희소행렬 추상데이터 타입
✅ Sparse matrix 개념

- 행렬 matrix
- m개의 행(row)과 n개의 열(colunm)로 구성
- 2차원 배열에 의한 matrix 표현 ⇒ A [ 6, 6 ]
- 희소행렬 sparse matrix
- 행렬의 값이 대부분 0인 경우를 가리키는 표현
✅ Sparse matrix 표현
- 2차원 배열을 이용하여 배열의 전체 요소 저장하는 방법
- 장점 : 행렬의 연산들을 간단하게 구현
- 단점 : 희소행렬의 경우 많은 메모리 공간 낭비
- 표현 방법
- 2차원의 경우 (row, col, value) 으로 표현
- 3차원의 경우 (row, col, depth, value) 으로 표현
- ex. ( (0, 0, 11) (0, 1, 22) ... (5, 6, 99) ) 으로 표현 (row major 표현방식)
✅ Sparse matrix ADT
- objects
- <row, column, value>, triple들의 집합
- row와 column은 정수
- functions
- for all a,b ∈ Sparse_Matrix/ c ∈ Matrix / u,v ∈ item / i, j, max_col, max_row ∈ index
spCreate(max_row, max_col): return an empty sparse matrix with m * n;spTranspose(a): return c where where c[j, i]=v when a[i, j]=v;spAdd(a, b): if (a.dimension = b.dimension) return c where c[i, j]=v+u when a[i, j]=v and b[i, j]=u else return error- 덧셈이 되기 위해서는, row와 col의 수가 같아야함. 같지 않으면 error를 반환하는 것
spMultiply(a, b): if (a.numcols=b.num_rows) return c where c[i, j] = sum{k=0}^p (a[i][k] * b[k][j]) , p=a.num_cols else return error;
희소행렬 연산의 C 구현
- ⚠️ 행렬 덧셈, 곱셈 방법
꼼수학_행렬의 기초연산(덧셈,뺄셈,곱셈)
희소행렬 기본 구조체
#defind MAX_TERMS 101 //term의 최대수+1 why? 0번째 통계치를 넣기 위해
typedef struct {
int row;
int col;
int value;
} term;
term a[MAX_TERMS];희소행렬 배열 표현

| index | row | col | value |
|---|---|---|---|
| arr[0] | 5 | 7 | 9 |
| arr[1] | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| arr[2] | 0 | 1 | 22 |
| arr[3] | 1 | 1 | 33 |
| arr[4] | 1 | 2 | 44 |
| arr[5] | 2 | 2 | 55 |
| arr[6] | 2 | 3 | 66 |
| arr[7] | 2 | 4 | 77 |
| arr[8] | 3 | 5 | 88 |
| arr[9] | 4 | 6 | 99 |
⚠️ arr[0]에는 행렬의 통계정보를 표현.
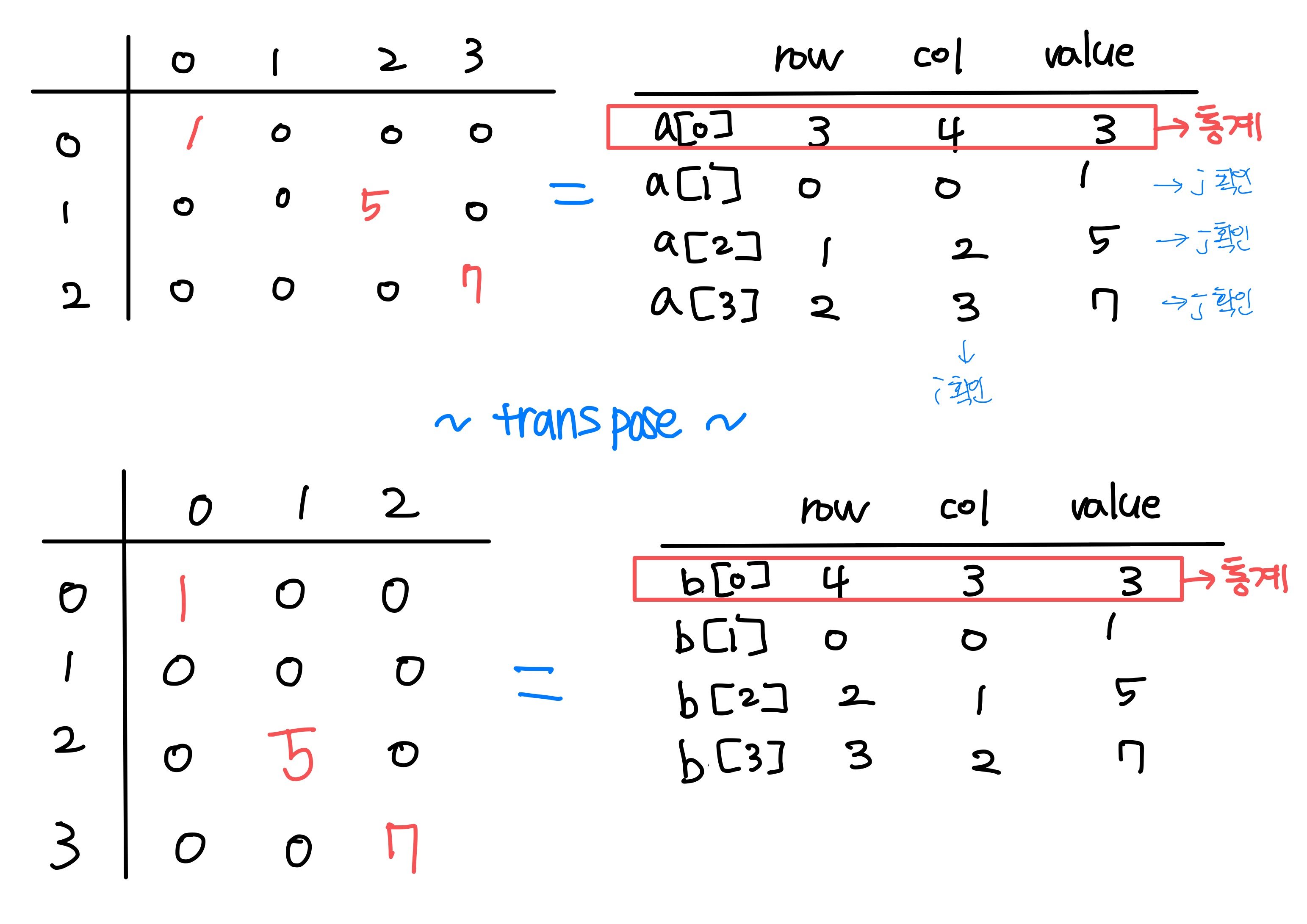
1️⃣ transpose matrix 알고리즘
✅ 개념
✅ 코드
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_TERMS 101
typedef struct {
int row;
int col;
int value;
} term;
term a[MAX_TERMS];
void transpose(term a[], term b[]){ //a:원행렬, b:전치행렬
int n, currentb;
// 전치행렬 b의 행,열,값 복사 -> b[0] 완성
n = a[0].value; //총 element수
b[0].row = a[0].col;
b[0].col = a[0].row;
b[0].value = n;
if(n > 0) { // 0이 아닌 원소가 있는 경우에만 전치 연산 수행
//0번째는 통계량을 가지고 있으므로 1부터 시작
currentb = 1;
for(int i=0; i<a[0].col; i++){ //a[0].col 만큼 반복, check의 횟수
// 0번째틑 통계량이므로 a에 접근하기 위한 j=1부터 시작
// //0이 아닌 원소 수만큼 반복, write 횟수
// 값이 있는 만큼(j번) 확인 후에 다시 i로 돌아가 열만큼(i번) 확인
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++){
// a.col을 b.row로 정렬하기 위해 0부터 탐색
// currentb는 b에 데이터가 들어간 인덱스 저장해둠
// 현재의 열에 속하는 원소가 있으면 b[]에 삽입
if(a[j].col == i){
// 새로운 데이터 값 정렬
b[currentb].row = a[j].col;
b[currentb].col = a[j].row;
b[currentb].value = a[j].value;
currentb++;
}
}
}
}
}
int main(void) {
// !! a[0]에는 통계값을 집어넣어야 함.
// a[0]에 들어가는 col과 row는 index가 아닌 갯수로 들어가야함
term a[4] = { {3,4,3}, {0,0,1}, {1,2,5}, {2,3,7} };
term b[4];
//원행렬 출력
printf("row: %d, low: %d, value: %d\n", a[0].row, a[0].col, a[0].value);
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++){
printf(" %d, %d, %d\n", a[i].row, a[i].col, a[i].value);
}
printf("\n\n");
//변형 알고리즘 적용
transpose(a,b);
printf("Transpose processing has been finished.\n");
printf("\n\n");
//전치행렬 출력
printf("row: %d, low: %d, value: %d\n", b[0].row, b[0].col, b[0].value);
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++){
printf(" %d, %d, %d\n", b[i].row, b[i].col, b[i].value);
}
printf("\n\n");
return 0;
}🎯 결과
row: 3, low: 4, value: 3
0, 0, 1
1, 2, 5
2, 3, 7
Transpose processing has been finished.
row: 4, low: 3, value: 3
0, 0, 1
2, 1, 5
3, 2, 7✅ 시간 복잡도
2️⃣ Fast transpose matrix 변형 알고리즘
✅ 개념
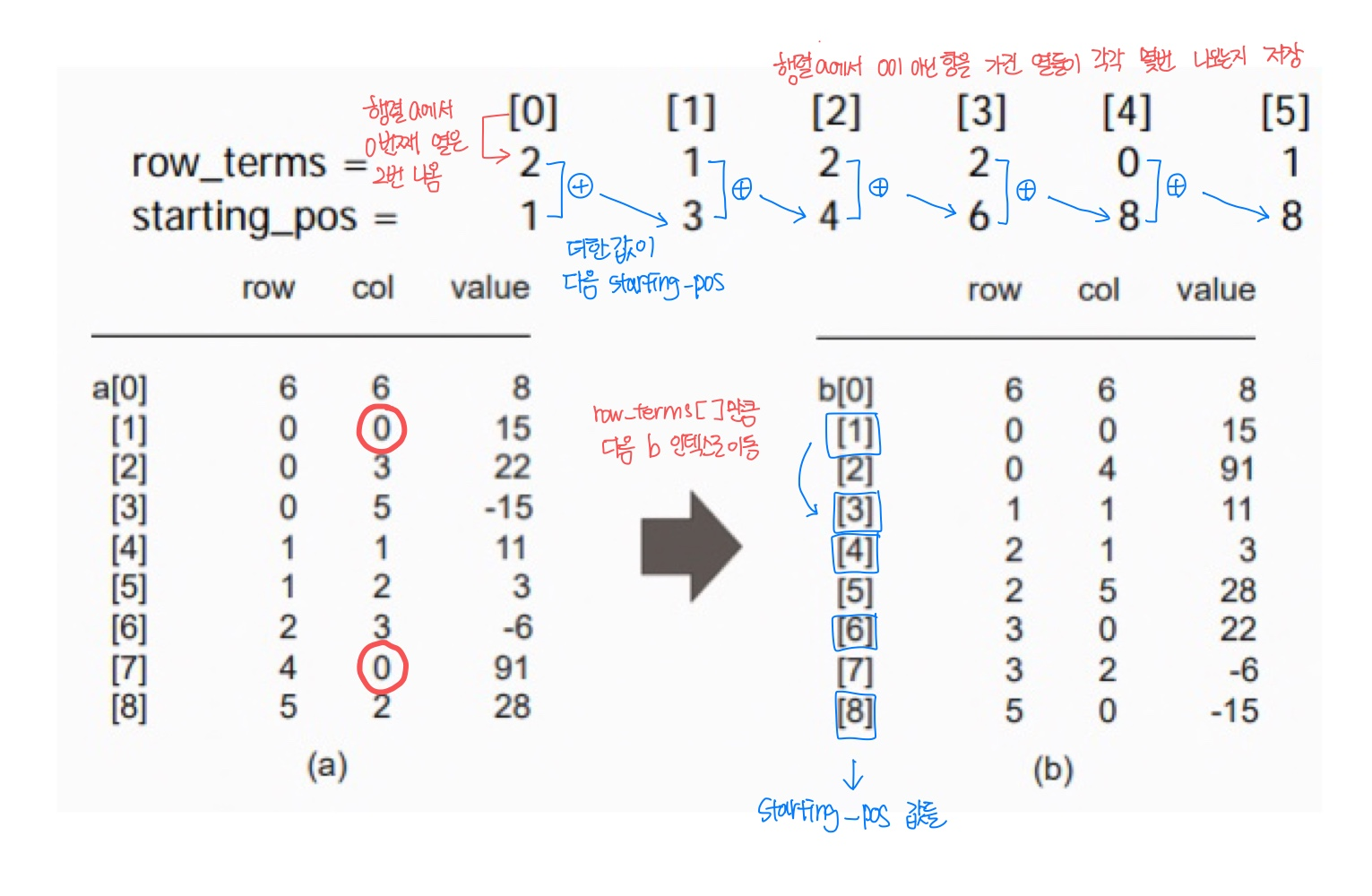
- 각 column이 저장될 곳을 미리 파악하는 방법
- row_terms : 원 행렬에서, 0이 아닌 값을 가진 열들이, 각각 몇 번 나오는 지 저장
- index 의미 : 원행렬에서 0이 아닌 값들을 가지고 있는 열의 index
- starting_pos : 자기 앞 열들이 몇 번 나오는지 저장
- 원행렬 index에는 row_terms 만큼 값을 가지고 있어 다음 시작하는 열을 알려줌
- row_terms : 원 행렬에서, 0이 아닌 값을 가진 열들이, 각각 몇 번 나오는 지 저장
- column index 저장을 위한 추가적인 공간이 필요
- 메모리에선 이전보다 손해를 보지만 시간 복잡도는 내려가는 효과를 보는 방법
✅ 코드
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_TERMS 101
#define MAX_COL 50
typedef struct {
int row;
int col;
int value;
} term;
term a[MAX_TERMS];
void fast_transpose(term a[], term b[]){
// (1) 필요한 변수 선언
int i, j;
int row_terms [MAX_COL], starting_pos [MAX_COL];
int num_cols = a[0].col, num_terms = a[0].value;
// (2) a[0]값 b[0]에 복사
b[0].row = num_cols;
b[0].col = a[0].row;
b[0].value = num_terms;
if ( num_terms > 0 ){
// (3) row_terms 완성
// (3-1) col 갯수만큼 row_terms의 배열 0으로 초기화
// (3-2) col->인덱스로 들어가짐. 인덱스에 해당하는 row_terms 값을 +1
for(**i=0; i<num_cols**; i++) row_terms[i] = 0;
for**(i=1; i<=num_terms**; i++) row_terms[a[i].col]++;
// (4) starting_pos 완성
starting_pos[0] = 1;
for(i=1; i<num_cols; i++){
starting_pos[i] = starting_pos[i-1] + row_terms[i-1];
}
// (5) transpose과정
for(i=1; i<=num_terms; i++){
j = starting_pos[a[i].col]++;
printf("(j = %2d) = (starting_pos[a[%2d].col]++) <= (starting_pos[%d]++)\n", j, i, a[i].col);
b[j].row = a[i].col;
b[j].col = a[i].row;
b[j].value = a[i].value;
}
printf("starting_pos : ");
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++){
printf("[%d]", starting_pos[i]);
}
printf("\n\n");
}
}
int main(void) {
// !! a[0]에는 통계값을 집어넣어야 함.
// a[0]에 들어가는 col과 row는 index가 아닌 갯수로 들어가야함
term a[9] = { {6,6,8}, {0,0,15}, {0,3,22}, {0,5,-15}, {1,1,11}, {1,2,3}, {2,3,-6}, {4,0,91}, {5,2,28} };
term b[9];
//원행렬 출력
printf("index row col value\n");
printf("--------------------------\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){
printf(" a[%d] | %d %d %d\n", i, a[i].row, a[i].col, a[i].value);
}
printf("\n\n");
//변형 알고리즘 적용
fast_transpose(a,b);
printf("\n\n");
printf("Transpose processing has been finished.\n");
printf("\n\n");
//전치행렬 출력
printf("index row col value\n");
printf("--------------------------\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){
printf(" b[%d] | %d %d %d\n", i, b[i].row, b[i].col, b[i].value);
}
printf("\n\n");
return 0;
}🎯 결과
index row col value
--------------------------
a[0] | 6 6 8
a[1] | 0 0 15
a[2] | 0 3 22
a[3] | 0 5 -15
a[4] | 1 1 11
a[5] | 1 2 3
a[6] | 2 3 -6
a[7] | 4 0 91
a[8] | 5 2 28
(j = 1) = (starting_pos[a[ 1].col]++) <= (starting_pos[0]++)
(j = 6) = (starting_pos[a[ 2].col]++) <= (starting_pos[3]++)
(j = 8) = (starting_pos[a[ 3].col]++) <= (starting_pos[5]++)
(j = 3) = (starting_pos[a[ 4].col]++) <= (starting_pos[1]++)
(j = 4) = (starting_pos[a[ 5].col]++) <= (starting_pos[2]++)
(j = 7) = (starting_pos[a[ 6].col]++) <= (starting_pos[3]++)
(j = 2) = (starting_pos[a[ 7].col]++) <= (starting_pos[0]++)
(j = 5) = (starting_pos[a[ 8].col]++) <= (starting_pos[2]++)
starting_pos : [3][4][6][8][8][9]
Transpose processing has been finished.
index row col value
--------------------------
b[0] | 6 6 8
b[1] | 0 0 15
b[2] | 0 4 91
b[3] | 1 1 11
b[4] | 2 1 3
b[5] | 2 5 28
b[6] | 3 0 22
b[7] | 3 2 -6
b[8] | 5 0 -15✅ 시간복잡도
O(columns + elements)
즉, ⇒
