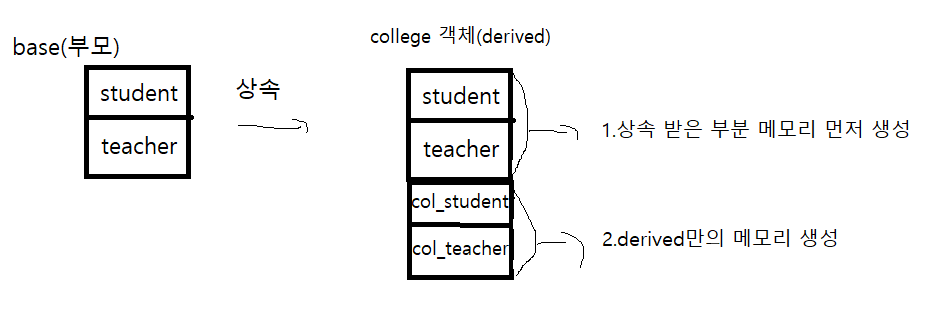
상속
부모(base),자식(derived) 관계
Is a 관계를 나타낼 때 사용(derived는 base이다)
접근 지정자
자식이 상속받은 거에 접근 정도를 지정
public,private,protected
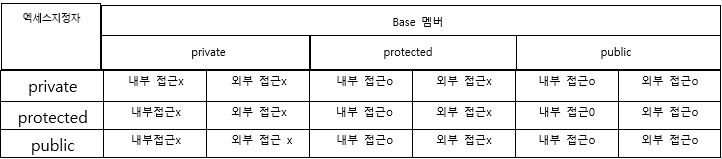
디폴트 접근 지정자
derived 가 class면 private
derived가 struct이면 public
상속 예시 코드
class school
{
private:
int student;
int teacher;
public:
int get_student(){return student;}
public:
school(){}
school(int _student,int _teacher ):student(_student),teacher(_teacher) {}
~school(){}
}
class college
:public school
{
private:
int col_student;
int col_teacher;
public:
//this->get_student()와도 같음
int get_student(){return col_student+school::get_student();}
//school::get_student()가 명시적 오버라이딩 함수 호출
public:
college(int _stu,int _tea,int _col_stu,int _col_tea): school(_stu,_tea)
,col_student(_col_stu),col teacher(_col_tea){ }
//college(int _stu,int _tea,int _col_stu,int _col_tea): stuend(_stu)
//,teacher(_tea)col_student(_col_stu),col teacher(_col_tea){ }
//멤버초기화는 자기 자신의 멤버에 대해서만 초기화 가능
//상속받은 것에서는 생성자를 통해 초기화 하거나
// base에 디폴트 생성자가 있다면 정의문에서 초기화 가능
college(){}
~college(){}
}생성자,소멸자
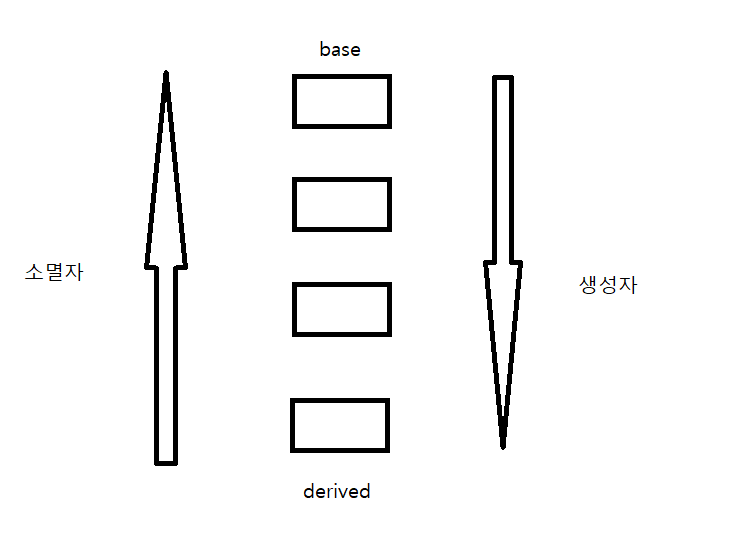
상속받은 부분에 대한 것은 상속받은 상속자/소멸자가 동작한다
생성자는 base->derived순으로, 소멸자는 그 반대로 동작한다
명시적 생성자 호출
멤버 초기화는 자신의 멤버만 초기화 가능
derived에서 base 클래스의 생성자를 명시적으로 호출 할려면 멤버 초기화 구문을 사용 해야 함
오버라이딩
상속 관계에 있어 base에서 먼저 정의한 함수를
동일한 이름을 사용해서 재정의 하는 것이다.(이름만 같고 매개변수,리턴값은 다를수 있다.)
오버라이딩한 함수를 호출 하는 방법
1.namespace 활용
//this->get_student()와도 같음
int get_student(){return col_student+school::get_student();}
//school::get_student()가 오버라이딩 함수 명시적 호출
2.객체를 통한 호출(함수가 public이어야 함)
상속관계에 같은 멤버 이름이 있다면 네임스페이스(::)을 활용하여 구분 호출 가능