AWS EC2

Amazon EC2
- Elastic Compute Cloud = Infrastructure as a Service
- Rent virtual machines (EC2 instance)
- Store data on virtual drvies (EBS)
- Distrubute load accross machines (ELB)
- Scale the services using an auto-scaling group (ASG)
EC2 sizing & configuration
- OS: Linux, Windows, Mac OS
- Compute power & cores (CPU)
- How much RAM
- How much store space
- Network attached (EBS & EFS)- Hardware attached (EC2 Instance Store)
- Network card: speed, Public IP
- Firewall rules: security group
- Boostrap script: EC2 User Data
User Data
- Bootstrap instance using EC2 User Data script
- Bootstrapping is launching commands when a machine starts
- Script is ran once at the instance first start
- Used to automate boot tasks such as
- Install updates, software- Downloading common files
- etc
- Runs with root user = has sudo rights
Instance types [1]
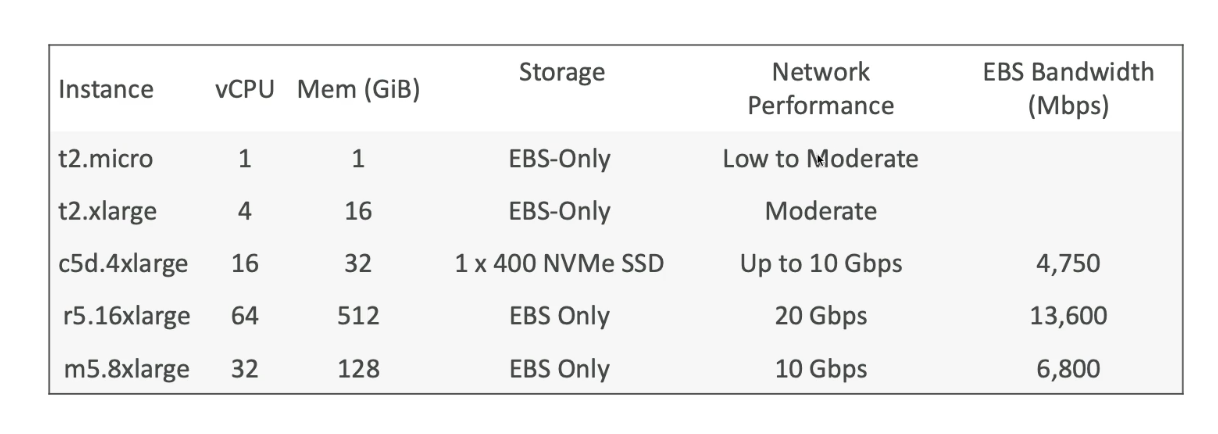
- vCPU: number of cores
- NVMe SSD: attached to EC2 instance
- Choose instance that best fits our application and use on demand
- Create key pair for SSH utility to access EC2 instance
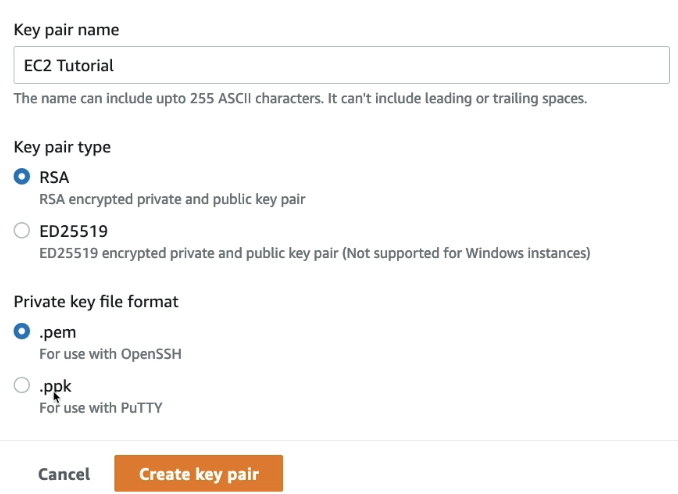
- .pem: for linux, mac, windows >=10
- .ppk: windows <10

- The script get executed when a machine starts
- Update -> install httpd webserver -> write a html file for the webserver
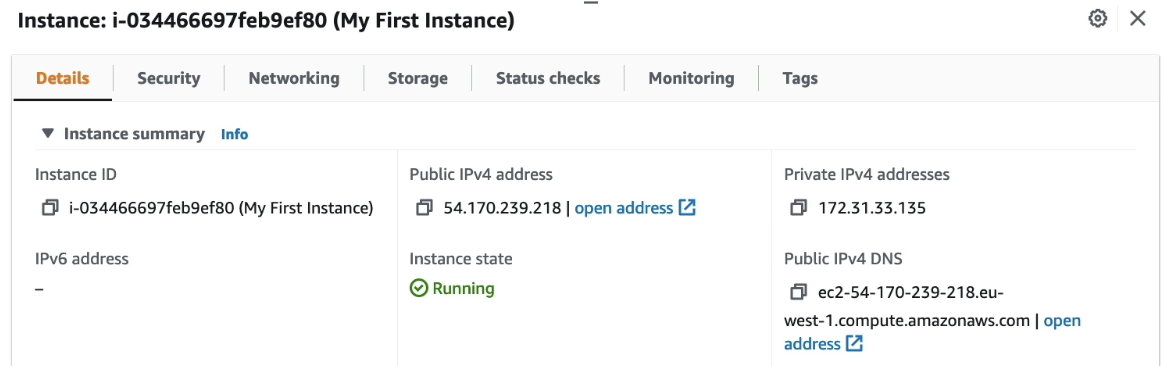
- Instance Id: unique identifier for the instance
- Public IPv4 address: Address to access EC2 instance
- Private IPv4 address: Address to access EC2 instance internally on the AWS network
Restart the instance!
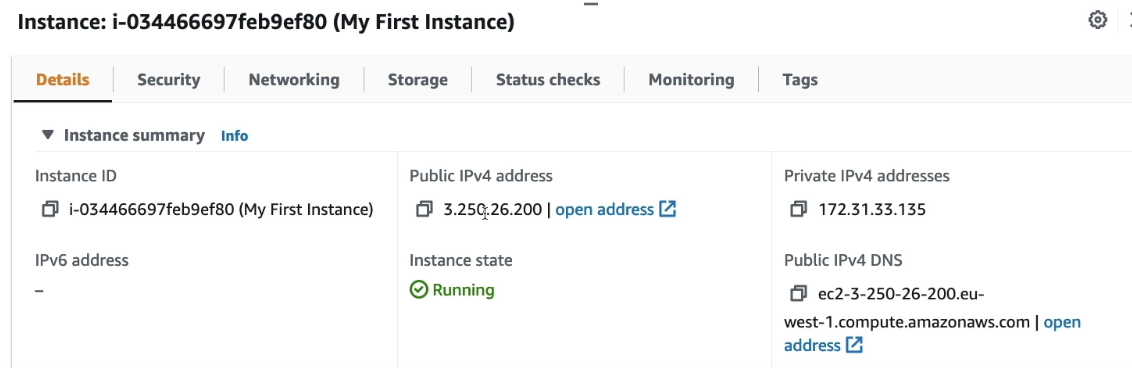
- Public IPv4 address has been changed to 3.250.26.200
- Private IPv4 address does not change
Instance types [2]
Instance name has naming convention ex) m5.2xlarge
- m: instance class
- 5: generation
- 2xlarge: size within the instance class
There are different types of EC2 instances optimised for different use cases
General Purpose
For diversity of workloads such as web servers or code repo
- Balance between compute, memory, and networking

- T, M family
Compute Optimized
For compute-intensive tasks that require high performance processors
- Batch processing workloads
- Media transcoding
- High performance web servers
- High performance computing (HPC)
- Scientific modeling & machine learning
- Dedicated gaming servers

- C family
Memory Optimized
For processing large data sets in memory
- High performance, relational/non relational databases
- Distributed web scale cache stores
- In memory database for Business Intelligence
- Real time processing of big unstructured data
- R, X1, High Memory, z familty
Storage Optimized
For storage intensive tasks that require high, sequential read and write access to large data sets on local storage
- High frequency online transaction processing (OLTP)
- Relvational & NoSql databases
- Cache for in-memory databases (ex. Redis)
- Data warehousing app
- Distributed file systems
Purchasing Options
On-Demand
- Pay for what you use
- Linux or Windows: billing per second after the first minute
- Others: billing per hour
- Highest cost but no upfront payment
- No long term commitment
For short term and un-interrupted workloads where you can't predict how the applicatoin will behave
Reserved
- Up to 72% discount compared to On-demand
- Reservation period: 1 year or 3 years (More discount for longer reservation)
- Payment options: no upfront, partial upfront, all upfront (More discount =>)
- Scope: Regional or Zonal (reserve capacity in an AZ)
- Buy and sell in the Reserved Instance Marketplace
For steady-state usage applications like database
-
Convertible Reserved Instance
- Change type, familty ,os scope, and tenancy -> more flexibility
- Up to 66% discount -
Reserve a specific instance attributes (Instance Type, Region, Tenancy, OS)
- Reserved Instances - long workloads- Convertible Reserved Instances - long workloads with flexible instances
Saving Plans
- Get a discount based on long term usage (up to 72%)
- Commit to a certain type of usage ($10/hour for 1 or 3 years)
- Usage beyond Savings Plans is billed On-Demand
- Locked to a specific instance familiy & AWS region
- Flexible across
- Instance size- OS
- Tenancy
Spot Instances
- The most cost-efficient
- Discount up to 90% compared to On-demand
- Can lose it at any point if max price is less than the current spot price (ex. bidding)
- Less reliable
For workloads that are resilient to failure like batch jobs, image processing, any distributed workloads, workloads with flexible start and end time
- Not for critical jobs or database
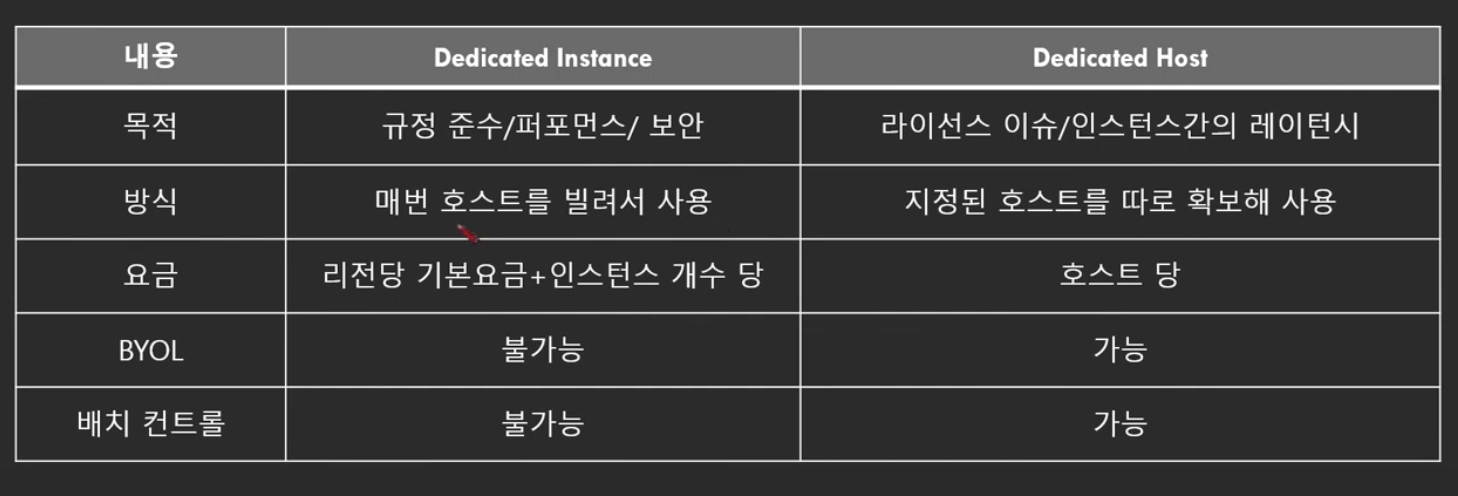
Dedicated Hosts
- The most expensive
- A physical server fully dedicated to your use
- Compliance requirements and existing server bound software liences
- Purchasing options
- On-demands: pay per second for active Dedicated Host- Reserved: 1 or 3 years
For software that has complicated licensive model or strong regulatory or compliance needs
Dedicated Instances
- Instances run on hardware that's dedicated to you
- Can share hardware with other instances in same account
- No contorl over the instance placement
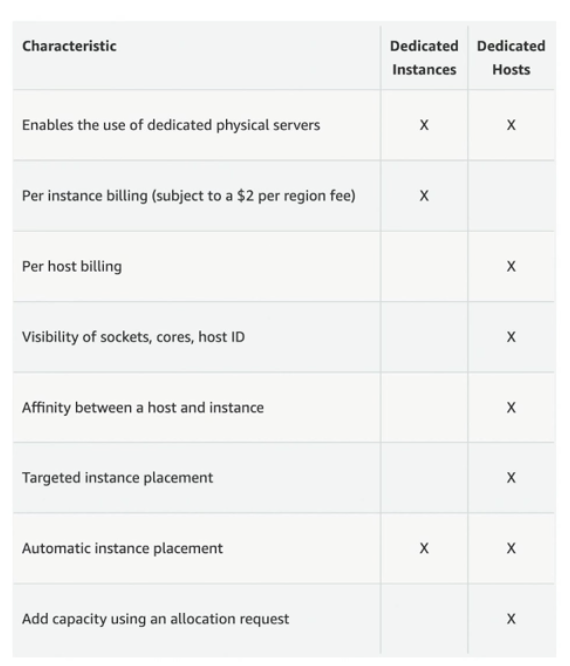
- Dedicated instances: own instance in own hardware
- Dedicated hosts: access to a physical server and gives visibility to the lower level hardware
Capacity Reservations
- Reserve On-Demand instance in a specific AZ for any duration
- Always have access to EC2 capacity when you need
- No time commitment, No billing discounts
- Combine with Regional Reserved Instances and Saving Plans to benefit from billing discounts
- Charged on demand whether you run instance or not
For short term, uninterrupted workloads that needs to be in a specific AZ
Spot Instances
- Define max spot price and get the instance while current spot price < max
- When price > max, choose stop or terminate with a 2 minute grace period

- Much cheaper than On-Demand price
Spot request
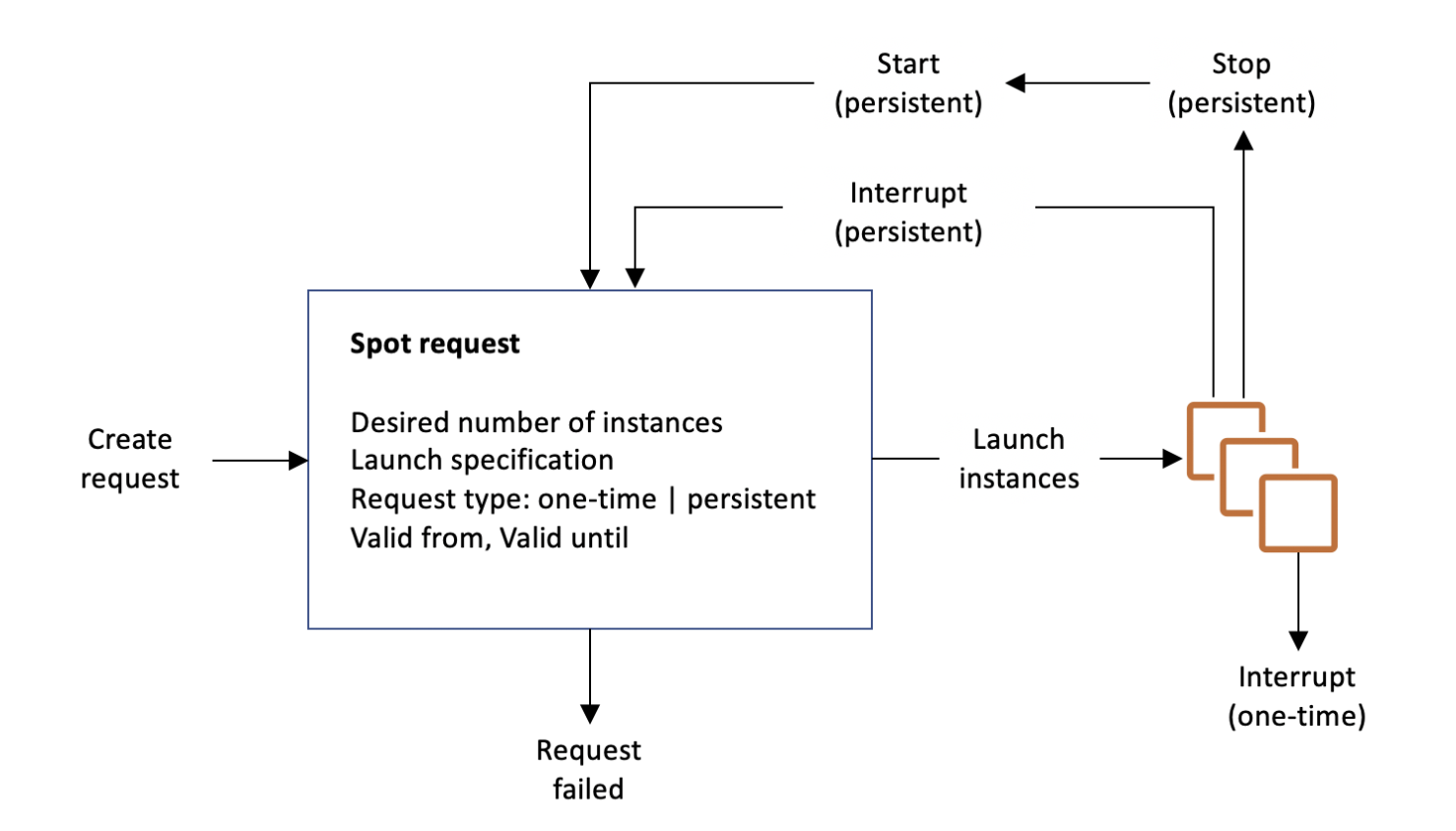
- Desired number of instances
- Maximum price
- Request type: One-time | Persistent
- One-time: If spot request is fullfilled, the spot request will go away- Persistent: Even though spot instances are stopped, the spot request will automatically restart the instances
- Valid from, Valid until: Start and expiration
- Launch specification: ex) instance type, os, az..
Termination
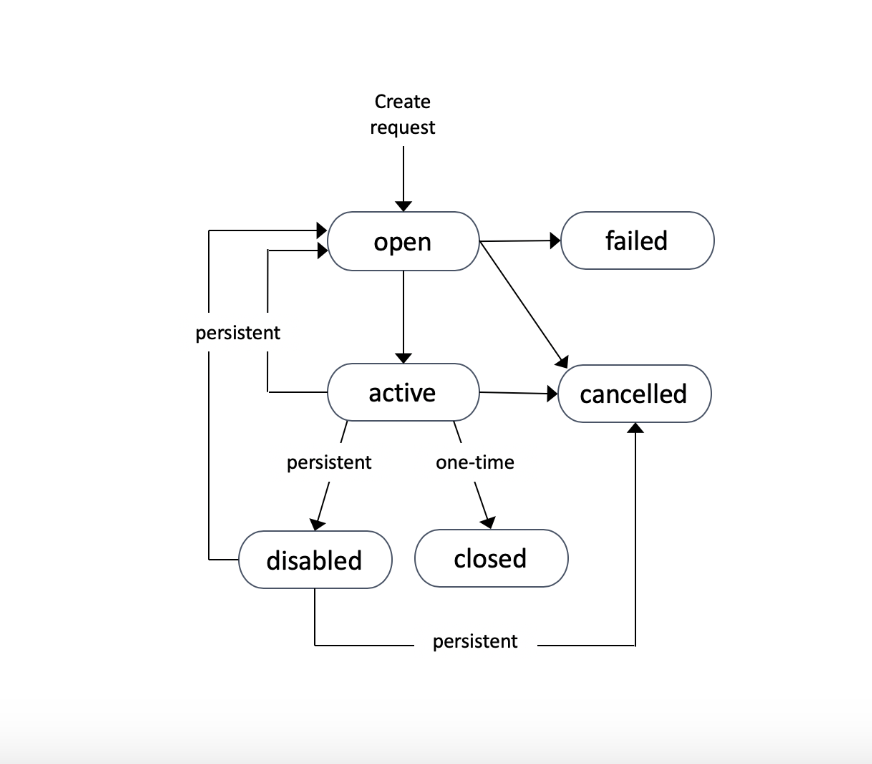
- Can only cancel Spot Instance requests that are open, active, or disabled
- Cancelling a Spot Request does not terminate instances
- First cancel a Sport Request and then terminate the assoicated Spot Instances
Spot Fleets
- Set of Spot Instances + optional On-Demand Instances
- Define possible launch pools (instance type, os, az..)
- Fleet chooses the best one from the multiple launch pools
- Fleet stops launching instances when reaching capacity or max cost
Strategies to allocate
- Lowest price from the pool: cost optimization, short workload
- Diversified: distributed across all pools, great for availability and long workloads
- Capacity Optimized: pool with optimal capacity for the number of instances
- price Capacity Optimized: pools with highest capacity and then select the one with lowest price (best choice for most workloads)
Spoot Fleets chooses the best that suits one of the 4 options from launch pools