✅다항식(Polynomial)
- a =계수(coefficient)
- x = 변수(variable)
- e =지수(exponent)
✅다항식 ADT
- object
- p(x) = a1 x^e1 + a2 x^e2 + ... + an * x^en
- <e, a> : 지수(exponent), 계수(coefficient)의 순서쌍
- functions
- Polynomial
ZeroP(): return p(X)=0 - Boolean
IsZeroP(p): if (poly) return FALSE else return TRUE - Coefficient
coef(p, e): if (<e,a> ∈ p) return c else return 0 - Exponent
maxExp(p): return max (최고차항 반환) - Polynomial
addTerm(p, c, e)if (<e,a> ∈ p) return error else return 삽입된 poly - Polynomial
delTerm(p, e)if (<e,a> ∈ p) return 삭제된 poly else return error - Polynomial
singleMult(p, c, e)return poly c x^e - Polynomial
polyAdd(p1, p2)return p1 + p2 - Polynomial
polyMult(p2, p2)return p1 * p2
- Polynomial
✅다항식 연산의 구현
- 다항식 생성
-
zeroP()와addTerm()을 이용해 생성 -
addTerm(addTerm(addTerm(zeroP(), a, 3), b, 2), 5, 0)= $a*x^3 + b*x^2+5$표
-
- 표현 시 가정
- 지수에 따라 내림차순으로 정렬
- 모든 항의 지수는 다름
- 계수가 0인 항은 포함하지 않음
✅ 표현방법
1️⃣ 모든 차수에 대한 계수값을 배열로 저장

typedef struct {
int degree;
float coef[MAX_DEGREE];
} polynomial;- 표현 : polynomial a = {5, {10, 0, 0, 0, 6, 3}};
⚠️ 0인 계수가 많은 경우 메모리 낭비가 심함
2️⃣ 지수와 계수가 존재하는 항만 배열로 저장
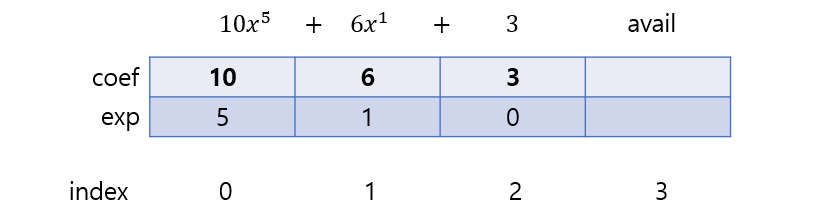
#define MAX_TERMS 100 // 지수가 존재하는 term 최대수
typedef struct {
float coef; //계수
float expon; //지수
} polynomial;
polynomial term [MAX_TERMS];
int avail = 0; // 다음 번 빈 슬롯의 array index 번호 유지-
표현 : terms[MAX_TERMS] = { {10,5}, {6,1}, {3,0} };
-
하나의 배열로 여러 개의 다항식 표현 가능
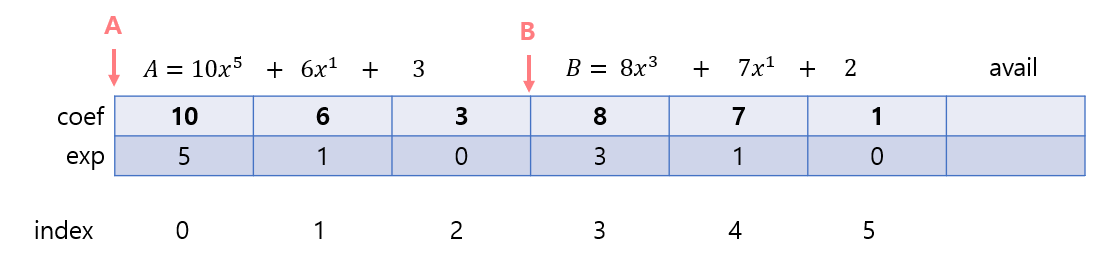
- 다항식의 덧셈 가능
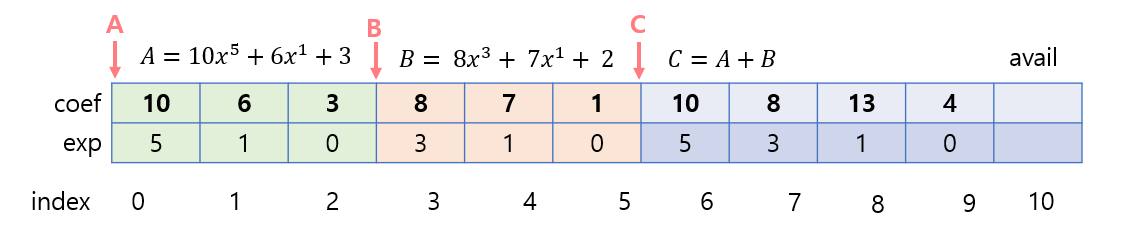
⚠️ 계수 0인 항이 적은 경우 메모리를 2배나 더 소모하게 됨
✅ 다항식 덧셈 함수 알고리즘 표현
polyAdd(p1, p2)
// p3 = p1 + p2 : 다항식 p1과 p2를 더한 결과 p3을 반환
p3 = zeroP();
while (not isZeroP(p1) and not isZeroP(p2) do {
case {
maxExp(p1) < maxExp(p2) :
p3=addTerm(p3, coef((p2), maxExp(p2)), maxExp(p2);
p2=delTerm(p2, maxExp(p2));
maxExp(p1) = maxExp(p2) :
sum=coef(p1, maxExp(p1)) + coef(p2, maxExp(p2));
if (sum != 0) then p3 = addTerm(p3, sum, maxExp(p1));
p1 = delTerm(p1, maxExp(p1));
p2 = delTerm(p2, maxExp(p2));
maxExp(p1) > maxExp(p2) :
p3 = addTerm(p3, coef(p1, maxExp(p1)), maxExp(p1));
p1 = delTerm(p1, maxExp(p1));
}
}
if (not isZero(p1)) then p1의 나머지 항들을 p3에 복사
else if (not isZeroP(p2)) then p2의 나머지 항들을 p3에 복사
return p3;
end polyAdd()while문 in → p1과 p2를 비교하여 큰 지수를 가진 것부터 p3에 복사
while문 out → p1이나 p2 중에 먼저 끝난 경우 나머지 항들을 p3에 복사
- wort case : A(x)와 B(x) 지수가 겹치지 않는 경우
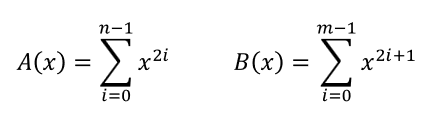
- while loop의 횟수 = m+n-1
- 시간복잡도 : O(n+m)
