
선형 자료구조란
선형 자료구조란 한 원소 뒤에 하나의 원소만이 존재하는 형태로, 자료들이 선형으로 나열되어 있는 구조를 가진다. 선형 자료구조는 대표적으로 배열(Array), 연결 리스트(Linked List), 스택(Stack), 큐(Queue) 등이 있다.
연결 리스트
연결리스트는 각 요소를 포인터로 연결하여 관리하는 선형 자료구조다. 각 요소는 노드라고 부르며 데이터 영역과 포인터 영역으로 구성된다.
연결리스트의 탐색은 선형시간이 소요된다. 그러나 요소를 추가하거나 제거하는 때에는 상수 시간이 소요된다. 추가하거나 삭제할 때 해당 요소를 포함 혹은 제외하여 앞, 뒤 포인터들만 제어하면 되기 때문이다.
기차를 예로 들 수 있다. 객차를 삽입하거나 없앨 때 연결 장치를 풀어 객차를 삽입하거나, 제거하면 된다. 반면, 5호차를 찾을 때 머리부터 찾아야하므로 탐색 시에는 순회를 해야한다.
연결리스트의 종류는 총 세 가지이다.
단일 연결리스트(Singly Linked List)
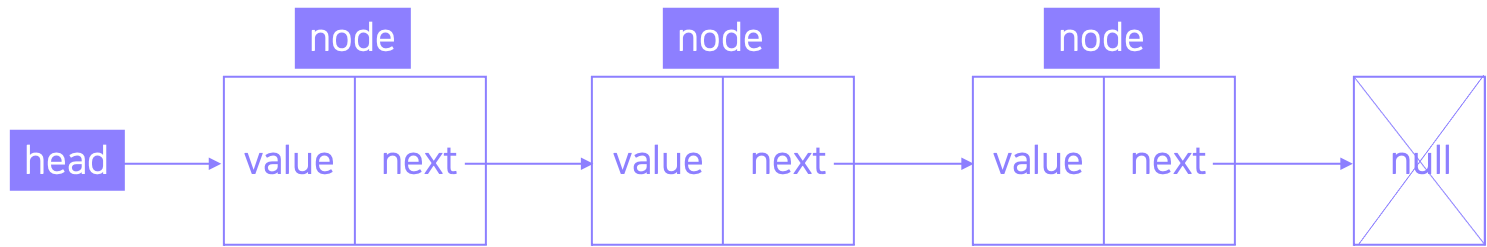
Head에서 Tail(끝)까지 단방향으로 이어지는 연결리스트이다. 각 노드는 데이터 영역(value)와 포인터 영역(next)로 이루어져 있으며, 헤드 포인터(화살표)를 출발점으로, 포인터 영역은 그 다음 원소를 가리키며 마지막 포인터는 항상 null이다.
단일 연결리스트를 구현한 것이다.
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class SinglyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
find(value) {
let curNode = this.head;
while (curNode.value !== value) {
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return curNode;
}
// 리스트 끝에 원소 추가하기
append(newValue) {
const newNode = new Node(newValue);
if (!this.head) { // 원소가 하나도 없는 경우
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
}
// node 다음에 원소 삽입
insert(newValue, node) {
const newNode = new Node(newValue);
if (!node) { // 맨 처음에 삽입하는 경우
let prevNode = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
this.head.next = prevNode;
} else {
newNode.next = node.next;
node.next = newNode;
}
}
remove(value) {
if (value === this.head.value) { // 삭제하려는 원소가 리스트의 첫 번째 원소인 경우
this.head = this.head.next;
} else {
let prevNode = this.head;
while (prevNode.next.value !== value) {
prevNode = prevNode.next;
}
if (prevNode.next) {
prevNode.next = prevNode.next.next;
}
}
}
display() {
let curNode = this.head;
let displayString = "[";
while (curNode) {
displayString += `${curNode.value}, `;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
displayString = displayString.slice(0, displayString.length - 2);
displayString += "]";
console.log(displayString);
}
size() {
let arr = [];
let curNode = this.head;
while (curNode) {
arr.push(curNode.value);
curNode = curNode.next;
}
console.log('리스트 크기: ', arr.length);
}
}
const linkedList = new SinglyLinkedList();
linkedList.append(1);
linkedList.append(2);
linkedList.append(3);
linkedList.append(4);
linkedList.append(5);
linkedList.remove(5);
linkedList.insert(10, linkedList.find(1));
linkedList.insert(99);
linkedList.display();
linkedList.size();remove를 통해 모든 노드와 연결이 끊긴 노드(삭제된 노드)는 가비지 컬렉터를 통해 메모리 상에서 자연스럽게 삭제된다.
맨 끝에 원소를 추가하는 append를 보며 설명을 해보면, 우선 append의 경우는 원소가 하나도 없는 경우와 원소가 있는 경우로 나누어 생각해야 한다.
append(newValue) {
const newNode = new Node(newValue);
if (!this.head) { // 원소가 하나도 없는 경우
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
}원소가 하나도 없는 경우에는 새로운 값으로 생긴 노드를 head로 지정해준다. 또한 원소가 본인 하나 밖에 없으므로 마지막 원소 tail도 본인으로 지정한다.
원소가 있는 경우에는 현재 마지막 원소의 다음(this.tail.next)을 새로 들어오는 노드로 지정한다. 그 다음에 마지막 원소(this.tail)를 새로 들어오는 노드로 지정하면 된다. 이렇게 하면 새로운 원소가 들어오기 전의 this.tail.next은 새로운 원소를 가리키게 되고 새로운 원소가 들어오게 되면서 이 원소가 this.tail이 된다.
이중 연결리스트(Doubly Linked List)
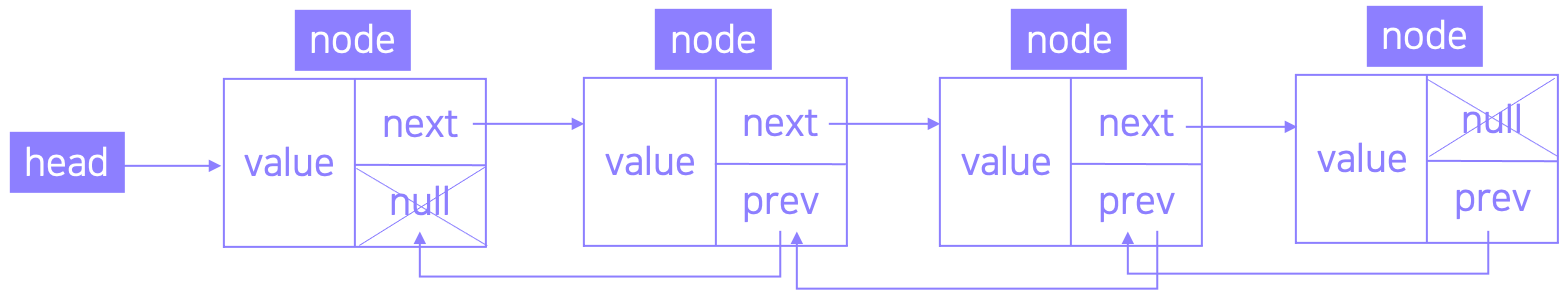
양방향으로 이루어지는 연결 리스트이다. 포인트 변수가 하나 더 추가되어 자료구조의 크기가 단일 연결리스트보다 조금 더 크다.
이중 연결 리스트는 현재 노드의 이전, 이후 노드를 찾아갈 수 있기 때문에 처음에서 끝, 끝에서 처음, 양방향으로 리스트 순회가 가능하다.
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
class DoubleLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
find(value) {
let curNode = this.head;
while (curNode.value !== value) {
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return curNode;
}
// 리스트 끝에 원소 추가하기
append(newValue) {
const newNode = new Node(newValue);
if (!this.head) { // 원소가 하나도 없는 경우
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
}
}
// node 다음에 원소 삽입
insert(newValue, node) {
const newNode = new Node(newValue);
if (!node) { // 맨 처음에 삽입하는 경우
let prevNode = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
this.head.next = prevNode;
prevNode.prev = this.head;
} else {
newNode.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = newNode;
newNode.prev = node;
node.next = newNode;
}
}
remove(value) {
if (value === this.head.value) { // 삭제하려는 원소가 리스트의 첫 번째 원소인 경우
this.head = this.head.next;
this.head.prev = null;
} else {
let curNode = this.find(value);
curNode.prev.next = curNode.next;
curNode.next.prev = curNode.prev;
}
}
display() {
let curNode = this.head;
let displayString = "[";
while (curNode) {
displayString += `${curNode.value}, `;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
displayString = displayString.slice(0, displayString.length - 2);
displayString += "]";
console.log(displayString)
}
size() {
let arr = [];
let curNode = this.head;
while (curNode) {
arr.push(curNode.value);
curNode = curNode.next;
}
console.log('리스트 크기: ', arr.length);
}
}환형 연결리스트(Circular Linked List)
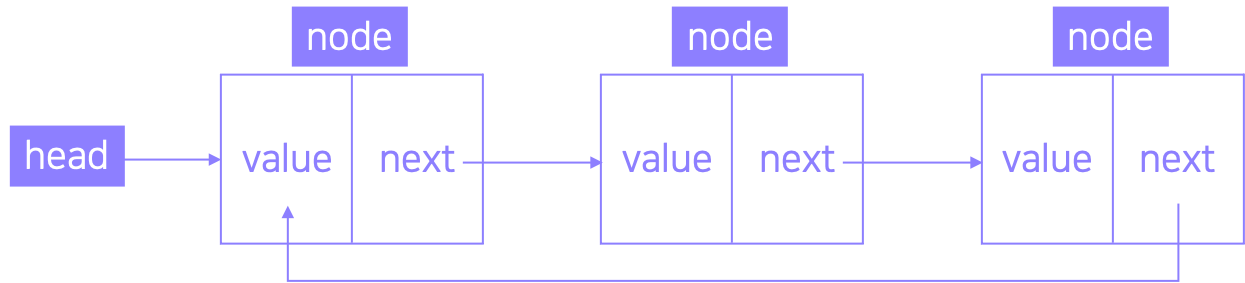
환형 연결리스트는 단방향(단일) 혹은 양방향(이중) 연결 리스트의 참조 정보를 갖는다. 마지막 원소의 포인터 영역이 첫 번째 원소를 가리켜 환형으로 되는 구조이다.
따라서 중간부터 탐색을 해도 한 바퀴를 돌 수가 있다. 환형 연결리스트를 구현하려면 탐색 종료 조건이 반드시 있어야 한다.
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class CircularLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
find(value) {
const headNode = this.head;
if (headNode.value === value) {
return headNode;
} else {
let curNode = headNode.next;
while (curNode.value !== value) {
if (curNode.value === headNode.value) { // 한 바퀴를 돌았지만 노드를 찾지 못한 경우
curNode = null;
break;
}
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return curNode;
}
}
// 리스트 끝에 원소 추가하기
append(newValue) {
const newNode = new Node(newValue);
if (!this.head) { // 원소가 하나도 없는 경우
this.head = newNode;
this.head.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
this.tail.next = this.head;
}
}
// node 다음에 원소 삽입
insert(newValue, node) {
const newNode = new Node(newValue);
if (!node) { // 맨 처음에 삽입하는 경우
this.head = newNode;
this.head.next = this.tail.next;
this.tail.next = this.head;
} else {
newNode.next = node.next;
node.next = newNode;
}
}
remove(value) {
if (value === this.head.value) { // 삭제하려는 원소가 리스트의 첫 번째 원소인 경우
this.head = this.head.next;
this.tail.next = this.head;
} else {
let prevNode = this.head;
while (prevNode.next.value !== value) {
prevNode = prevNode.next;
}
prevNode.next = prevNode.next.next;
}
}
display() {
let curNode = this.head;
let displayString = "[";
while (true) {
displayString += `${curNode.value}, `;
if (curNode.next.value === this.head.value) break;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
displayString = displayString.slice(0, displayString.length - 2);
displayString += "]";
console.log(displayString);
}
size() {
let arr = [];
let curNode = this.head;
while (true) {
arr.push(curNode.value);
if (curNode.next.value === this.head.value) break;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
console.log('리스트 크기: ', arr.length);
}
}
const linkedList = new CircularLinkedList();
linkedList.append(1);
linkedList.append(2);
linkedList.append(3);
linkedList.append(4);
linkedList.append(5);
linkedList.remove(2);
linkedList.insert(10, linkedList.find(1));
linkedList.insert(99);
linkedList.display();
linkedList.size();
console.log(linkedList.find(1));만약 제가 고려하지 못한 부분이 있다면 알려주세요, 감사합니다 :)
