Authentication 메커니즘
인증 (Authentication)
-
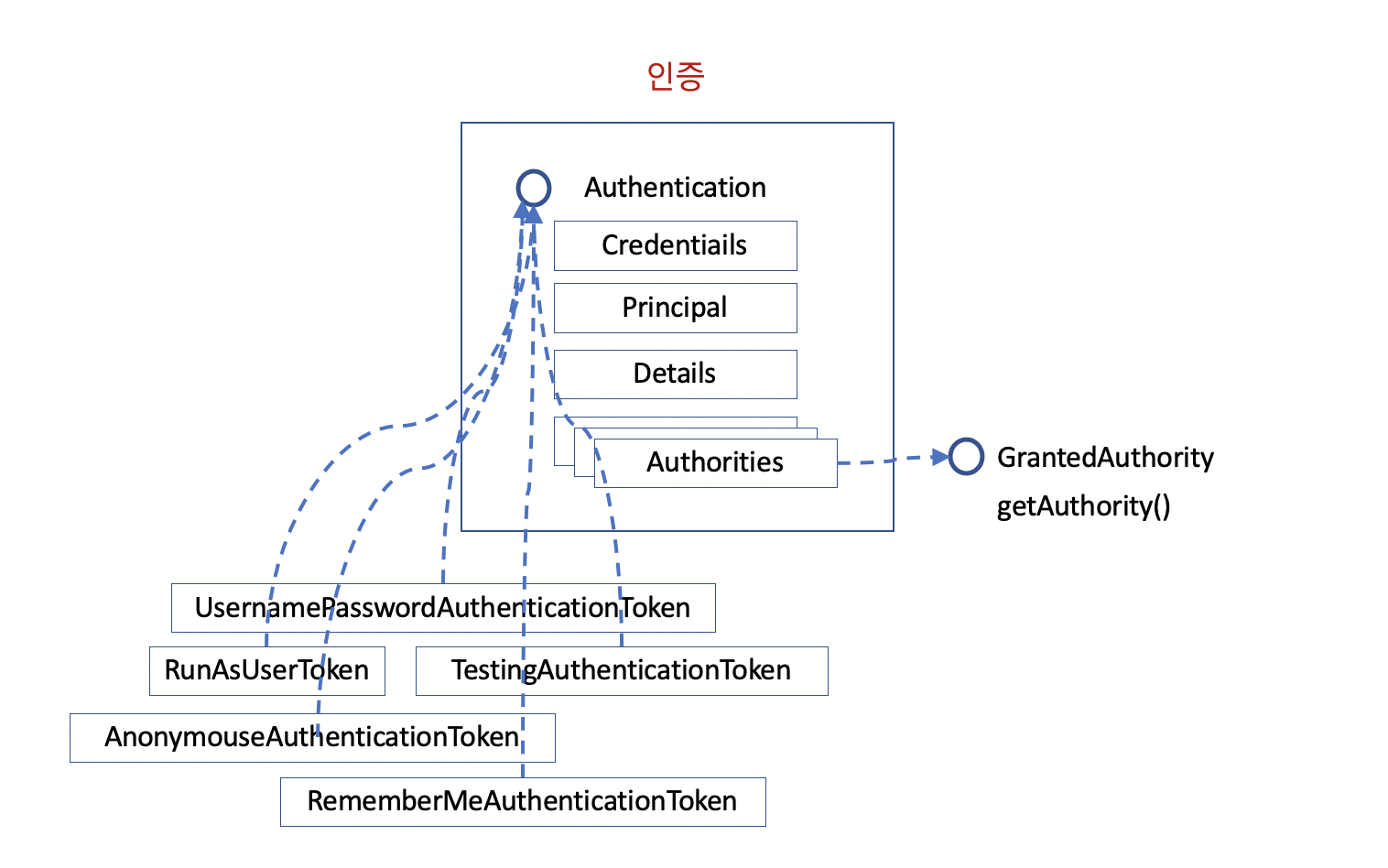
Authentication 는 인증된 결과만 저장하는 것이 아니고, 인증을 하기 위한 정보와 인증을 받기 위한 정보가 하나의 객체에 동시에 들어 있습니다. 왜냐하면, 인증을 제공해줄 제공자(AuthenticationProvider)가 어떤 인증에 대해서 허가를 내줄 것인지 판단하기 위해서는 직접 입력된 인증을 보고 허가된 인증을 내주는 방식이기 때문입니다. 그래서 AuthenticationProvider 는 처리 가능한 Authentication에 대해 알려주는 support 메소드를 지원하고, authenticate() 에서 Authentication을 입력값과 동시에 출력값으로도 사용합니다.
- Credentials : 인증을 받기 위해 필요한 정보, 비번등 (input)
- Principal : 인증된 결과. 인증 대상 (output)
- Details : 기타 정보, 인증에 관여된 된 주변 정보들
- Authorities : 권한 정보들
- Authentication 을 구현한 객체들은 일반적으로 Token(버스 토큰과 같은 통행권) 이라는 이름의 객체로 구현됩니다. 그래서 Authentication의 구현체를 인증 토큰이라고 불러도 좋습니다.
- Authentication 객체는 SecurityContextHolder 를 통해 세션이 있건 없건 언제든 접근할 수 있도록 필터체인에서 보장해 줍니다.
인증 제공자(AuthenticationProvider)
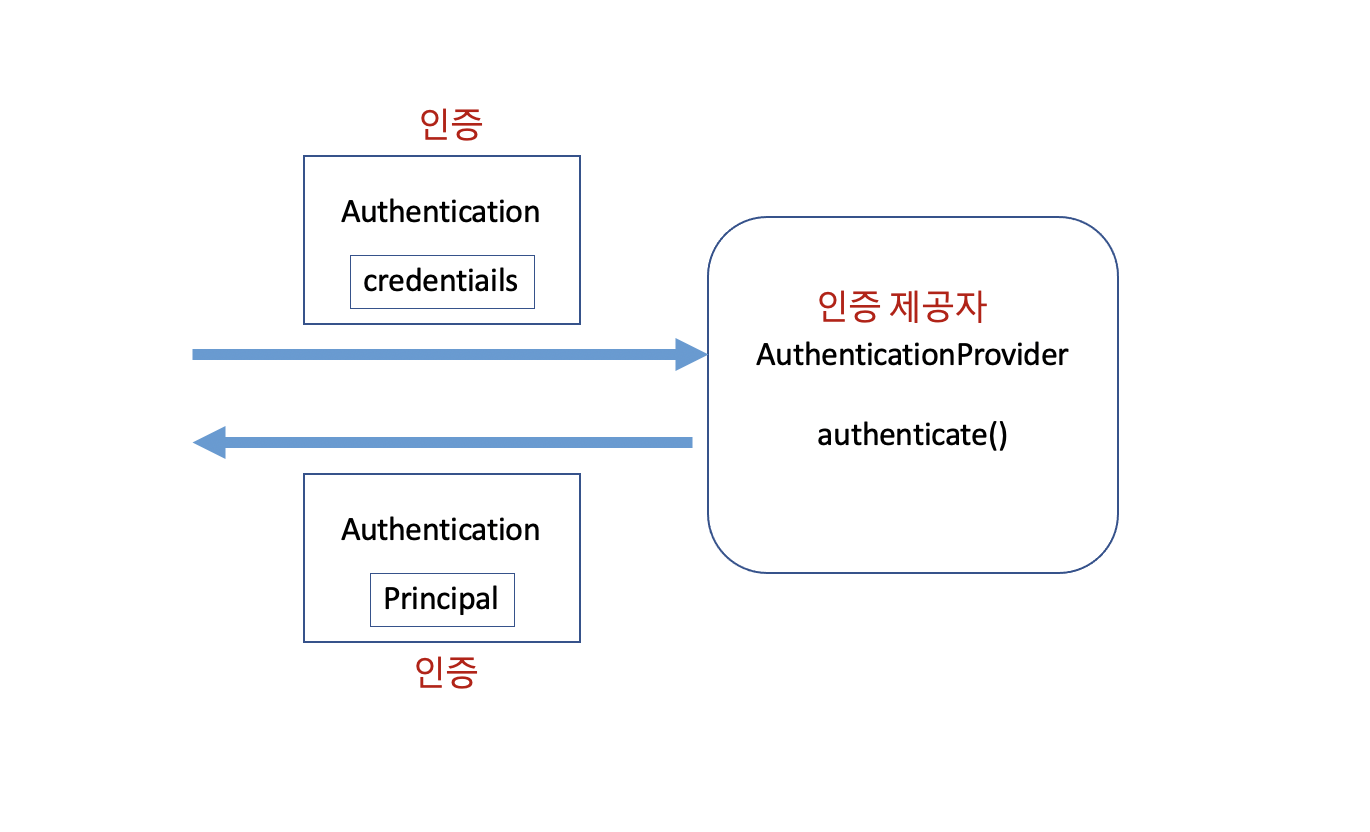
- 인증 제공자(AuthenticationProvider)는 기본적으로 Authentication 을 받아서 인증을 하고 인증된 결과를 다시 Authentication 객체로 전달 합니다.
- 인증 제공자는 어떤 인증에 대해서 도장을 찍어줄지 AuthenticationManager 에게 알려줘야 하기 때문에 support() 라는 메소드를 제공합니다. 인증 대상과 방식이 다양할 수 있기 때문에 인증 제공자도 여러개 올 수 있습니다.
인증 관리자(AuthenticationManager)
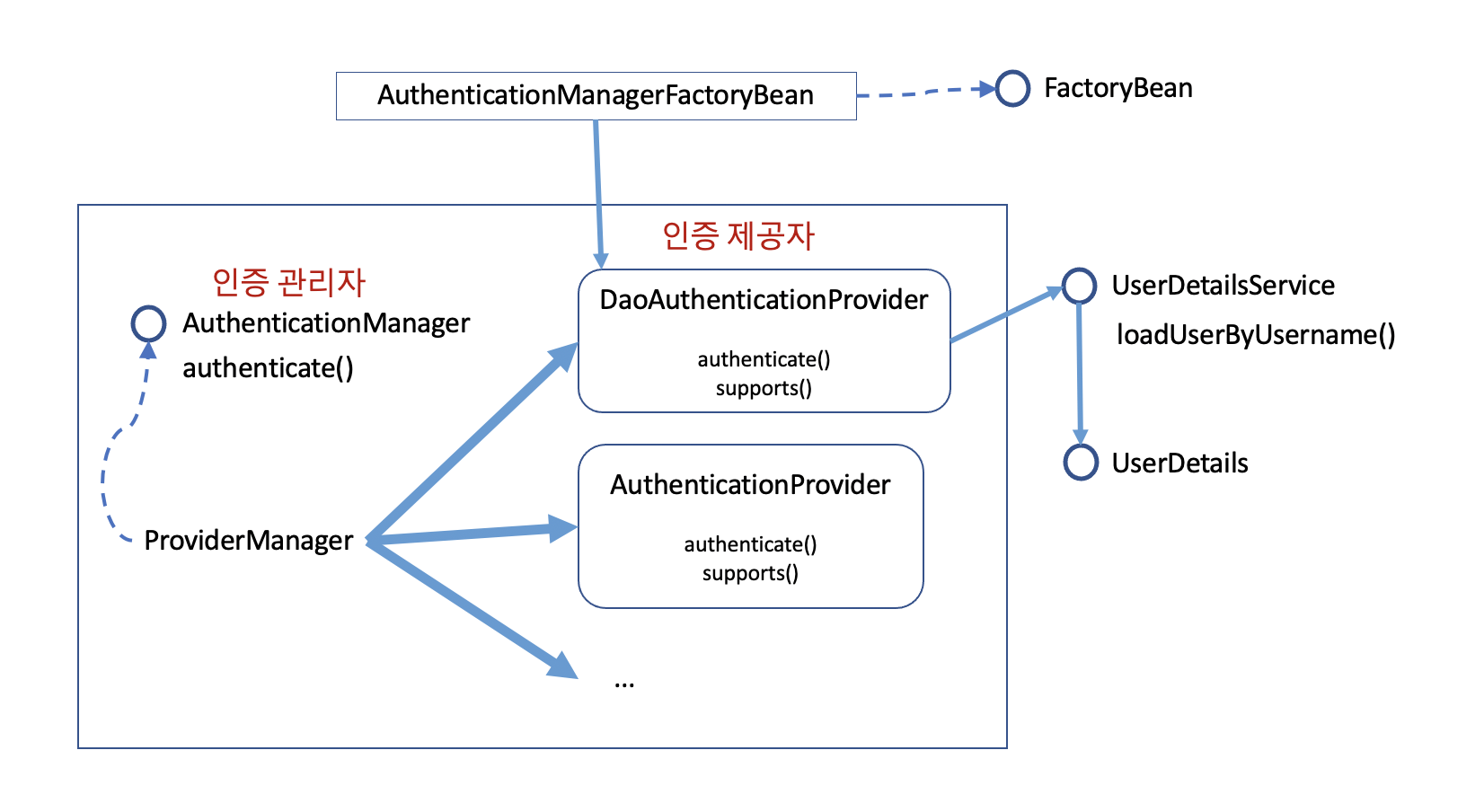
- 인증 제공자들을 관리하는 인터페이스가 AuthenticationManager (인증 관리자)이고, 이 인증 관리자를 구현한 객체가 ProviderManager 입니다.
ProviderManager 도 복수개 존재할 수 있습니다. - 개발자가 직접 AuthenticationManager를 정의해서 제공하지 않는다면, AuthenticationManager 를 만드는 AuthenticationManagerFactoryBean 에서 DaoAuthenticationProvider 를 기본 인증제공자로 등록한 AuthenticationManage를 만듭니다.
- DaoAuthenticationProvider 는 반드시 1개의 UserDetailsService 를 발견할 수 있어야 합니다. 만약 없으면 InmemoryUserDetailsManager 에 [username=user, password=(서버가 생성한 패스워드)]인 사용자가 등록되어 제공됩니다.
AuthenticatioProvider 구현
custom AuthenticationProvider를 구현해야 하는 이유
우리는 Spring Security의 기본 AuthenticationProviders를 구현한 DaoAuthenticationProvider 활용합니다.
user details를 우리가 DaoAuthenticationProvider에 집어넣게 된다면 DaoAuthenticationProvider는 엔드 유저를 인증하는 일을 할 것입니다.
DaoAuthenticationProvider는 우리가 엔드 유저 인증 도중에 고려하고 싶은 대부분의 시나리오를 제공하고 기본 구현 논리는 많은 작업들에 있어 충분하고도 남습니다.
하지만 실제 현업에서 우리는 다소 복잡한 요구사항들을 마주할 것입니다.
예를 들어 엔드 유저들 중 18세 이상의 나이를 가진 사용자들만 시스템에 접근을 허용하거나 허용 국가 목록에 있는엔드 유저들의 접속만을 허용하는
요구 사항이 있을 수도 있습니다
나만의 맞춤 인증 논리를 가지고 싶을 때마다 나만의 AuthenticationProviders를 작성해야 한다는 것입니다
이 사진을 보면 다양한 접근을 통해 최종 사용자를 인증하고 싶다는 요구 사항을 가질 수도 있습니다
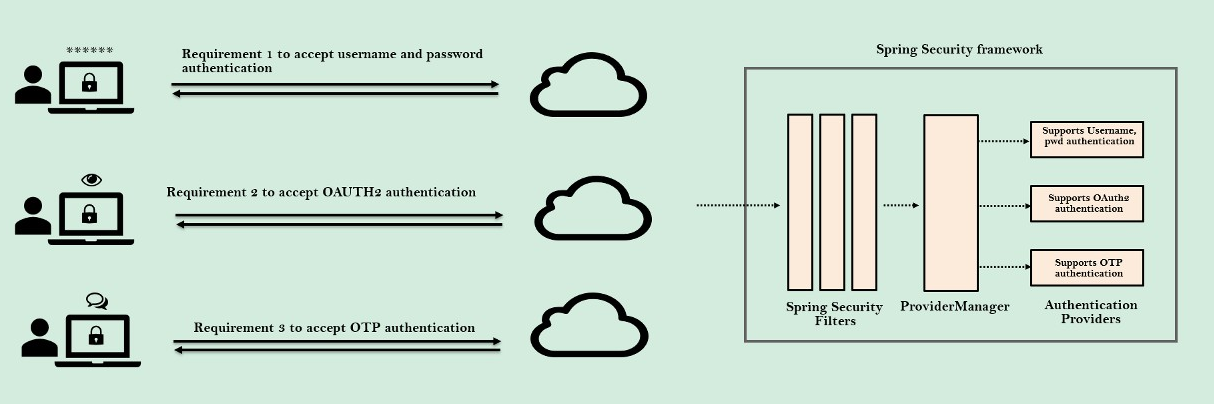
- 첫 번째 접근은 유저 이름과 비밀번호를 통한 접근입니다
- 두 번째 요구 사항은 OAuth 2.0 인증을 사용하고 싶어합니다.
- 세 번째 인증 요구 사항은 OTP 또한 인증의 일부로 사용하고 싶다는 것입니다
이런 상황들에서는 당연히 여러 개의 AuthenticationProviders를 작성할 수 있습니다
AuthenticationProvider의 구조
AuthenticationProviders 인터페이스 안에는 두 가지 추상 메소드가 있습니다
ublic interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}authenticate()
첫 번째는 authenticate() 메소드입니다. Authentication 객체를 입력받고 반환합니다. 메소드 내에서 사용자 정의 인증 로직을 구현할 수 있습니다. AuthenticationProviders로부터 출력하는 인증 객체 안에서 말입니다.
supports()
두 번째 추상 메소드는 supports입니다.
supports() 메서드는 AuthenticationProvider가 특정 유형의 인증 객체를 처리할 수 있는지 여부를 결정하는 메서드입니다. 즉, 이 메서드는 해당 인증 프로바이더가 특정 타입의 인증 객체를 처리할 수 있는지를 확인합니다.
일반적으로 supports() 메서드는 파라미터로 전달된 Authentication 객체가 해당 인증 프로바이더가 지원하는 인증 객체인지를 판단합니다.
이 supports() 메소드를 사용하려면 우리는 Spring Security 프레임워크에 AuthenticationProviders의 도움으로 지원하고 싶은 인증의 종류를 알려주어야 합니다. 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 인증 방식은 유저 이름과 비밀번호의 도움을 받는 것입니다.
만약 유저 이름과 비밀번호 인증의 형태로 지원하고 싶다면
"나는 유저 이름 비밀번호 인증 방식을 방식을 지원하고 싶다"라고 지원 방식 내에서 언급해주어야 합니다.
DAOAuthenticationProvider로 가서 supports 메소드를 보면
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class
.isAssignableFrom(authentication));
}"나는 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 형태의 모든 인증을 다룰거야"라는 의미의 간단한 코드가 보이실 겁니다.
Custom AuthenticationProvider의 구현
@Component
public class EazyBankUsernamePwdAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
private final CustomerRepository customerRepository;
private final PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
public EazyBankUsernamePwdAuthenticationProvider(CustomerRepository customerRepository, PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder) {
this.customerRepository = customerRepository;
this.passwordEncoder = passwordEncoder;
}
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
String userName = authentication.getName();
String pwd = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
List<Customer> customer = customerRepository.findByEmail(userName);
if (customer.size() > 0) {
if(passwordEncoder.matches(pwd, customer.get(0).getPwd())) {
List<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>();
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(customer.get(0).getRole()));
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(userName, pwd, authorities);
} else {
throw new BadCredentialsException("Invalid password");
}
} else {
throw new BadCredentialsException("No user registered with this details");
}
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication));
}
}와 같이 작성 후 디버깅모드로 supports()메소드의 return 부분과 authenticate()메서드내의 String pwd 부분을 브레이크 포인트로 지정하고 로그인을 진행해보면 ProviderManager가 AuthenticationProvider 내에 supports 메소드를 주입시키려고 하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
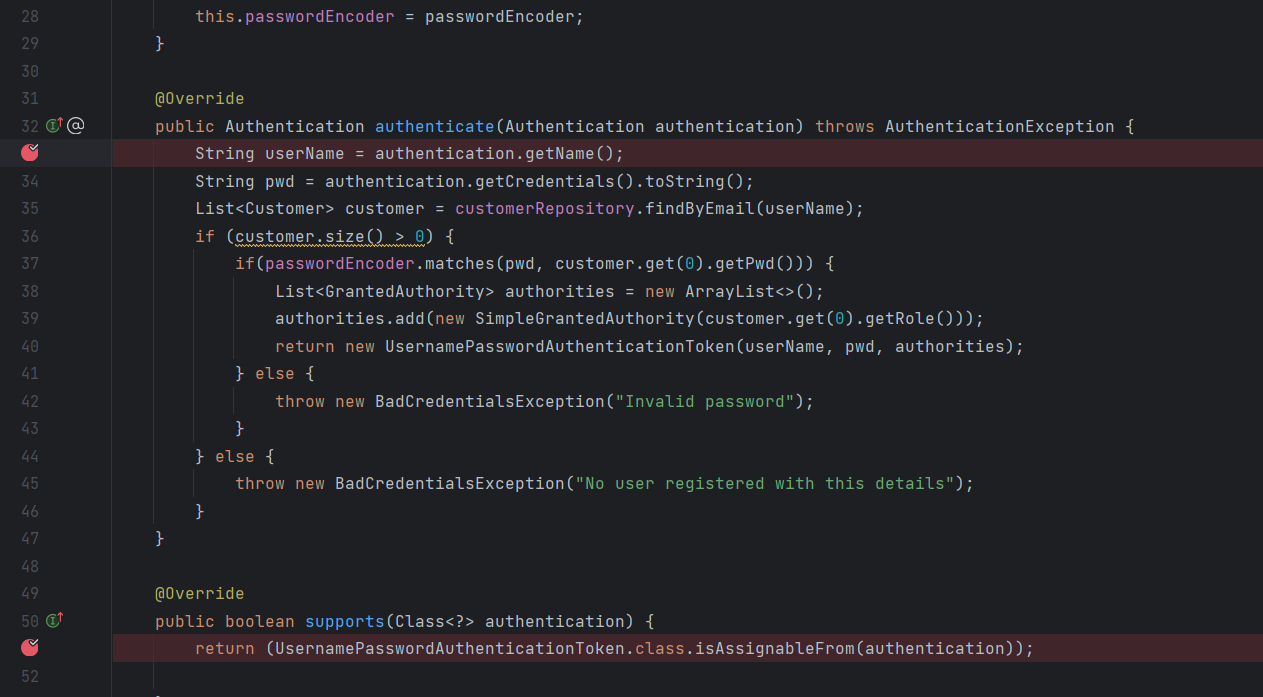
그 후 authenticate() 메소드의 인증 로직을 수행 한 뒤 모든 조건이 충족되었다고 느낄 때 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken에 대한
객체를 생성할 수 있습니다.
정리
- 만약 우리가 Spring Security 프레임워크로 충족되지 않는 사용자 정의 인증 요구 사항이 있다면 AuthenticateProvider로 나만의 인증로직을 만들 수 있다.
