나의 representation vector 로 만듦
- [Metrics.1]의 scalar mixing weights 를 활용
- probing classfier: 를 각각의 task 에 맞게 학습시킴
Metrics
1. scalar mixing weights
- 어떤 layer가 가장 관련이 높은지
- 방법
- 각각의 task 마다 scalar parameter 와 attention parameter 가 학습됨
- 는 정규화된 attention weight ()
- 결과
- probing model이 학습되고 나면, 각각의 layer가 해당 task에 얼마나 기여하는지 살펴보기 위해 학습된 coefficients를 추출.
- weight 값이 높다면 해당 layer 가 task와 관련된 많은 정보를 담고 있는 것
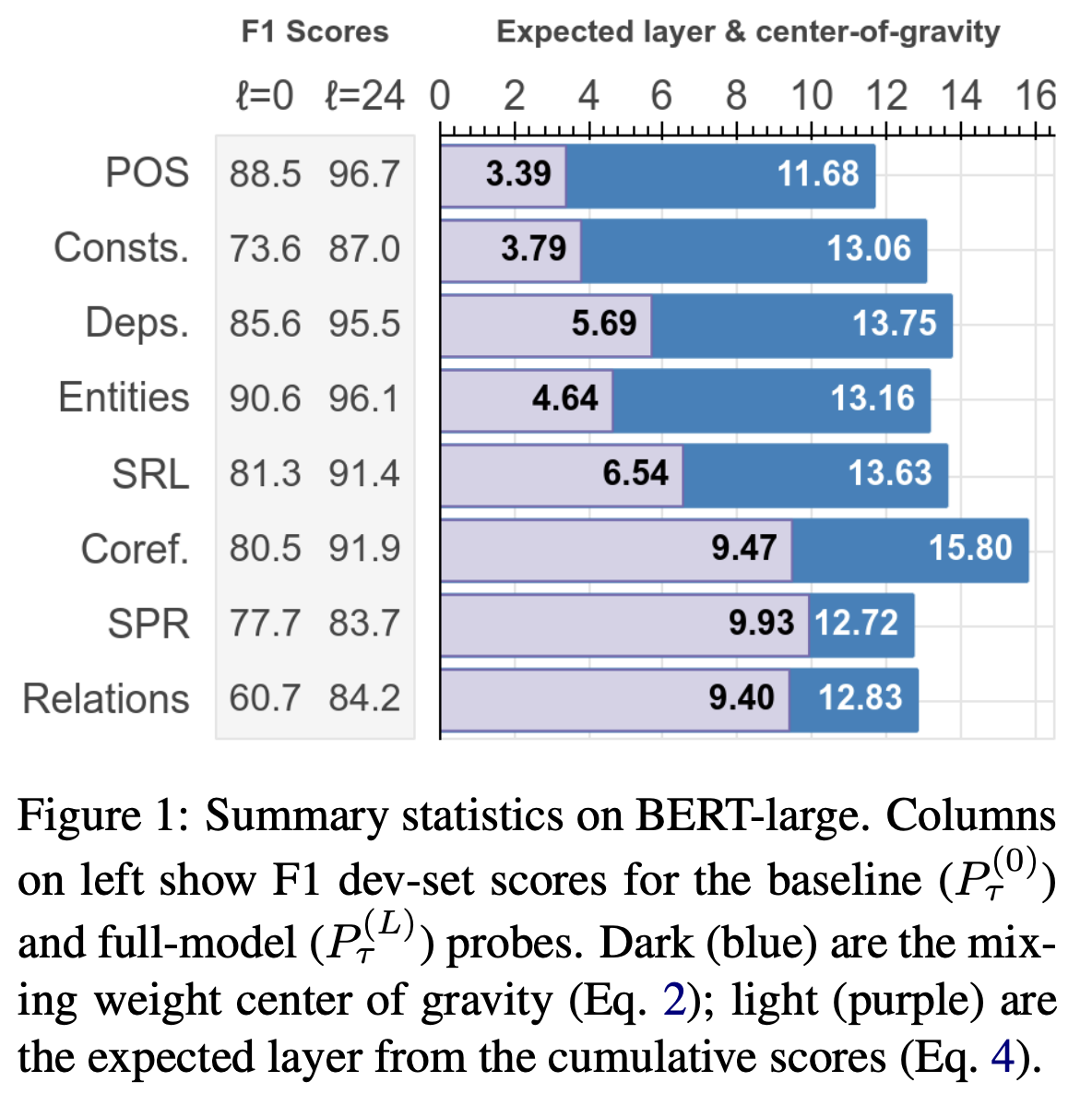
- mixing weight 의 center of gravity
- 각각의 task에 기여하는 layer 의 평균
- 값이 높다면 higher layer 에서 해당 task에 필요한 정보를 가지고 있음
2. Cumulative Scoring
- 어떤 layer에서 task의 정답을 맞추는지
- 특정 범위의 정보는 여러 layer에 걸쳐 확산될 것이고, encoder는 higher layer 에서 어떤 정보를 삭제할 지 결정할 것
- mixing weights는 parameter를 학습할 뿐 data의 layer에 대한 분포에 대응하지 않음
- 방법
- : task 별 classifier 를 1의 scalar mixing 을 활용하여 layer 별로 학습시킴. 즉, 한 task 당 layer 개수 만큼의 classifier 가 생김.
- 번째 classifier 는 이하의 모든 layer에 대하여 학습됨. 즉, 은 BoW 임베딩만 활용하므로 문맥 정보가 없는 baseline에 해당함. 반면, 은 모든 layer 를 활용한 것.
- 결과
- 직관에 부합함. 더 많은 layer 를 학습할 수록 성능이 좋아짐.
- 성능의 차이 계산:
- Expected Layer
- task의 정답을 맞출 것으로 예상되는 layer
Results
1. Linguistic Patterns
- POS tagging -> parsing -> NER -> semantic roles -> coreference 순서로 task를 해결함.
- constituents 는 coreference 보다 먼저 represent 된다는 Peters (2018) 의 주장에 부합
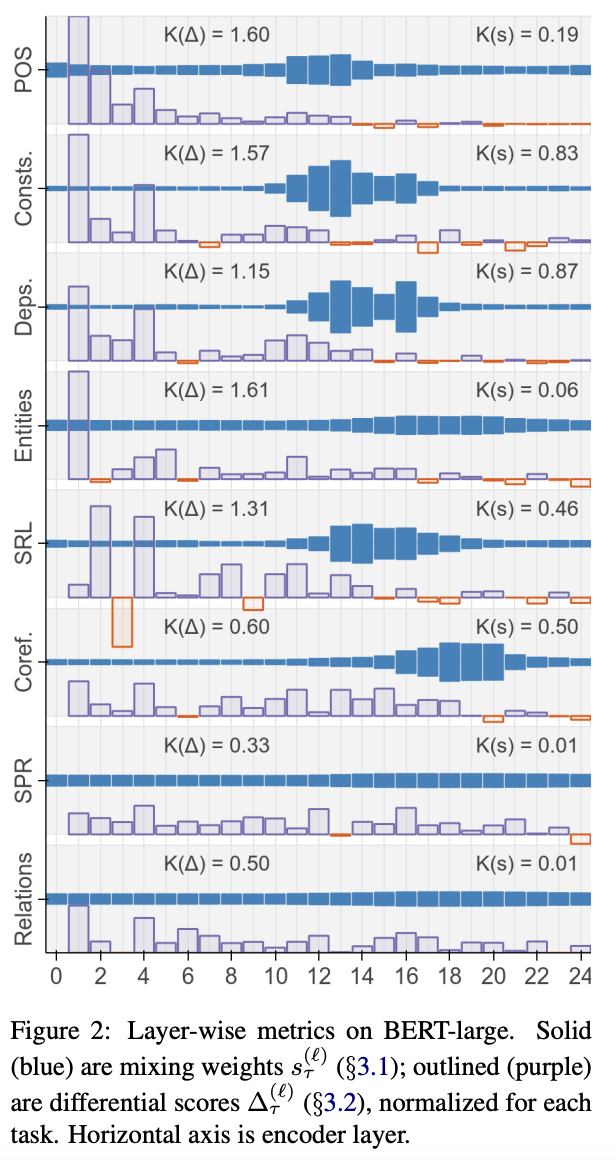
- : 각 task마다 값()이 얼마나 non-uniform 한 지 측정
- semantic task 들은 와 값이 높은 경향이 있음. 즉, 특정 몇몇 layer 가 압도적으로 문제 해결에 기여하는 것이 아닌, 넓은 범위에서 대다수의 layer 가 활용된다는 뜻.
- 향후 연구에서 BERT 가 추상적인 것을 표현하기 어려워 해서 여러 layer 를 사용하는 것인지, 의미적 정보는 본질적으로 localize 하기 어려워서인지 이유를 밝혀야 함.
2. Comparison of Metrics
- Figure 2를 보면 초반의 몇몇 layer 에서 differential score가 가장 높음. 즉, 대다수의 문제는 초반에 올바르게 분류됨.
- 반면, mixing weights 는 후반부(9-20)에 집중되어 있음.
3. Comparison of Encoders
- stretching effect